2.18 - 2.32 Human & Plant Nutrition
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Last updated 11:40 AM on 1/11/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
carbs
they’re the bodies main fuel for supplying our cells with energy
2
New cards
proteins
growth and repair of tissues
3
New cards
lipids
they are used as an energy store, as insulation and to make cell membranes
4
New cards
vitamin A
makes a light sensitive chemical in the retina of our eyes. a vitamin A deficiency could cause night blindness
5
New cards
vitamin A sources
fish liver oils and carrots
6
New cards
vitamin C
sticks together cell lining surfaces such as the mouth
7
New cards
vitamin C sources
fruit and veg
8
New cards
vitamin D
needed for growing bones
9
New cards
vitamin D soruces
fish liver oils and make in skin while in sunlight
10
New cards
mineral - calcium
used to make teeth and bones
11
New cards
calcium sources
dairy products
12
New cards
mineral - iron
part of haemoglobin, in red blood cells which helps carry o2
13
New cards
iron sources
red meat and eggs
14
New cards
water
hydration
15
New cards
fibre
gives the muscles of our guts something to push against as food moves through the intestine and prevents constipation
16
New cards
fibre sources
whole grain bread and brown pasta/rice
17
New cards
pregnancy and energy requirements
energy requirements increase as energy is needed to support the growth of the developing foetus as well as the larger mass the mother has to carry around
18
New cards
age and energy requirements
the amount of energy young people need increases towards adulthood as this energy is needed for growth. energy in adults decrease as they age
19
New cards
activity levels and energy requirements
the more active, the more energy required for movement as muscles are contracting more and respiring faster
20
New cards
mouth
food is mechanically broken apart by teeth and tongue and is mixed with saliva which contains amylase enzymes by chemical digestion
21
New cards
oesophagus
tube linking mouth to stomach. it has muscles in its wall which contract and relax to push the swallowed food - saliva mix (known as the bolus). this process is called peristalsis
22
New cards
stomach
produces gastric juice which contains HCl, killing any pathogens in the food/drink the low PH provides the optimum temperature for protease. the wall of the stomach is very muscular so therefore food is further squashed and it churns so that the gastric juice comes into contact with the bolus
23
New cards
liver
produces bile, which contains alkaline substances to neutralise the acidic solution from the stomach and emulsifies fat
24
New cards
gal bladder
stores bile and when the muscular wall of this organ contracts, bile is pushed into the first part of the small intestine which is called the duodenum
25
New cards
pancreas
produces digestive enzymes as well as substances which neutralise the HCl that comes from the stomach.
26
New cards
1small intestine: duodenum
most of the digestion takes place here
27
New cards
2 small intestine: ileum
where the absorption of the food molecules takes place. the ileum is lined with villi to increase the surface area over which absorption takes place and has think walls to reduce the distance of diffusion
28
New cards
large intestine: colon
absorbs water into the blood via osmosis
29
New cards
large intestine: rectum
faeces is stored here until time for egestion (pooing)
30
New cards
pancreatic juice contains
amylase, protease and lipase
31
New cards
amylase
carbs - maltose
32
New cards
protease
proteins - peptides - amino acids
33
New cards
lipase
lipids - glycerol and fatty acids
34
New cards
maltase
maltose - glucose
35
New cards
components of a balanced diet
carbs, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, water and dietary fibre
36
New cards
photosynthesis is the conversion of light energy to
chemical energy
37
New cards
photosynthesis equation
6 CO2 + 6 H20 → C6 H12 06 + 6 O2
38
New cards
plant gets 6 CO2 as…
it diffuses into the leaf from the stomata
39
New cards
plants get 6 H20 as…
its taken up by the roots and transported thru the xylem and into the leaves
40
New cards
limiting factor is
anything that in short supply prevents photosynthesis from occurring at its max rate
41
New cards
limiting factors in photosynthesis are
temp, light intensity and CO2 conc
42
New cards
increase temp =
more ke, therefore rate of collisions between enzyme and substrate increase
43
New cards
more light =
faster rate, which will continue until some other factor prevents the rate of reaction from increasing further because it is in short supply
44
New cards
more CO2 =
faster rate
45
New cards
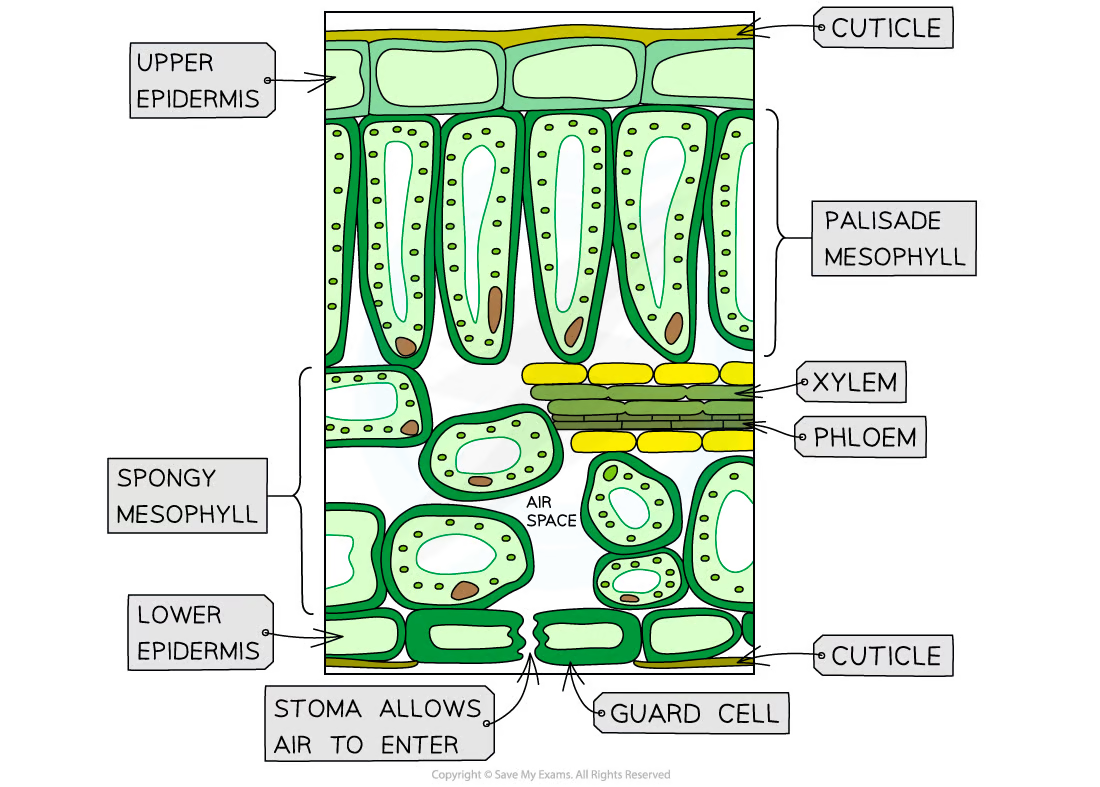
structure of a leaf includes
cuticle, upper epidermis, palisade mesophyll, spongey mesophyll, vascular bundles, lower epidermis, cuticle, guard cells, stomata
46
New cards
large s.a of leaf
a large s.a means its easier for co2 and absorpiton of light for photosynthesis
47
New cards
upper epidermis
thin and transparent for CO2 to diffuse quicker and for light to enter the palisade mesophyll underneath it
48
New cards
palisade mesophyll
tightly packed with chlorophyll, to absorb max light
49
New cards
spongey layer
air spaces to allow CO2 to diffuse through the leaf
50
New cards
mineral ions are needed for
plant growth
51
New cards
magnesium ions are needed for
chlorophyll
52
New cards
nitrate ions are needed for
amino acids
53
New cards
we can affect the rate of photosynthesis by changing the
light, chloroplast and CO2
54
New cards
light can be changed by
leaving plant in a dark room for 24 hours
55
New cards
chloroplasts can be changed by
leaving plant in boiling water and adding ethanol
56
New cards
CO2 can be changed by
adding potassium hydroxide to plant to remove CO2 and leaving plant in dark room for 24 hours to ensure all the starch is used up