Unit 4 Organelles + Cell Transport
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What do the cilia and flagella do?
they are little hairs around the cell whicdh give it mobility both towards nutrients or away from toxins.
What does the chloroplast do?
In plants it contains chlorophyll which turns light into chemical energy which does photosynthesis.
What does the cell membrane do?
Semipermeable layer that allows some stuff in: maintains homeostasis.
What does the ribosomes do
makes proteins in all cells (mdae by nucleolis)
What does the endoplasmic reticulum do (smooth)
smooth: stores and detoxifies Ca++
What does the rough ER do
protein fctory with the ribosomes as workers: then sends them to the golgi
What does mitochondria do
Breaks poly to monomer to make ATP, all parts depend (organic materials to usable materials)
What does the golgi apparatus do
From the ER, it processes and sorts proteins for teransport (fedex)
What does the cytoskeleton do
A web around and in the cell supporting structure and cell organization
What do vacuoles and vesicles do
sacs of stuff that are transported in animals: plants are REALLY big, stores water and nutrients and keeps the outside crisp.
What is the nucleus
Has cell DNA: instructions for making proteins.
Whhat is the cell wall
Structural support to plant and fungi cells
What are lysosomes
Packets of enzymes that break down old stuff and waste.
What is the structure of the cell membrane
Phospholipid bilayer
What is simple diffusion and what molecules does it work on (specific + broad)? Passive/active?
Works with small, nonpolar molecules. Goes from high to low pressure naturally with no helping protein, making it passive. Co2 + O2
What is facilitated diffusion and what molecules does it work on (specific + broad)? Passive/active?
H to L diffusion with large molecules like glucose and water. Needs a carrier protein to open the protein channel (gated channel).
What is active transport and what molecules does it work on (specific + broad)? Passive/active?
Movement from L to H (against the gradient). Uses a “pump” and ATP to actively transport stuff. An example is pumping Sodium out of the cell (Na+) and K+ (potassium) into the cell.
What’s examples of active transport and the types of molecules that htey act on
Endocytosis: foloding cell membrane around molecules that need to be taken in
Phagocytosis: large solid, Pinocytosis = liquid.
ExocytosisP removal of materials from cell by merging vesicles with the cell membrane.
What is osmosis?
Passing water from High to Low through aquaporin proteins. Simple diffusion
What are the different “tonics” of concentration of a solute external to the cell?
Isotonic = same solute concentration as the cell
Hypertonic: higher solute concentration than the cell
Hypotonic: lower solute concentration than the cell.
What is osmotic pressure
pressure exerted by water (hypotonic) onto a hypertonic solution
Why are cells small?
To maximize their surface area to volume ratio so that they can diffuse better.
If they have high volume, then there is a large area to diffuse with a low entry access to diffuse it.
What are the consequences to the cell of putting it into a hypertonic solution?
The cell wall/membrane will shrink due to the exodus of water from the cell so it can travel from high to low pressure, which shrinks and shrivels the cell.
Thsi is CRENATED cells in animals and PLASMOLYSED cells in plants.
when an animal dies it shrivels and you cremate it: revitalize it with plasma
What are the consequences to the cell of putting it into a hypotonic solution?
Osmotic pressure of water against the cell = membrane explodes/collapses, which makes the cell lysed in animals and turgid in plants.
LAPT
What is osmolarity?
#of solute particles per liter
What is the path of nitrogenous waste?
ammonia - liver - urea - kidneys - urine.
What does the liver do in the excreory system?
converts excess protein to urea
What does the kidney do in the excretory system?
it removes urea, excess water, and salt while filtering blood and helpful things out.
what are the three kidney processes?
filtration: large blood cells get filtered out and small waste (water/urea/salt/amino) go through (strainer0
reabsorption: water moves out by osmosis and the filtrate (the stuff that went thru the strainer) has its good stuff (glucose) reabsorbed thru passive and active transport
secretion: through the loop of the nephron thru active transport and out urine tube.
What’s the purpose of the salt gradient of the kidney
Pull and reclaim water
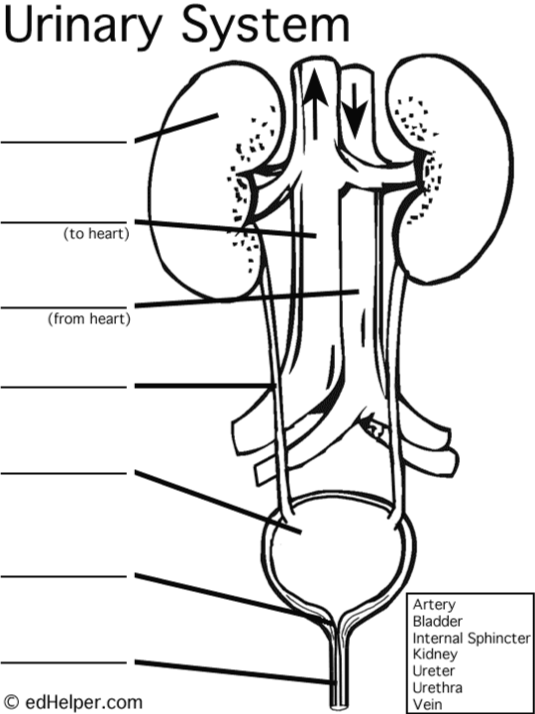
Label this diagram
always review, visualize learning (artery right, vein left)
victory through academic commitment (veins to heart, arteries come from heart)
how does reabsorption work
when filtrate (waste that goes thru strainer) goes down the loop and good stuff (ions, glucose) is absorbed out thru passive and active transport.
how does secretion work
substances moving from active transport into the looip of the nephron to be discarded
how is water filtered out from filtrate
there’s a salt gradient that goes from low pressure to high pressure when you go down the loop: forcing water to move by osmosis out
when you go back up the loop: its hypotonic: to prevent flow of water into urine, we pump salt out (active transport)
then it goes back down, concentration increases, water si filtered out, and waste products like urea end up in urine and are transported to ureter.