Unit 1 Nutrition
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Dry Matter
Non-water component of feed/food
Dry matter vs As Fed
Without water (%) vs. with water (%)
Why is it important to put things on a DM basis?
COST and Nutrient value
people don’t want to pay for water
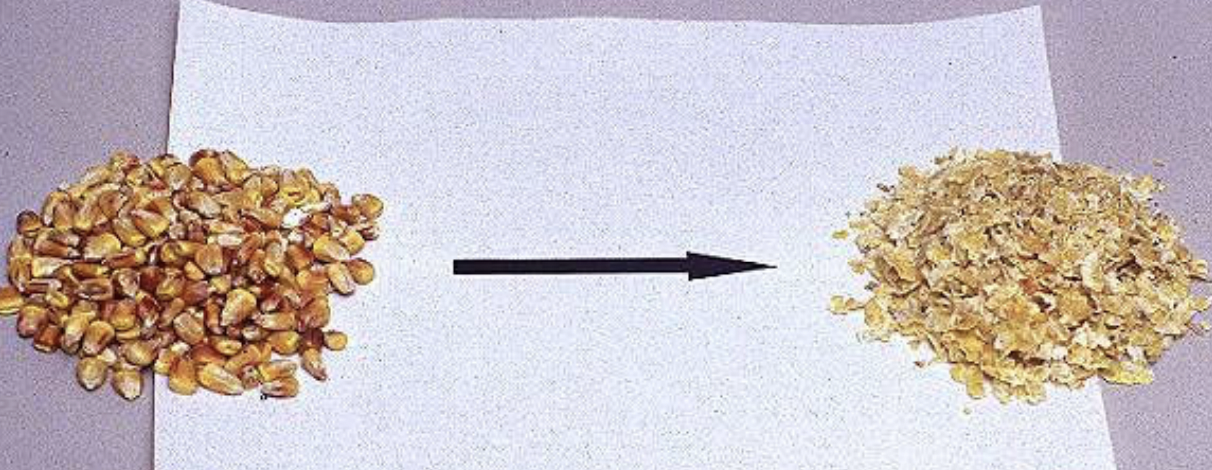
What does food/feed processing do?
Increases surface area
Increases digestibility
( ↑ surface area = ↑ digestability)
Grain Elevators
store bulk grain harvested by farmers and keep it nice and dry
Feed Mills
process those grains and other ingredients to create animal feed
increase surface area and dry
Conversions:
100mg / 1 g
1 ton = 907.18 kg
454 g / 1 lb
2.2 lb / 1 kilo
Fermentation
Microorganism + Glucose = VFA/Lactate/alcohol + CO2
Process of transforming carbohydrates(sugars and starches) into alcohol and CO2 or organic acids through yeast, bacteria, or a combination of the two.
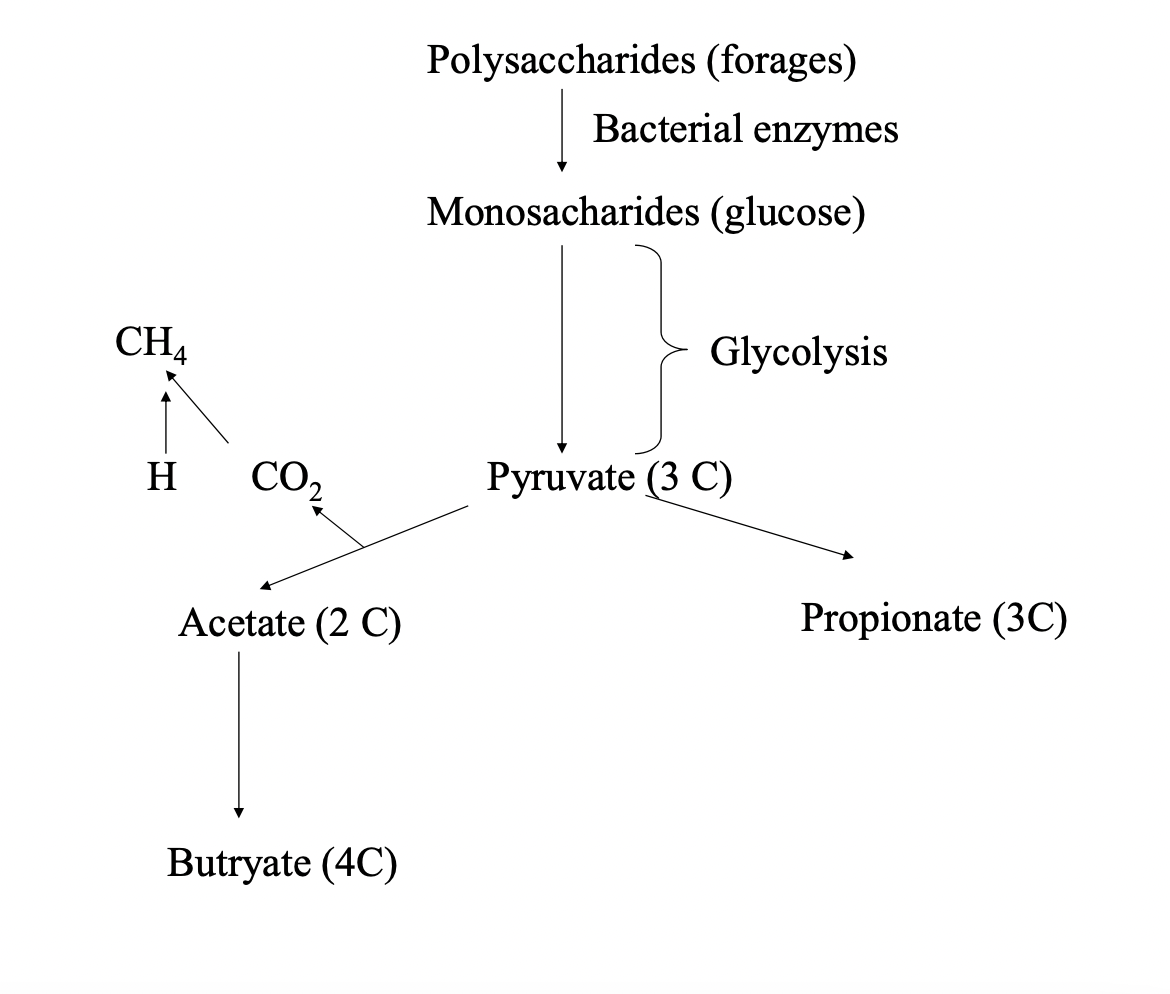
Types of Fermentation
Rumen and hind gut fermentation
via microorganisms
Alcohol fermentation
via microorganisms
Lactic acid fermentation - in oxygen deprived muscle cells
Bread making
via microorganisms
What animals eat the entire plant? (stalk, leaf, and seed)
Ruminants:
cows
beef
sheep
goats
Equine
What animals eat the seed of the plant?
Monogastrics:
pigs
chickens
dogs
equine
human
etc.
Ruminants:
feed lot beef
Goal of a plant
reach reproductive maturity
develop and protect viable seeds
not be consumed
Goal of ruminant farmer
harvest high quality
harvest adequate tonnage
Goal of ruminant
extract energy from starch
extract energy from fiber
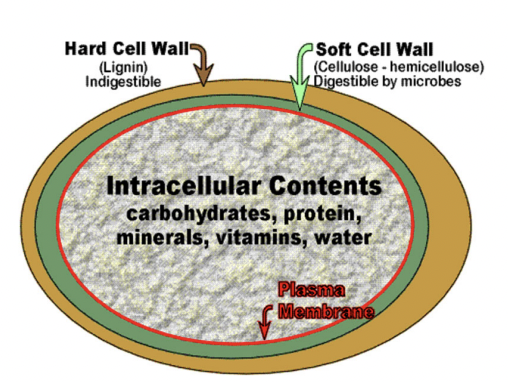
Plant Cell Structure
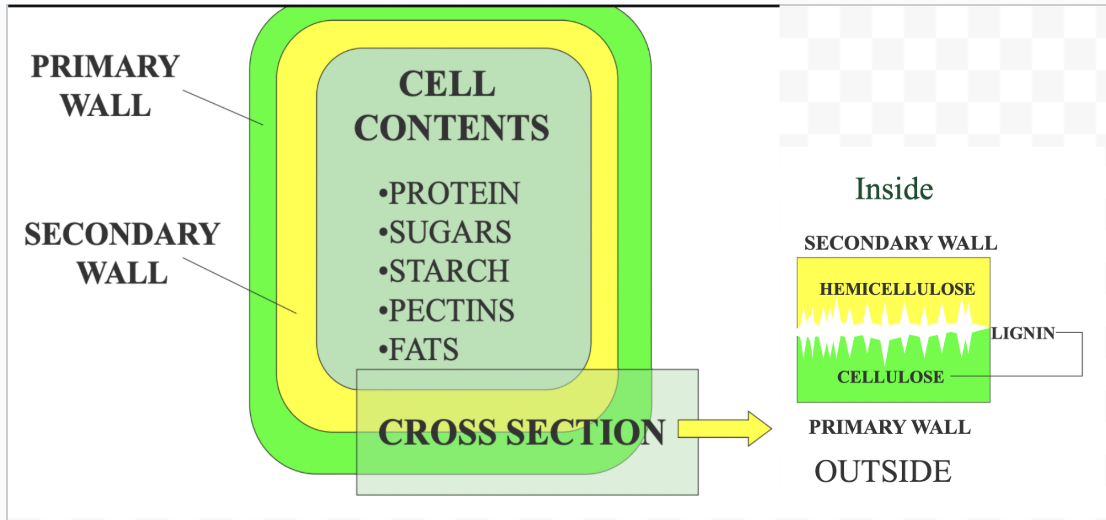
Pectin
Non-structural carbohydrate - potentially digestible
Key roles in plant growth, development, and defense against stress
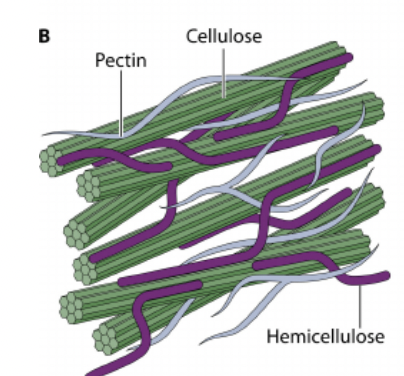
Cellulose
Structural Carbohydrate - potentially digestible
a strong, rigid, carbohydrate molecule that forms the primary structural component of plant cell walls
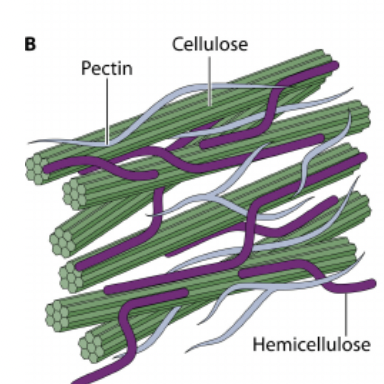
Hemicellulose
Structural Carbohydrate - potentially digestible
Support by cross-linking with cellulose and lignin
Lignin
Structural carbohydrate - INDIGESTIBLE
providing structural support
(↑ maturity = ↑ lignin = ↓ digestability)
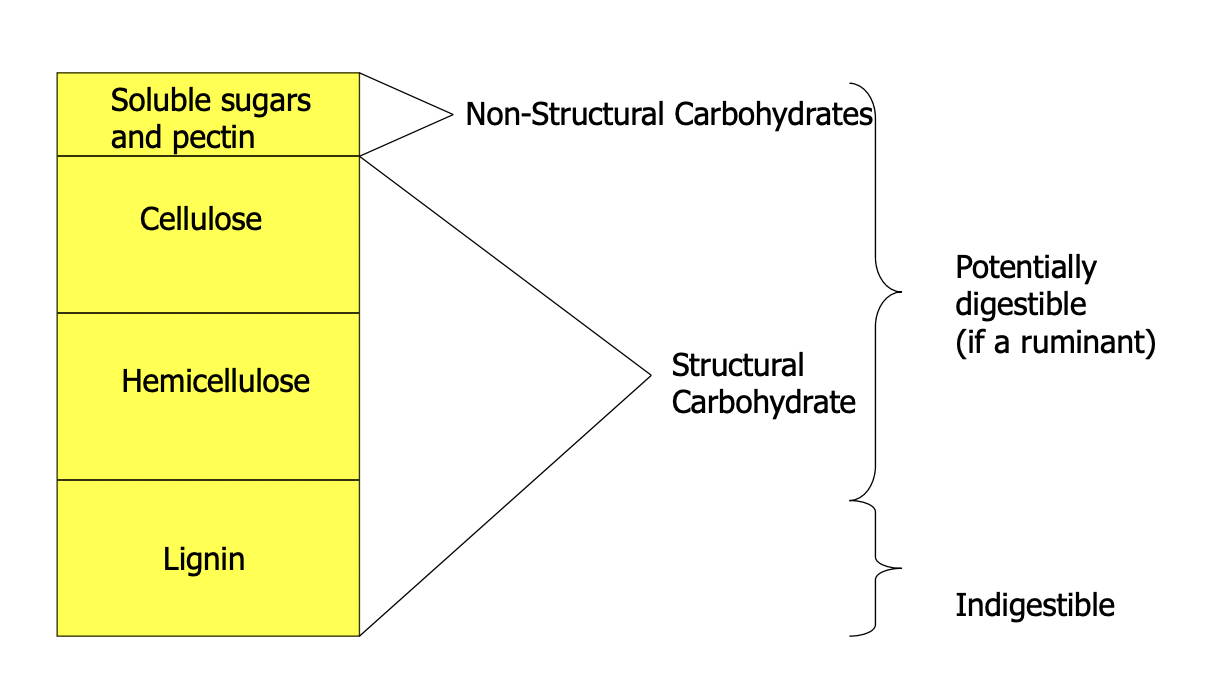
Components of Feed: Carbohydrates
Forage quality over time
Plants vs Animals
Plants: Photosynthesis to get energy
Animals: Amino Acid Synthesis from inorganic N to get energy
Photosynthesis
The uptake of nutrients occurs at both the roots and the leaves
roots absorb water and minerals from the soil
Carbon dioxide diffuses into leaves from the surrounding air through stomata
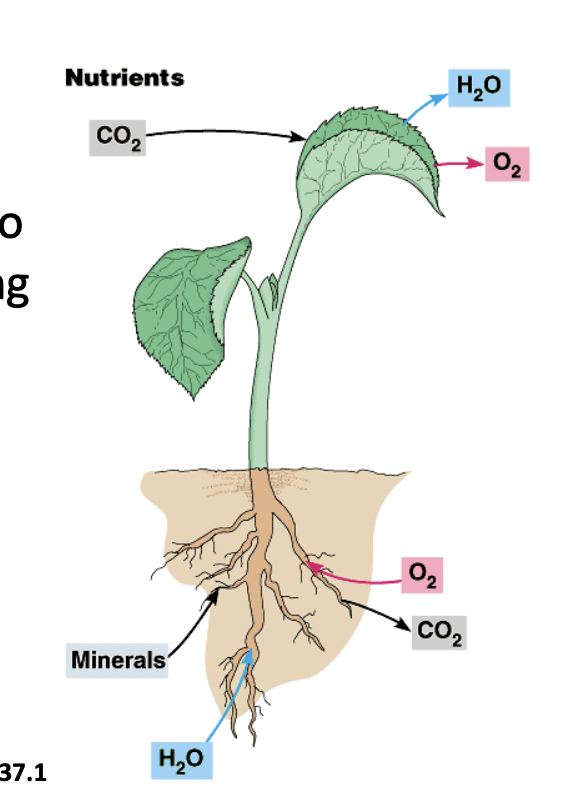
__% of Dry matter in plansts are organic substance while the other —% is inorganic substance.
95% organic substance (carnohydrate, cellulose in cell walls)
5% inorganic substance
Classes of Plant feeds
Forages
Grains
Roots, Tubers
Byproducts
Concentrates
often the seed of the plant
contain high “concentration” of digestible energy per unit weight and volume
Roughages/Forages
Leaves and stems of grasses (incl. cereals), legumes, brassicas
Defined by the fraction of cell wall
As cell wall increases, feeds become bulkier: requires greater volume to hold equal weight of substance
Cereal Grains
Produced by plants of the GRASS family, grown primarily for their seeds
Production has been increasing over the years
EX. Wheat, Barley, Rice, Maize, Millet, Rye, Oats, Triticale, Sorghum
Grains fed to US livestock
Corn, Sorghum, Oats, Barley
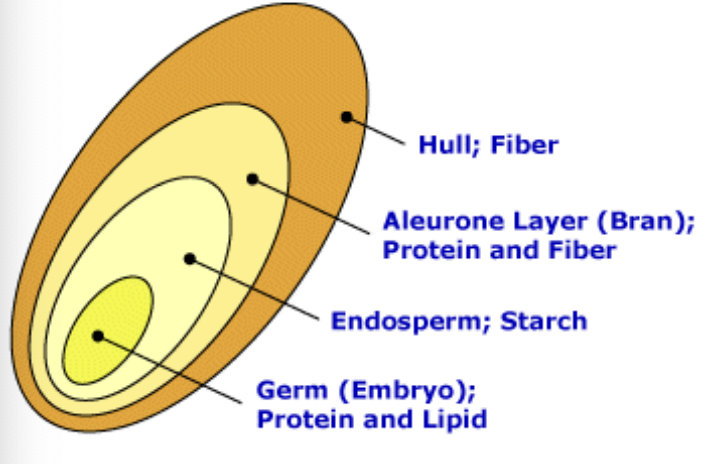
Grain Structure
Nutrient Contect of cereal Grains
Generally Highly digestible
Seed Hulls:
Heavy Hulls (barley and oats) known as rough grains
Rice hulls almost totally indigestable because of high lignin and silica content.
Types of Corn
Dent: “field corn” - feeding and industrial products
Flint: “indian corn” - hard exterior, grown in central and south america, decorative
Sweet: human consumption, more sugar at same maturity
50% of sugar converted to starch in 24 hours… Eat fresh!
Flour: soft kernel, easy to grind
Popcorn: type of flint corn, very hard hull
moisture inside kernel turns to steam and builds pressure to pop
Corn is reffered to as ____ in other countries
maize
Corn will produce more _____ per unit of land than any other grain crop
Digestible energy
It is a very digestible, palatable feed
Roots, Tubers
Turnip
Byproducts
Cereal seed coats, oilseed meals
Two families of cultivated forages
Grasses & Legumes
Grasses
creating seeds that have a lot of starch
bluegrass, ryegrass, bermudagrass, fecue, timothy grass, foxtail, sorghum, bromegrass, orchardgrass, quackgrass, and canarygrass
Legumes
Nitrogen fixation plants
have long roots rich in proteins and minerals
alfalfa, vetch, sainfoin, birdsfoot trefoil, clover
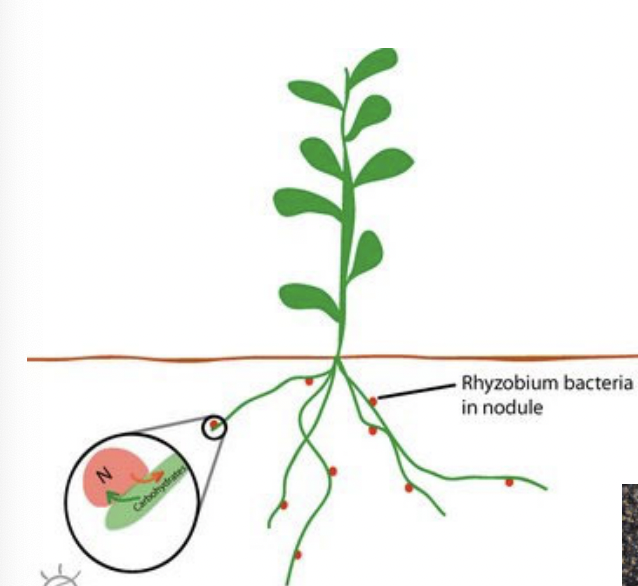
Nitrogen fixation
Enrich the soil by forming a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Rhizobia (within root nodules), which convert atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms.
plants require ammonia or nitrate to synthesize amino acids, but lack ability to convert atmospheric N2 into ammonia (NH3)
Symbiotic relationships between plants and bacteria evolved
Nirtogen-fixing bacteria supply nitrogenous minerals in the soil by converting N2 to NH3 via nitrogen fixation
Parts of plants: leaves
more nutritious
higher in non- structural carbohydrate and protein
lower in structural carbohydrate
Parts of plants - Stems
less nutritous
higher in sturctal carbohydrates = less digestable
vascular tissue
Parts of Plants - inflorescence (flowering part)
less important as a feed component
Parts of plants - Fruit
Cereal grain (starch-rich)
Oilseed (protein and lipid rich)
Parts of plant - Roots
generally unimportant except in few cases
Forage nutritive value
Composite of of:
nutrient density
digestibility
Apparent digestibility (%) =

Apparent digestibility
Not all nutrients that ‘disapeared’ were utilized by animl
microbial utilization and synthesis
GIT secretions
digestive enzymes (proteins)
GIT epithelium turnover
Generalized fecal composition
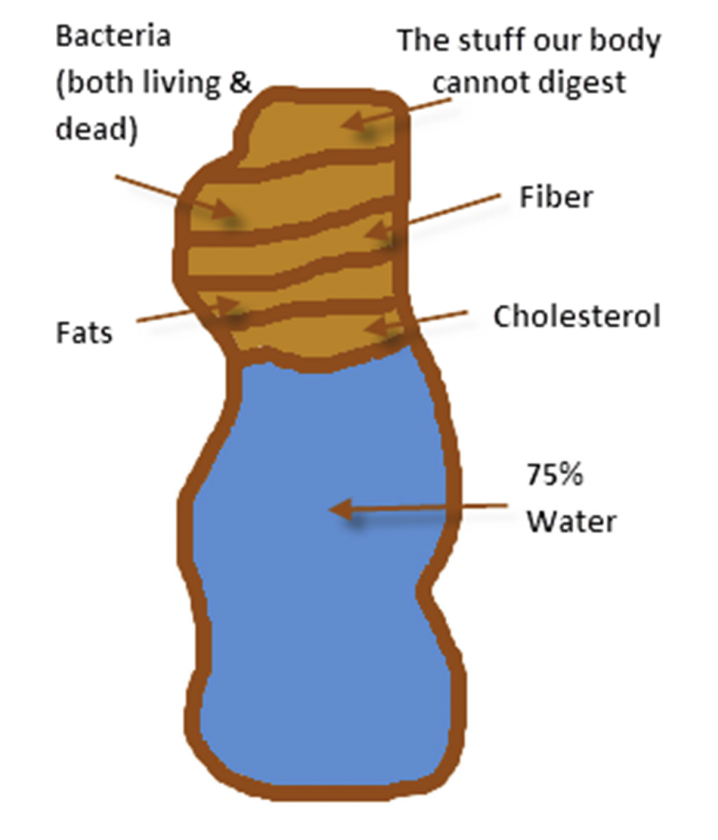
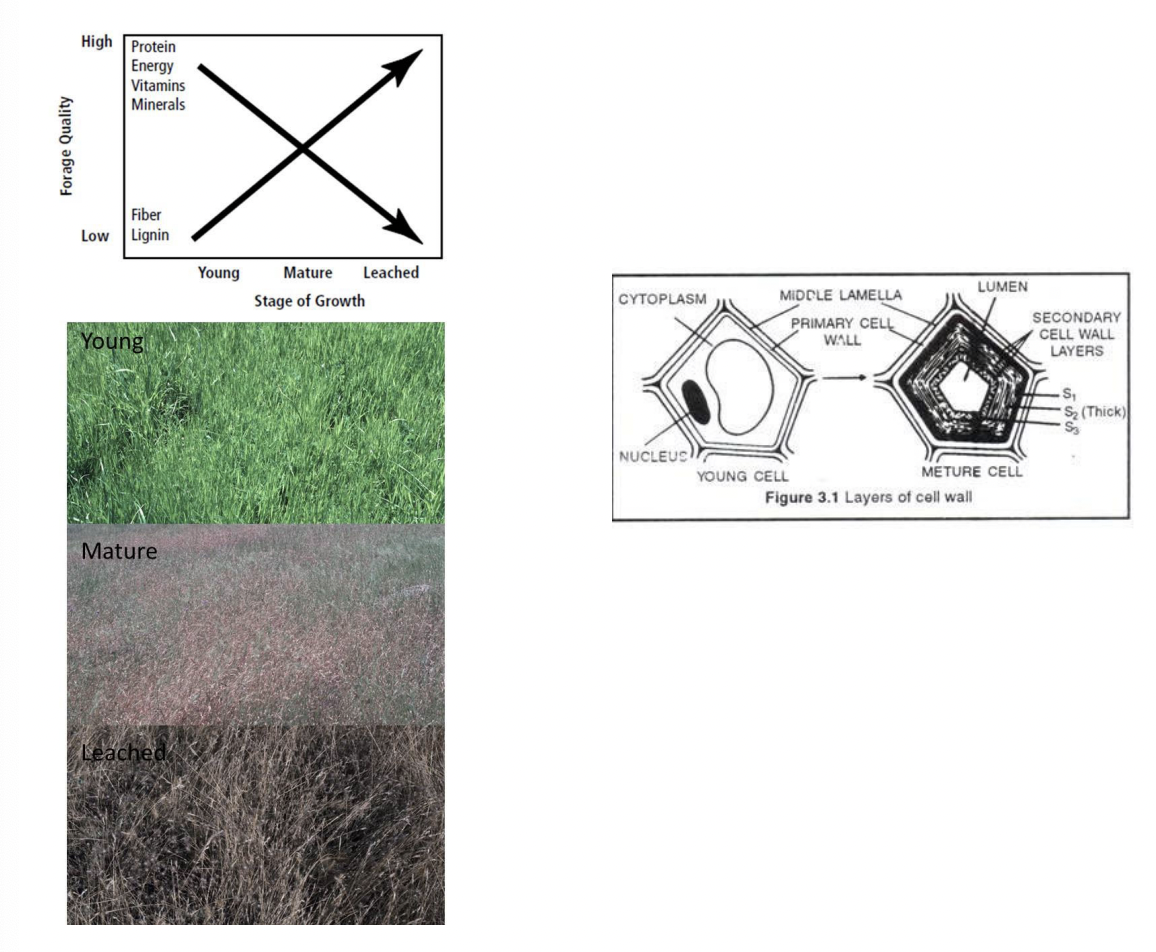
Factors affecting nutritive value:
Maturity: increased maturity = increased lignin = decreased digestibility
Leaf-Stem Ratio: high leaf stem ratio is desirable because leaves contain more nutrients and less structural carbohydrates
decreases with maturity
fiber in leaves is more digestible than in stems
Stressors
Temp
high temp = increase lignification & increased activities of lignin synthetic enzymes
Light Intensity
low light = decrease lignification
Moisture deficit
delayed plant maturity = increased digestibility
Moisture excess
delayed plant maturity = increased digestibility
Soil fertility
lignification generally lower if low soil fertility
Assessment of quality attributes
crude protein
fiber
some assessment of digestibility
used to partially determine cost of feedstuff
Forage quality and animal performance
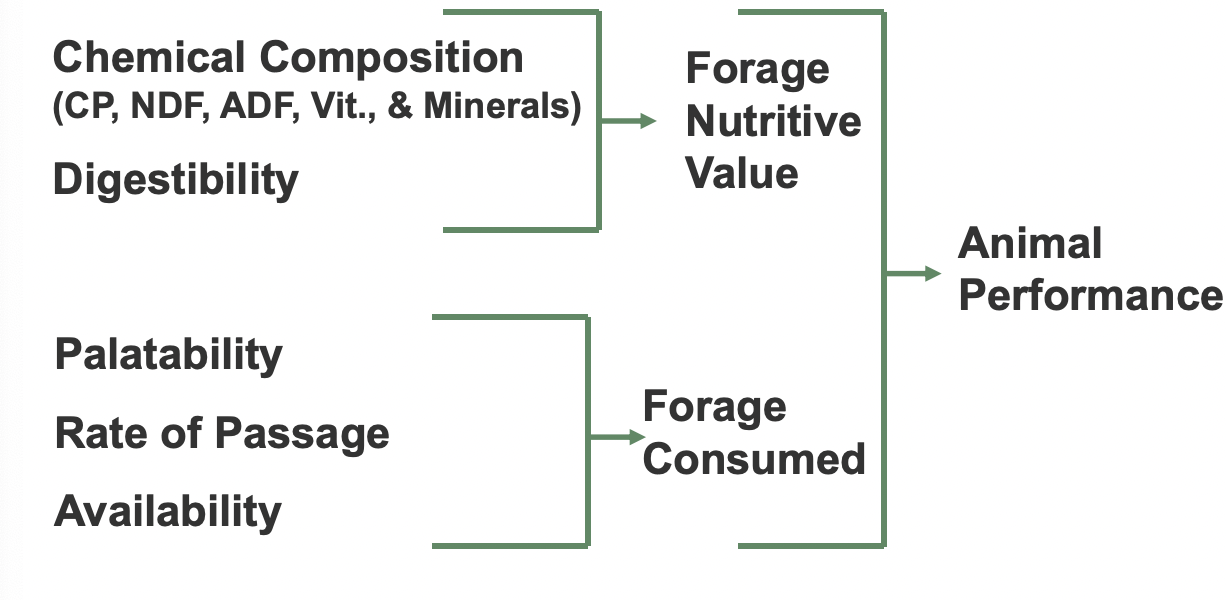
Laboratory Assessment of feed
chemical evaluation
Detergent System
In vitro digestion
Chemical evaluation: Detergent system
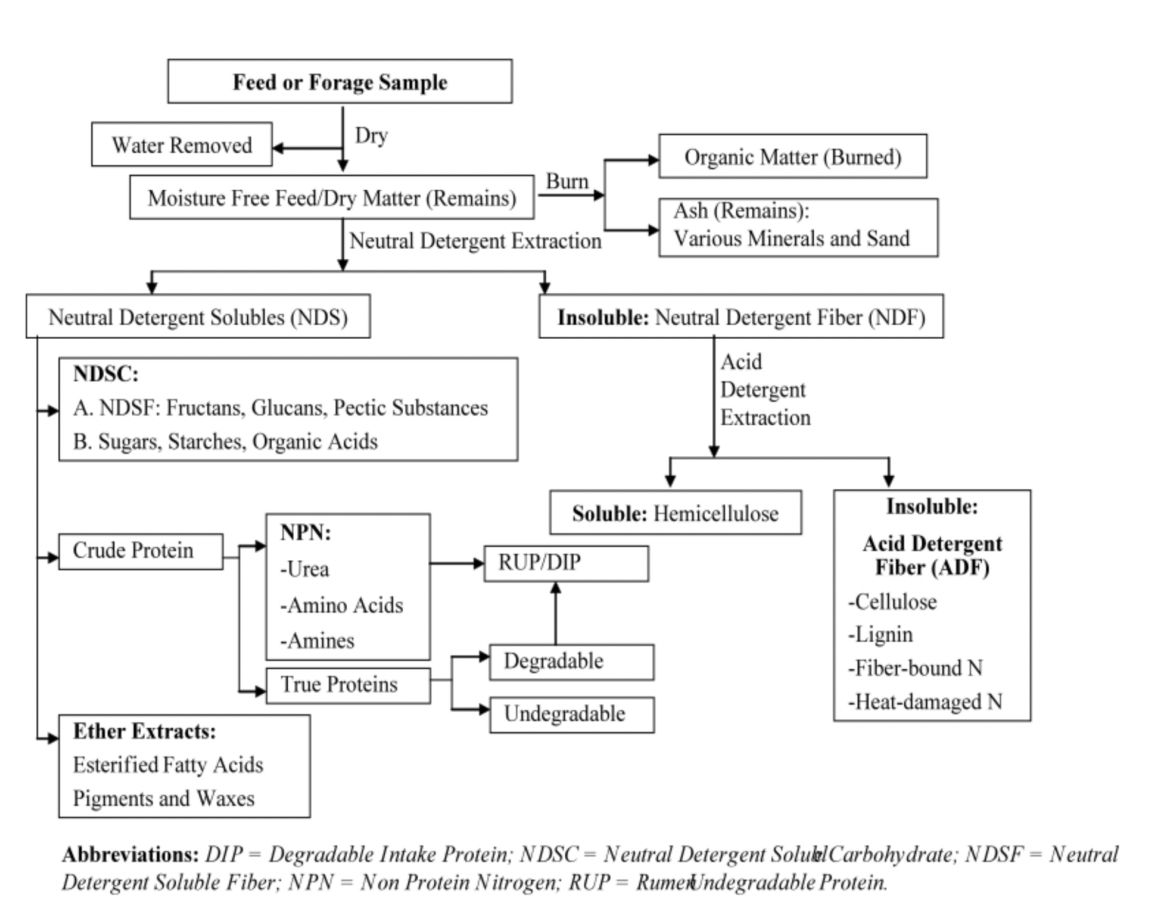
NDF
A neutral detergent that dissolves plant pectins, proteins, sugars and lipids; leaving fiber parts behind (cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose)
Residual (or insoluble) remains include:
Cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin
Considered a close estimate of total fiber constituent feedstuff
Why do plants produce NDF?
Protection
“exoskeleton” on seeds
Once barrier breached, bacteria and fungi infiltrate and produce mycotoxins
Structure
plant grow to sunlight and oppose gravity
Metabolic function
lignan “exoskeleton” reduces the loss of water
drought resistant plants have increased NDF
drought stress stimulates lignin production
ADF
Acid detergent recovers cellulose and lignin, and removes hemicellulose
includes the least digestible portion of forage (lignin and cellulose)
Feeds with ADF are lower in digestibility
ADF is often used to calculate _______ content of feed... because:
Energy
because energy content of feed is related to it’s digestibility
Van Soest System
In vitro vs in vivo
In vivo: in life, experiment preformed in living organism
In vitro: preformed in lab
In vitro digestion:
Simulates:
Rumen digestion (48 h incubation in rumen fluid at 39˚ C)
Gastric digestion (48 h incubation in pepsin solution at pH 2)
Dacron Bag
to measure the digestibility and degradation of feedstuffs in the rumen.
Small, porous bags containing feed samples are placed into the rumen for a set period, removed, and the amount of feed material that has disappeared is measured to determine its degradability.

Animal Assessment 3 major approaches
Digestion Trial
Balance Trial
Production (growth, lactation) trial
Digestion Trial
Requirements:
Individual feeding
Need to know diet chemical composition
need to know how much feed each animal consumes
Quantitative feces collection, separated from urine
need chemical composition of feces
Adequate # of animals (>5)
Adequate sampling period (>7d)
Minimal disruption of feed intake
measure what is intaken vs what is shit out
Balance Trial
Requirements same for digestion trial, PLUS measurement of urinary losses
N balance = N intake - (fecal N + urinary N)
Production Trial
Applications
Titrate maximal or optimal responses to:
total feed intake
intake of specific nutrients
Compare the nutritional value of different feed ingredients fed at the same level
Production Trial: Efficiency of feed utilization
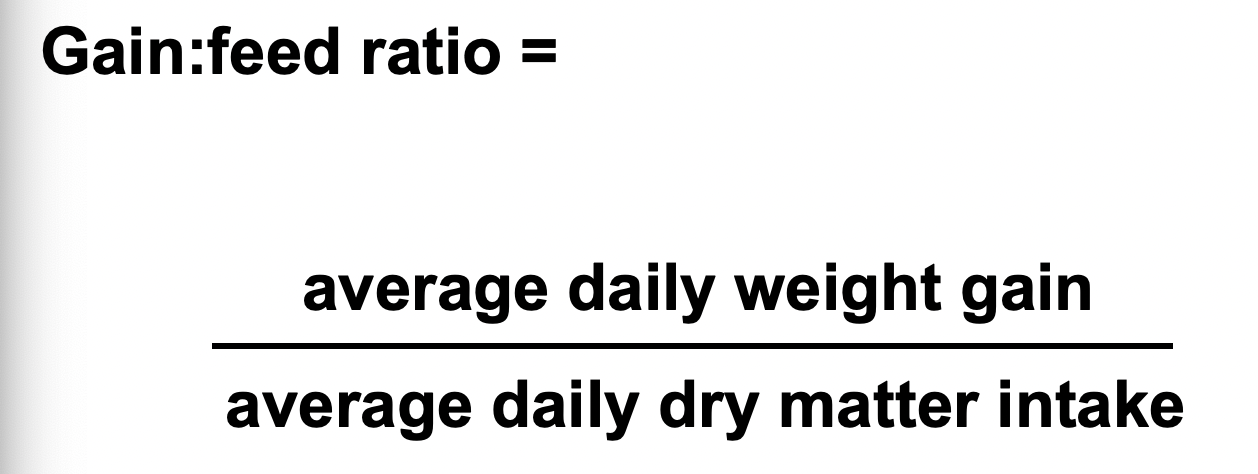
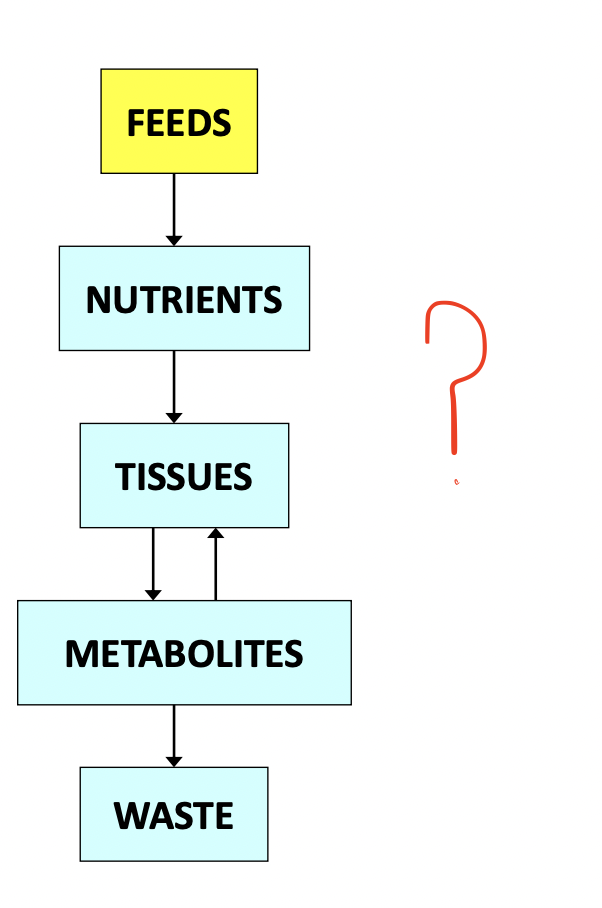
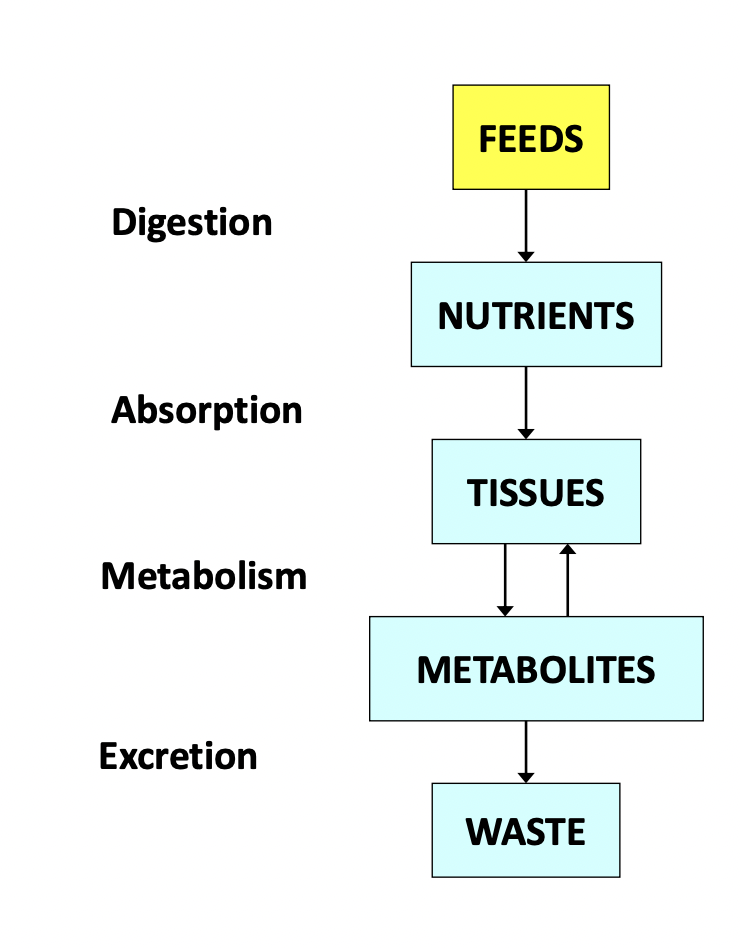
Nutrition involves processes of:
Ingestion - apprehension of feed, chewing, and swallowing to the initial digestive organs
Digestion - reduction of food to utilize form; physical and chemical processing of ingested food
pre-ingestion processing of feed starts the digestive process
Absorption - active transport and passive diffusion
Metabolism - post-absorptive utilization of nutrients
Essentail Nutrient vs Nonessential nutrient
Essentail Nutrient: a nutrient an animal’c body cannot make, they need to eat it
Nonessential nutrient: nutrient that the body can make sufficient quantities of
Essentail nutrients:
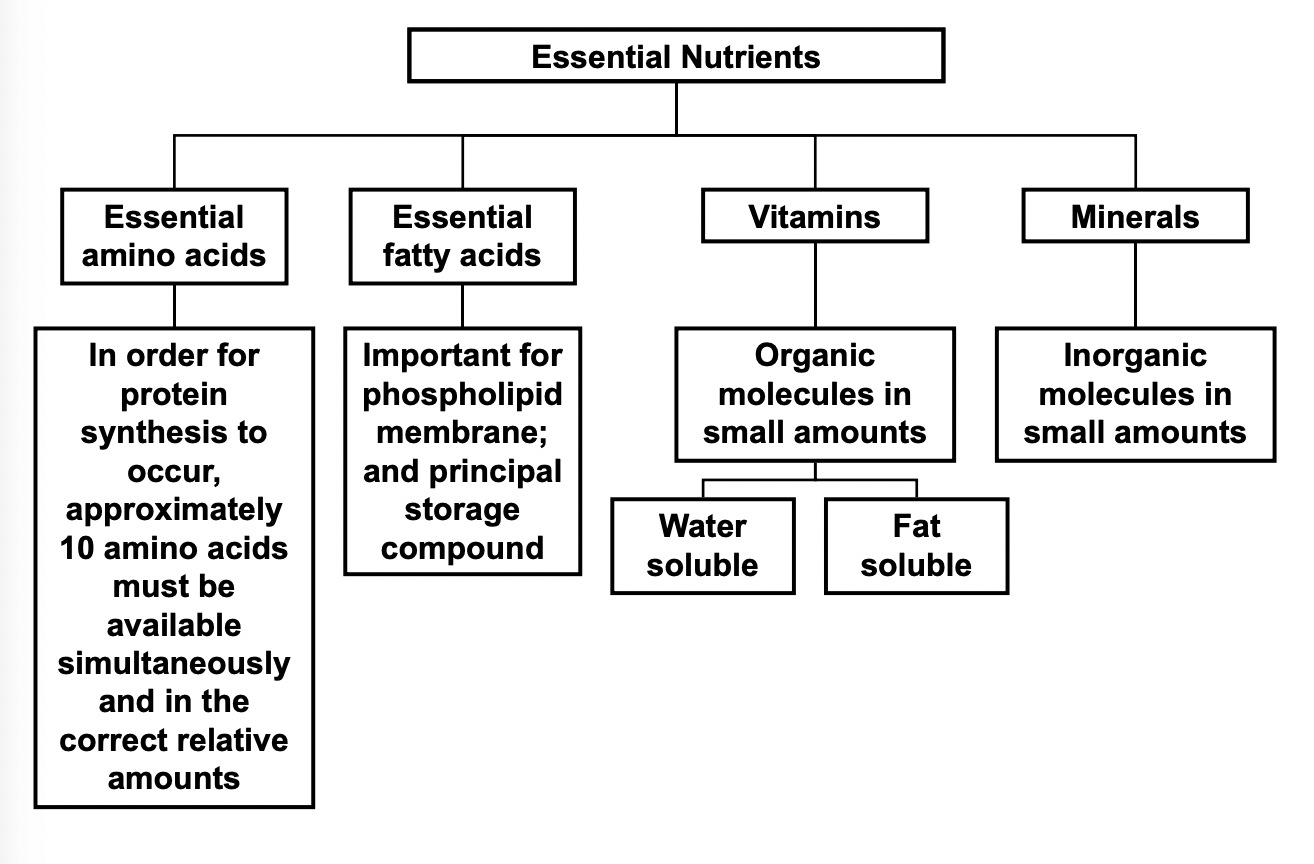
Macronutrient
A nutrient that is provided (not necessarily required) in large amount in diet
carbohydrates
proteins
lipids
water
Micronutrient
A nutrient that is needed in relatively small amounts in diet
vitamins
minerals
The GIT does not absorb ________ because __________________.
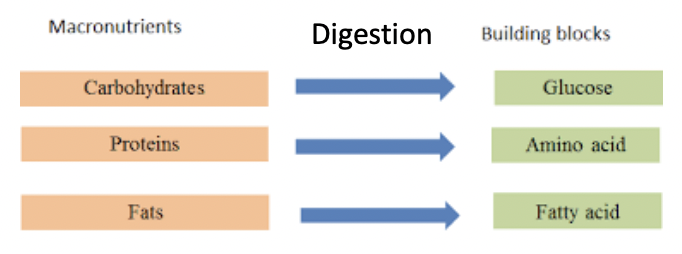
Macronutrients because they are too large
Must break down the macros into simplest building blocks through digestion
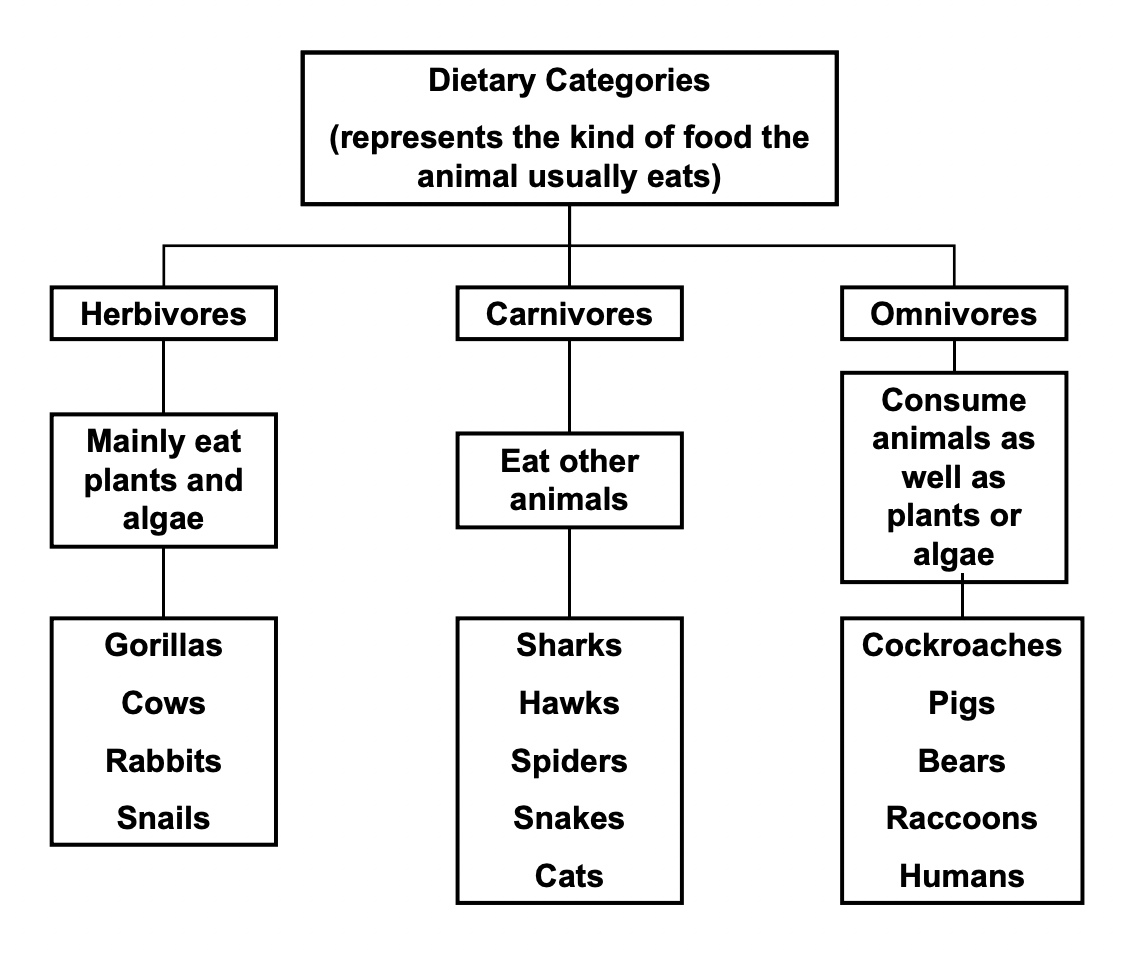
Dietary Categories
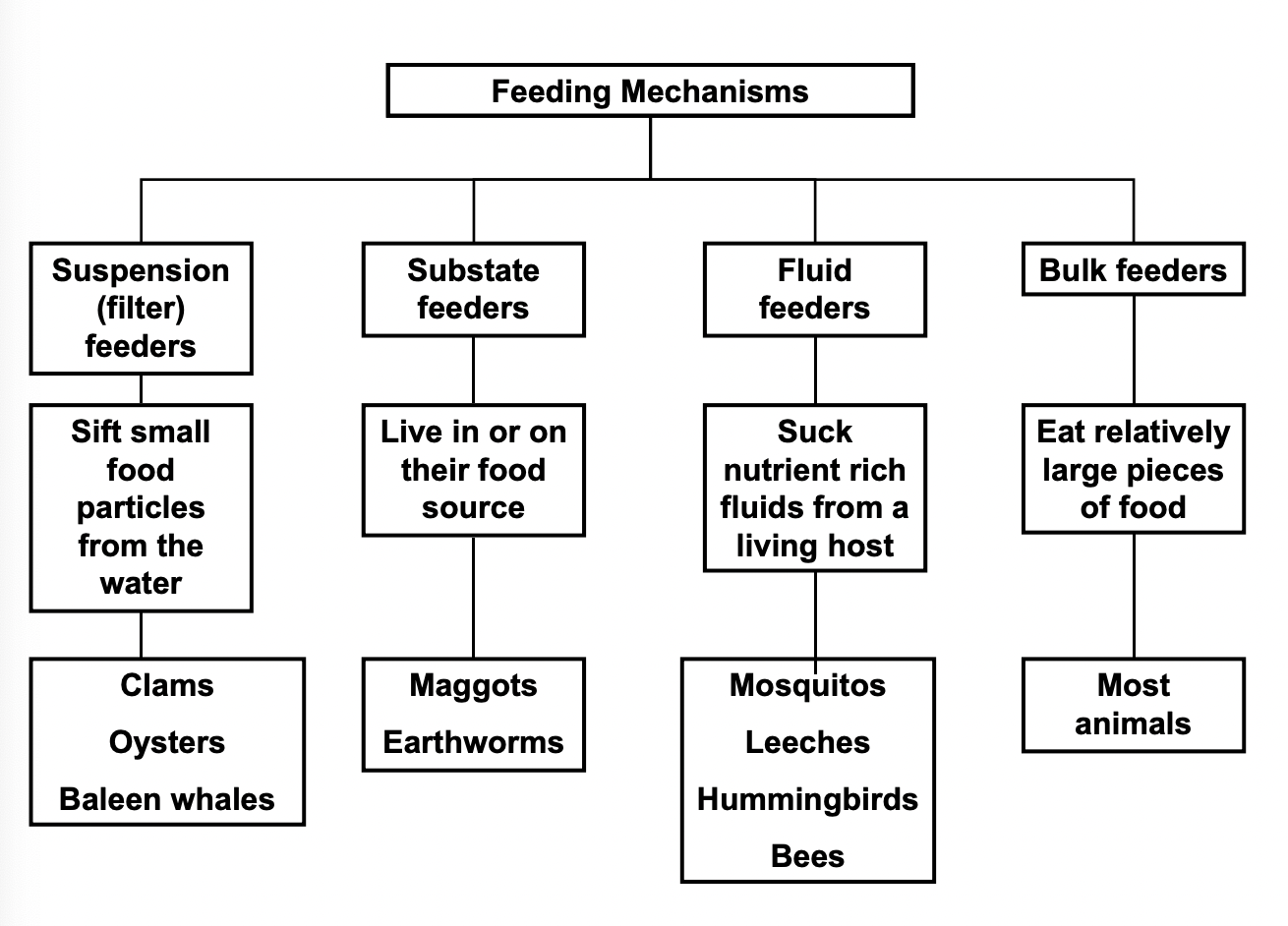
Feeding Mechanisms
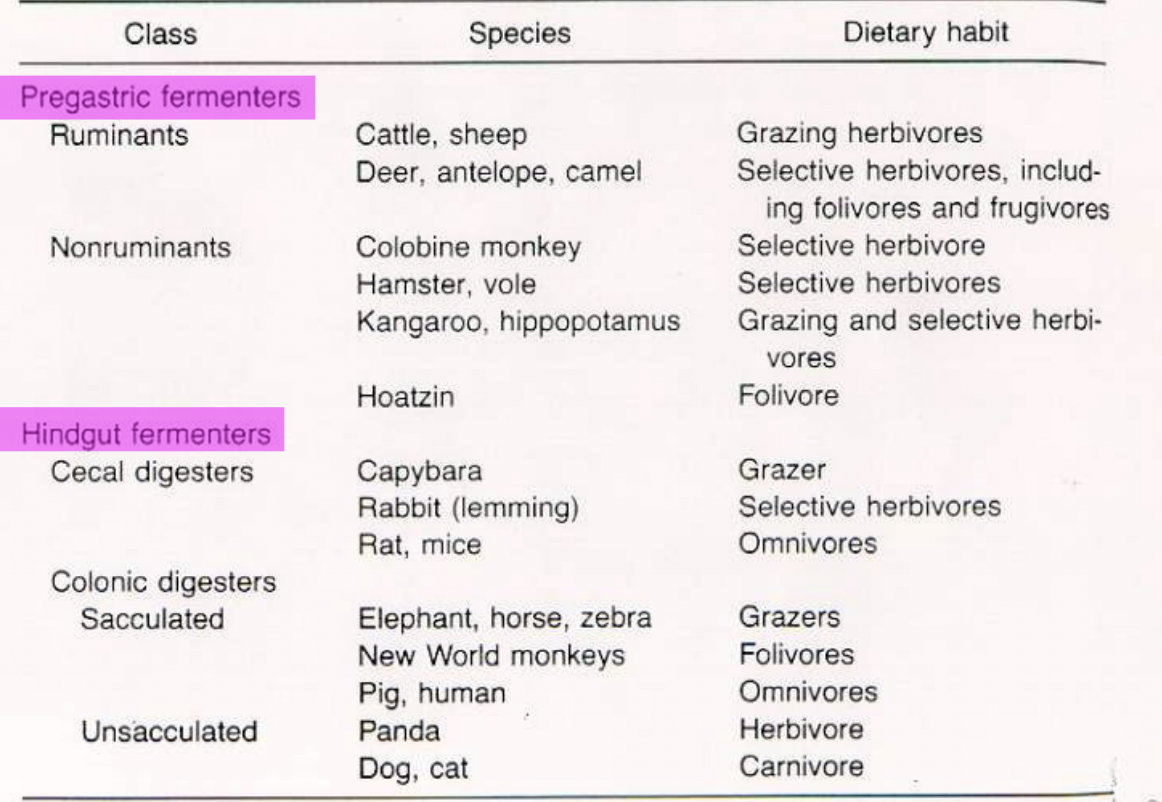
Anatomical Classification
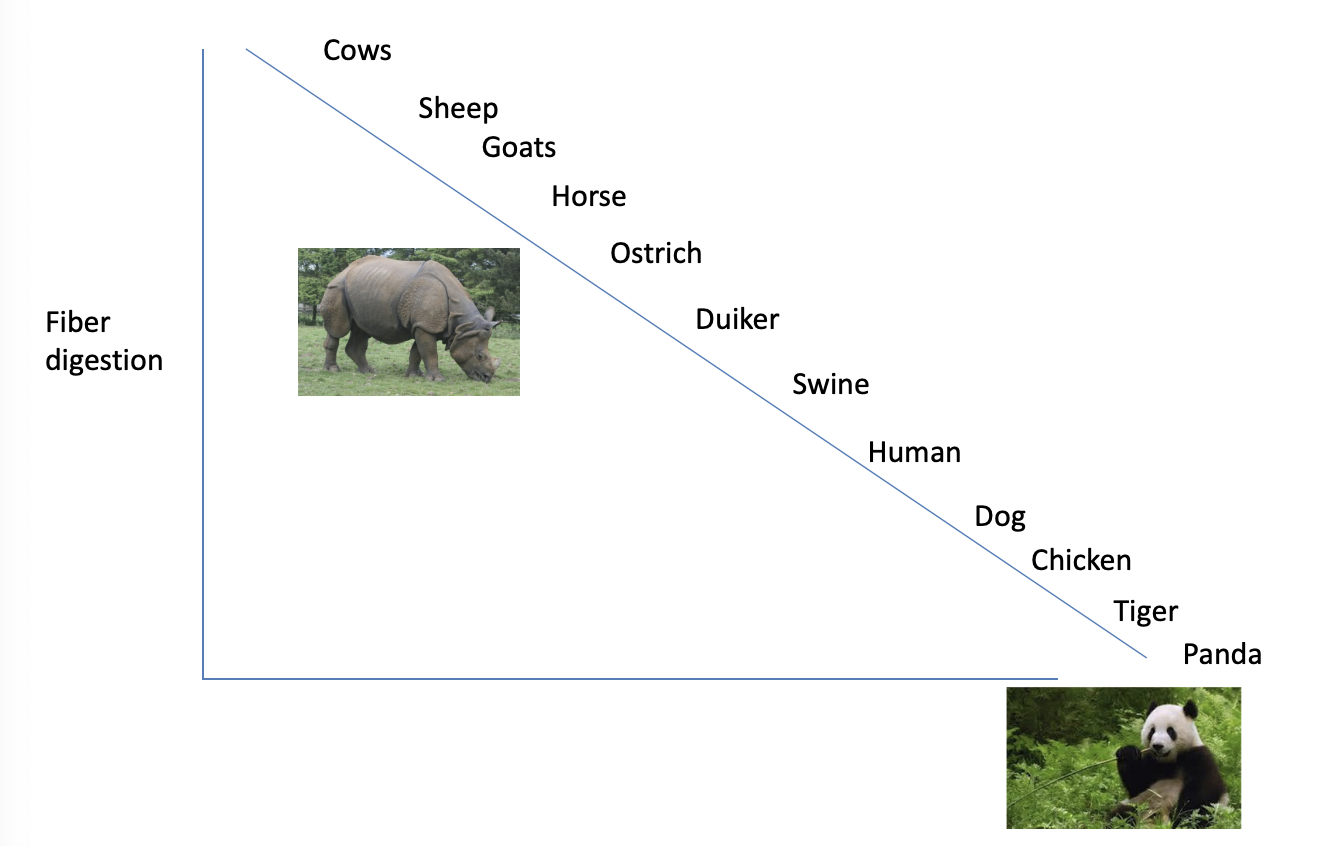
Significance of fermentative digestion
ALL mammals have some fermentative capsity
Importance is directly related to fiber consumption
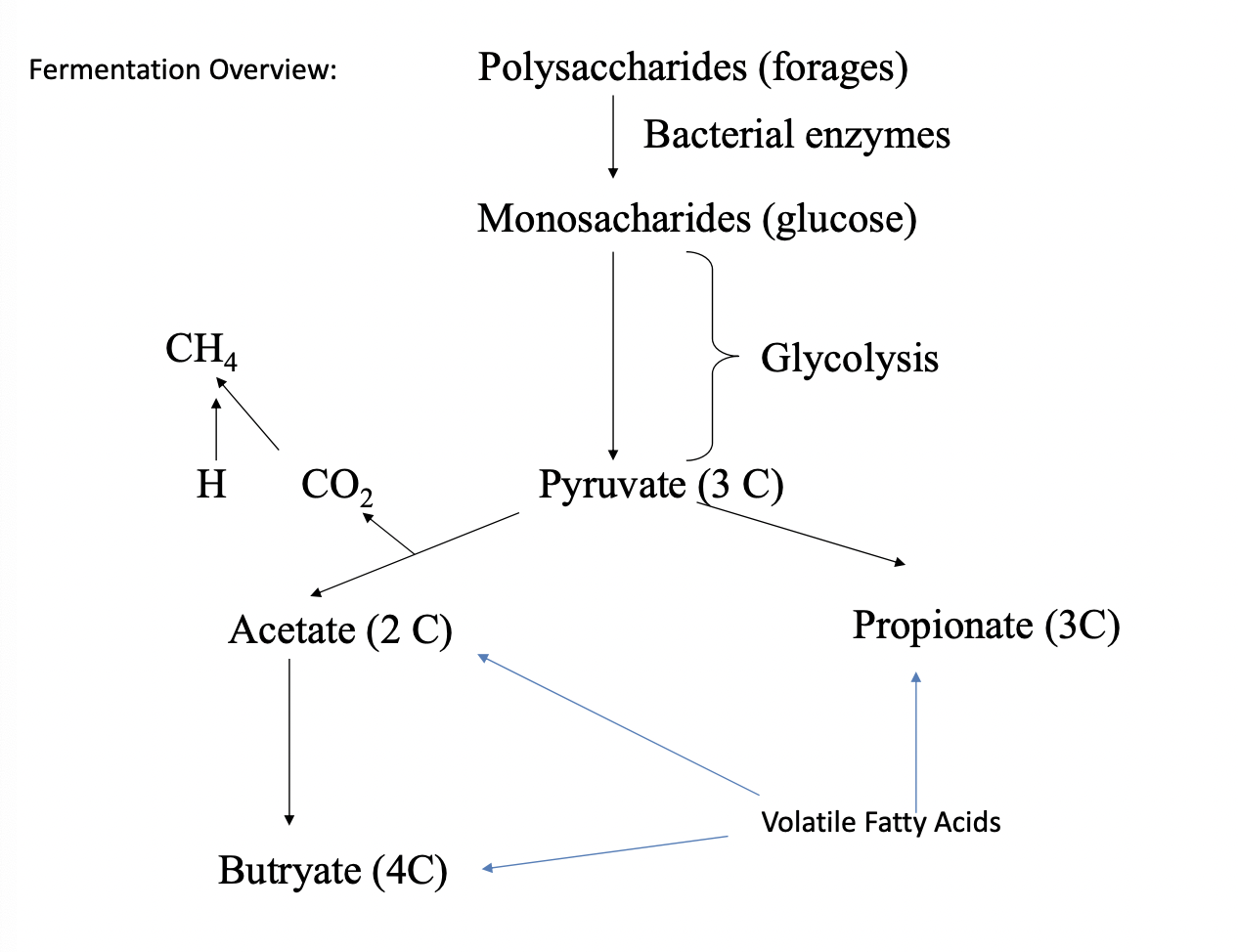
3 vial fatty acids
Make ~25 ATP through microorganisms/fermentation
Fiber digestion differences
Pregastric fermenters - Ruminants
Fermentation in thr umen comes before the stomach
Food is processed (digested) by microorganisms; carbohydrates are fermented to volatile fatty acids (VFAs)
VFAs are absorbed straight through rumen walls - this is how ruminants get their energy
True stomach (acidic or glandular) is used to digest microorganisms - this is how ruminants get their protein
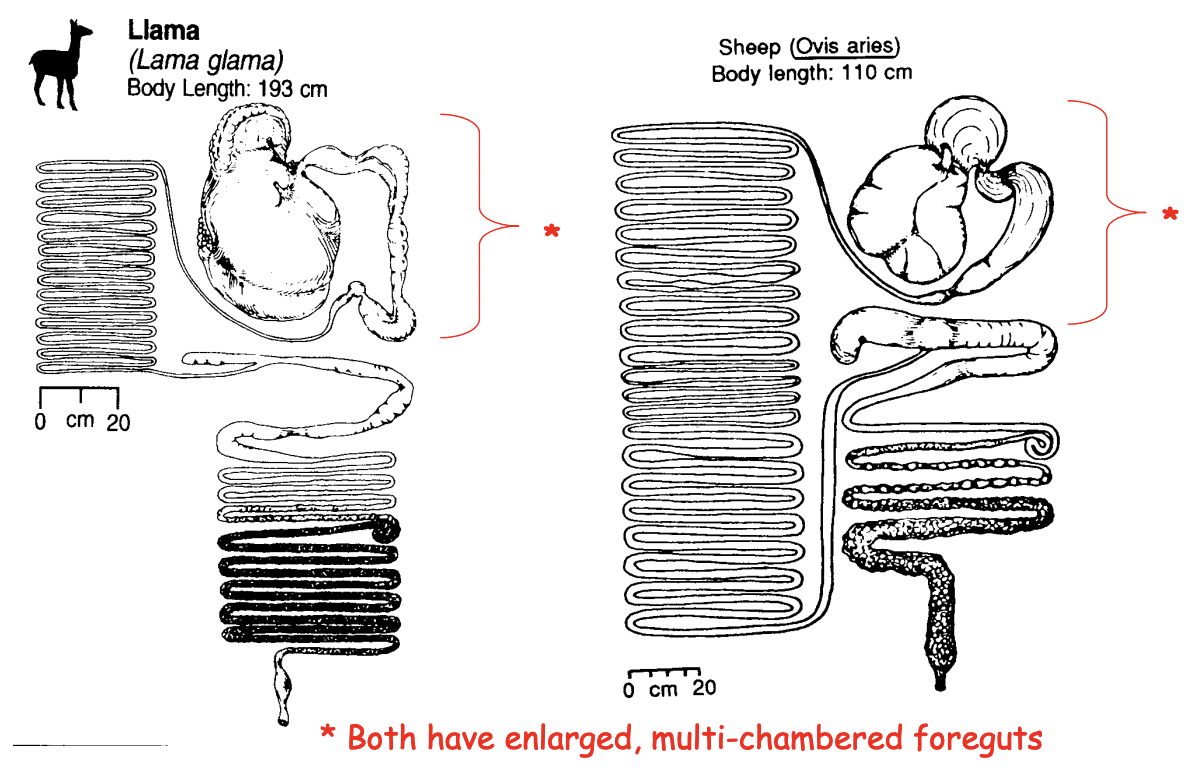
Ruminants - pregastric fermenters
Pre-gastric germenters - nonruminants
Take advantage of sacculated stomach
allows for some fermentation capacity
not as extensive as a rumen
animals must select more digestible forages
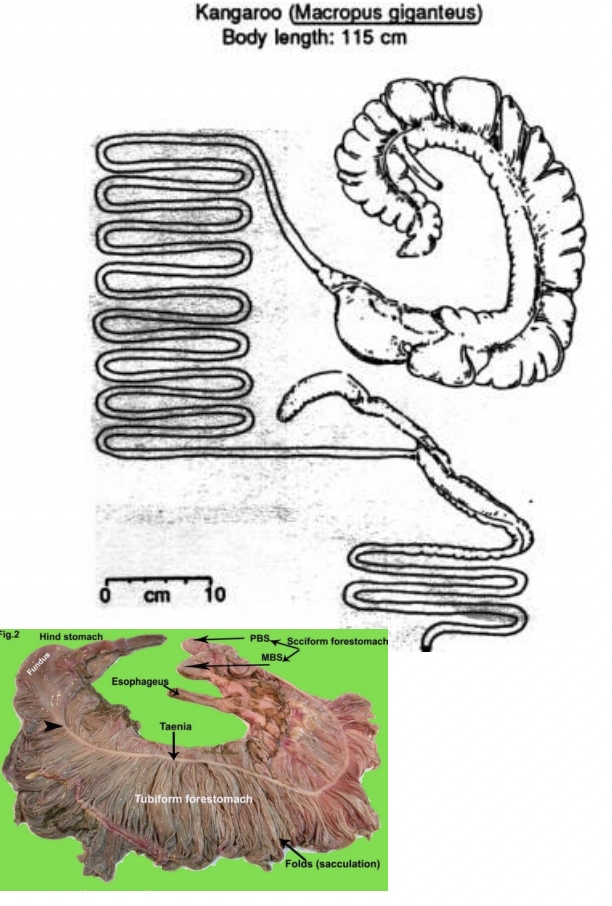
Non-ruminant: pregastric fermenter
Shows sacculated stomach
Post-gastric (hind gut) fermenters
Fermentation chambers come after the stomach and the small intestine
microorganisms can ferment what is not digested in small intestine
VFAs are abosrbed through hindgut epithelia
Excess microorganisms are defecated
Hind gut fermenters miss out on microbial protein!
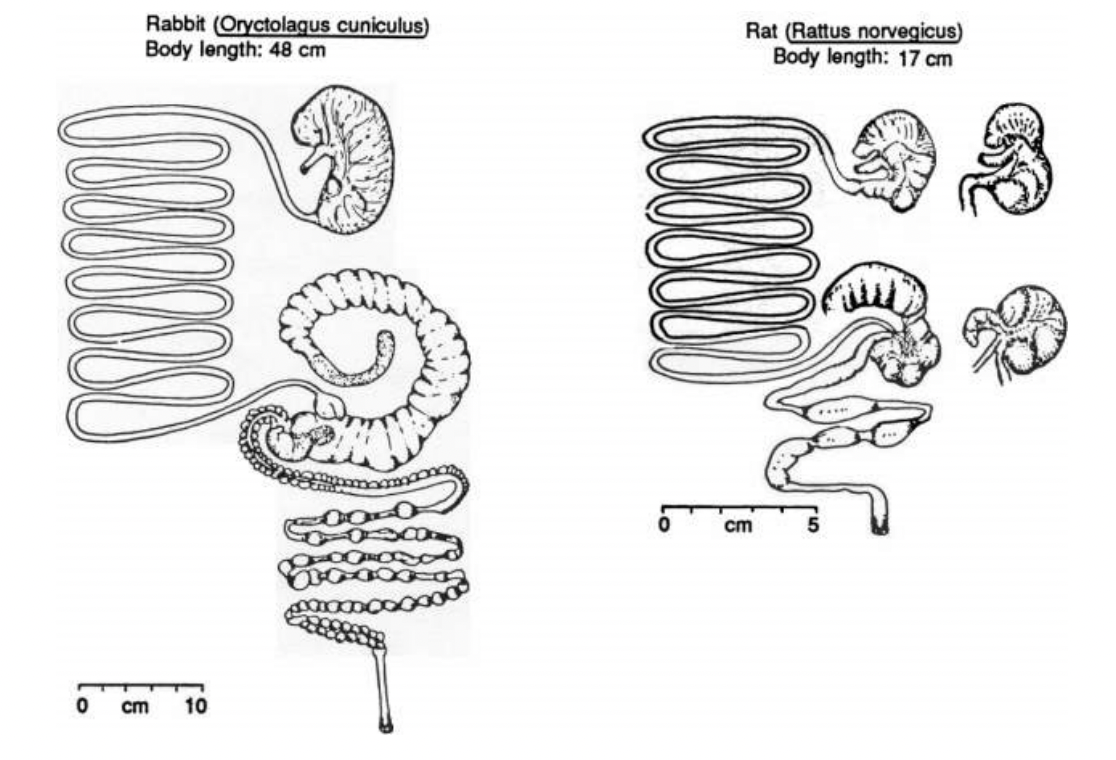
Cecal Fermenters - most of fermentation occurs in the cecum
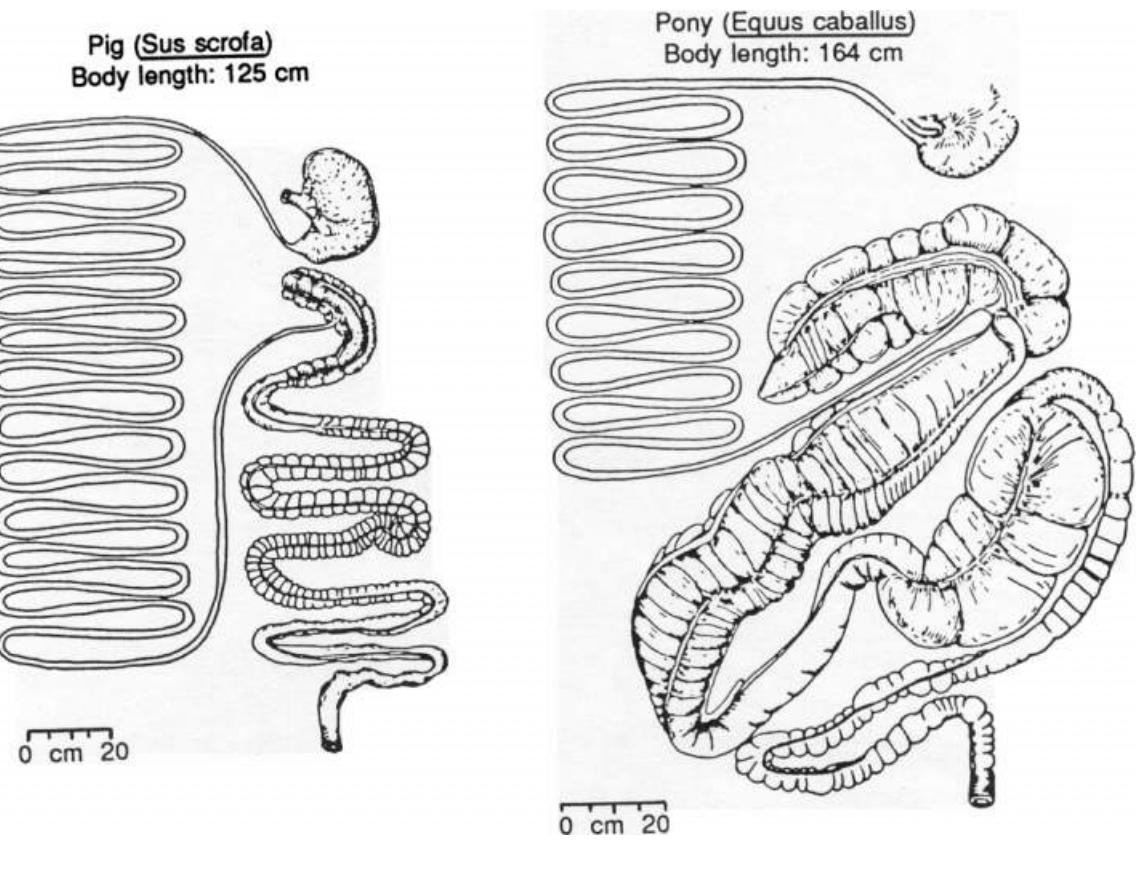
Colon Fermenters - most of fermentation occurs in colon
Can see sacculated colon
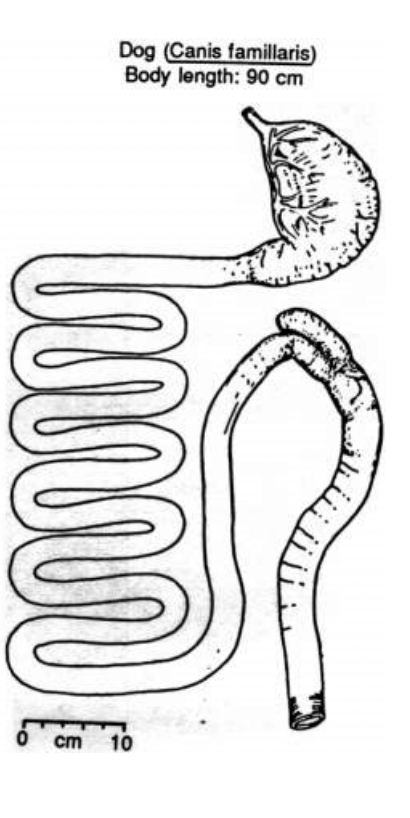
Colon fermenters - most of fermentation occurs in colon
Has unsacculated colon - likely carnivore/ eats highly digestible foods
Adaptations to feed sources
Prehension, Mastication, & Deglutition
Gastric Capacity and structure
Intestional length and functions
Prehension
Seizing and conveying feed into mouth
Mechanisms vary with behavior and diet
Forelimbs (primates, raccoon)
Snout (elephant, tapir)
Tongue (anteater, cow, sheep)
Lips (horse, sheep, rhinoceros
Beak (birds
Drinking varies as well (suction, ladle tongue)
Mastication (or chewing)
To crush the food, increase surface area, and allow enzymes to act on molecules
carnivores only to reduce size of particle to small enough to swallow
herbivores chew continuously
Adaptations with teeth
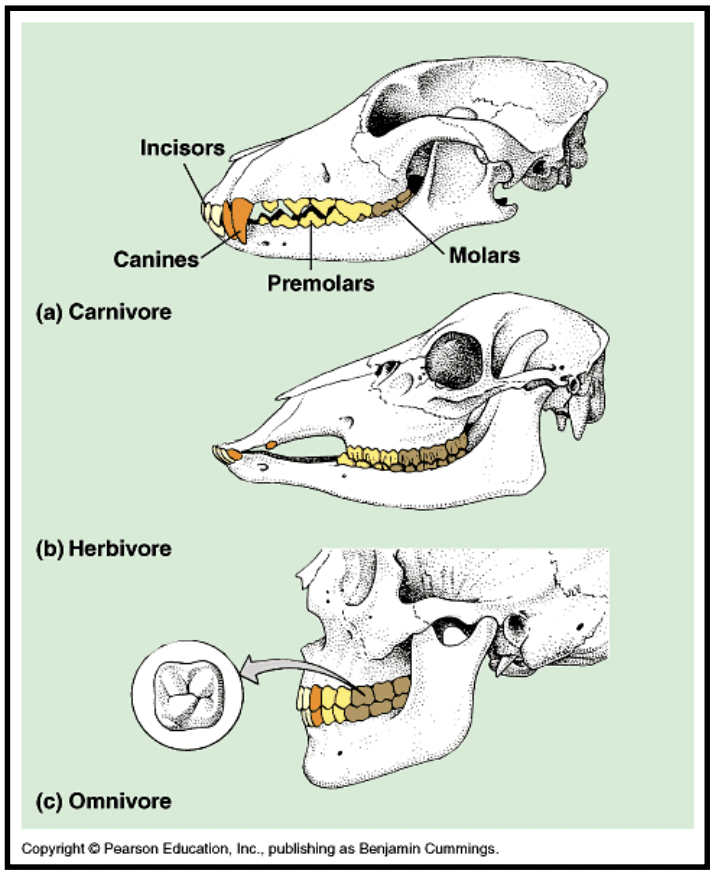
Mechanical digestion
Physical breakdown of food
teeth & grinding increase surface area (allows for easier digestion
Bacetria living in mouth feed off nutrients sticking to teeth (cause tooth decay)
Deglutition (swallowing)
Swallowing: reflux initiated by presence of food in pharynx
Propulsion of food to stomach by esophageal peristalsis
varies little with diet
Quantity and composition of saliva varies considerably
Functions of saliva
moisten feed (salt and water)
Lubrication (aids swallowing)
Starch and lipid digestion (amylase and lipase): species dependant
Salivation comparison

Gastric capacity and structure
Capacity greatest in pre-gastric fermenters; stomach = reservoir
small stomach in carnivores related to nutritive density of diet
distribution and composition of epithelial lining varies between species and dietary adaptations
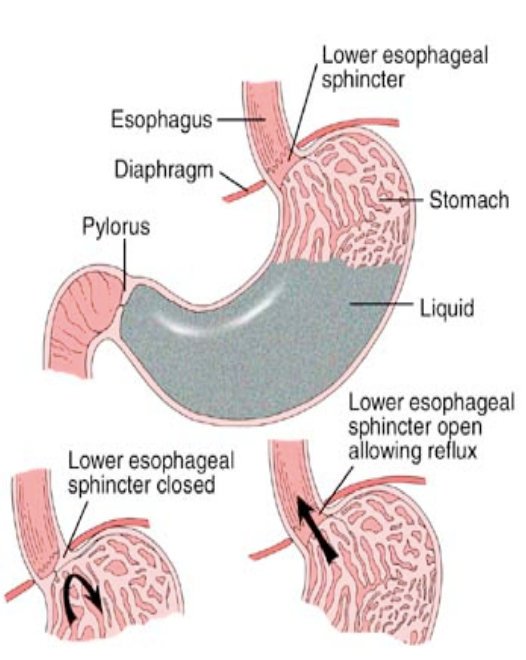
Sphincters
Circular muscles that control the movement of food into and out of the stomach
Intestinal length and functions: Small intestine
less variable - but generally shorter in carnivores
meat more digestible = shorter length (carnivores)