14- Infections of the Urogenital System II
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
describe the shape of lepto
motile, tightly coiled spiral orgs w hooked ends (like a question mark)
describe lepto bacteria characterisitcs
-gram negative
-need darkfield
-sero and epi diverse w ove 250 serovars
where can lepto be found
ponds, rivers, moist soil and mud
pathogenic strains of lepto can persist where in the body?
renal tubules and genital tract of animals
where does lepto replicate?
ONLY in host!!!
describe lepto in the environment
-can survive a long time esp in moist places
-high temp and acidic pH of undiluted urine is detrimental
what favors growth for lepto?
common in late summer/early fall
ambient temp, neutral pH
what serves as the main sources of lepto infection?
carrier animals/rodents
describe direct transmission of lepto
contaminated urine
venereal or transplacental transfer
describe indirect lepto transmission
contaminated water
contaminated environment
what are maintenance hosts for lepto
hosts that become long term (asymptomatic) carriers and sources for transmission
rodents: icterohaemorrhagiae
cattle: hardjo
dogs: canicola
what are incidental hosts for lepto?
hosts that acquire infection from carriers leading to acute dz
dogs, cattle, human: icterohaemorrhagiae
human: canicola
how does lepto penetrate the body?
thru intact MM of mouth, eyes, nose
OR
scratched/water softened skin
where does lepto travel after penetrating thru the skin
-enters systemic circulation
-multiplies rapidly and spreads to many tissues like kidney tubular epithelium, spleen, genital tract, CNS
the extent of damage from lepto depends on?
the virulence of diff serovars and susceptibility of host species
what are the virulence factors of lepto?
adhesions (LipL32, LenA-F)
factor H-binding proteins
hemolysin
LPS
describe the transmission cycle of lepto
-bacteria shed in urine of carriers
-enter animals thru skin/MM
-humans infected thru contact with urine
in many places what does rainy season equate to?
lepto szn
what issues do temperate regions bring in relation to lepto?
-significant vet problem
-homeless people
-water sport outbreaks
10% of people experience Weil’s syndrome with severe lepto, describe it
jaundice
renal dysfunction
pulmonary hemorrhage
high fatality
most people who get lepto experience the milk anicteric phase, describe it
flu symptoms without yellowing of skin
describe the acute form of canine lepto
-affects puppies
-fever, blood stained feces, MM hemorrhage, epistaxis
-high mortality
describe the uremic type of canine lepto
-mainly affects kidneys
-anorexia, lethargy, pu/pd
-urine = glucose, protein, sediment
-oliguria, anuria, renal azotemia (most cases)
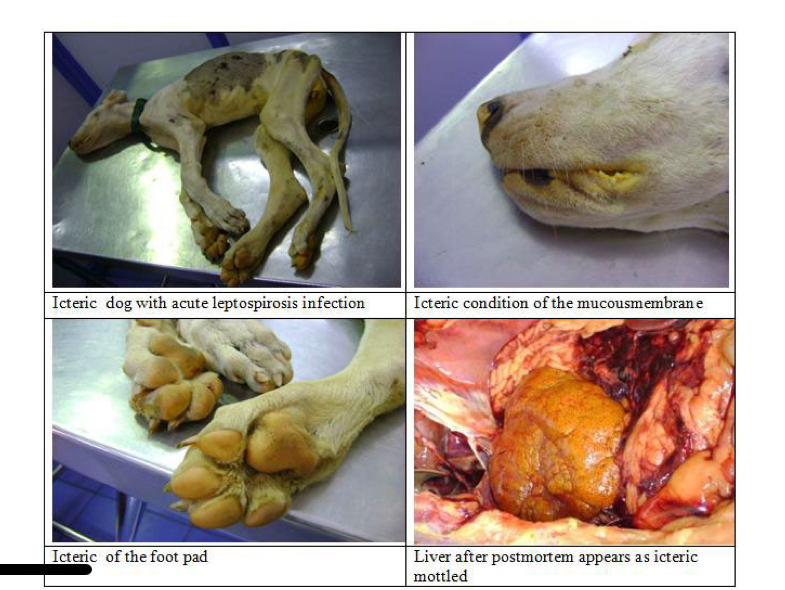
describe the icteric type of canine lepto
-peak signs 6-8 days post onset
-focal hepatic necrosis
-icterus, hypoalbuminemia
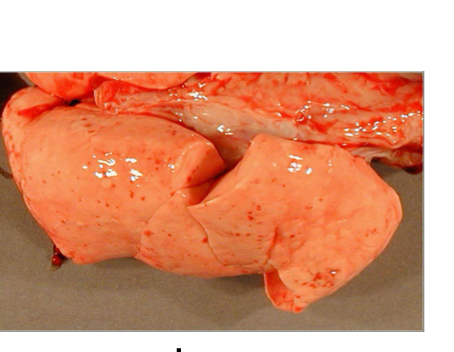
common signs of lepto on lungs
petechiae scattered thru-out
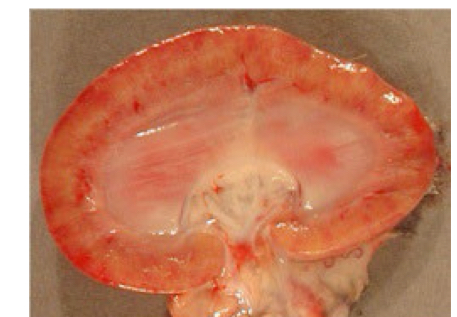
common signs of lepto on kidney
cortex has pale appearance consistent with nephritis
symptoms of lepto in cattle
-abortions
-replacement heifers can develop dz with pyrexia and agalactia (no milk prod)
tx / control of lepto in cattle
streptomycin / amoxi
monovalent and multivalent vacc
clinical signs of lepto in horses
-abortions and renal dz in young horses
-equine recurrent uveitis (moon blindness) which is persistent infection and molecular mimicry w lepto antigens with eye components
lepto hardjo: cattle, sheep, humans
abortions, still births, flu illness, kidney and liver dz
lepto bratislava: pig, horse, dogs
repro failure, abortions
lepto canicola: dogs
nephritis
lepto grippy: cattle, pigs, dogs
systemic dz in young animals, abortion
lepto ictero: cattle, sheep. pig
acute septicemia in young animals, abortions
lepto copenhageni: domestic animals and humans
peracute and acute dz, abortion in animals
lepto pomona: cattle, sheep
hemolytic dz in calves, lamb, abortions
lepto pomona: pigs
repro failure, septicemia in piglets le
lepto pomona: horses
abortions, ERU (moon blindness)
clinical path of lepto
urine: hematuria, pyuria, proteinuria, glucose
blood: increased BUN and creatinine (azotemia) in 90% of animals
describe bacterial cultures for lepto
-not routine
-can be isolated from blood in within 7-10 days but avoid citrate anticoagulant
-if 2 weeks after, alkalize urine and use mult samples w EMJH media
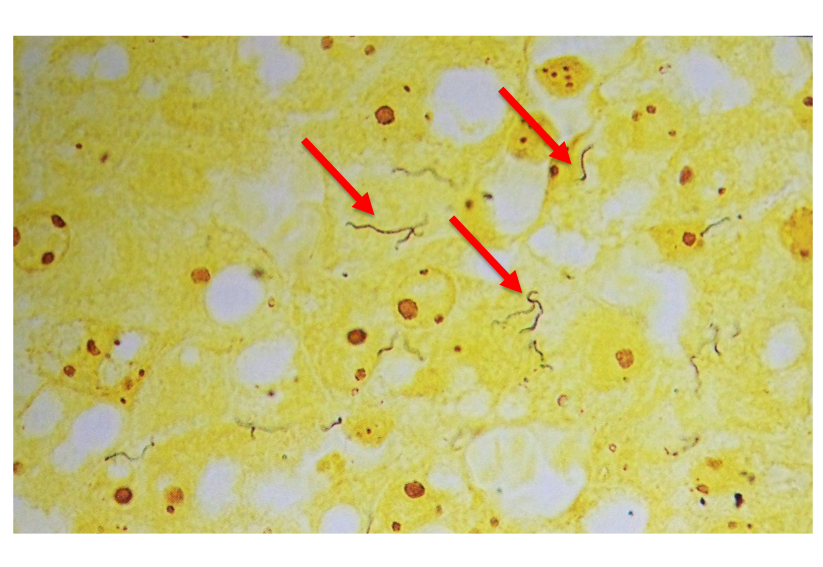
what is this
lepto in the liver impression smear of a dog
dx of lepto
-micro agglut test (MAT) is most common
-single high titer in unvacc dog = POSITIVE
-prefer to have rising titer w 4-fold inc
what is looked for on a PCR test for lepto?
qPCR (lipl32) from urine, blood, eye fluid, tissues
are there vaccines for lepto?
yes but cant distinguish between vaccine and infection
is there zoonotic risk for lepto?
YES SO BEWARE