Macro Molecules
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
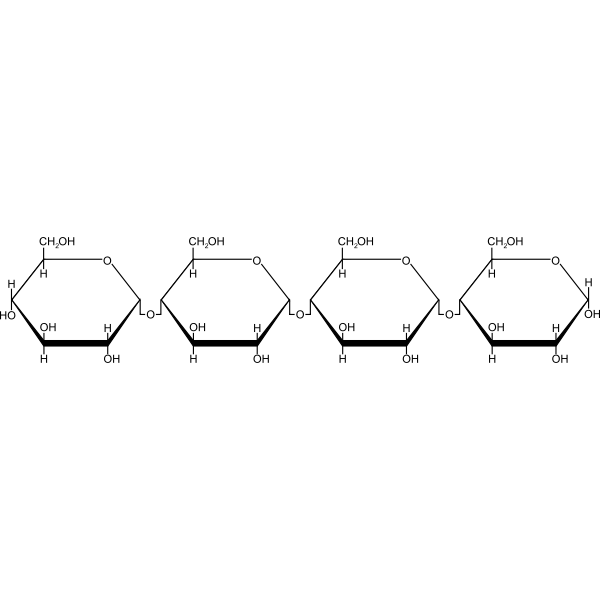
Carbohydrates (Monomer)
Monosaccharides
Lipids (Monomer)
Do not contain monomers but instead contain glycerol and three fatty acids.
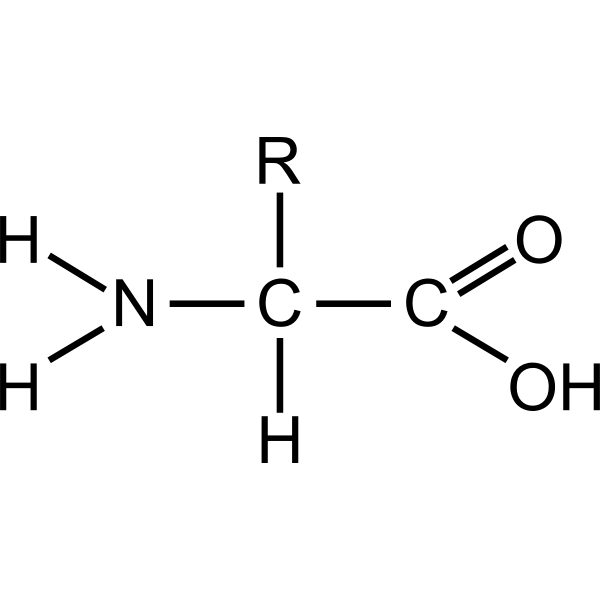
Proteins (Monomer)
Amino Acids
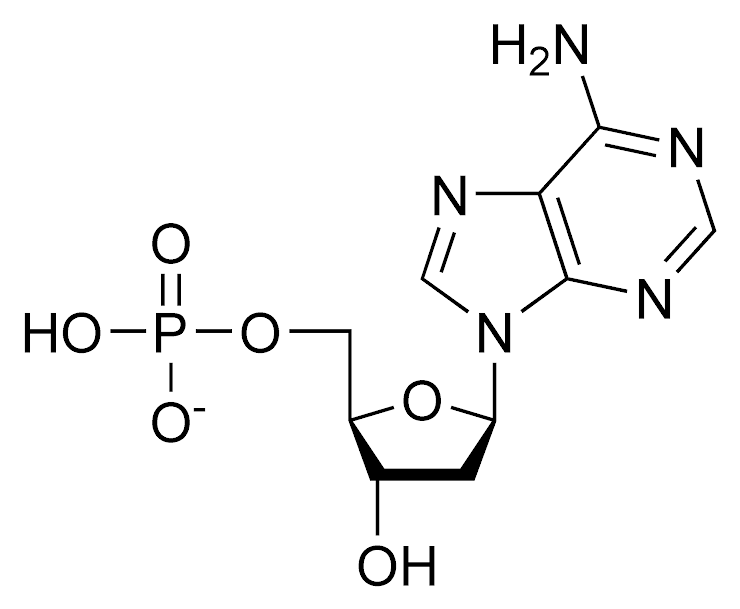
Nucleic Acids (Monomer)
Nucleotides
Carbohydrates (Elements)
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen (1:2:1)
Lipids (Elements)
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen (Sometimes Phosphorus) (sulfur maybe) (1:2:<1)
Proteins (Elements)
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, (sulfur ocassionally)
Nucleic Acids (Elements)
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
Carbohydrates (Function)
Fast Source of energy caused by ATP, Structural support for organisms and cells, Structure for plants, provides structure and strength for exoskeleton of insects
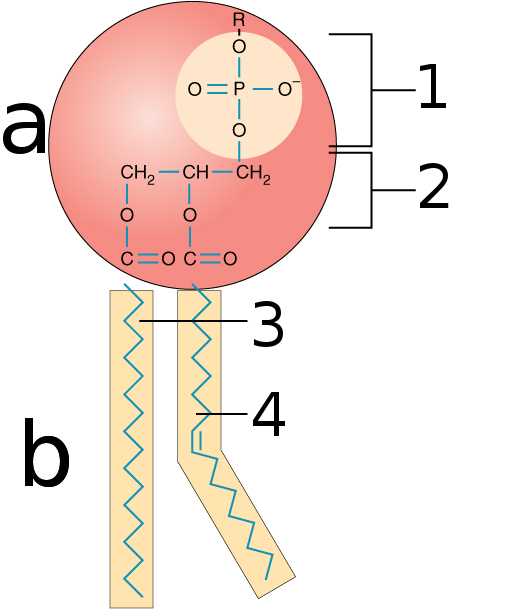
Lipids (Function)
Controls what comes into and out of the cell in the membranes (MAJOR PART), Stores energy, absorbs vitamins, Makes hormones, Insulators, Long term energy source
Proteins (Function)
Forms tissue, hair, and collagen, regulate cell processes, structure and support, Cell communication, Transport molecule
Nucleic Acids (Function)
Carries genetic info, Acts as instructions for cells to make up organism
Carbohydrates (Examples)
Starch, Cellulose (Plants), Lactose, Glucose, Maltose, Chitin (Fungai), Glycogen (Animals)
Lipids (Examples)
Steroids, Cholesterol, Oils, Waxes, Venoms, Estrogen, Testosterone, Triglyceride
Proteins (Examples)
Skeletal Muscle, Insulin, Antibodies, Enzymes, Hemoglobin (Transport Substances)
Nucleic Acids (Examples)
Dna, RNA
Carbohydrates (Picture 1)
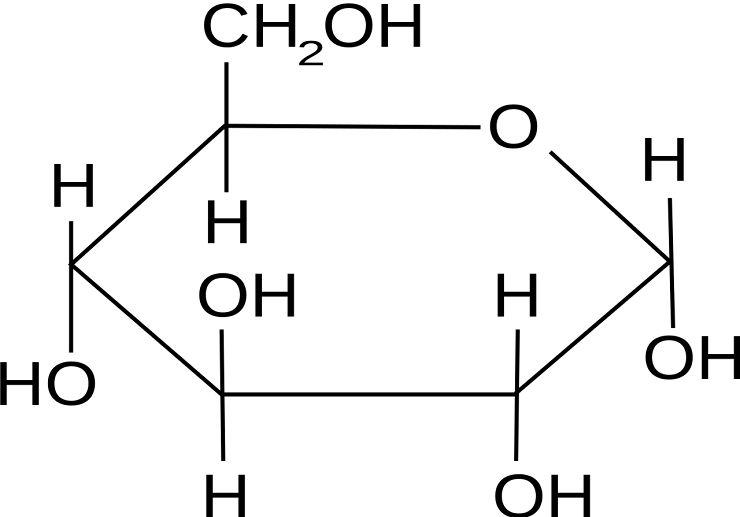
Lipids (Picture 1)
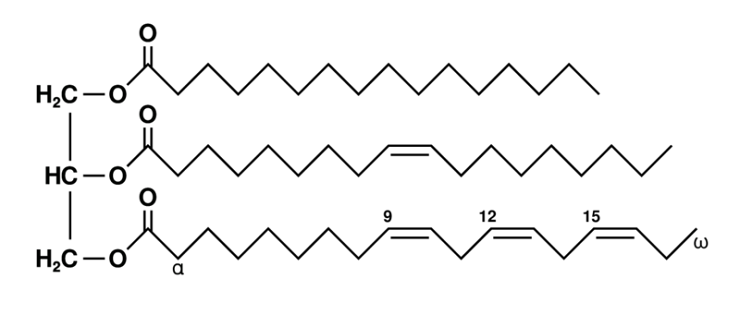
Proteins (Picture 1)
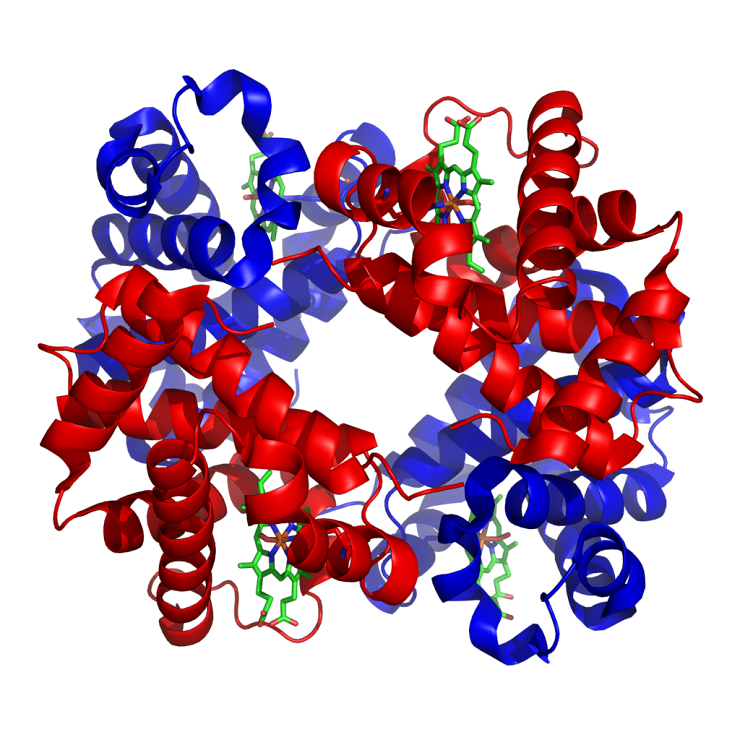
Nucleic Acids (Picture 1)
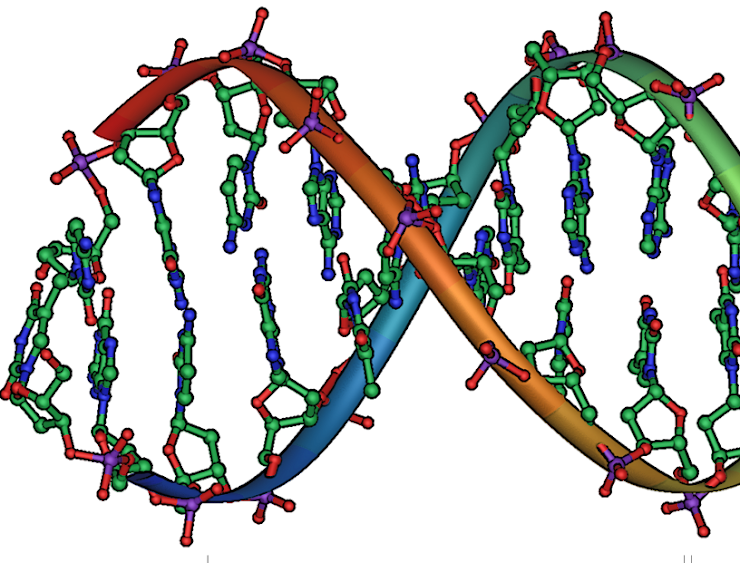
Carbohydrates (Picture 2)
Lipids (Picture 2)
Proteins (Picture 2)
Nucleic Acids (Picture 2)
Polymers
When a bunch of monomers are put together and the more are added to create an organic molecule
Phospholipids
A group of polar lipids that consist of two fatty acids, a glycerol unit, and a phosphate group which esterified to an organic molecule
Monomers
Building blocks of macromolecules such as monosaccharides, amino acids, and nucleotides
Hydrolysis
Polymer reduced to monomer and needs water to start reaction
Dehydration Synthesis
Joins monomers together to make polymers by loosing water