NHP Principles of colony management and medical management
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
How does the guide differ from the AWA regarding NHP housing requirements?
The 2011 Guide recommendations differ from current
Animal Welfare Regulations in that the Guide states that
optimal cage measurements should not be based solely
on floor space (engineering standards)
What enrichment tool has been the most successful at reducing abnormal behaviour in NHPs?
Social housing as a form of enrichment
has been shown to be one of the most effective methods
of preventing and reducing abnormal behavior
Define Positive Reinforcement Training (PRT)?
\PRT is defined as a form of operant conditioning
where an animal receives a reward for performing
a desired behavior
What is the purpose of the Quality of Life Committee and what personnel should be in this committee at a minimum?
Quality-of-
Life (QOL) committee. The QOL committee is composed
of a veterinarian, a veterinary pathologist, a veterinary
technologist, a behaviorist, a colony manager, and an
animal technician involved with the daily care of the
animal. A QOL committee is formed when an animal is
diagnosed with a life-threatening or debilitating chronic
condition and requires more intense monitoring for pain
or distress. An individual behavioral ethogram is developed
for the animal that enables the QOL committee to
quantitatively assess the loss of normal behaviors for
the individual animal, and thus assist the veterinarian in
making a more informed decision regarding the quality
of life and whether euthanasia is appropriate
What are the low and high temperature thresholds for NHPs according to the AWA and what is the maximum amount of time NHPs can be exposed to these extremes?
The Animal Welfare
Act requires that these temperatures not drop below 45°F
or exceed 85°F for more than four consecutive hours.
Recommended environmental temperature range for most NHPs?
The recommended environmental temperature settings
for most nonhuman primates is 64–84°F
Air changes and lighting for NHPs?
10-15 air exchanges per hour
30 - 70% humidity (min of 50% for tamarins and marmosets)
12 / 12 hr light dark cycle (reverse for aotus)
Define guide definitions of cleaning and sanitation?
As stated in the Guide (2011), effective
sanitation is composed of two elements, cleaning and
disinfecting. Cleaning is defined as the removal of dirt
and waste products, while disinfection is the reduction
or elimination of pathogenic microorganisms.
What CFR created a final rule which states that blood, body
fluids, and tissues infected with human disease agents
must be handled in compliance with OSHA standards?
29 CFR Part, 1910.1030, the Occupational Exposure to Bloodborne Pathogens: Final Rule, which states that blood, body
fluids, and tissues infected with human disease agents
must be handled in compliance with OSHA standards.
What is the minimum BSL for working with NHPs?
2
What is the most frequently found zoonotic disease found in NHP caretakers?
Simian foamy virus, likely transmitted through animal
bites, has not been reported to cause disease in human
beings, but it is the most frequently found zoonotic virus
in occupationally exposed nonhuman primate caretakers
What are the most significant zoonotic pathogens at risk to personnel working with NHPs?
Simian foamy virus, likely transmitted through animal
bites, has not been reported to cause disease in human
beings, but it is the most frequently found zoonotic virus
in occupationally exposed nonhuman primate caretakers
(Switzer et al., 2004). Macacine herpesvirus 1 (McHV-
1) also commonly referred to as herpes B virus, simian
immunodeficiency virus (SIV, a retrovirus closely related
to HIV-1 and HIV-2), tuberculosis, and bacterial gastroenteritis
caused by Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia, and Campylobacter spp. are some of the more serious pathogens that can be transmitted to personnel.
what does an NHP quarantine program do?
The quarantine program provides for segregation of new animals for the time necessary to acclimate them to their new environment
and carry out diagnostic procedures for the
detection of adventitious infectious agents.
How long must an NHP be quarantined at a CDC regulated primate import facility when imported to the USA ?
31 days
What is the quarantine period for an NHP once arrived at a research facility?
30 days
What is the total number of days an NHP must be in quarantine for from import to use at a research institute?
61 days
What is the minimum amount of time an NHP has to acclimate before being assessed by a veterinarian?
72 hours
How is Tuberculosis assessed in a quarantined NHP?
Upon physical exam, 72 hours after arrival, NHP will receive Mantoux tuberculin skin test intradermally in the eyelid
The eye will be evaluated for reaction at 24, 48, 72 hours
The NHP will receive a TST TB test every 2 weeks until the quarantine is over
What type of reaction does the mantoux tuberculin skin test assess?
A delayed hypersensitivity reaction
What happens if the NHP shows a reaction on the TB test?
NHP should be sedated and the eye assessed by touch, as its more sensitive to look for hardening and induration
NHP should recieve another TB test on the opposite eye and potentially one on a shaved area of the abdomen
The entire room should be considered exposed and the quarantine extended
What are the TST Reaction grades 1-5: Bring Every Monkey Down Now
1: Bruising
2: Erythema
3: Minimum swelling
4: Dropping of the eyelid
5: Necrosis of the eyelid
What grades of TST should be reported?
3 - 5
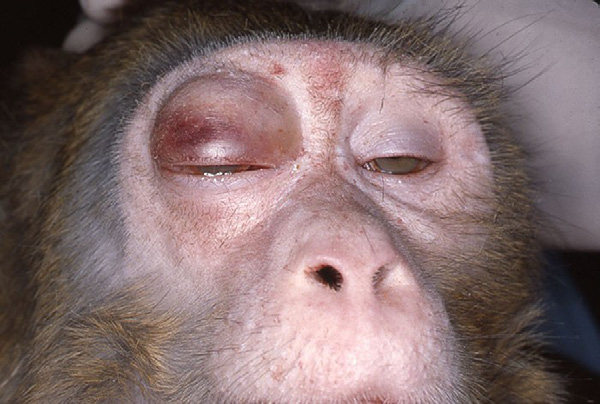
What is being demonstrated here?
positive TB Test
What are the three most common vaccines in NHPs?
Rabies, Measles, and tetanus
Which retroviruses are commonly tested in macaques during quarantine?
SIV, STLV, and SRV
Which herpesvirus is tested for in macaques during quarantine?
Alpha Herpes virus, Macacine herpes virus 1
Which paramyxovirus is tested for in macaques during quarantine?
measles
What diagnostics are used for these viruses, how is sensitivity and specificity considered?
Highly sensitive tests are used first (typically indirect
enzyme immunoassay (EIA) or multiplexed fluorometric
immunoassay (MFIA)) to mitigate false negatives maximally. But Specificity of these tests are usually poor, so more false positives
If there is a positive, a more specific test is used in serial such as western blot, to decide the final ruling on true positive or negative. Additional serodiagnostic tests that often have greater DSp, and thus a lower rate of FP results, include IFA, WIB, hemagglutination inhibition, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
What is required to calculate the positive and negative predictive values in a population?
Diagnostic sensitivity, specificity and the prevalence of the disease in the study population
What happens to the positive and negative predictive value as the prevalence increases?
PPV increases, NPV decreases
What is the most critical aspect of control of TB in research NHP populations?
Availability of TST
What document provides a good framework for managing herpes B in a NHP colony?
2003 NRC publication Occupational Health and Safety in the Care and Use of Nonhuman Primates is an excellent guide for developing an effective program
Most common blood collection site in NHPs? What are others?
Femoral vein most common, other common sites in adult animals are the saphenous and cephalic vein
What is the max blood volume that can be taken in a sample? With is the time interval until it can be done again?
The maximum blood volume that can be safely taken during a
sample collection is 10–15% of total blood volume, not
taken more frequently than once every 2 weeks
Where can CSF be taken? Which one is preferred?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can be collected from the
cisterna magna or the lumbar area (preferred because its the safest).
How is CSF chemistry different when taken from lumbar vs. the cisterna magna?
lumbar fluid to have higher concentrations of total protein,
albumin, and IgG and lower concentrations of glucose
and potassium
What are the anatomical landmarks for cisterna magna CSF collection?
CSF in the nonhuman primate
should be collected at the junction of a line that bisects
the cranial wings of the atlas and a line extending caudal
from the external occipital protuberance
What is the preferred site for bone marrow aspiration? What are the other possible sites?
Preferred: Iliac crest.
others: Trochanter of femur, tibial tuberosity, greater tubercle of the proximal humerus, sternum, rib, and ischial tuberosity
What is the dose per kg of SUBQ fluids per site allowed in NHPs?
5 ml / kg in each site
What size kgs for NHPs can a net be used to capture?
Up to 3.5 kgs
How long should the NHPs be trained for on vests?
The animals can be conditioned/trained to accept the tether and
vest in as little as 1 week
What is a risk of using CO2 powered chemical restraint guns?
Due to small distances in most research settings, there is high risk of bone fracture and internal organ damage when using CO2 powered guns
What maximal range is recommended for use of blow pipe chemical restrain devices
Up to 15 meters maximum
What organizations provided guidance for dental care on canine teeth in NHPs?
The Animal Welfare Act, Animal Care Policy
#3, states that non-medical canine tooth removal, or
reduction that exposes the pulp cavity, is not considered
appropriate veterinary care. The policy also states that in
some behavioral or breeding situations it may be acceptable
to reduce canine teeth as long as the pulp cavity is
not exposed.
the Animal Welfare Act, Animal Care Policy
#3, states that non-medical canine tooth removal, or
reduction that exposes the pulp cavity, is not considered
appropriate veterinary care. The policy also states that in
some behavioral or breeding situations it may be accept
able to reduce canine teeth as long as the pulp cavity is
not exposed
What position is best for capturing thoracic radiographs of NHPs?
nonhuman primate thoracic radiographs
should be made with the animal in an upright posture,
with images acquired during full inspiration
What are some general benefits of endoscopy in NHPs?
Benefits of endoscopy include the following: possible avoidance of surgery if a condition can be diagnosed and/or corrected endoscopically (e.g., removal of a gastrointestinal foreign body), a less invasive surgical procedure (e.g., laparoscopy), easier
biopsy acquisition with more precise lesion targeting,
and enhanced visualization of disease processes.
what is the preferred diagnostic modality for soft tissue, CSF and fat?
MRI
Why is MRI preferred over CT from a safety perspective? When is it contraindicated?
One advantage of MRI compared to CT is that MRI does not use ionizing radiation, and thus does not increase the risk for radiation-induced cancers. One advantage of MRI compared to CT is that MRI does not use ionizing radiation, and thus does not increase the risk for radiation-induced cancers.
What type of tissue is CT the preferred modality for?
CT is the preferred imaging technique for bone, thoracic structures, and certain masses/neoplasia
What are some conditions acupuncture can be used for?
Acupuncture is used as a treatment for various conditions
such as chronic pain, osteoarthritis, stress, nausea/
vomiting, hypertension, and stroke.
What is the principle approach for why acupuncture works?
The majority of defined acupuncture points correspond to neurovascular bundle locations, and stimulation
of these points generates a peripheral afferent signal
that can initiate endogenous opioid release