Life sciences
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
The meristem occurs in which parts of the plant?
in the tips of roots and stems
A deficiency of… causes the thyroid gland to swell and form a goiter
iodine
if a person wants to increase his/hers sodium intake through his/diet, they can eat more…
Salt, meat and milk
Is this true or false, not all tumors are harmful
true
Proteins consist of
amino acids
cuticle
waxy layer that prevents water loss from plants
Guard cells
Bean-shaped cells that surround the stomata in the leaf’s epidermis
mammogram
an x-ray picture of a persons breasts that is used to detect signs of cancer
rickets
a dishes that arises as a result of deficiency of vitamin d
Carbohydrates
organic compounds consisting of C, H, and O
nucleic acids
are nitrogenous compounds found in all cells
structure of nucleic acids
contain elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus.
they are made up of building blocks called nucleotides
RNA is found in:
the nucleolus, cell cytoplasm and on the ribosomes
DNA is found in:
the nucleus
RNA plays the role in
building the required proteins from the amino acids
Vitamins contain the elements
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, as well as nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur in some cases
lack of vitamin A
poor vision and night blindness
lack of vitamin B1
Beri-Beri (nervous disorder accompanied by stunted growth and blood circulation )
lack of vitamin B2
metabolic disorders, stunted growth, sores in mouth, eye damage
lack of vitamin B12
Pernicious anaemia and nervous disorders
lack of vitamin C
scurvy, gum bleeds and nose bleeds
where it is found: vitamin E
plant oils, wheat germ, wheat bran, nuts, seeds, dark leafy green vegetables
where it is found: vitamin D
milk, butter, eggs, fish, liver , sunshine on the skin
where it is found: vitamin C
oranges, lemons, grapefruit, green vegetables and potato
where it is found: vitamin B12
meat, eggs, liver and dairy products
where it is found: vitamin B2
liver, eggs, milk, yeast
where it is found: vitamin B1
whole grains of cereal, wheat germ, nuts, seeds of legumes, yeast
where it is found: vitamin A
fish oils, liver, leafy vegetables, yellow/orange fruits
Stomata
small openings in the pants epidermis
phloem
transports food from the leaves to other parts of the plant
A macro element
Calcium and Potassium
DNA
store hereditary information
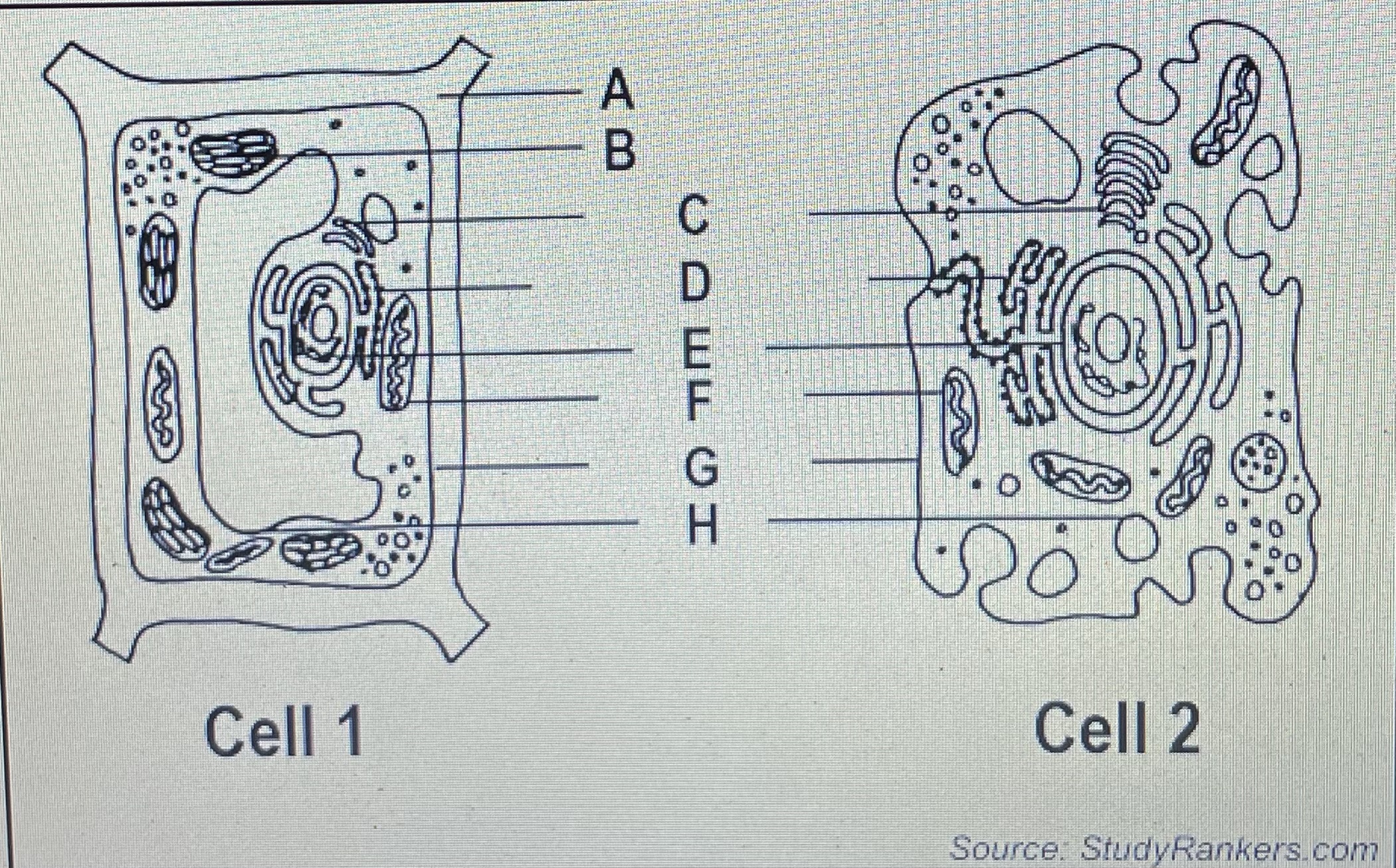
Identify the parts labelled as A and H
A - cell wall H- vacuole
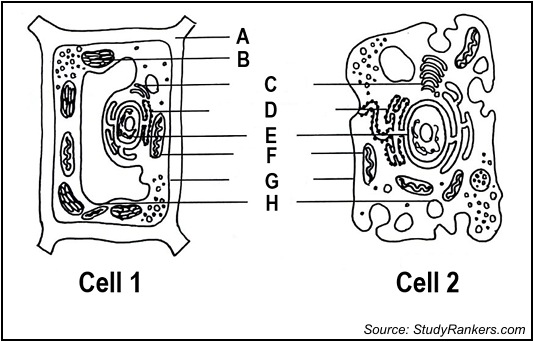
state which cell is an animal cell
2- animal cell
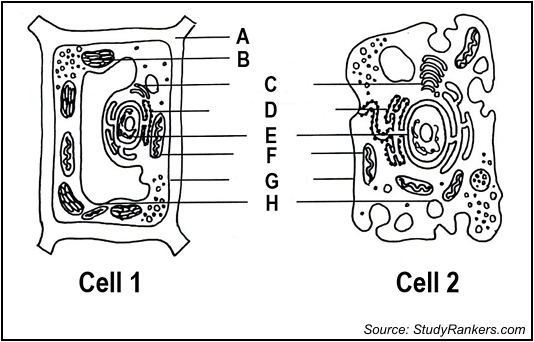
Which letter is responsible for the production of food by photosynthesis
B- chloroplast
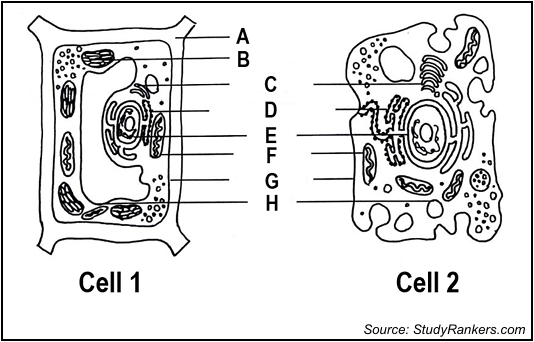
which cell is the plant cell
cell 1
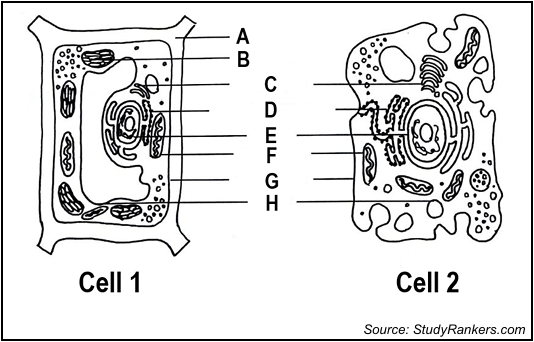
give the letter of the part responsible for the control of the cell’s activity
E- nucleus
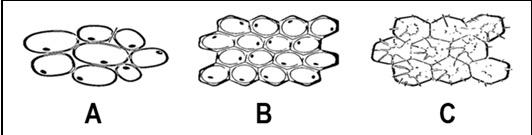
Name the Tissue A (found in plants)
Parenchyma
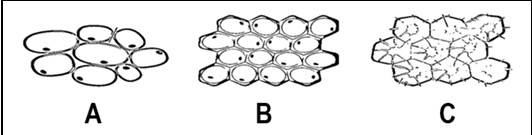
Name the Tissue B (found in plants)
Collenchyma
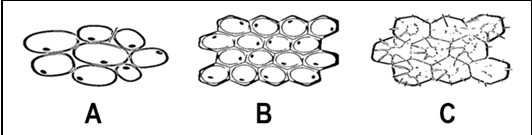
Name the Tissue C (found in plants)
Sclerenchyma
Mitosis
The division of the nucleus
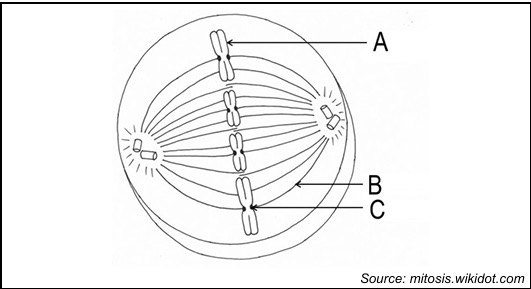
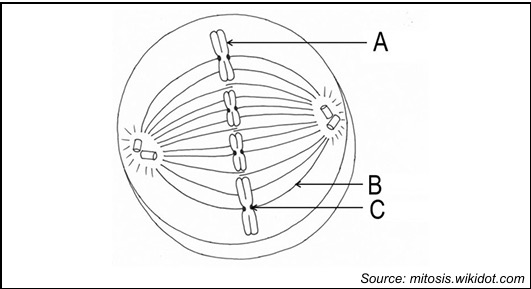
identify A
Chromosome
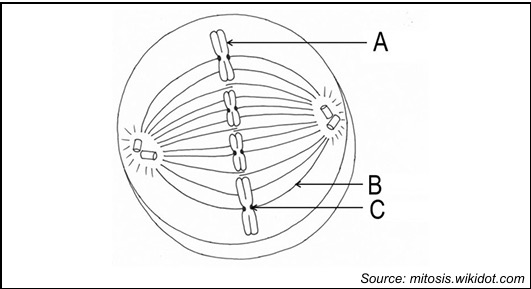
identify b
spindle fibre
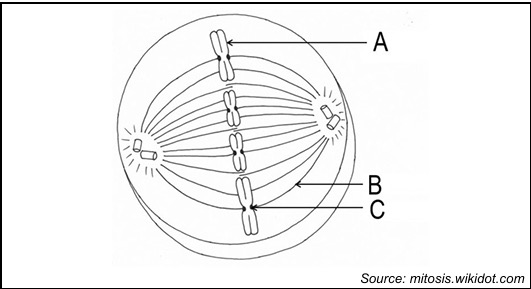
identify c
centromere
what is the name of the imaginary line on which the chromosomes form in this phase
equator
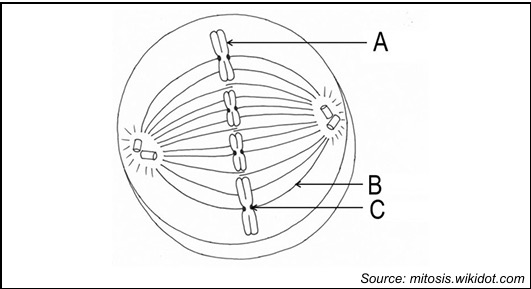
what is the name of the phase that follows this phase
Anaphase
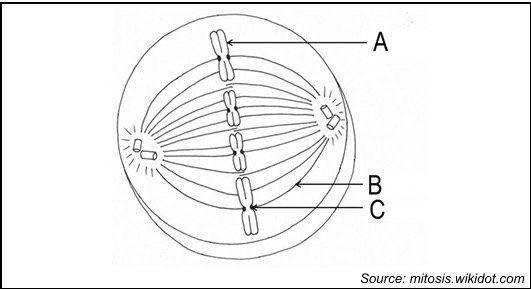
what phase is this
metaphase
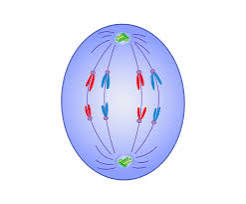
what happens during the Anaphase
the spindle fibres contract and pull the chromatids to opposite ends of the cell, called the poles
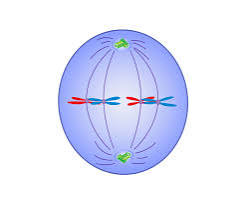
what happens during the metaphase
The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, called the equator. Spindle fibres attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes.
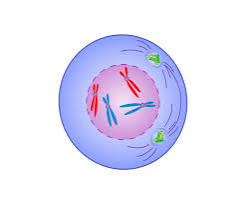
what happens during the prophase
The chromosomes condense and become visible. The nuclear membrane breaks down and spindle fibres begin to form.
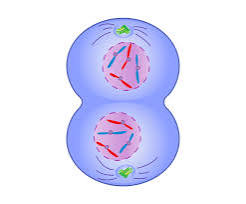
what happens during telophase
The chromosomes decondense and new nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes at the poles.
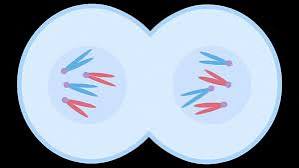
what happens during cytokinesis
The cytoplasm divides, resulting in two identical daughter cells.
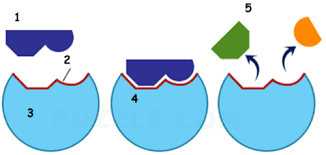
name part 1
Substrate
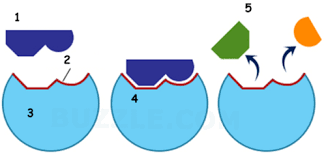
name part 2
Active site
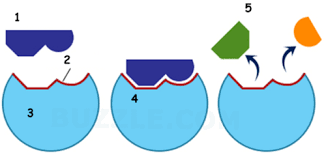
name part 3
enzyme
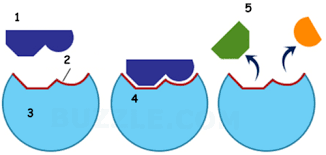
Name part 4
Enzyme substrate complex
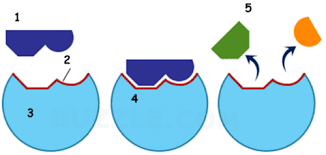
name part 5
products
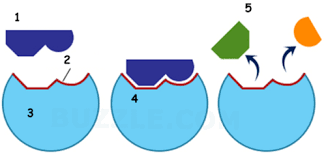
is this reaction catabolic or anabolic
catabolic
Catabolic
a destructive reaction
Anabolic
a building reaction
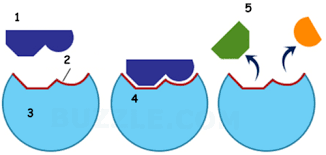
What is the function of an active site (2)
It speeds up the reaction by lowering the activation energy without changing itself
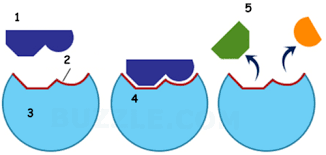
How is the Active site (2) affected by the change in ph
the part denatures and losses its specific form and function
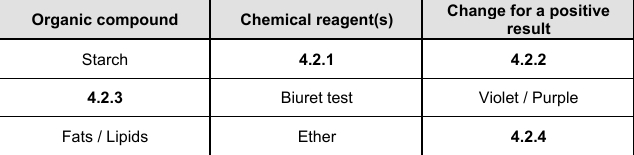
4.2.1
Iodine solution
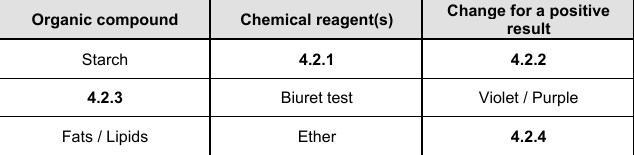
4.2.2
Blue black
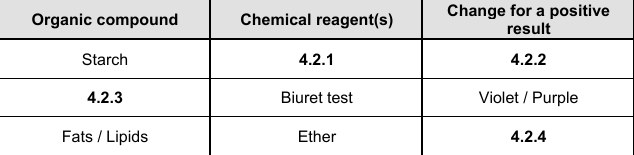
4.2.3
Proteins
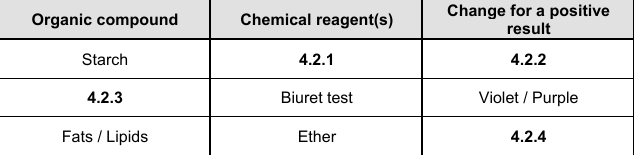
4.2.4
Translucent fatty spot
organic compounds
contain carbon and hydrogen
Carbohydrates ie. glucose, starch and cellulose
provide energy to living organisms
Monosaccharides
single sugars
How do we test for glucose
Benedict’s solutions
Disaccharides
2 single sugars join to form double sugars ie. sucrose
Lipids
(fats and oils) store energy
How do we test for lipids
ether or alcohol
unsaturated fats
mainly found in plants and liquids at room temperature
saturated fats
found in fats that come from animals and are solid at room temperature
Proteins
enzymes that keep a cell alive and made up of amino acids
Catalyst
is a substance that speeds up the rate of chemical reaction without being changed
Function of Nucleic acids
play an important role in controlling the structures and functions of the cell
RNA
Ribonucleic acid
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Water
is the most important inorganic molecule for living organisms
Minerals
ie. calcium , magnesium
Macro-elements
minerals needed in large quantities by plants and animals
micro elements
minerals needed in small quantities by plants and animals
Calcium
found in dairy products and needed for strong teeth and bones
fertilizers
plants require inorganic nutrients
cell theory
all living things consists of one or more cells
calculating magnification
total magnification= magnifying power of the eyepiece x magnifying power of the object lens
Cell measurement unit
micrometres (1000um=1mm)
Cytoplasm
a fluid like substance that fills the space inside the cell membrane
organelles
found in the cytoplasm
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Vacuoles, Nuclei, Cell membranes
examples of organelles
Cell membranes
made of phospholipids and proteins
The process of cellular respiration takes place inside the…
Mitochondria
epidermis
covers the surface of the plant
guard cells
allow gasses to enter and exit the leaf
chlorenchyma
contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis and are found in leaves and stems but not roots
parenchyma
found below the epidermis
xylem
transports water and mineral salts (found in roots, stems and leaves of plants.)