Unit 3 - Learning Process and Culture
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1: Learning 2: Thinking and Language 3: Personality 4: Culture and Society
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
conditioning
the process of training influencing one’s mind so that they say/do a particular thing without thinking about it
stimuli
something that evokes a specific action
classical conditioning
one stimulus leads to a direct response, which leads to another stimulus (Pavlov’s dog)
Pavlov’s dog (Ivan Pavlov)
thought of food > mouth watering > actual food
unconditioned stimulus (US)
an untrained “cause” (food > salivation)
unconditioned response (UR)
an untrained reaction (salivation because of food)
conditioned stimulus (CS)
a trained “cause” (ring of bell)
conditioned response (CR)
a trained reaction (salivating because of ringing of bell)
The Little Albert Experiment
When a child was allowed to play with a white rat, he showed no fear. He did show fear when a steel bar was struck behind his back. When the psychologist paired the rat with a loud noise, the child cried. Soon afterwards, when the rat was presented but no noise sounded, he cried. The child also showed fear when presented with a similar stimuli (anything small, white, and fuzzy), showing that stimulus generalisation had occurred.
counterconditioning
a pleasant stimulus is paired repeatedly with a fearful one, counteracting the fear (trying to re-condition Little Albert to NOT be afraid of the rabbit)
operant conditioning
learn to do or not to do through reinforcement and punishment (primary and secondary reinforcers/punishments)
positive reinforcers
adding something to continue a behavior
negative reinforcers
taking something away to continue a behavior
positive punishment
adding something to stop a behavior
negative punishment
taking something away to stop a behavior
latent learning
hidden learning, comes out when needed (cognitive map) (fight or flight)
observational learning
based on what actions/behaviors that are observed (social learning theory “monkey see, monkey do”)
language acquisition device (LAD)
a theory that suggests humans have an innate ability to learn or acquire language
to spread and improve relations
Why is language important?
trait approach
individuals personality traits are fixed from early learning
surface traits
personality elements can be directly observed (first impressions)
source traits
underlying/base personality traits (true personality, in-depth investigation)
psychoanalytic approach
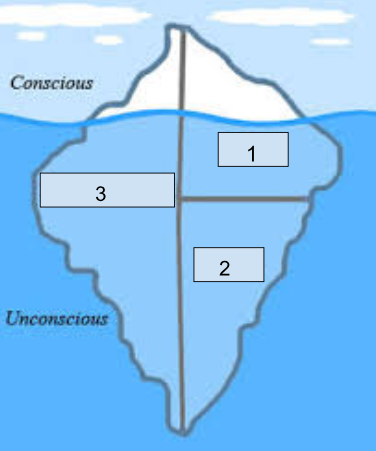
a theory that argues our personality is greatly influenced by our unconscious/subconscious thought (driven by internal conflict)
ID
the part of your personality that demands instant gratification (devil)
superego
the part of your personality that has abstract thinking, and demands a higher level of morality (angel) (the part that you WANT people to see)
ego
the balance/compromise of the true you (angel and devil)
defense mechanisms
where the ego comes up with excuses for the ID winning over to make themselves feel better
repressions
where the ego pushes down the unpleasant emotion that the ID provides to avoid said unpleasant emtion (rationalization)
inferiority complex
the ego will create defense mechanisms due to a sense of feeling lesser leading to the ID winning more often
sociocultural approach
individuals personality is shaped by the culture and society around them
norm
the typical established standard that society believes individuals should follow in everyday life
folkways
expected behavior but without much (if any) reaction from society if broken (cursing in public)
mores
have great moral significance, but not law (Kaepernick)
taboo
typically actions or items of such high social significance that could lead to legal action (family relations)
laws
similar to mores (socially unacceptable) but they’re enforced by individuals of authority (stealing)
social sanctions
motivators/incentives to get people in continue following or to stop breaking social norms
formal sanction
a sanction implemented by a person of authority (speeding = ticket from COP)
informal sanction
a sanction implemented by a person of equal or lower societal status (yelling at someone during a movie)
values
a concept/ideal that is seen as important to a majority of society
cherishing things/concepts more or less
What influences human behavior?
material culture
tangible things that have great value to a specific culture
(American Flag, Bald Eagle, Statue of Liberty)
non material culture
non tangible things that have great value to a specific culture (religion, freedom, ideas)
universals
things that are known throughout majority or maybe even the entire world
particulars
things that are known to a specific area/culture
ideal culture
desired culture/behavior of the society → Setting high standards → society seeks a Utopia (having perfect attendance in an entire school)
real culture
true and expected culture/behavior of the society (what the actual attendance in a school is)
cultural diffusion
the spreading out of culture (can lead the mixing of cultures into another)
counterculture
a group of people who purposefully attempt to go against the social norm
ethnocentrism
the act of judging another culture based on the values and standards of one's own culture, but not doing anything about it (silently judging)
culture shock
the struggle/incapability to adapt or adjust to new social norms due to shock/surprise
1: Ego
2: ID
3: Superego
Label the iceberg