ochem lab quiz 2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What type of spectroscopy is this: measures the bond vibration frequencies in a molecule and is used to determine the functional group
infrared (IR)
What type of spectroscopy is this: fragments the molecule with ionization and measures the masses (molecular weight)
mass spectrometry (MS)
What type of spectroscopy is this: detects signals from hydrogen atoms and can be used to distinguish isomers
nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
used to show correlations seen between hydrogen atoms in a molecule
1H NMR
gain structural information from carbon atoms
13C NMR
What type of spectroscopy is this: uses electron transitions to determine bonding patterns
ultraviolet
What is the benzene range in 13C NMR
about 95-175
what is the equation for EU and what does it mean
EU = 1/2(2(C) + N + 2 - H - X) number of pi bonds or rings
at what cm^-1 peak in IR does the NH bunny ears/cow udders appear
3200-3500
what are the two different (IR) molecular vibrations
stretching (valence bond vibrations 4000-1500 cm-1) and bending (deformation vibrations below 1500)
what type of bonds have the highest frequency/wave number of absorption (cm-1)
atoms single bonded to ONLY one hydrogen (2500-3600, ex. OH, NH, CH)
what is the order of bonds from highest to lowest frequency/wave number of absorption (cm-1)
bonds to H, triple bonds, double bonds, single (carbon) bonds
what does a strong IR peak transmittance at around 2900 mean
C-H bond
How do sp2 and sp3 CH bonds differ in appearance on IR spectra
slightly above 3000 is sp2 or sp, below is sp3 (sp2 is shifted left)
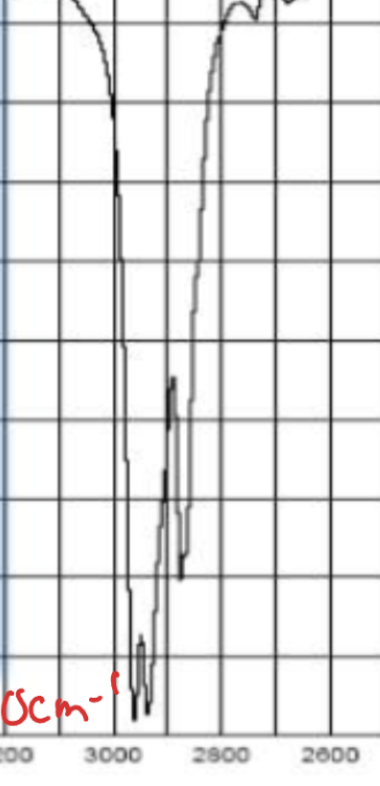
what does this pattern between 2800 and 3000 cm-1 (IR) mean
alkanes
What do the cow udders/bunny ears (two peaks) in IR between 3200-3500 cm-1 indicate
NH bond
What does a strong peak in IR around 1700ish usually indicate
C=O (double bond)
What does a strong peak in IR around 1100ish usually indicate
C-O (single bond)
What does a doublet of doublets between 7 and 8 ppm indicate on H NMR
aromatic ring (with 2 different groups 1,4 to each other)
what causes a downfield (higher number) shift in NMRs
higher electronegativity (or proximity to EN/EWG) and internalization
What carbon has a singlet at 2.1ppm
the alpha carbon (next to C=O)
Which type of NMR is 0-12 ppm
1H NMR
Which type of NMR is 0-220 ppm
13C NMR
How does proximity to oxygen or other EWG (ex. Nitrogen) impact NMR ppm
more deshielded = shift downfield (higher numbers)
What does a sharp peak around 3300 cm-1 indicate
alkyne