kinetics and equilibrium
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Collision theory
If two molecules collide they may react if at activation energy and at right orientation
Steric hindrance
-when the shape of the molecules influence reactions
-large molecules can prevent reactions
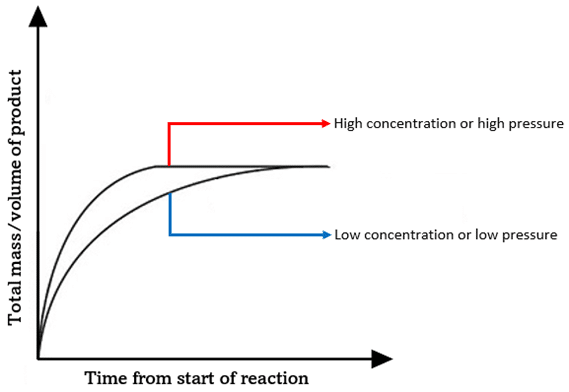
Effect of concentration / pressure on rate
-if conc increases, there are more frequent collisions so more successful collisions
-on a graph, a higher conc has a higher tangent levels off first
The effect of surface area
For heterogeneous reactions involving a solid, a larger surface area leads to a faster reaction
Exposes more reactant particles
Applies to catalyst too
Homogeneous Catalyst
The catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants
Heterogeneous catalyst
The catalyst is in a different phase to the reactants
Example of catalyst in industry
Hager process- heterogeneous catalyst
Benefits of catalysts
-save energy costs and fewer co2 emissions
-more desired product quicker
How does catalyst work in terms of surface
Solid catalyst provides surface where gas molecules can absorb and then react. The product molecules then desorb from the surface and more reactant molecules take their place
Conditions for dynamic equilibrium
-reversible reaction
-closed container
Features of dynamic equilibrium
-the rate of the forwards reaction is equal to the rate of the backwards reaction
-both forwards and backwards reactions are continuously happening
-the concentration of reactants and products remain constant
Effect of temperature change on equilibrium
Increase temperature, the endothermic reaction is favoured
Increase pressure
Favours reaction with less moles
Why do we need to compromise conditions
Rate of reaction and yield