Ch. 10 Muscle Tissues and Organization
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Properties of Muscle Tissue
excitability, conductivity, contractility, elasticity, extensibility
Excitability
ability to respond to a stimuli
Conductivity
ability to transmit an electrical charge along the sarcolemma
Contractility
ability to generate tension via shortening cell length (allows for movement)
Elasticity
ability of muscle to return to original (resting) length
Extensibility
ability to be stretched beyond resting length (lengthening of muscle cell)
Skeletal muscle is considered an ____
organ
Features of Skeletal Muscle Tissue
striated (actin/myosin)
usually attached to bones
various shapes and sizes of skeletal muscles
Primary functions of Skeletal Muscle
Movement, Maintaining posture, Protection/support, Regulation of materials, Heat production
Movement
bones move when skeletal muscle contracts
Maintaining posture
contraction of muscles keep head and neck up
Protection/support
arrangement of fibers
Regulation of material
sphincters located at orifices of GI and urinary tracts (allows for expulsion of feces and urine)
Heat production
energy for contraction → heat
Muscle sizes
muscle, fascicle, fiber, myofibril
Fascicle
makes up the muscles
made up of muscle fibers
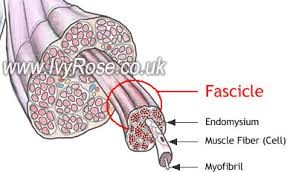
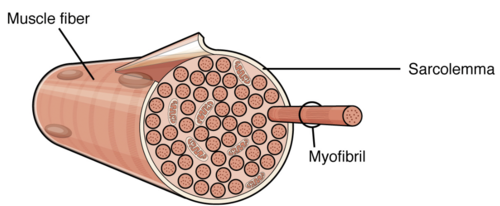
Muscle Fiber/muscle cell
makes up the fascicle
made up of myofibrils
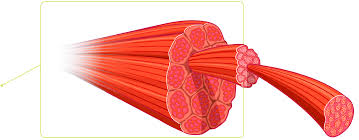
Myofibrils
makes up the fascicle
made up of myofilaments
Myofilaments
short contractile proteins
composed of thick and thin filaments (actin and myosin)
Function of Connective Tissue (CT)
provides protection, sites for blood vessels and nerves, attachments to skeleton
distributes tension to attachment sites
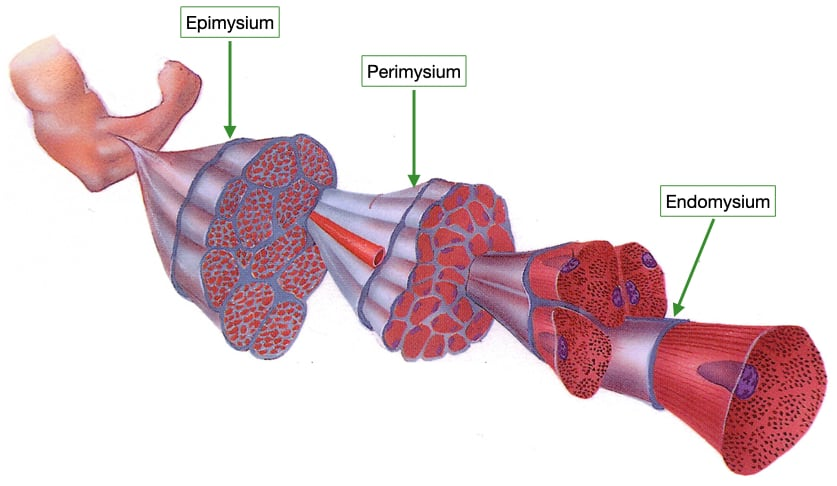
3 layers of CT
Endomysium (within)
Perimysium (around)
Epimysium (upon)
Endomysium
surrounds each fiber
Areolar CT with reticular fibers
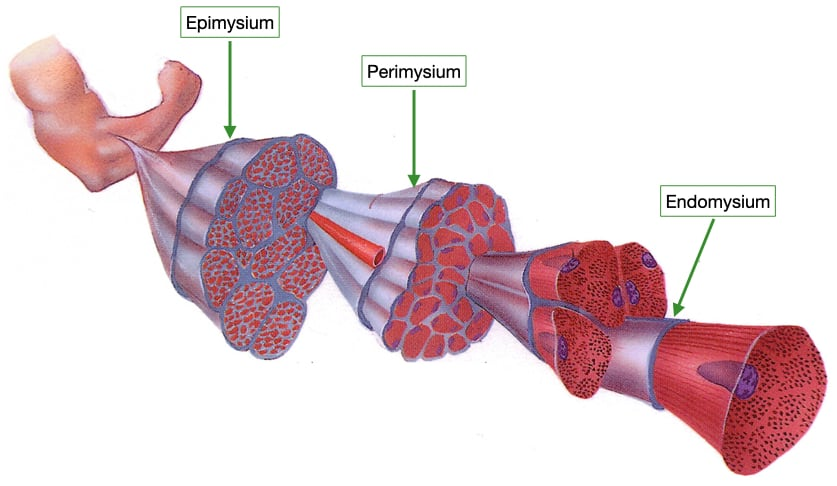
Perimysium
surrounds each fascicle
dense irregular connective tissue
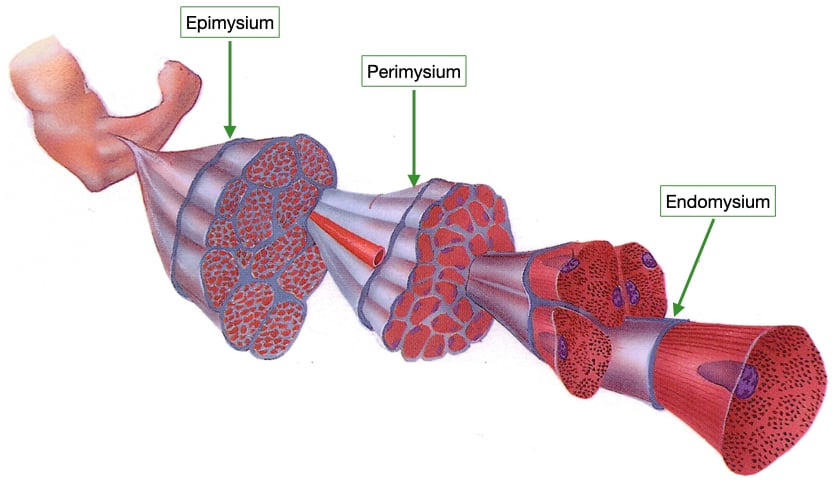
Epimysium
surrounds entire skeletal muscle
dense irregular connective tissue
Deep fascia
sheet of dense irregular CT
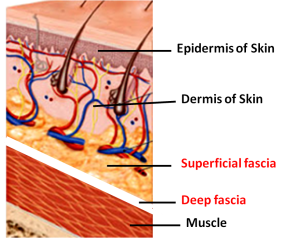
Purpose of the Deep Fascia
separates individual muscles
binds together muscles with similar functions
distributes vessels (nerves blood)
Superficial fascia
areolar and adipose CT (subcutaneous layer)
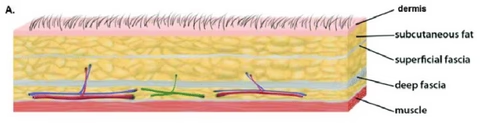
Purpose of the Superficial Fascia
separates skin from muscle
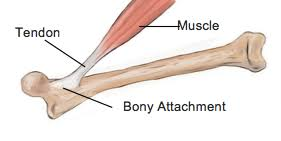
Tendons
attaches muscle to bone, skin or another muscle
(CT layers merge to form tendons)
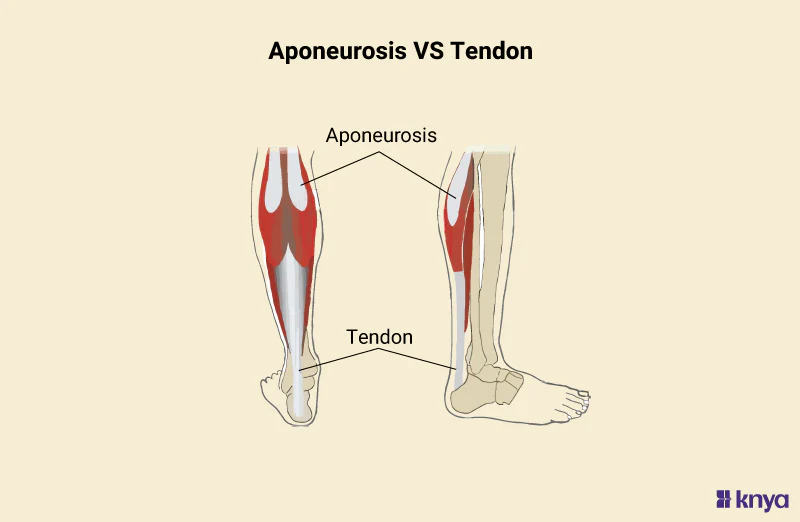
Aponeurosis
tendon that forms a thin, flattened sheet
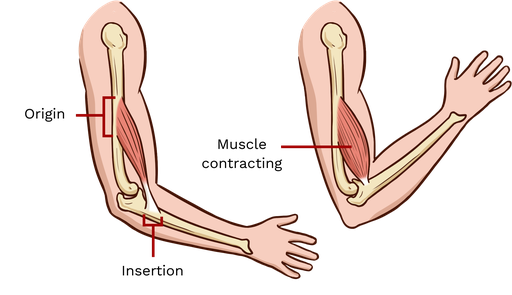
Muscle Attachments
skeletal muscles extend over a joint and attach to bones on either side of the joint
origin, insertion
Origin of Muscle Attachments
less mobile attachment site
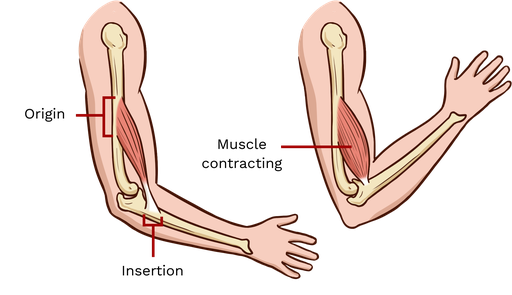
Insertion of Muscle Attachments
more mobile attachment site
Blood Vessels
travel/extend through perimysium and epimysium
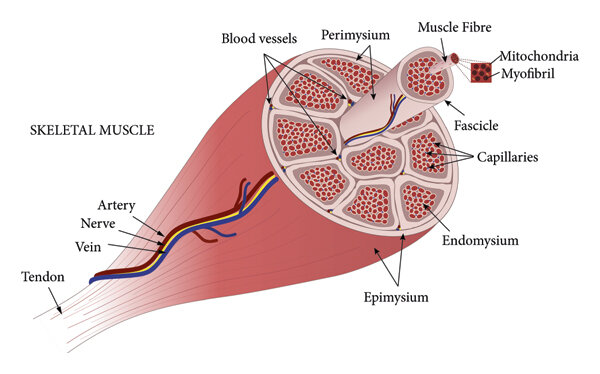
What are the functions of blood vessels
deliver nutrients and oxygen to muscles
remove waste products
Nerves
controlled by somatic (voluntary) motor neurons
axons
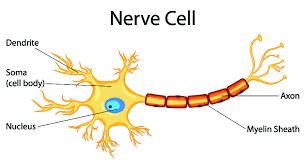
Axons of somatic motor neuron
pass through all 3 layers of CT to create junctions with skeletal muscle fibers
Components of muscle cells (muscle fibers)
Sarcolemma
Sarcoplasm
Mitochondria (-300 per fiber)
Multinucleated
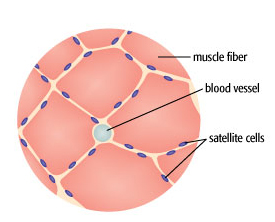
Satellite cells
Transverse tubules
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Satellite cells
help with repair and regeneration of skeletal muscle tissue
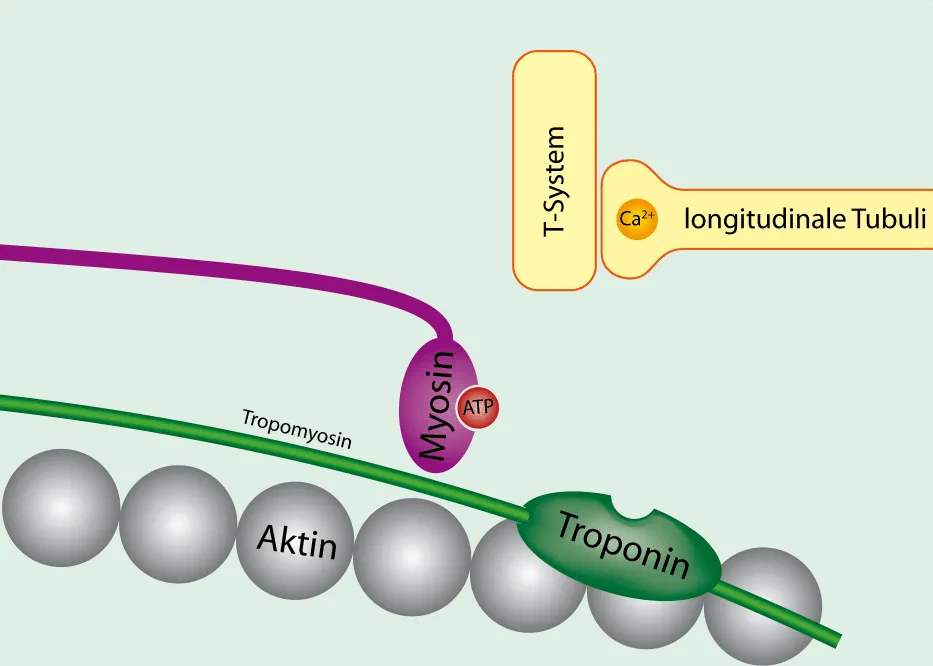
Transverse tubules (T-tubules)
invaginations of the sarcolemma that extend into the sarcoplasm
carries impulses from sarcolemma
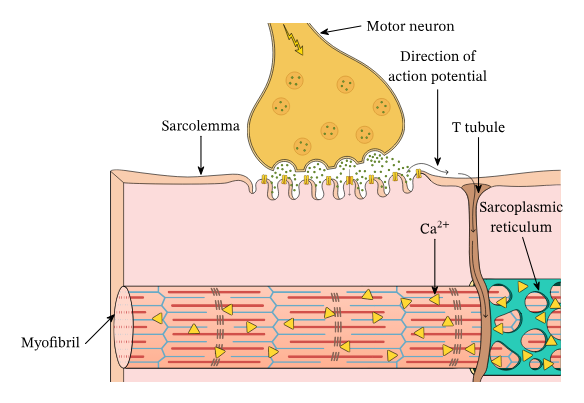
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
internal membrane complex
stores Ca2+
Terminal cisternae
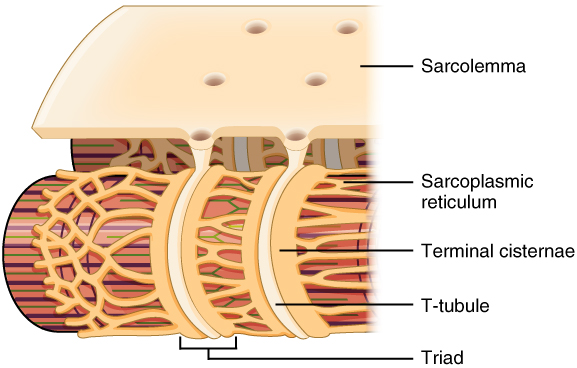
Terminal cisternae
expanded ends of SR that are in contact with T-tubules
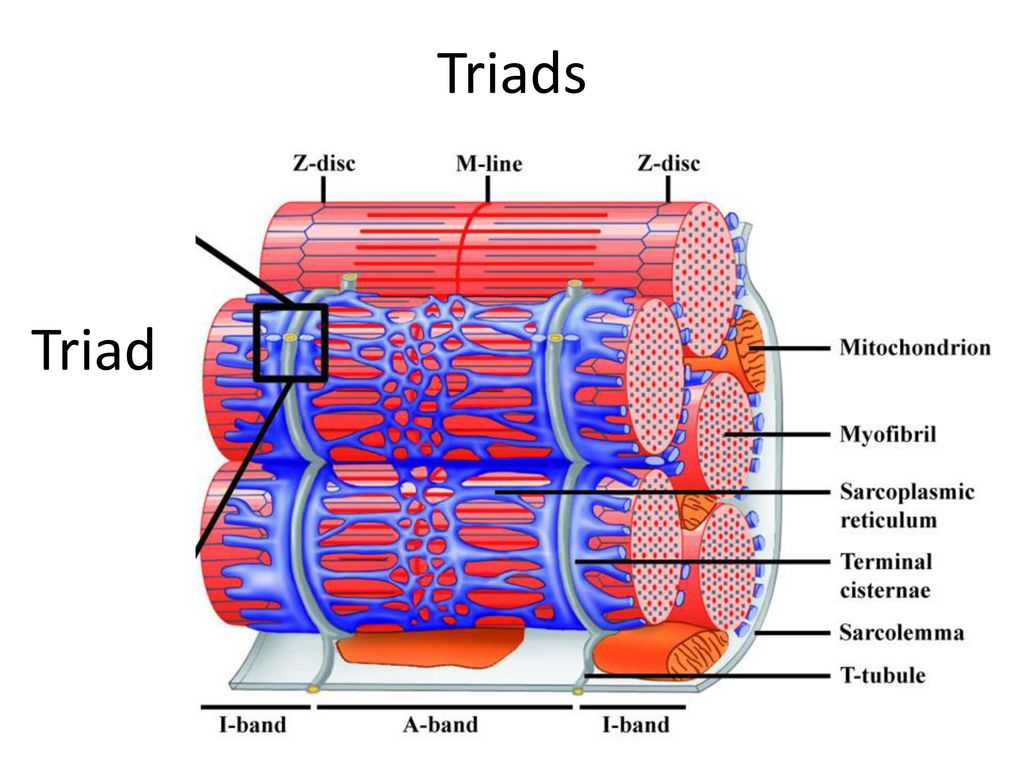
Triad(2 per 1 t-tubule)
Myofilaments
strands of proteins which allow for contraction
thick - myosin
thin - actin
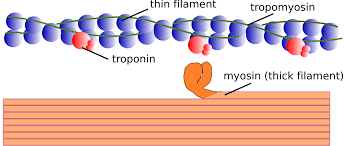
Thick filaments (myosin)
composed each myosin has 2 strands
heads form cross-bridges with thin filaments during contraction
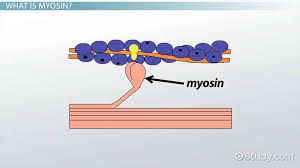
Cross-bridges
temporary connection formed between the myosin head (from a thick filament) and the actin filament (thin filament) within a muscle cell

Thin filaments (actin)
2 twisted protein strands wrapped around each other
Regulatory proteins:
Tropomyosin
Troponin
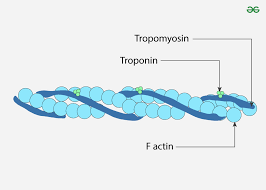
Tropomyoisin
protein that covers binding sites for myosin heads
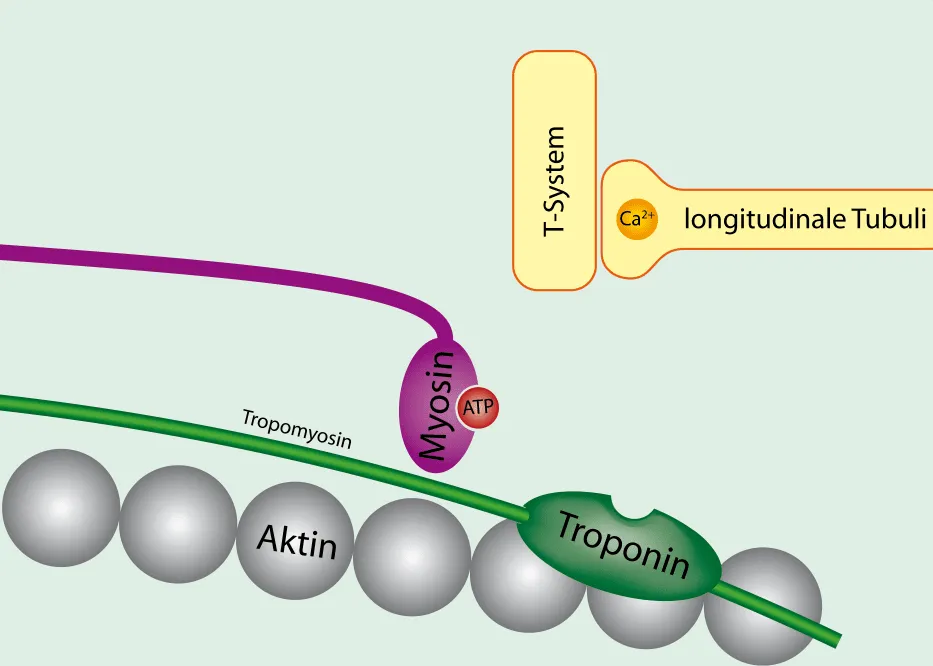
Troponin
attached to actin and provides binding site for calcium
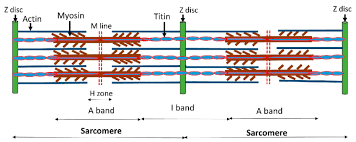
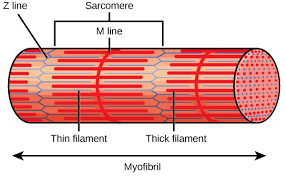
Sarcomere
functional unit of skeletal muscle fibers
in skeletal and cardiac muscles
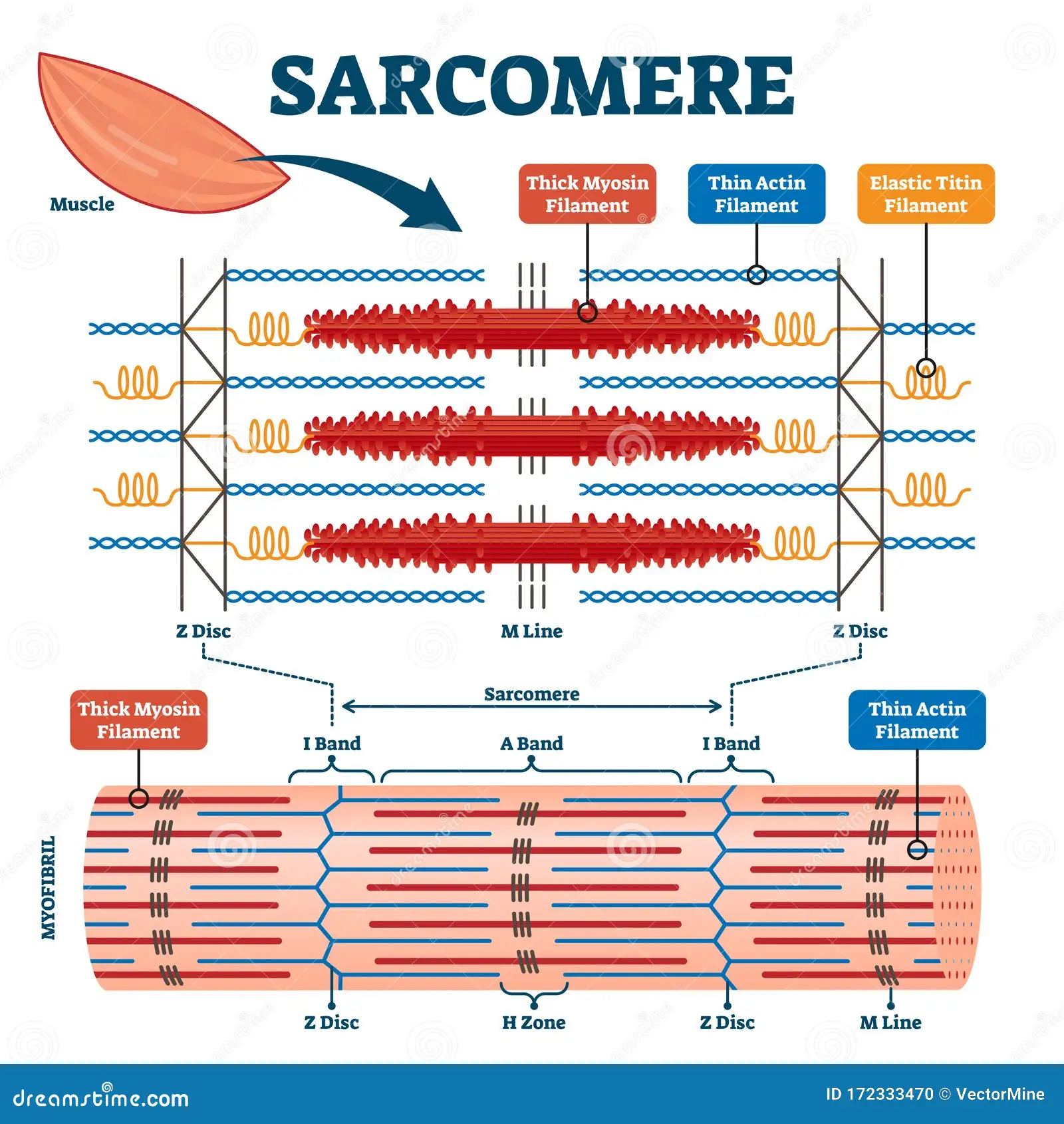
Z disc (Z lines)
ends of sarcomere
serves as anchors for thin filaments
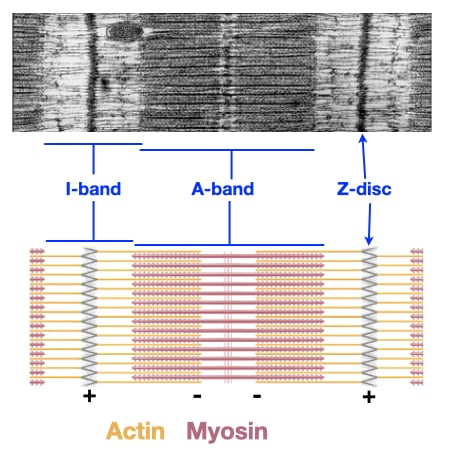
I band
extend from Z discs
contains only thin filaments (actin)
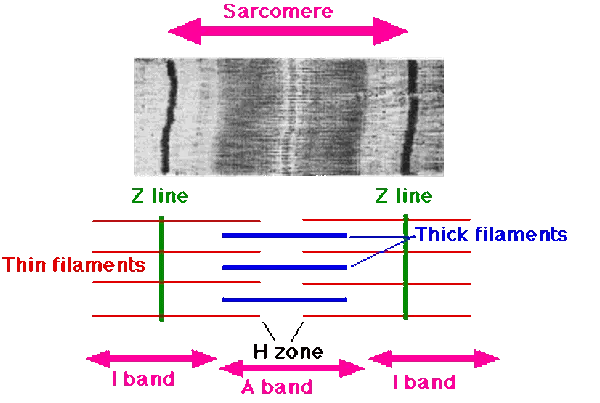
A band
central region of sarcomere
where thin and thick filaments partially overlap
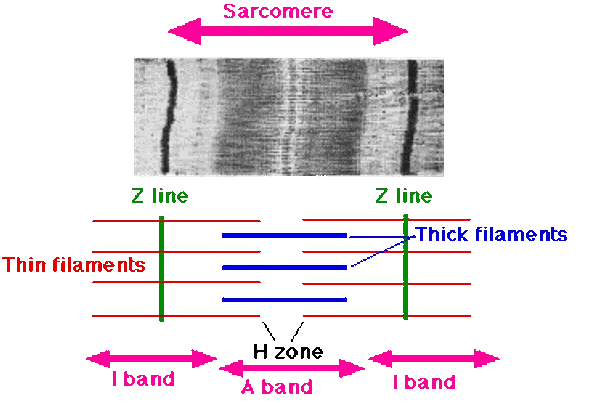
H zone
most central portion of A band
contains only thick filaments
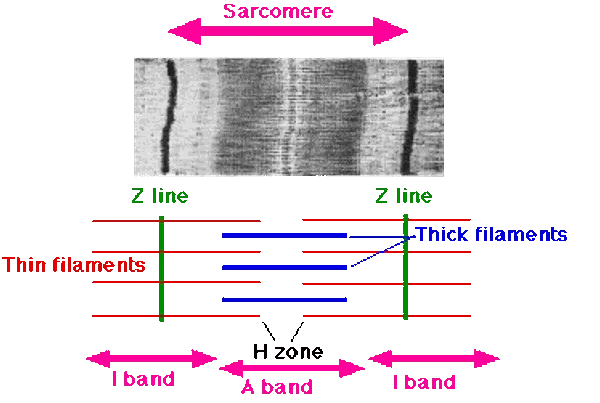
M line
thin transverse protein meshwork in center of H zone
attachment site for thick filaments
Sliding Filament Theory
sarcomeres shorten when the thick filaments attach to the thin filaments and pull them towards the center of the sarcomere
Motor unit
single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates
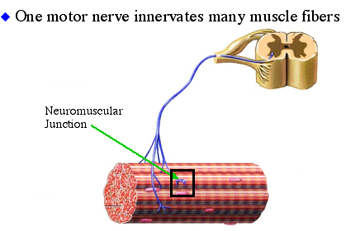
Size principle
size of the motor unit and indicates degree of control
Big MU - quadriceps femoris
Little MU - eyeball
All-or-Nothing Principle
when a motor unit is stimulated, all muscle fibers within it contract
Type 1 Muscle Fiber
slow oxidative (aerobic)
Type 2a Muscle Fiber
fast oxidative/glycolytic
Type 2b Muscle Fiber
fast glycolytic (anaerobic)
Cardiac Muscle (involuntary)
in myocardium (wall of heart)
autorhythmic
striated
mitochondria (aerobic)
controlled by automatic nervous system
Autorhythmic
able to generate electrical impulses without nerve stimulation
Smooth muscle (involuntary)
controlled by automatic nervous system and in walls of viscera and blood vessels
one central nucleus
Muscular hypertrophy
increase in muscle size (not number
Muscular dystrophy
decrease/wasting of muscle tisue
Rigor Mortis
skeletal muscles lock into a contracted position a few hours after the heart stops beating
calcium remains bound to troponin
ATP is not available (cross-bridges can’t detach)