Class Exam 1
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
what phylum do all mammals belong to
phylum chordata
what is the first of the distinct features of the chordata
the notocord
what is the second of the distinct features of the chordata
dorsal hollow nerve cord
what is the third of the distinct features of the chordata
pharyngeal slits or gill slits
what is the fourth of the distinct features of the chordata
tail
what are the three defining features of the subphylum vertebrata
true back bone, endoskeleton, cranial cavity (skull)
what is the first subclass of the class mammalia
prototheria (monotremes, egg layers)
what is the second subclass of the class mammilia
theria (marsupials and true placentals)
What are some distinguishing features of mammals
mammary glands, hair, endothermic, (most) bear live young, increased brain size
what is pelage hair
stiff guard hairs and downy underfur
what is the primitive pattern of mammal hair
Dreiartgruppen (hair in threes)
what are some advantages of hair
coloration, insulation (hot and cold), tactile purposes (think whiskers)
what is the hair folicile
living cells in the skin from which the hair grows
what is hair
nonliving dead epidermal cells strengthed by keratin
what is the medulla of the hair
The inner layer of cells
what is the cortex of the hair
middle layer of cells
what is the cuticular scales of the hair
outer layer, scale like, can be used to ID species
the alveoli connect to the milk ducts which open into nipples in all but what mammals
monotremes
what triggers mammary gland development
estrogen
milk production is stimulated by the secretion of what chemicals
prolactin and somatotropin
the command for milk production comes from what area of the brain
the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland (link to the placenta)
Nursing suppresses what
ovulation
what chemical in the brain must be released for milk “letdown”
oxytocin
what are the main components of milk makeup
water, lipids, protein, sugars, minerals
in what group are nipples first found
marsupials
what are scent and musk glands used for
mark territory, defense, attract mates
what do the sebaceous glands help with
water repelent, skin protectant
what is adipose tissue
Body fat that stores energy and insulates the body.
what is the heart set up in mammals
four chambered, two distinct halves
what is unique about mammilian red blood cells
no nucelus
why do mammilian cells have no nucleus and are disc shaped (expecept in cammels)
allows them to hold more O2
what is a choriovitelline placenta
combination of yolk sac and chorion, found in marsupials
what is a chorioallantoic placenta
complex placenta providing greater nutrient exchange, found true placental mammals
what do the vili do in the placenta
facilitate nutrient and gas exchange between mother and embryo, increase surface area for absorption.
what is a peramelid placenta
Basically an inbetween of a chorioallantoic and choriovitelline placenta, found in the order Permaelemorphia
what is the baculum
penis bone, not found in elehants, whales, humans, monotremes, hoofed mammals
what is cecal fermentation
A digestive process where herbivores break down fibrous plant material using microbial fermentation.
what is the advantage of a multi chambered stomach
more efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients by breaking down food in stages
what waste product do mammals produce
urea
what part of the ear is unique to mammals
the external pinna
what is the function of the external pinna
captures and funnels incoming sound waves
what are the three mammilian ear bones
incus, malleus, stapes
what are rods in the eye
Photoreceptor cells responsible for low-light vision
what are cones in the eye
Photoreceptor cells that detect color and are responsible for high acuity vision.
what is the basal rate of metabolism
minimial cost of maintaining body functions at rest
what is the general trend of basal metabolic rates in relation to size
increases with decreasing body size
what is the peripheral nervous system
sensory and motor system
what is the neopallium of the brain
the “control center” that processes information and motor outputs
what does the wrinkling of the brain imply
surface of the brain simpily trying to keep pace with increased volume of the brain, not a sign of increased intelligence
what is the corpus callosum
bridge betwwen brain hemispehres, NOT present in monotremes and marsupials
what is ossification
bones being hardened by calcium salts and fusing of bones
what are the advantages to better, complete ossification of bones
better joint formation, stable anchor for muscles
relative to reptiles, mammals and ____ and ____ bones
fewer, simpler
what are the advangtages to having less and simpler bones
more flexibility, less developmental costs, increased limb speed, decreased mass
what is determininant bone growth
bones don’t continously grow, ossification happens early, well formed joints
what did the fusion of the pelvic girdle do for mammals
allowed for a more upright stance with limbs in the center of gravity allowing for rmore efficent movment
what is the epiphysis of a bone
articular surface of long bones
what is the diaphysis of a bone
bone shaft
what is the epiphyseal plate of a bone
cartiliege zone between the diaphysis and the epiphysis that allows for bone growth.
what is the axial skeleton
head, backbone, ribs
what is the first vertebral division
the cervical (neck) - usually seven
what is the second vertebral division
the thoracic (chest), where the rib attaches
what is the third vertebral division
lumbar (lower back), largest vertebrate, back muscle attachment
what is the fourth vertebral division
sacral (pelvis region), pelvic girdle attachment
what is the fifth vertebral division
caudal (tail)
what is the appendicular skeleton
limbs, classic 1 block - 2 block bone pattern, makes up limbs
what is a sutural joint
immovable joint found in the skull
what is a symphyseal joint
slightly moveable joint, found in jaw, discs, pubis (in females)
what is a synovial joint
a fully moveable joint characterized by a fluid-filled cavity, allowing for a wide range of motion.
what is a gliding joint
a joint that can slide side to side of back to front
what is a hinge joint
a joint that can bend in one plane only (ie the knee)
what is a ball and socket joint
a joint with several planes of movment
what are the two main components of the skill
cranium and mandible
what is the premaxillary bone
anterior portion of the upper skull, origin of upper incisors
what is the nasal bone
anterdorsal surface following premaxillary
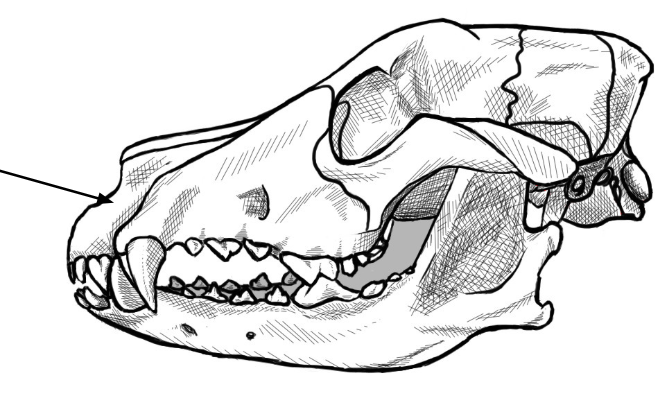
What is this arrow pointing to
premaxillary
what is the maxillary bone
behind premaxillary, includes bones of all upper teeth excpet incisors
what is the intraorbital foramen
small opening in the maxilla located below the orbit that allows for the passage of nerves and blood vessels.
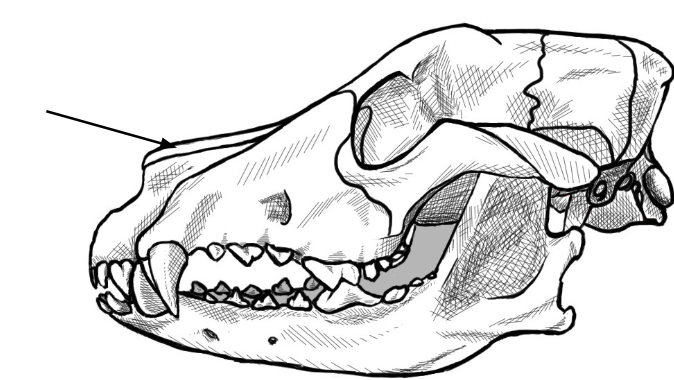
what is this arrow pointing to
nasal bone
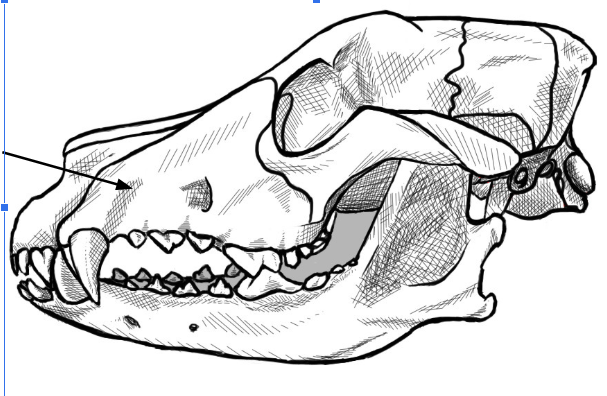
what is this arrow pointing to
maxillary bone
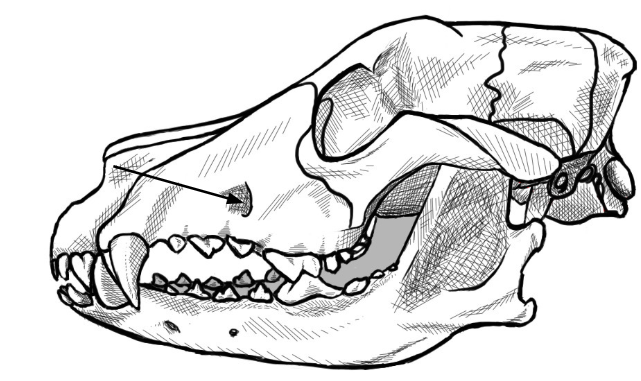
what is this arrow pointing to
intraorbital foramen
what is the frontal orbital
eye socket
what is the lacrimal
opening for tear duct, small bone on anterior portion of the frontal orbital
what is the frontal of the skull
the bone set right beind the maxillary in between that and the parietal
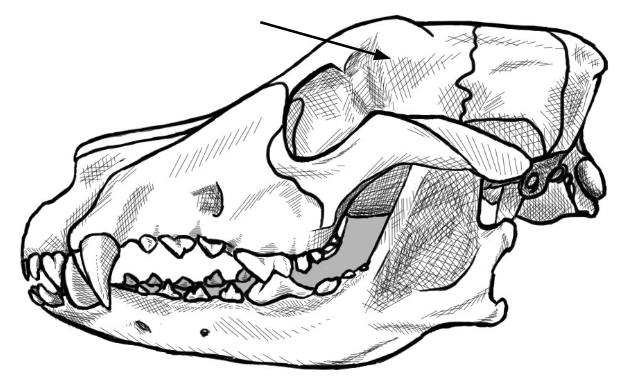
what is this arrow pointing to
frontal bone of the skull
what is the parietal of the skull
bone behind the frontal but before saginal crest
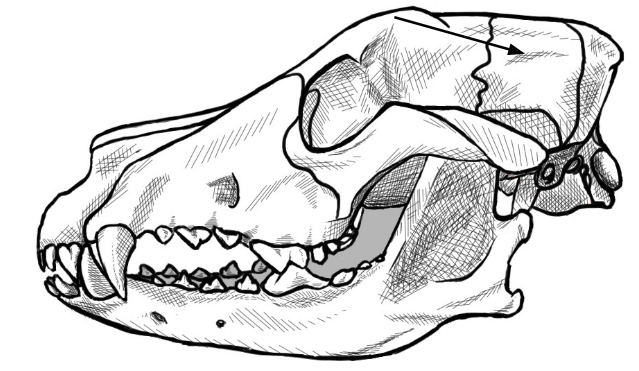
what is this arrow pointing to
parietal bone of the skull
what is the sagital crest
a bony ridge along the midline of the skull, serving as an attachment point for skull muscles.
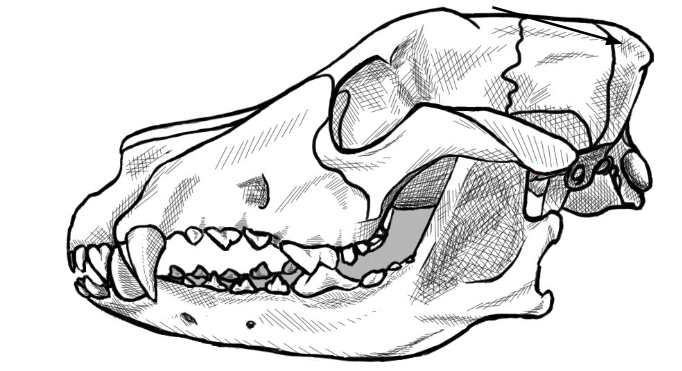
what is this arrow pointing to
saginal crest
what is the foramen magnum
large opening in base of skull for spinal cord
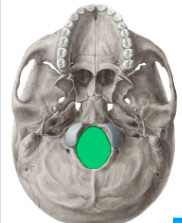
what is the name of the skull part that is highlighted in green
foramen magnum
what is the occipital bone
back of the skull, surrounds the foramen magnum
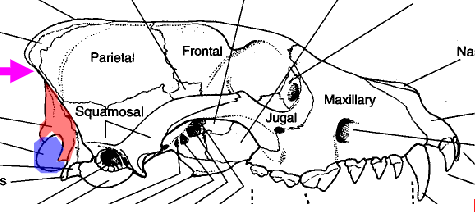
what is the area in red refering to
occipital
what is the occipital condyle
rounded protrusions that articulate with the first cervical vertebra, facilitating head movement.
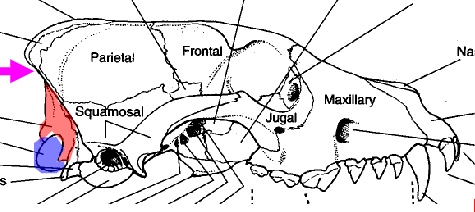
what is the area in blue referring to
occipital condyle
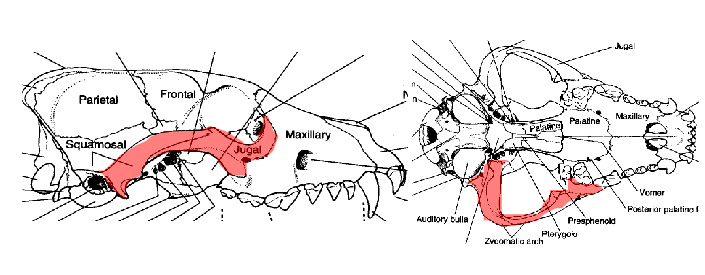
what is the highlighted bone
zygomatic arch (actually two bones)
what is the zygomatic arch
two arched bones protecting the orbit
what is the name of the bone closest to the eye socket in the zygomatic arch
jugal bone
what is the name of the bone farthest away from the eye socket in the zygomatic arch
squamosal bone
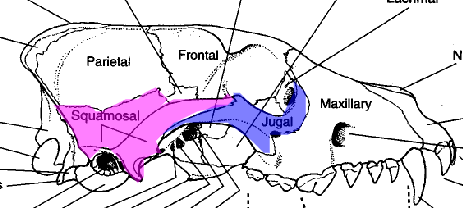
what is the area in blue referring to
jugal bone