MLS 2213 Unit 9 Lipids
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
What is optimal total cholesterol?
Less than 200
What is borderline total cholesterol?
200-239
What is high risk cholesterol?
>240
What is optimal LDL?
Less than 100
What is above optimal LDL
100-129
What is borderline risk LDL
130-159
What is high risk LDL
160-189
What is optimal HDL
60 or higher
What is borderline HDL
40-59
What is high risk HDL
Less than 40
What are optimal triglycerides?
Less than 150 mg/dL
What are borderline triglycerides?
150-199 mg/dL
What are high triglycerides?
Greater than 200 mg/dL
What is average risk total cholesterol/HDL ratio for men and women
Men = 5.0
Women 4.5
What is half average risk total cholesterol/HDL ratio for men and women
Men = 3.4
Women = 3.3
What is double risk total cholesterol/HDL ratio for men and women
Men = 9.5
Women = 7.0
What is average risk LDL/HDL ratio for men and women
Men = 3.5
Women = 3.2
What is half risk LDL/HDL ratio for men and women
Men = 1.0
Women = 1.5
What is double risk LDL/HDL ratio for men and women
Men = 6.3
Women = 5.0
How long should a patient be fasting before a lipid panel?
12 hours
What type of specimen is suitable for lipid testing and how should it be stored if not able to be tested immediately?
Plasma is typically preferred but serum is acceptable
Serum or plasma should be separated from the cells and kept cold but not frozen
How does atherosclerosis happen?
Theres injury to the blood vessels which causes LDL and calcium to increase
LDL and platelets penetrate the artery which can calcify and slowly enlarge
How does high lipid levels lead to higher risk of atherosclerosis
Elevated lipid levels, particularly LDL cholesterol, contribute to the development of atherosclerosis by promoting plaque formation in the arteries, leading to narrowed blood vessels and increased risk of cardiovascular events.
What are some risk factors for atherosclerosis?
Age
Gender
Men more than women until menopause
Heredity
Diabetes
Dietary fat intake
Smoking
Obesity
Hypertension
Impaired glucose tolerance
What lipids are in apolipoprotein class A?
HDL
Chylomicrons
What apolipoprotein class are HDL and chylomicrons?
Apolipoprotein class A
What apolipoproteins are in class B?
LDL
VLDL
IDL
What apolipoproteins class are LDL, VLDL and IDL
Class B
What apolipoproteins class are chylomicrons
Class C
What are apolipoproteins class C
Chylomicrons
Why test for apolipoproteins A, B and a
They have a high correlation to cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis risk
What are the two ways the HDL decreases atherosclerosis risk?
By blocking the LDL receptors of cell membranes
HDL activated LCAT and as HDL removed cholesterol from the cell membrane LCAT esterified the cholesterol which is then stored in the cell of HDL
What is the LDL calculation using the Friedewald method
Total Chol - [HDL-C + (TG/5) ]
Why does Friedewald not work for people with low triglycerides?
If someone has low triglycerides then with the Friedewald method, it calculates a higher LDL
Why does Friedewald not work for people with high triglycerides?
The Higher your Triglycerides are, the Lower your LDL-Cholesterol becomes
Why does Friedewald not work for people with chylomicron remnants?
Chylomicrons are mostly triglycerides so they’ll mess with the calculations
What is the reference method for total cholesterol
Liebermann-Buchard method
What reagents are used in the Leibermann-Buchard method
Acetic anhydride
Glacial acetic acid
Sulfuric acid
sodium sulfate
What is the preferred method for total cholesterol
Trinder cholesterol oxidase
What are the reagents used in the Trinder cholesterol oxidase method?
Cholesterol oxidase
hydrogen peroxide
Cholesterol ester hydrolase
How is the Trinder cholesterol oxidase method work?
Unesterified cholesterol is turned into hydrogen peroxide by cholesterol oxidase
The hydrogen peroxide then oxidizes a compound which becomes red
What reagents are used in testing HDL using the precipitate method
Heparin and Manganese Chloride
Dextran Sulfate and Calcium or Magnesium salts
Magnesium Chloride and Phosphotungstic Acid
What method is used for testing HDL using the precipitiation method
Reagents are added to the sample that cause the precipitation of VLDL and LDL which only leaves HDL so it can be tested
What reagents are used in testing HDL using a direct method
IgG antibodies
Cholesterol oxidase
Cholesterol ester hydrolase
What method is used to test HDL using the direct method
IgG antibodies against LDL, VLDL, and chylomicrons are added to the specimen. Then cholesterol oxides then cannot react with anything bound by antibodies
What is the method used to calculate LDL called?
Friedwald
What level of triglycerides does friedewald calculation become invalid
400
What are the reagents used in testing for LDL
IgG antibodies to VLDL, HDL and chylomicrons
What is the method used to test for LDL
IgG antibodies added to the sample to bind to VLDL, HDL, and chylomicrons. The sample is then added to a tube with a mesh that filters out anything that is bound by an antibody. This allows LDL to pass through the mesh
What is the method used to test for triglycerides using the glycerol kinase method?
Lipase is used to hydrolyze the fatty acid off of the triglyceride.
The Glycerol is the substrate for Glycerol Kinase, which converts Glycerol to Glycerol-3-Phospate and ADP. From here the various methods link to other enzyme systems to get either a colored product or NADH.
What are the reagents used to test for triglycerides using the glycerol kinase method?
Lipase
Glycerol kinase
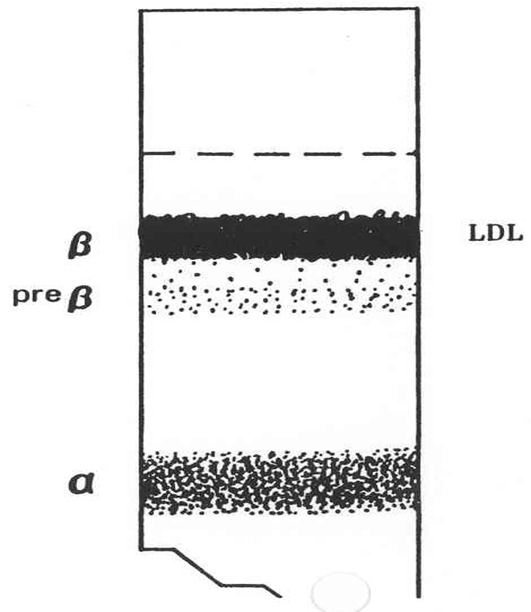
What lipoprotein is in the albumin band
Free fatty acids
What lipoprotein is in Alpha 1 band
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
Alpha
Phospholipids
What lipoprotein is in the Alpha 2 band
VLDL
pre-beta
Triglycerides
What lipoproteins are in the Alpha 2/Beta bridge
Intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL)
Floating beta
Cholesterol
Triglycerides
What lipoproteins are in the Beta band
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
Beta
Cholesterol
What lipoproteins are in the gamma band
Chylomicrons
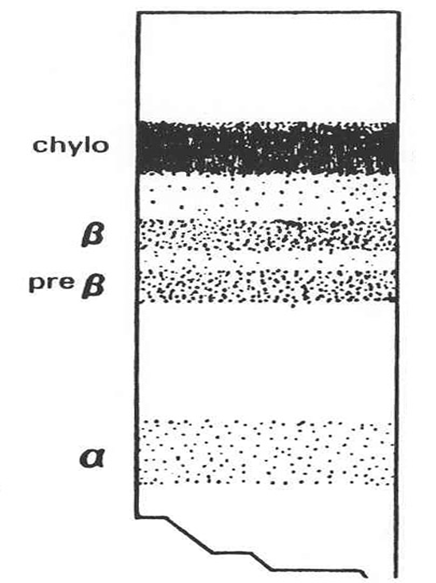
What does the serum look like in hyperlipoproteinemia type 1, what fraction is elevated and what lipoprotein is elevated?
Layer of chylomicrons on clear serum
A slight decrease in alpha band and huge elevation in chylomicron band
TG values can reach as high as 10,000 mg/dL
VLDL usually normal, HDL and LDL are slightly decreased.
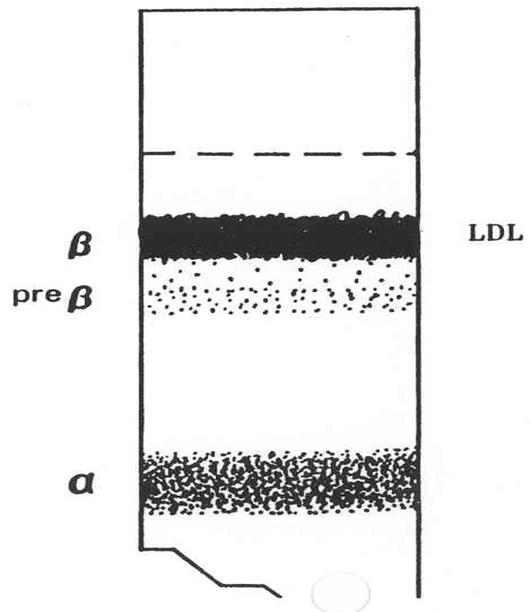
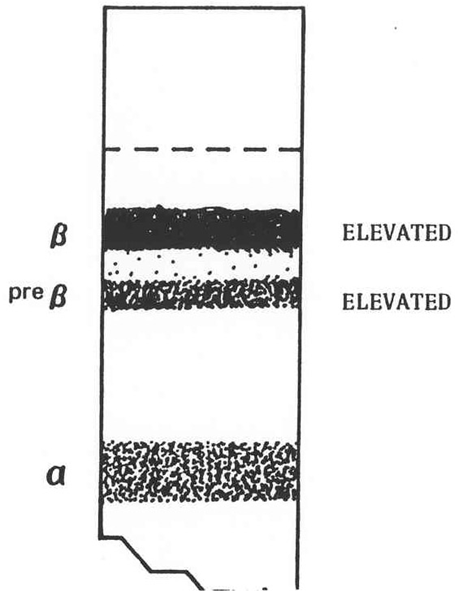
What does the serum look like in hyperlipoproteinemia type IIa, what fraction is elevated and what lipoprotein is elevated?
Usually clear serum
Increase in Beta band
Large increase in LDL. Normal TG
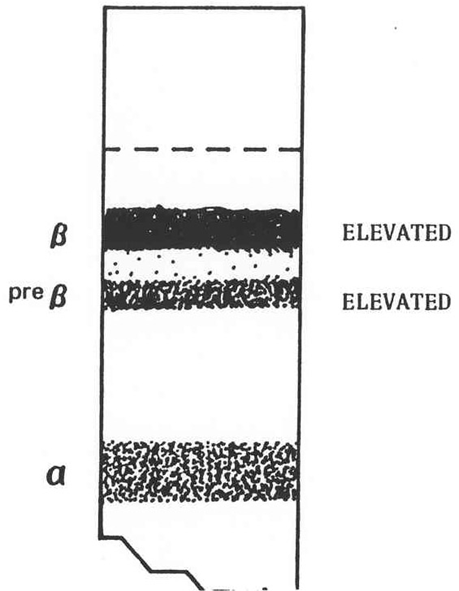
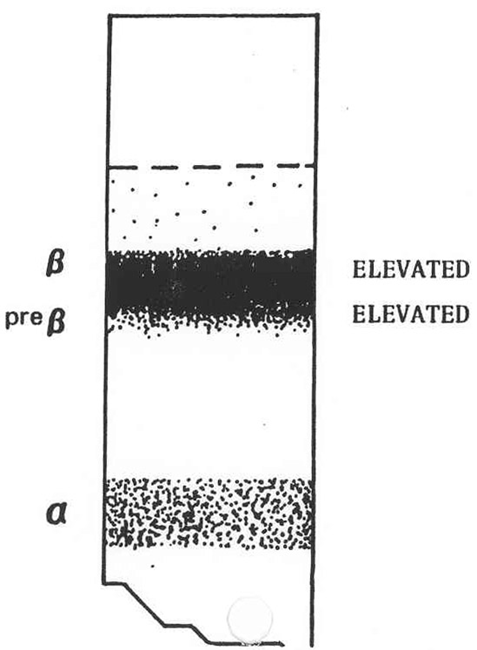
What does the serum look like in hyperlipoproteinemia type IIb, what fraction is elevated and what lipoprotein is elevated?
Clear or faintly turbid, no chylomicrons
Beta and Pre beta
This has a large increase in the LDL, and a slight increase in VLDL
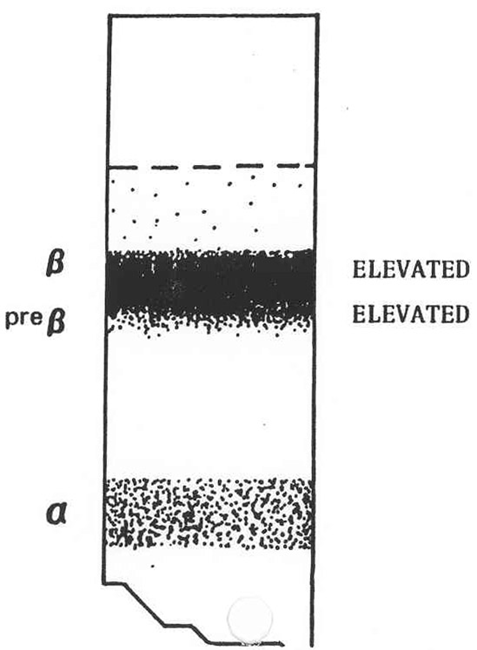
What does the serum look like in hyperlipoproteinemia type III, what fraction is elevated and what lipoprotein is elevated?
Turbid, creamy layer on top
Can cause broad Beta, high chylomicrons
High chylomicrons and VLDL
What does the serum look like in hyperlipoproteinemia type IV, what fraction is elevated and what lipoprotein is elevated?
Turbid with no chylomicrons
Pre beta band is elevated
High elevation in VLDL. There can be a slight increase in LDL, but TG are the big ones.
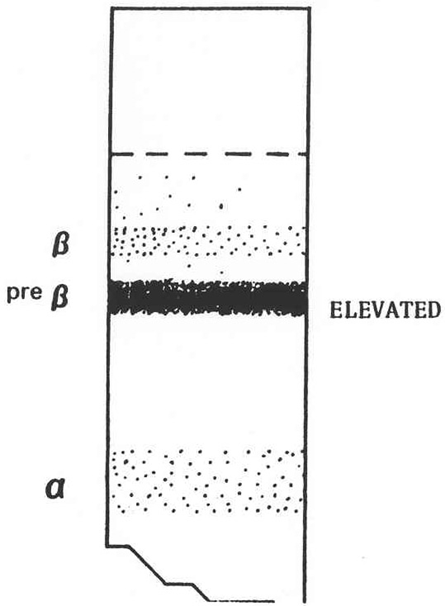
What does the serum look like in hyperlipoproteinemia type V, what fraction is elevated and what lipoprotein is elevated?
Creamy layer over turbid layer
Pre beta and chylomicrons
Increase in VLDL and persistence of chylomicrons.
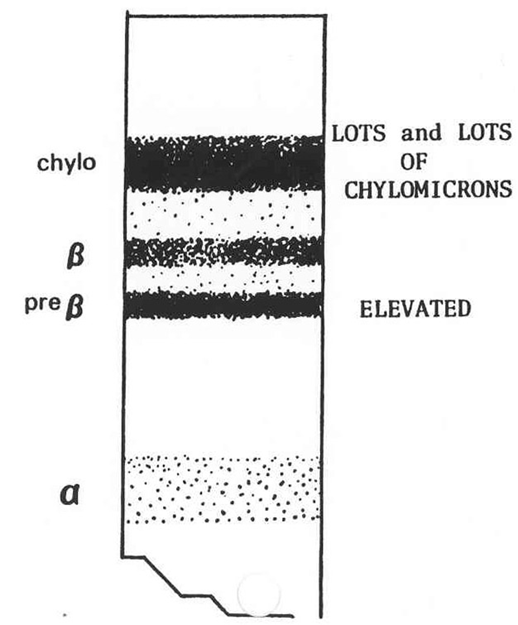
What is this?
Type V
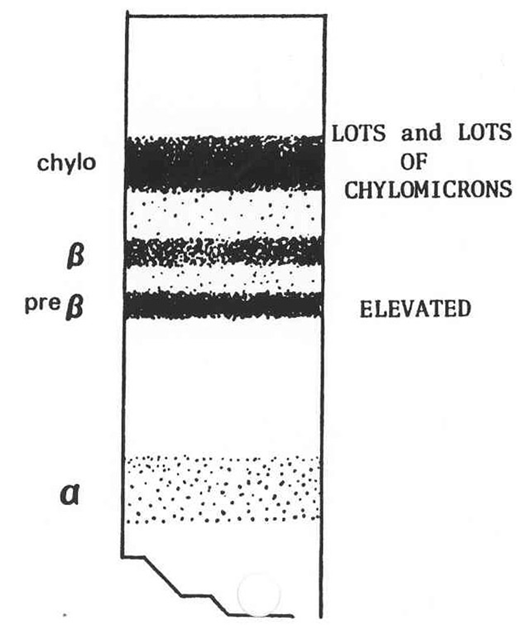
What is this?
Type I - missing lipoprotein lipase
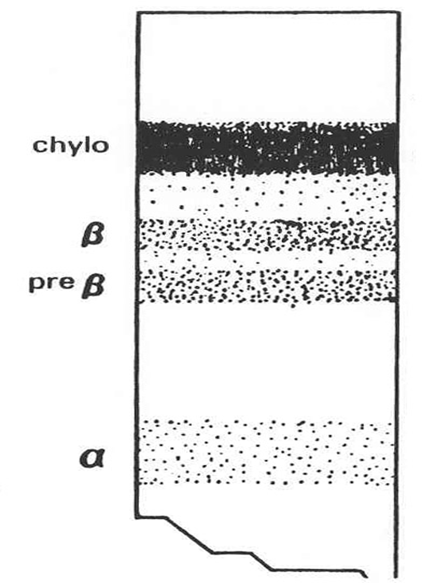
What is this?
Type IIa
What is this?
Type IIb
What is this?
Type III
What is this?
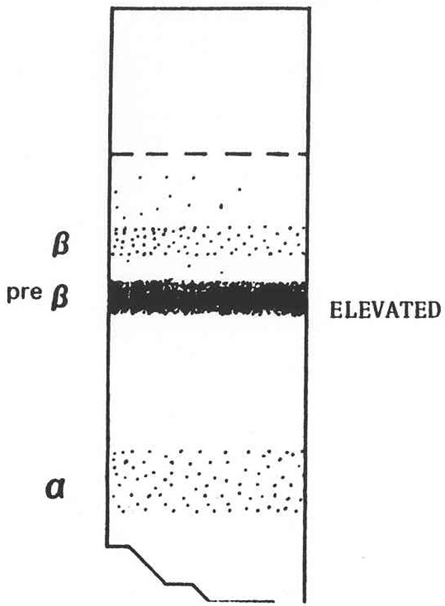
Type IV
What is the most abundant lipoprotein class in lipoprotein electrophoresis?
LDL
What is lipoprotein X?
An abnormal LDL that migrates between the Chylomicron and Beta band
Appears in hepatobiliary obstructs
Since patients will have other symptoms way before the band will apear has no clinical significance
What phospholipid is found in amniotic fluid that can measure lung development?
Lecithin
What are the two tests used to test for fetal lung maturity
FPOL
Lecithin/Sphingomyelin ratio
Why is a lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio done instead of another test?
This method can be done regardless of the hydration status of the mother.
What L/S ratio indicates mature lungs?
>2.0
What L/S ratio indicated immature lungs?
<1.6
What L/S ratio indicates an indeterminate result?
1.6-2
What must be considered when doing an L/S ratio on a diabetic mother? How is this circumvented?
Diabetic mothers have much higher L/S ratio. If P-glycerol is also detectable with a L/S ratio >2 that indicates mature lungs
In a diabetic pregnant mother, what does a L/S of >2.0 and an undetectable PG mean?
Immature fetal lungs
fatty acid
fatty acid, glyceride, phospholipids, cholesterol
nonpolar, polar
albumin
glycerol
monoglyceride
diglyceride
triglyceride
disease correlation
phospholipid
cholesterol
lipoproteins
apolipoprotein
exogenous
endogenous
HDL, chylomicrons
LDL, VLDL, IDL
exogenous
electrophoresis migration
ultracentrifugation
albumin