enzymes
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
what are enzymes
Enzymes are biological catalysts — special proteins that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms without being used up themselves.
why are enzymes important
Enzymes are important because they speed up the chemical reactions needed for life, allowing cells to function efficiently at normal body temperatures.
features of an enzyme
; reusable, specific, reversible, and speed up but not create reactions
what do enzymes do in terms of the rate of reactions
Enzymes increase the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy of a reaction
activation energy (Ea)
The minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction
reaction rate in terms of Ea
The higher the EA is, the slower the chemical reaction will be
What is the purpose of a biological catalyst?
To lower the activation energy of a reaction and increase the reaction rate.
What is the role of catalysts and why are they so important?
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the temperature or pressure needed to start one, without itself being consumed during the reaction. We need enzymes to speed up our metabolic reactions in a way that won't cause damage. Factors like heat are usually used to speed up chemical reactions, however this does not work well in biological systems.
Be able to identify the active site of the enzyme and the importance this site has on the mode of action
The active site of an enzyme is a specific region on its surface with a unique three-dimensional shape. It can be identified as the area where the substrate binds, because its shape and chemical properties are complementary to the substrate.
The active site is crucial to the enzyme's mode of action because it is where the enzyme-substrate complex forms
: What is the process of lowering activation energy to increase reaction rate called?
catalysis, the factors are called catalysts
What are the catalysts for biochemical reactions in living organisms?
enzymes
what biomolecule is most enzymes
proteins
Why are enzymes specific to the reactions they catalyse?
Because of their active site.
the active site
The region where substrate molecules bind to undergo a chemical reaction
What makes an enzyme's active site specific?
It is uniquely suited to bind a particular substrate.
Where does the specificity of an enzyme's active site come from?
From the particular amino acids the active site is made from.
Why can't enzymes bind all substrates?
Because substrates whose shape is not compatible with the active site cannot bind.
catabolic
breaking down
anabolic
building up
process of catalsying a reaction
To catalyse a reaction an enzyme will bind to one or more reactant molecules, its substrates. This can either be catabolic or anabolic
Substrate then binds to the active site
It will temporarily form an enzyme-substrate complex, this is where the catalytic action happens
The substrates are converted to products, and then released. The active site is now available again, and the enzyme is in its original state
Enzymes are reusable
the suffix most enzymes have
Most enzyme names are formed by adding the suffix -ase to the name of the substrate
The exception to the rule are the first enzymes that were originally studied e.g. proteases such as pepsin and trypsin
lock and key model
Is an outdated model, and not used frequently since it doesn't recognise the flexibility of enzymes
The lock is the enzyme and the key is the substrate. Only the correctly sized key (substrate) fits into the keyhole (active site) of the lock (enzyme)
induced fit model
As the enzyme and substrate come together, their interaction causes a mild shift in the enzyme's structure that confirms an ideal binding arrangement between the enzyme and the substrate. This dynamic binding maximizes the enzyme's ability to catalyze its reaction.
non-protein helper molecules
Cofactors and Coenzymes
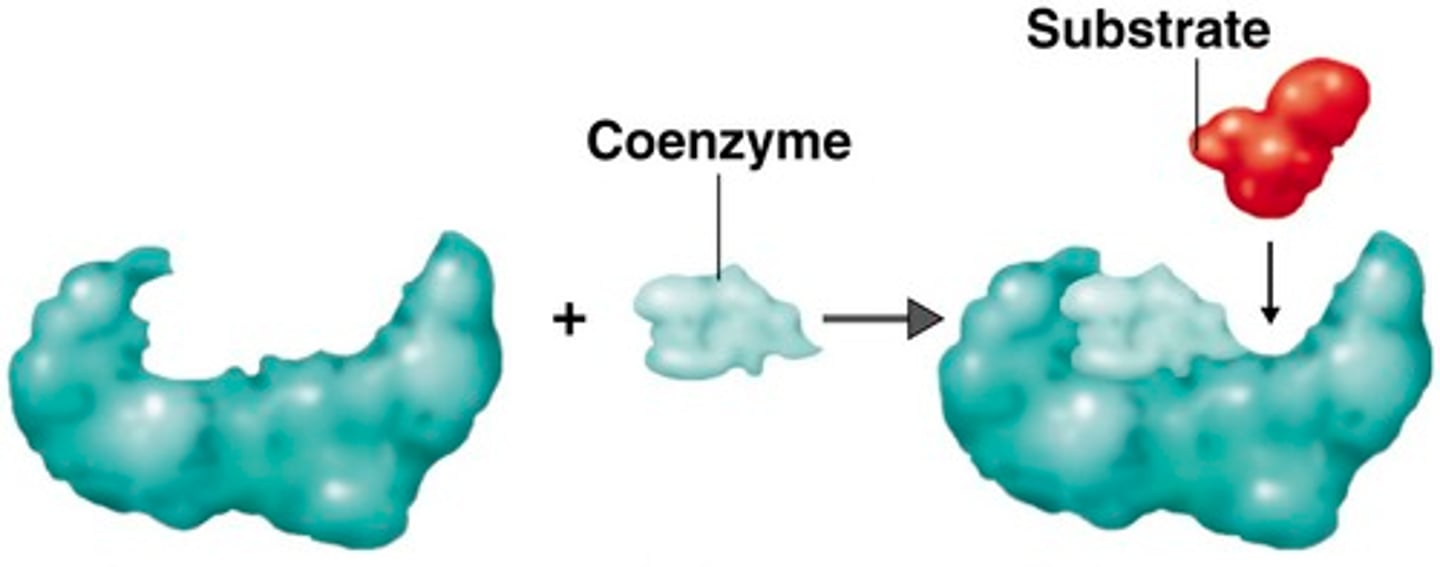
What are cofactors in relation to enzymes?
Molecules that bind to enzymes to activate them; many enzymes are only active when bound to cofactors.
A subset of Cofactors are called
coenzymes. These are organic molecules
competition inhibition
The inhibitor molecule will bind to the active site and block binding of the substrate.
The inhibitor "competes" with the substrate for the enzyme.
This form of competition is reversible by increasing substrate concentration
noncompetition inhibition
The inhibitor will not block the substrate from binding to the active site.
Instead, it will attach at another site (known as the allosteric site) on the enzyme and still block the reaction. This is known as allosteric regulation.
Both inhibitor and substrate can be bound at the same time.
What can inhibitors do in terms of reaction rate
Inhibitors can slow down reaction rate
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Temperature
pH
Substrate Concentration
Enzyme Concentration
In order for a reaction to occur, enzymes require....
..optimal conditions
denaturation
denaturation refers to the process where a protein or nucleic acid loses its native structure and function due to the disruption of its secondary, tertiary, and/or quaternary structure
How does temperature generally affect enzyme activity?
Higher temperatures usually increase the rate of reaction.
What happens to enzymes if the temperature is above their optimal range (e.g., above 40°C in humans)?
The enzyme denatures, changing the active site so it no longer works.
What is the optimal temperature for most human enzymes?
Around 37°C.
What happens if enzymes are exposed to lower temperatures than their optimum?
They do not denature but the rate of reaction decreases because molecules have less kinetic energy.
Why are amino acid residues in the active site important?
They often have acidic or basic properties that are crucial for catalysis.
How can changes in pH affect enzyme activity?.
They can alter the R-groups of amino acids, making substrate binding difficult.
What happens to enzymes at extreme pH values outside their range?
The enzyme denatures.
Why is the tertiary structure of proteins like enzymes important?
it must be maintained for the enzyme to function, as it forms regions like the active site.
What happens if an enzyme loses its 3D structure?
The active site is altered, preventing successful substrate binding.
What causes enzyme denaturation?
Exposure to high heat or strong acids/bases.
what happens if you increase enzyme concentration
It will speed up the reaction, as long as there is substrate available to bind too.
what happens if you increase substrate concentration
It will increase reaction rate until all the available enzymes are bound. At this point, all enzymes will be saturated and working at their maximum rate.
how to tell if an inhibitor is competitive in a chemical reaction
If the inhibitor (name) is a competitive inhibitor, increasing the glucose (substrate) concentration results in higher amounts of glucose-6-phosphate(product) being formed. At very high concentrations of glucose, the amount of glucose-6-phosphate formed would be similar to that of the uninhibited enzyme. This is because competitive inhibition can be overcome by adding more substrate to the enzyme.
how to tell if the inhibitor is non-competitive in a chemical reaction
If the inhibitor (name) is a non-competitive inhibitor, increasing the glucose concentration beyond a certain concentration will not result in any further formation of glucose-6-phosphate (substrate). This is because non-competitive inhibition cannot be overcome by adding more substrate to the enzyme, as it does not compete with the substrate for the active site.
what do anabolic reactions do
require energy (building molecules up)
means products would have a higher amount of energy than reactants
what do catabolic reactants do
release energy (break molecules apart)
means products would have a lower amount of energy than products
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a
catalyst
How do enzymes lower the activation energy?
It depends on the enzyme..
Bringing the substrates together in the right orientation
Creating an environment within the active site that is favourable to the reaction
Bending substrate molecules within the enzyme-substrate complex in a way that facilitates bond breaking, i.e. reaching the transition state within a reaction
Taking part in the reaction; active site residues forming temporary covalent bonds with substrate molecules during the process
endothermic
absorbs energy
exothermic
releases enerygy
are anabolic reactins always endo or exo thermic?
endothermic
are catabolic reactions always endo or exo thermic?
exothermic
what do anabolic reactions require a lot of
activation energy
how can the cell complete an anobolic reaction that requires such energy
by coupling the anabolic enderthermic reaction with a catabolic exothermic reaction
lock and key model strengths and weaknesses
Strengths:
Simple and easy to understand
Explains the high specificity of enzymes
Weaknesses:
Does not explain why enzymes can change shape during reactions
Cannot fully account for how enzymes stabilise the transition state
induced fit model strengths and weaknesses
Strengths:
Better explains how enzymes lower activation energy
Accounts for enzyme flexibility and transition state stabilisation
More accurate representation of enzyme action
Weaknesses:
More complex and less intuitive
Harder to visualise compared to lock-and-key
What impact will reversible inhibitors have on enzyme action
reversible inhibitors slow down enzyme-catalysed reactions by reducing successful substrate binding or catalysis, but because binding is temporary, normal enzyme function can be restored once the inhibitor is removed.
What impact will irreversible inhibitors have on enzyme action
Irreversible inhibitors permanently reduce enzyme activity by binding strongly (often covalently) to the enzyme, usually at or near the active site. This binding permanently alters the enzyme's structure, preventing the substrate from binding or being converted into products.