Zoology Slides
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Protozoa
animal-like features, no cell wall, have at least one motile stage in life cycle, most ingest food
Protozoa were historically placed in one phylum, but that placement is incorrect. True or False
True
Choanoflagellate
Sister to all animals
Autotrophic organisms
synthesize their own organic molecules. e.g, phtosysntehsis
Heterotrophic organisms
in addition to making organic molecules, need to consume nutrients from external sources
Mixtotrophic organisms
Do heterotrophic and autotrophic processes alike (both)
True or False: Amoebas are most closely related to animals.
True
A flagella and cilia allow organisms to do what?
Move or propel themselves through their environment.
Pseudopodia
Temporary projections allowing protozoans to crawl through the environments.
What are the different parts of animal cells?
Nucleus, golgi aparatus, cytoplasm, ribosomes, rough endoplasmic recticulum, smooth er, cell membrane and vacuoles etc.
What is Phagocytosis?
Process by which food particles brought into cell: the invagination of plasma membrane surrounds food particle
Food vacuole
food particle contained in membrane-bound vesicle
Once a food particle enters a cell, they are transported to the ____________ organelle in the cell. He contains digestive enzymes to digest the food.
Lysosomes
Contractile Vacuoles are associated w/
osmoregulation
Excretion of metabolic wastes is associated w/…..
Diffusion. e.g, Ammonia
When we digest proteins, we produce ammonia. True or false?
True
Our kidneys help us to maintain ________ balance in your body
water balance
Sexual Reproduction
Procreation where
Asexual Reporductions via Binary Fission
You take one cell and you split it into two. You get a genetically identical daughter cells( aka clones)
Jellyfish switch between __________ and ______ reproduction during their life cycle.
sexual; asexual
Facultative Parthenogenesis
A sexual reproduction in animals that normally reproduce sexually
Cyst
dormant form of an organism, resistant external coverings and shutdown of metabolism
Encystment
The entering of a cyst state by an organism
excystment
When an organism exits a cyst state.
Is hibernation a type of cyst?
No, cyst states occur within Unicellular Eukaryotes. Hibernation occurs in animals.
Endosymbiotic Theory of
Brain-Eating Amoeba
Nearly Entirely Fatal
There are 3 more animal-like clades.
Excavata, Chromalveolata and unikonta.
Unikonta
Includes unicellular and multicellular heterotrophs; includes choanoflagellates and animals
Within Unikonta, there are two phylum. What are they
Amoebazoans and Opisthokonta
Opisthokonta
animals, fungi and unicellular taxa
Origin of Multicellularity
Have only one cell to do all your processes, digestion, respiration etc or a Jack of all trades. That would increase your cell size, but increasing cell size is not practical. So multicellularity allows cells to do one job and specialize, while using less energy.
With more surface area, you maximize the diffusion of _________ in your body.
Nutrients
Multicellularity means that
you have plenty of surface area for metabolic processes.
Choanoflagellates
sister taxon to all animals (metazoans). They are colonial organism( multiple cells that have
meta means
multi
To be multicelullar, you need to have
multicellularity
Portuguese Manawar
Is a multicellular organism with cellular specialization that looks like a Jellyfish
Benefits of Multicellularity
Large size, more resistance
Cyte
cell.
What is an example of homology between animal cells and choanoflagellates?
Cell-to-cell signaling of Choanoflagellates are similar to proteins used by animals.
What is Phylum Porifera’s synapamorphy?
Sack-like bodies w/ pores and canals.
Phylum Porifera
are filter-feeders and are sessile adults and motile embryos
How does Phylum Porifera Feed?
Feed by collecting suspended particles from H2O pumped through internal canal systems
Sister Taxa
Two species that share the most common recent ancestor
Colonial Organisms
Need to live together, and all the cells do the same job
For Multicellular Organisms, They need to have cell specialization and cell ___________
differentiation.
Synapomorphy
Shared derived characteristic of the spcific clade
Choanocytes of sponges are very similar to ____________. And what is there purpose?
choanoflagellates. They help w/ water flow and movement of food particles.
What are spicules?
Rigid; they are the structural components that make up the body of sponges. Think of them as skeletal structures for sponges
Pylum Porifera: How do they feed?
They filter feed. Water enters through pores( dermal ostia) in outer layer of cells (=pinacoderm). Food particles are filtered out of the water by (choanocytes).
Porocytes all sponoges to close the pores that allow water in. True or false?
True
By having more canals (maximizing its surface area), sponges are able to hold more choanocytes, which allow them to filter-in. More Choanocytes, better _________
food particles better; filtration
Spongin
is a connective tissue for sponges
What are the different body types of Phylum Porifera(Sponges)?
Ascon/Asconoid, Leucon/Leuconoid and Sycon/Syconoid;
How are the different body types of Phylum Porifera(Sponges) different?
ascon types are smaller due to the fact that they have fewer canals, sycon types can get bigger because they are more convoluted, leucon types have a maximum surface area, given them the maximum nutrition
Mesohyl, Choanocytes
gelatinous connective tissue; draw food into the sponge
Amoebocytes(Archaeocytes)
Mobile cells, can change into any cell, carry food to other cells
Pinacocytes
Cells of pinacoderm, contractile - Regulate SA(Surface Area) + Water
Collencyte
produce collagen and help form spicules
How does asexual reproduction occur in Sponges( Phylum Porifera)? How do they do sexual reproduction?
bud formation; monoecious (Hermaphrodite) or can be giving birth and living w/n the body of the mother (viviparous)
Viviparity vs Ovaparity
Vivi - means live, ova- means eggs
Name the Taxonomy of Phylum Porifera. There are 4
4 classes: Calcispongiae, Hexactinellida, Demospongiae and homoscleromorpha
Bifurcation
the splitting into two of a clade, leading to two sister taxa
Phylum Porifera: What trait characterizes Calcispongia? Homoscleromorpha?
spicules of calcium carbonate; small or absent spicule
Phylum Porifera Sister Taxa
phylum Porifera: What trait characterizes Hexactinellida? Demospongiae?
six-rayed siliceous spicules; have siliceous spicules, but not six rayed
What are the two sister taxa groups in Phylum Porifera
Sister Taxa 1: Homoscleromorpha and Calcispongiae, Sister Taxa 2: Demospongiae and Hexactinellid
Phyla Cnidaria and Ctenophora: Diploblastic? Diploblasts have a new stage in development called gastrulatiom.
2 embryonic cell layers from which adult structures develop; produces cell layers of adults
Phyla Cnidaria and Ctenophora: Diploblasts display radial or biradial symmetry. What is radial symmetry? Biradial symmetry?
The same symmetry regardless of what way they are cut; can only be cut from top to bottom to have identical pieces.
Phylum Cnidaria: Where does the name come from? What are cnidocytes?
There is a synapomorphy of cnidarians called cnidocytes; stinging cells of the Cnidarian
Cnidaria: Polyps vs Medusae? Sone cnidarians spend part of life as ______ and part of their life as medusa.
Polyps have a hydroid form and sessile, whereas Medusae have a jellyfish form and is free-floating or swimming; polyps
Phyla Cnidaria: Medusa have statocysts and ocelli. What do statocysts do? What does ocelli do?
sensory structures for orientation; serves for light reception
Typical Dimorphic Life Cycle: A poly produced a medusa by means of _____ reproduction by budding off a clone of itself. Then, through _____ reproduction forming a zygote, which develops into a motile planula larva to then become a _____.
asexual; sexual; polyp
What is the benefit of the Dimorphic Life Cycle? The Polyp is associated with the asexual section of the cnidarian life cycle and the medusa is the _____ portion of the life cycle.
organisms capitalized on both open water and bottom environments and it cuts down on intraspecies competition; sexual
Cnidarian: Epidermis? Gastrodermis? Mesoglea?
derived from ectoderm and contains cnidocytes; derived from endoderm, lines gut cavity for digestion ; between the epidermis and gastrodermis
Phylum Cnidaria are mostly —-nivorous? They have gland cells. What do they do? Where does intracellular digestion occur?
carnivorous, gland cells discharge enzymes and begin extracellular digestion; in the gastrodermis
Salivary amylase breaks down food on your tongue with digestive enyzmes even before you chew your food. That’s why it tastes sweeter after a minutre, because your tongue is breaking the food down into simpler components, and simpler carbs taste sweet. True or False?
True
Phylum Cnidaria: Nervous system: What is the Diffuse Nervous System? What is a nerve net?
nerve cells at base of epidermis and gastrodermis, interconnected into a nerve net with nerve ring around mouth; process stimuli from all directions
Phylum Cnidaria: What are the four classes of Phylum Cnidaria that we need to know? Phylotomy?
Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Cubozoa and Anthozoa; a point from which two or more new branches emerge
Phylum Cnidaria: What is Class Hydrozoa? THey include polyps and _____ and what does that ______- do??
mostly marine and colonial, asexual polyp and sexual medusa; Zooids who feed the colony
What characterizes class Scyphozoa?
includes more large jellies, most dift/swim in open sea, no velum on medusae, margin of bell w/ indentations, strobilation. Lappets (lobes) flanking indentations, sense organ between lappets (rhopalium), 4 oral arms to catch/ingest prey,
Diploblastic organisms have 2 embryonic layers which are…? THe ectodermis is adult animals becomes the ______.
Ectoderm and endoderm; skin
What type of symmetry do these different groups have: Porifera, diploblasts and Triploblasts
Porifera has no symmetry, diploblasts has radial symmetry and triploblasts
Phylum Cnidaria: Class Cubozoa. What are their synapomorphies?
polyp inconspicuous or unknown, bells square, tentacles(s) at each corner
Phylum Cnidaria: Class Anthozoa synapomorphies?
no medusa, only polyp, gut w/ septa(walls
Coral Reef has an obligate symbiotic relationship with a cyanobacterium, which give them their ____
color
Phylum Ctenophora Synapomorphies
8 rows of comb-like plates of cilia (ctenes) used for locomotion, 2 tentacles (biradial symmetry), unidirectional digestion(So they can eat while digesting)
What do the tentacles of Phylum Ctenophora have on them?
They have colloblasts, which are the glue cells Phylum Ctenophora use for drawing clades.
What is bilateral symmetry? How do you know if Bilateral symmetry is present?
Symmetry defined by animals that have a head(posterior) and tail(posterior) ends; you know when the body can be divided along one plane into two identical halves
Bilaterians are __blastic. What are the different parts of your previous answer?
triploblastic; ectoderm, mesoderm and endodermt
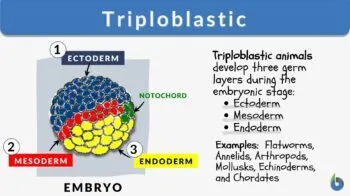
There are three body types of bilaterians; name them. Pseudocoelomate vs coelomate
Aceolamate, pseudocoelomate and coelomate.’ pseudocoelomates don’t have mesoderm lining their entire body whereas coelomates do, aceolamate has no mesodermal tissue
What does the A in A-coelomate mean? What does the pseudo in pseudocoelomate mean? What are the two groups of Protostomia?
“A” means lacking ; Pseudo means “false”; Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa
Phylum Bilateria: Protostomes? Deuterostomes?
first opening becomes month; second hole becomes the mouth, blastopore becomes anus
Convergent evolution is the process by which unrelated organism develop similar traits, whereas ____ is the of that evolution
result
Phylum Platyhelminthes: Any synapomorphies?Their external boy covering is known as and what characteristics do they have?
There is no single synapomorphy for this phylum; a neodermis, bilaterla symmetry, triploblastic bodies and are acoelomate
Phylum Platyhelminthes: Aceolomate as no ___dermal tissue, so they don’t have any orgran systems. What are the four classes of this phylum? Which are parasitic?
meso; turbellaria, trematoda, monogenea, Cestoda; trematoda, monogenea, Cestoda
Phylum Platyhelminthes: What is the synapomorphy of Clade Neodermata? Epidermis a
The neodermis;
Phylum Platyhelminthes: Clada Tubrellaria has rhabdites. What are they? Clade neodermata adaptations to livng in the body
tubrellarians w/ rhabdijtes in ciliated epidermis; resistant to immune system + digestive juices