Session 10: Fracture Basics
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a fracture (#)
A break or discontinuity in bone (or cartilage) resulting from mechanical forces which exceed bone's ability to withstand them
Primary bone healing vs secondary bone healing
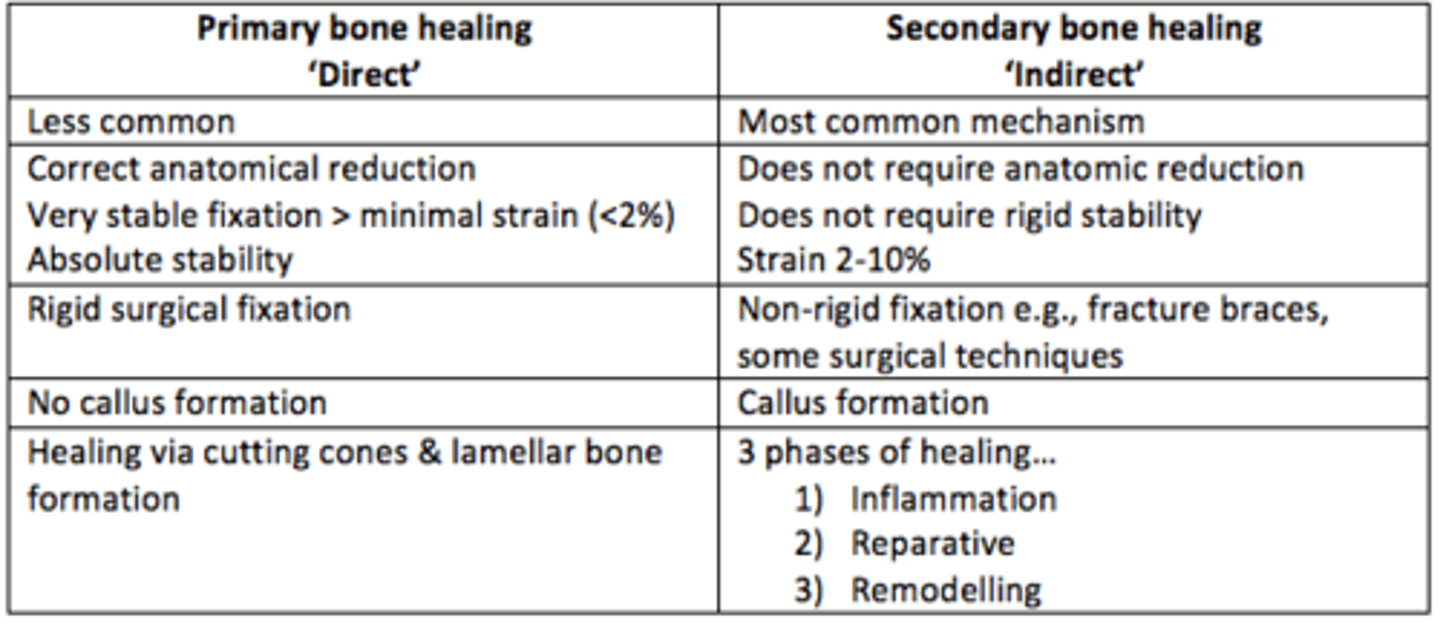
Secondary bone healing
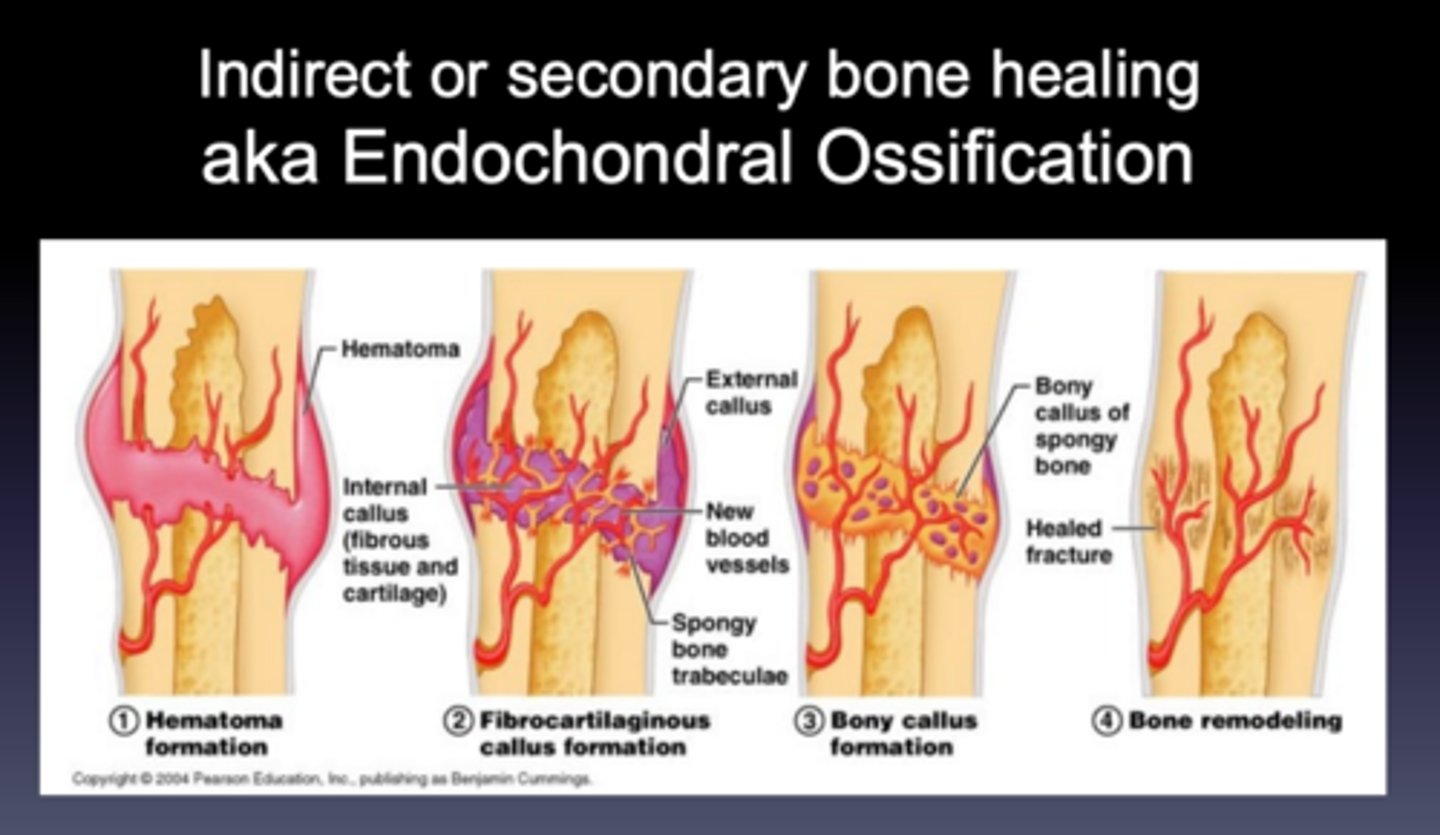
Endochondral ossification
The repair process that is characterized by the formation of fracture callus, which then remodels to form new bone
Approximate healing times for bones in upper limb
Child = 3 weeks
Adult = 6 weeks
Approximate healing times for bones in lower limb
Child = 6 weeks
Adult = 12 weeks
Union
How well the broken bone is aligned
Direct fracture
Break occurs at point of impact
Direct trauma to fracture site
Due to high energy trauma (e.g., comminuted fracture)
Indirect fracture
No direct trauma to fracture site e.g., spiral fracture
Pathological fracture
Fracture through abnormally weak bone (due to disease) e.g., osteoporosis, cancer, infections
Fragility fracture
Fall from standing height or less
Osteoporotic fracture
Bone fracture that occurs in individuals with compromised bone mass density; most common at the spine, hip, and wrist.
Fragility due to osteoporosis
Examples
- Neck of femur fracture
- Colles (distal radius fracture)
- Vertebral fracture
Fracture classification
Three "either/or" fracture classifications
Position of bone ends after fracture
Nondisplaced—ends retain normal position
Displaced—ends out of normal alignment
Completeness of break
Complete—broken all the way through
Incomplete—not broken all the way through
Whether skin is penetrated
Open (compound) - skin is penetrated
Closed (simple) - skin is not penetrated
Open fractures
A fracture in which the bone is broken and there is an open wound in the skin.
Direct communication between fracture site & external environment
- Skin & soft tissue damage
- Neurovascular injury
- Infection
Often fractures classified based on soft tissue damage and vascular damage (Gustillo-Anderson classification)
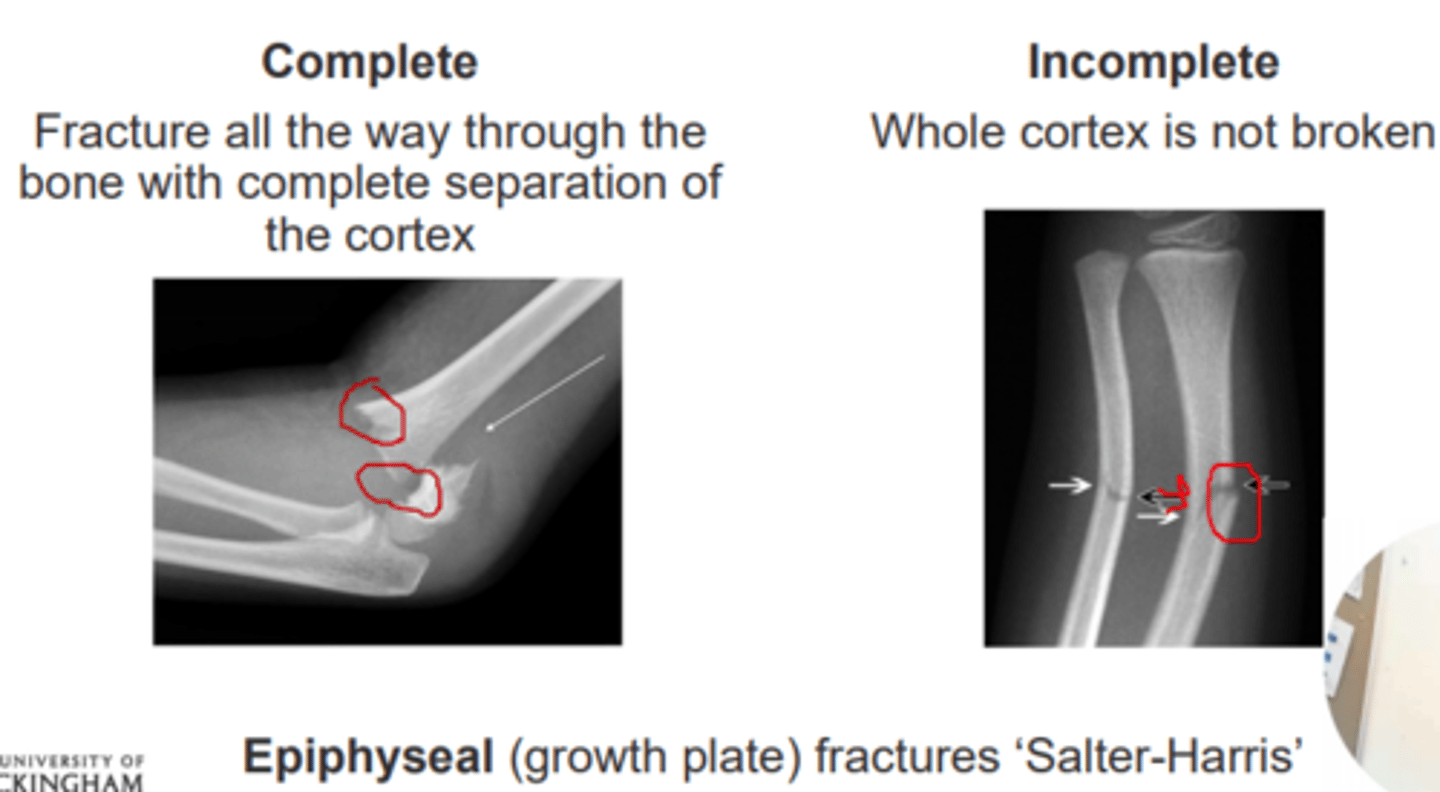
Complete fractures
Bone fragments are completely separate
Fracture all the way through the bone with complete separation of the cortex
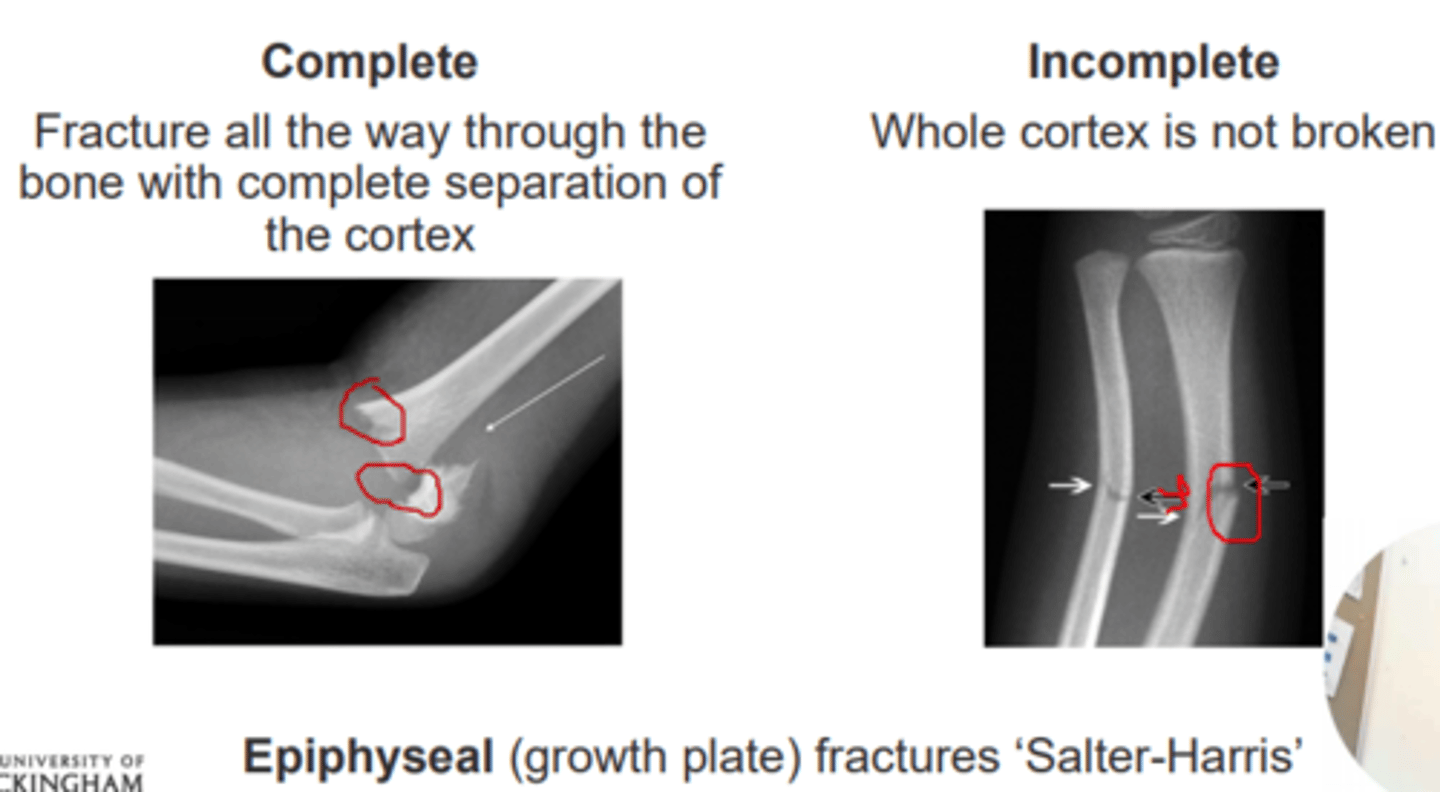
Incomplete fractures
Go through only part of the bone
Whole cortex is not broken
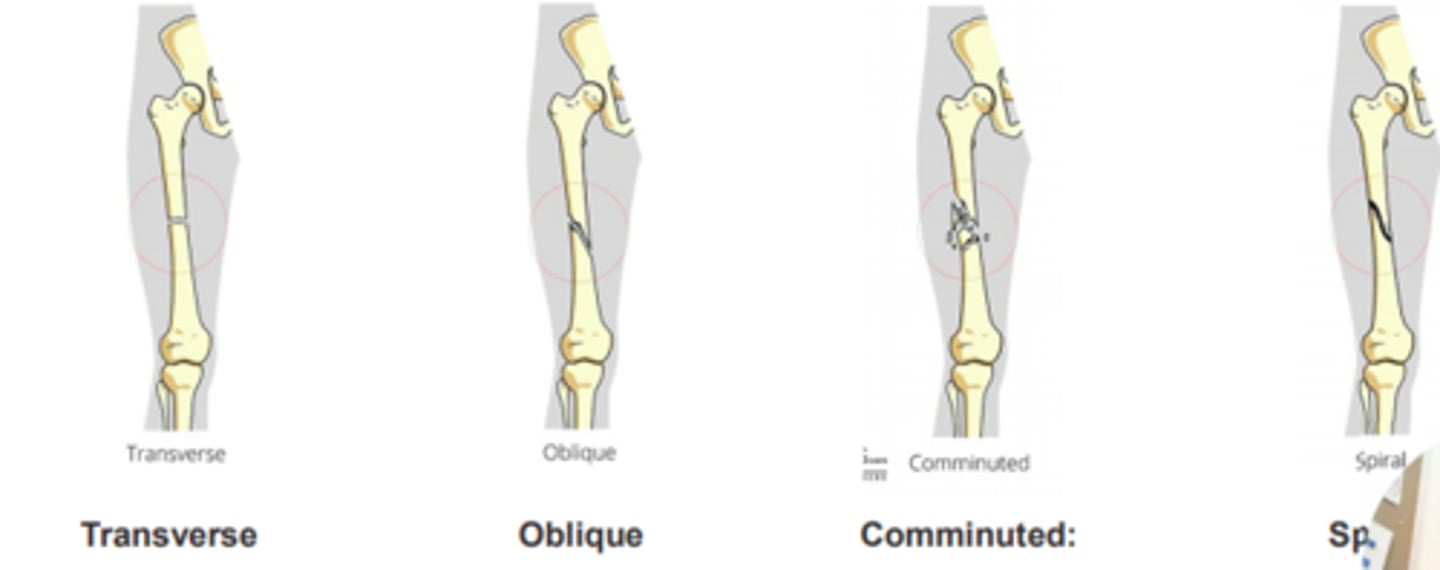
Types of complete fractures
Transverse
- Straight across the bone
Oblique
- Oblique line across the bone
Comminuted
- More than 2 parts to the fracture
Spiral
- Twisting motion
- Fracture like looks like a corkscrew
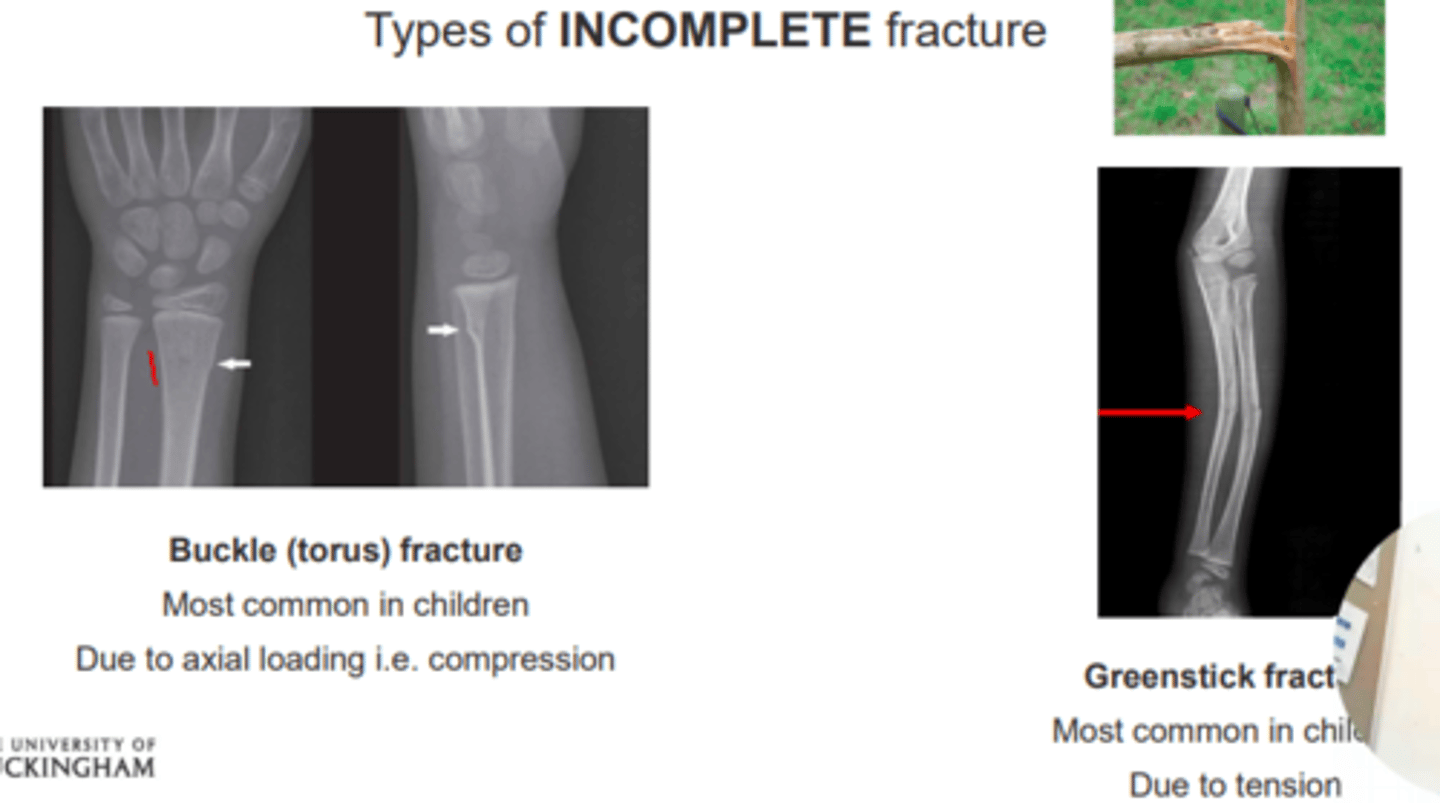
Types of incomplete fractures
Buckle (torus) fracture
- Most common in children
- Due to axial loading e.g., compression
Greenstick fracture
- Most common in children
- Due to tension
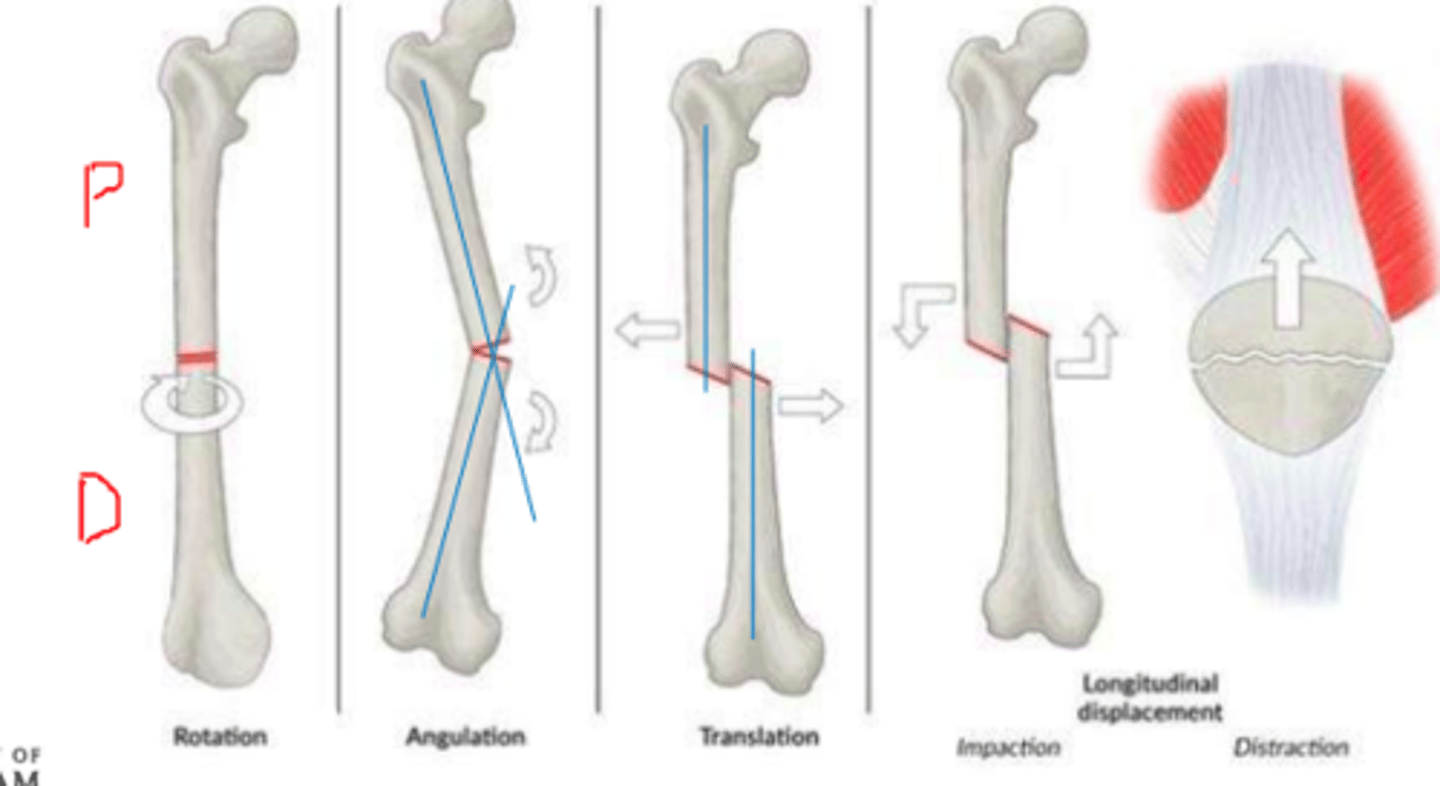
Displacement fracture
Movement of distal fragment in relation to the proximal component
Rotation
Angulation
Translation
Longitudinal
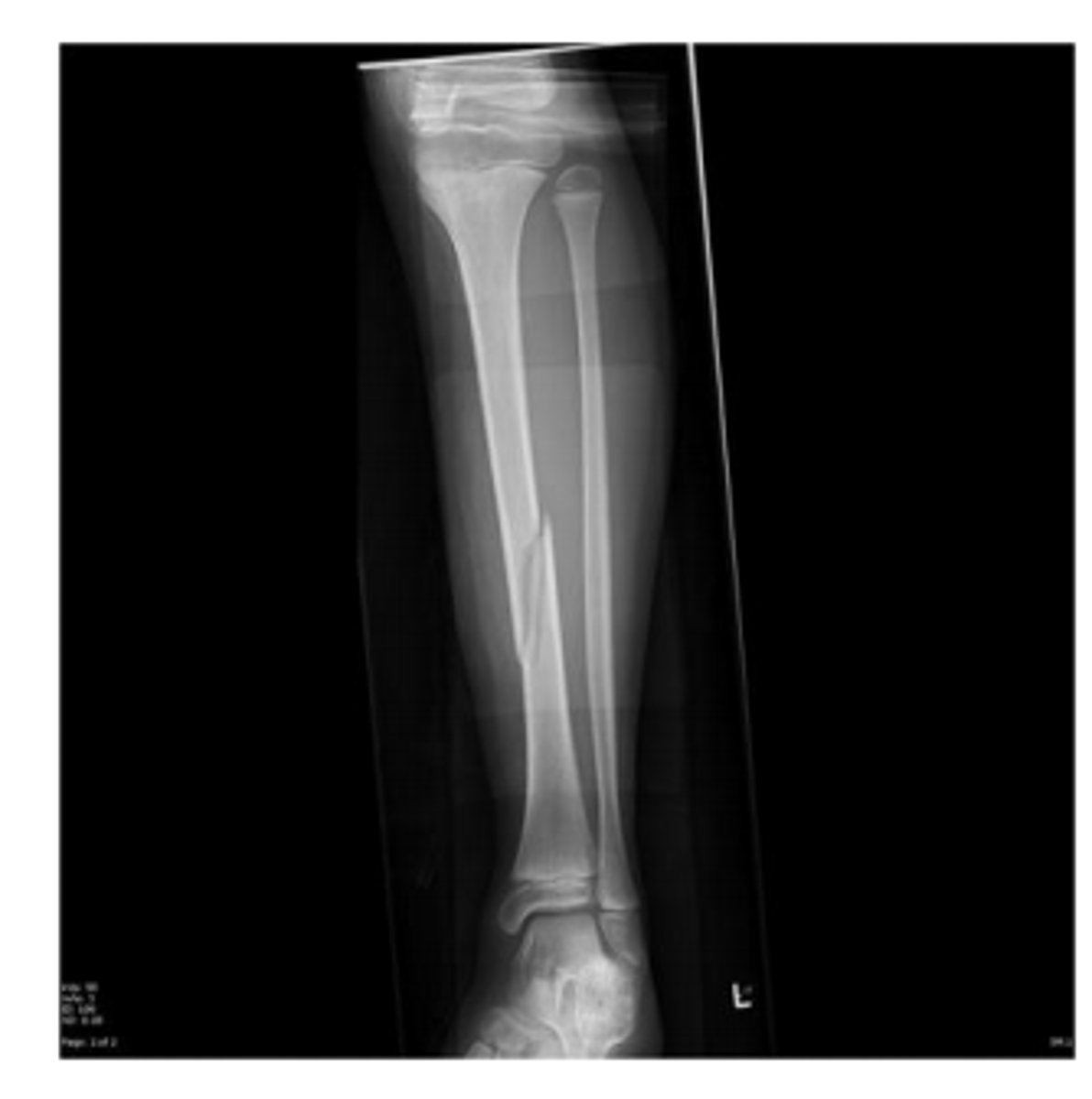
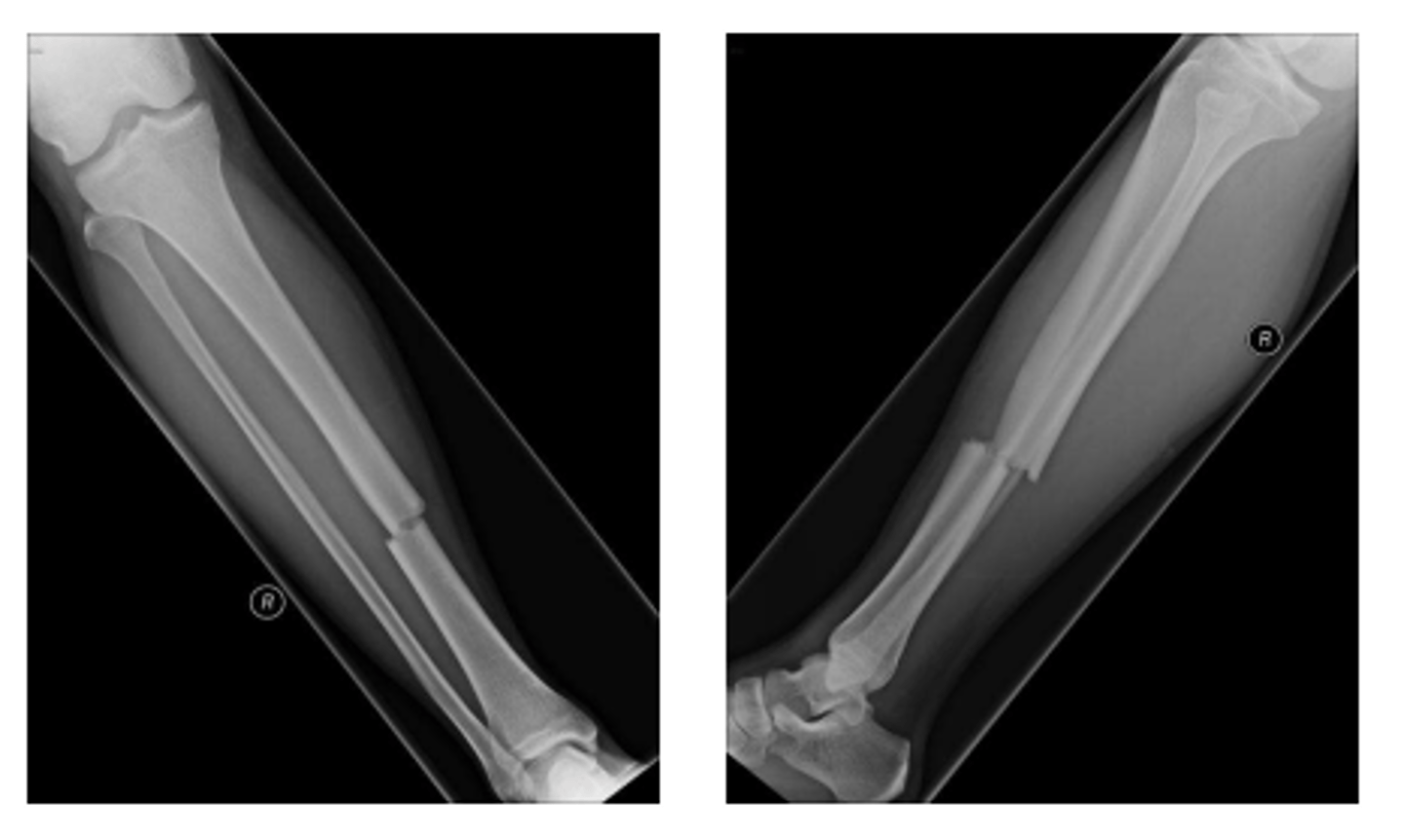
What is the most appropriate description for this fracture?
Oblique fracture
How would you describe the displacement of this fracture?
Translation
Systemic trauma assessment (ATLS) in major trauma
Airway maintenance & C-spine protection
Breathing and ventilation
Circulation and haemorrhage control
Disability
Exposure

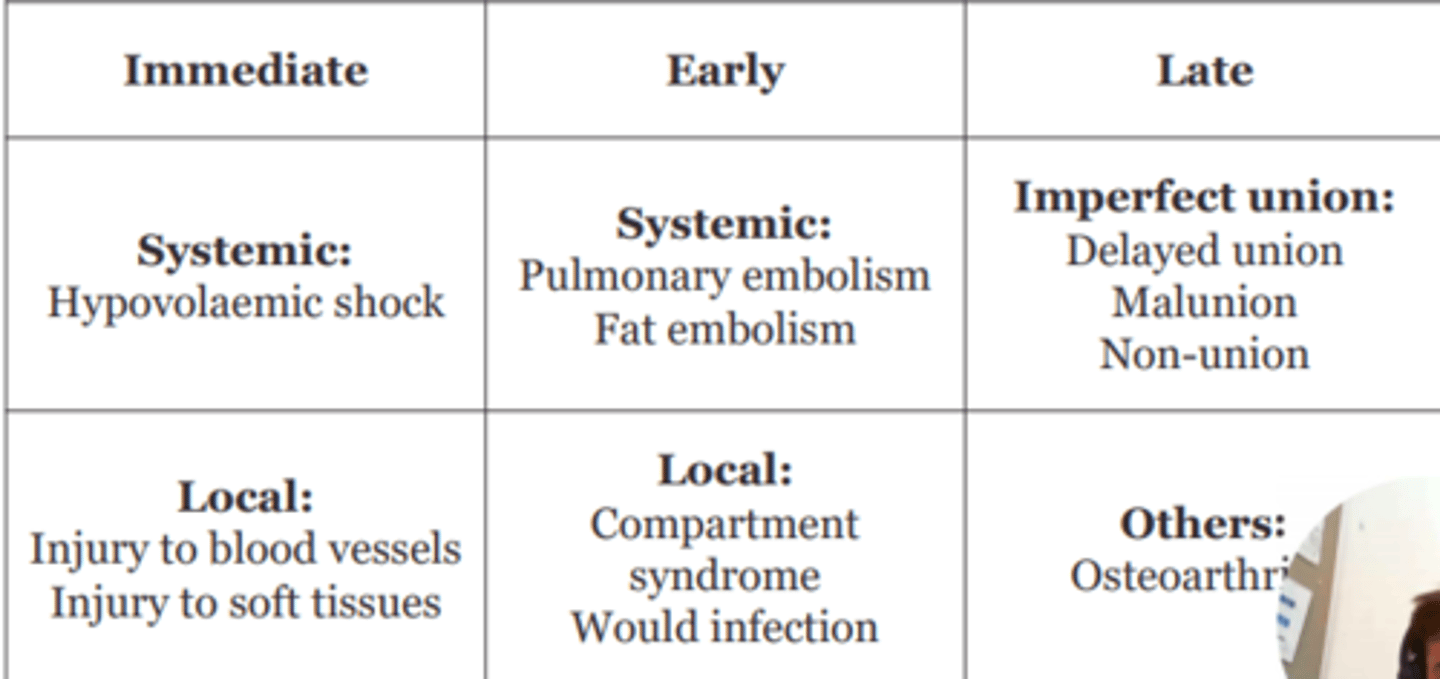
Fracture complications can be classified as...
- Immediate: within few hours
- Early: within few weeks
- Late: months-years later
AND
Local vs. systemic
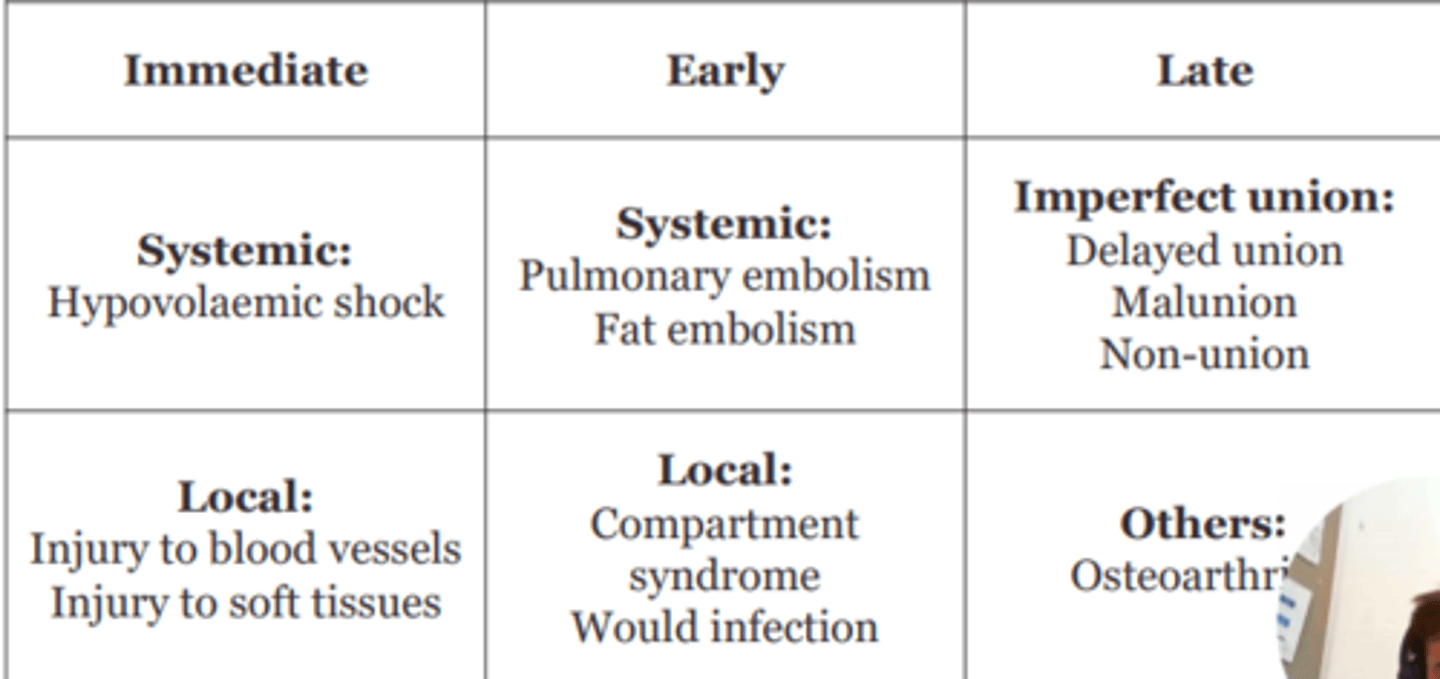
Give some examples of systemic complications of fracture
Hypovolaemic shock
Pulmonary embolism
Give some examples of local complications of fracture
Injury to blood vessels
Injury to soft tissues
Compartment syndrome
Wound infection
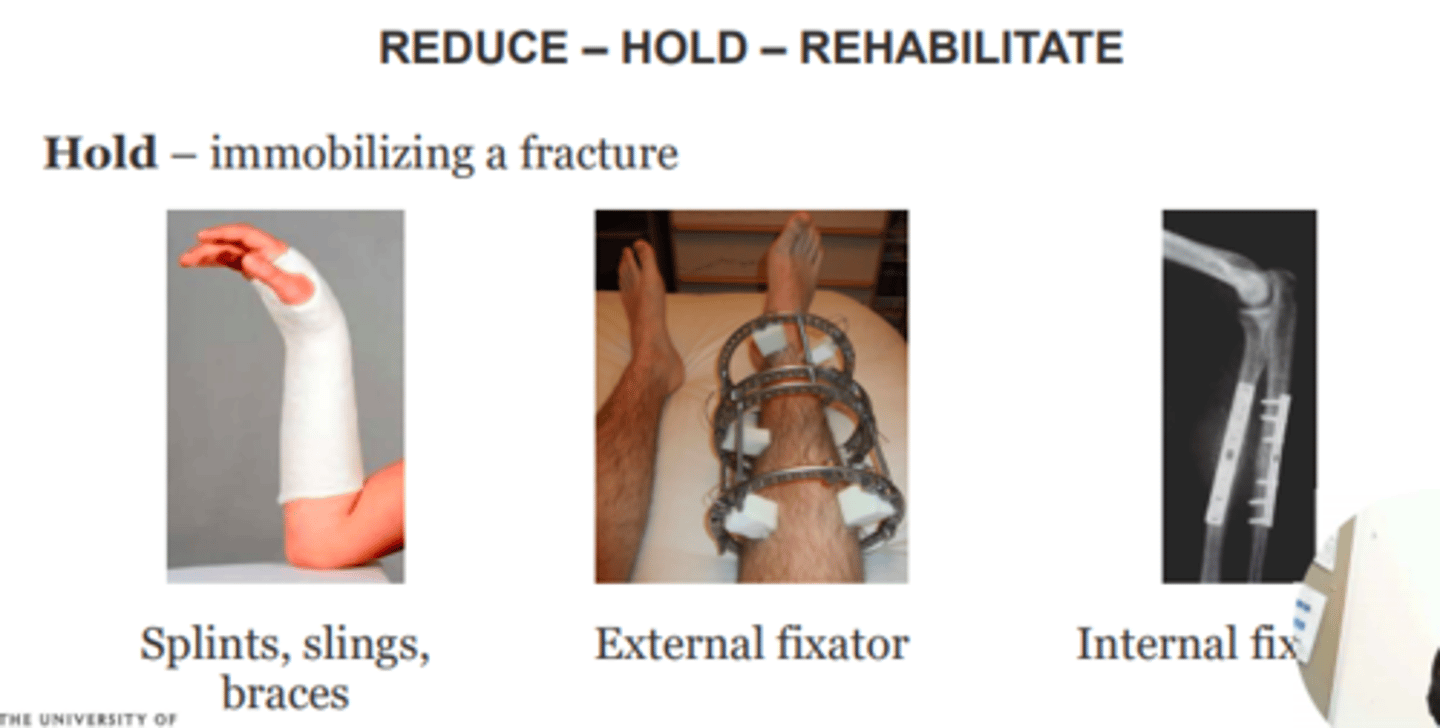
Fractures are managed in three steps...
1) Reduce
Restore anatomical alignment of fracture/dislocation
2) Hold
Immobilisation of fracture e.g., splints, slings, braches, internal/external fixation
3) Rehabilitate
Intensive physiotherapy
What are the benefits of the reduction step of fracture management?
- Reduce pressure & traction on surrounding soft tissues
- Tamponade bleeding
