🧬 Biology Semester One - Revision
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes; cells, respiration, photosynthesis, inheritance, selection, evolution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what is an allele ?
"allele" is the word that we use to describe the alternative form or versions of a gene.
what is the role of mitochondria ?
the mitochondria is the powerhouse in a cell, its role is to produce energy.
why is DNA important ?
DNA stores genes and transfers them to offspring.
what are the differences between plant and animal cells?
Plant cell have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole.
Animal cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts and have small vacuoles.
Plant cells are more box-shaped; animal cells are more rounded.
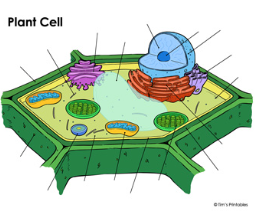
what are the parts on this plant cell ?
nucleolus, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplast, cell wall, mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, vacuole, cell membrane
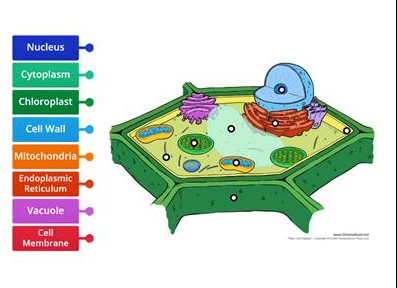
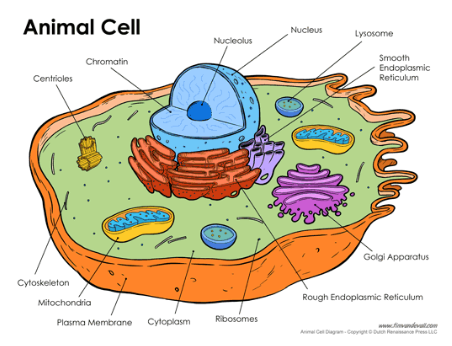
what are the parts on this animal cell ?
nucleolus, nucleus, lysosomes, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, ribosomes, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, mitochondria, cytoskeleton, centrioles, chromatin
what are the three adaptations ?
Type of Adaptation | What it Means | Example |
|---|
Structural | A body part or physical feature that helps it survive | A polar bear’s thick fur to stay warm |
Behavioural | A way the organism acts or what it does to survive | Birds migrating in winter |
Physiological | An internal body process or chemical function | A snake producing venom |
how do structural, behavioral, and physiological adaptations help an organism survive ?
structural: helps the organism blend in, protect itself, or get food.
Example: a giraffe’s long neck lets it reach high leaves.behavioural: helps the organism avoid danger or find food by changing how it acts.
Example: birds migrate to warmer places to survive the cold.physiological: helps the organism’s body work better in tough conditions.
Example: camels store fat in their humps for energy in the desert.
how does natural selection work ? (use variation, phenotype/adaptation, selection pressure, selective advantage)
Variation means individuals have different traits.
Some phenotype/adaptations help individuals survive better.
Selection pressure (like predators or climate) makes survival harder.
Those with a selective advantage are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Over time, these traits become more common in the population.
what is the selection pressure in an environment acting on a species
Selection pressure is anything in the environment that affects which individuals survive and reproduce. It can be:
Predators (e.g., animals that hunt the species)
Climate (e.g., extreme cold or drought)
Food availability (e.g., scarce or changing food sources)
Competition (e.g., fighting for mates or resources)
Disease (e.g., viruses or bacteria that harm the species)
Human activity (e.g., pollution, hunting, habitat loss)
Example: If a population of rabbits lives where foxes hunt them, the foxes are the selection pressure because they influence which rabbits survive.
what is speciation ?
the formation of new species
what is temporal isolation ?
a type of isolation that occurs when populations do not interbreed with each other because they reproduce at different times. (sympatric isolation)
what is geographic isolation ?
a type of isolation in which two allopatric species do not mate because of different in courtship behaviour. (allopatric isolation)
what is reproductive isolation ?
a type of isolation that occurs when two groups of animals live close enough to one another to interact, but are unable to interbreed with one another.
what is Charles Darwin’s theory ?
pass favourable traits to offspring
happens to a population over a long period of time
survival of the fittest
population lifetime
what is convergent evolution with examples ?
when animals that aren’t closely related end up looking/acting alike because they live in similar environments or have similar ways of life