Bones and Bone Markings
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
skull (cranium)
composed of two sets of bones: the cranial bones and facial bones
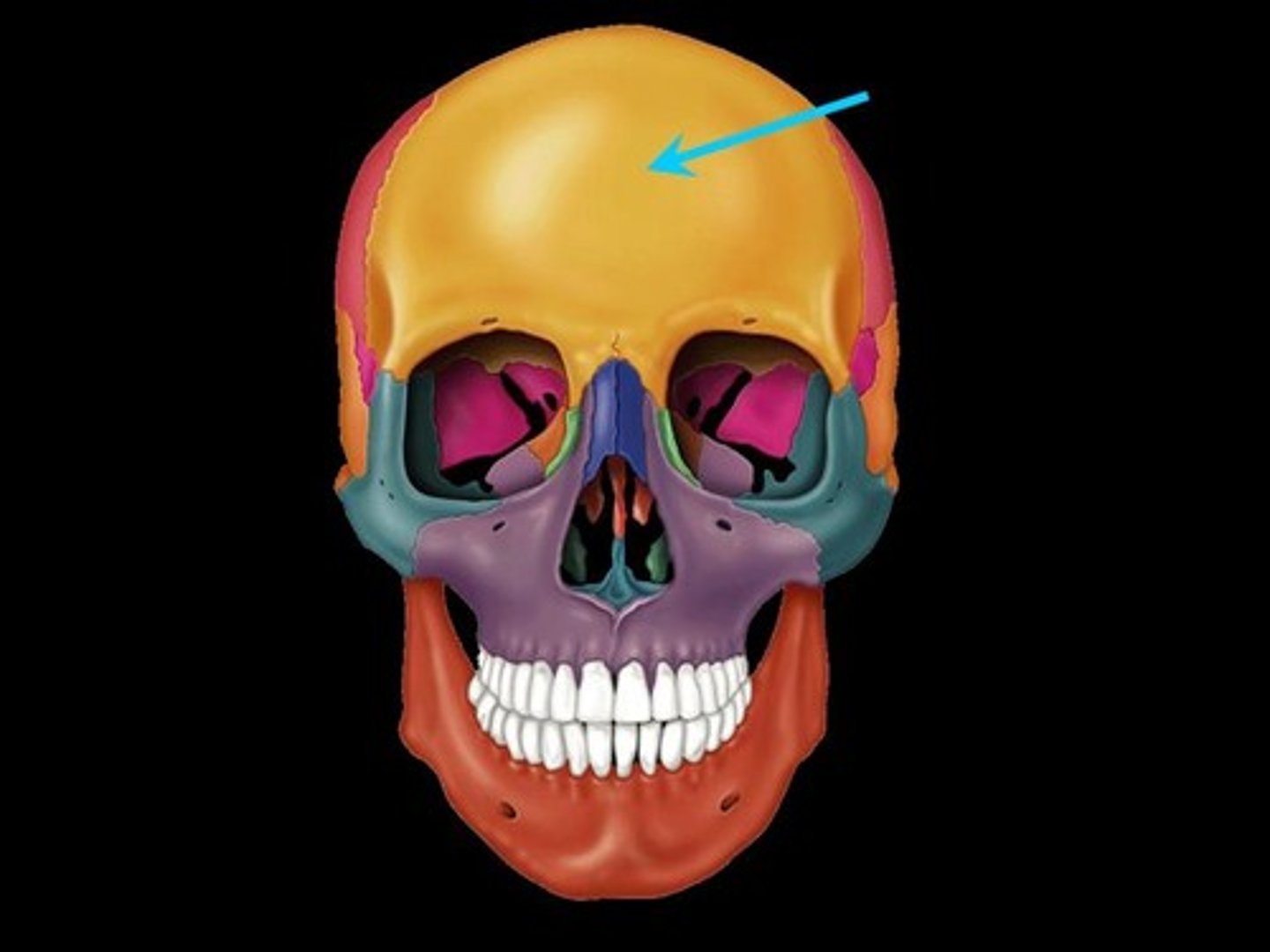
frontal bone
bone that forms the forehead
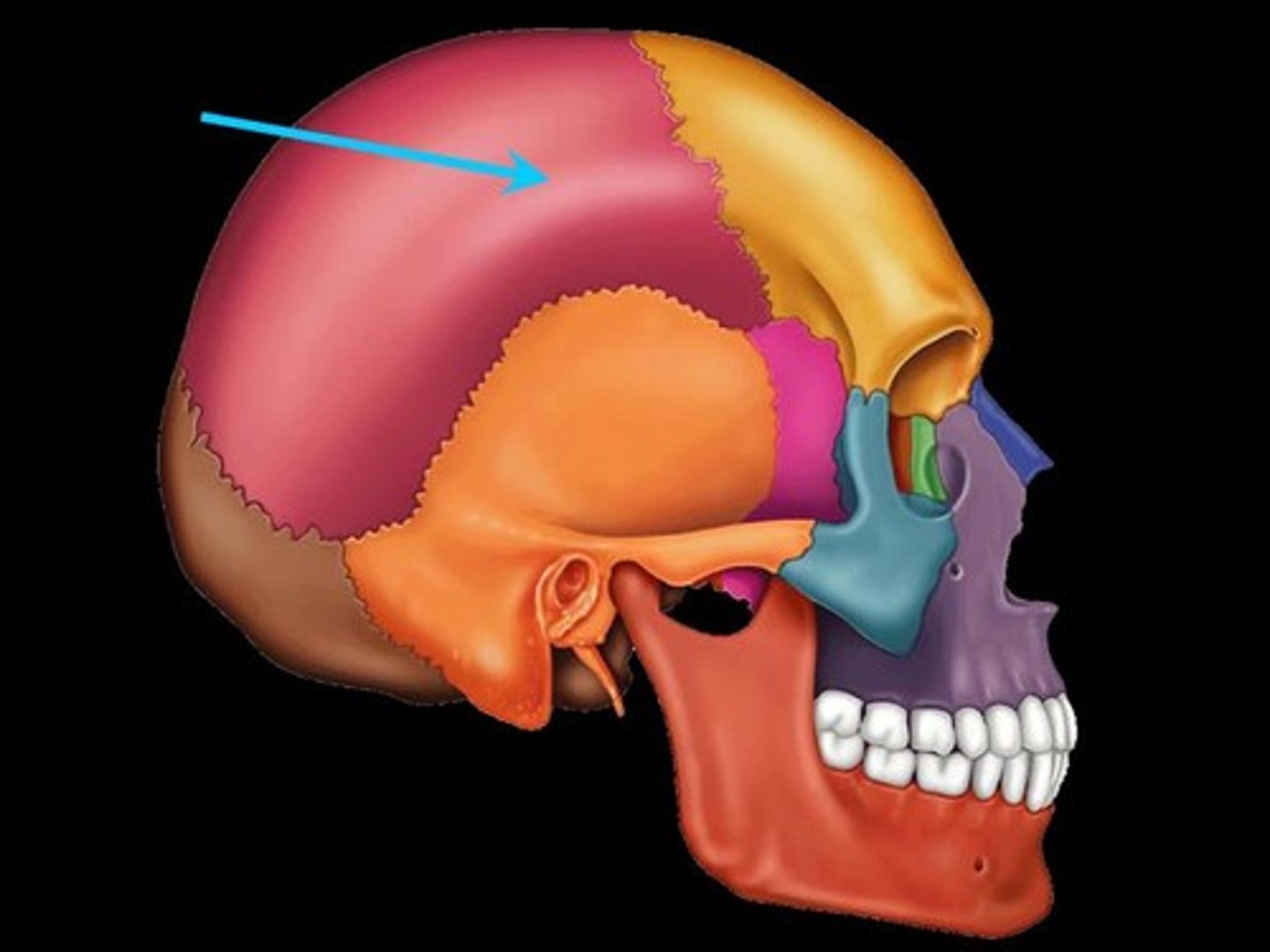
parietal bone
either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones and forming the top and sides of the cranium
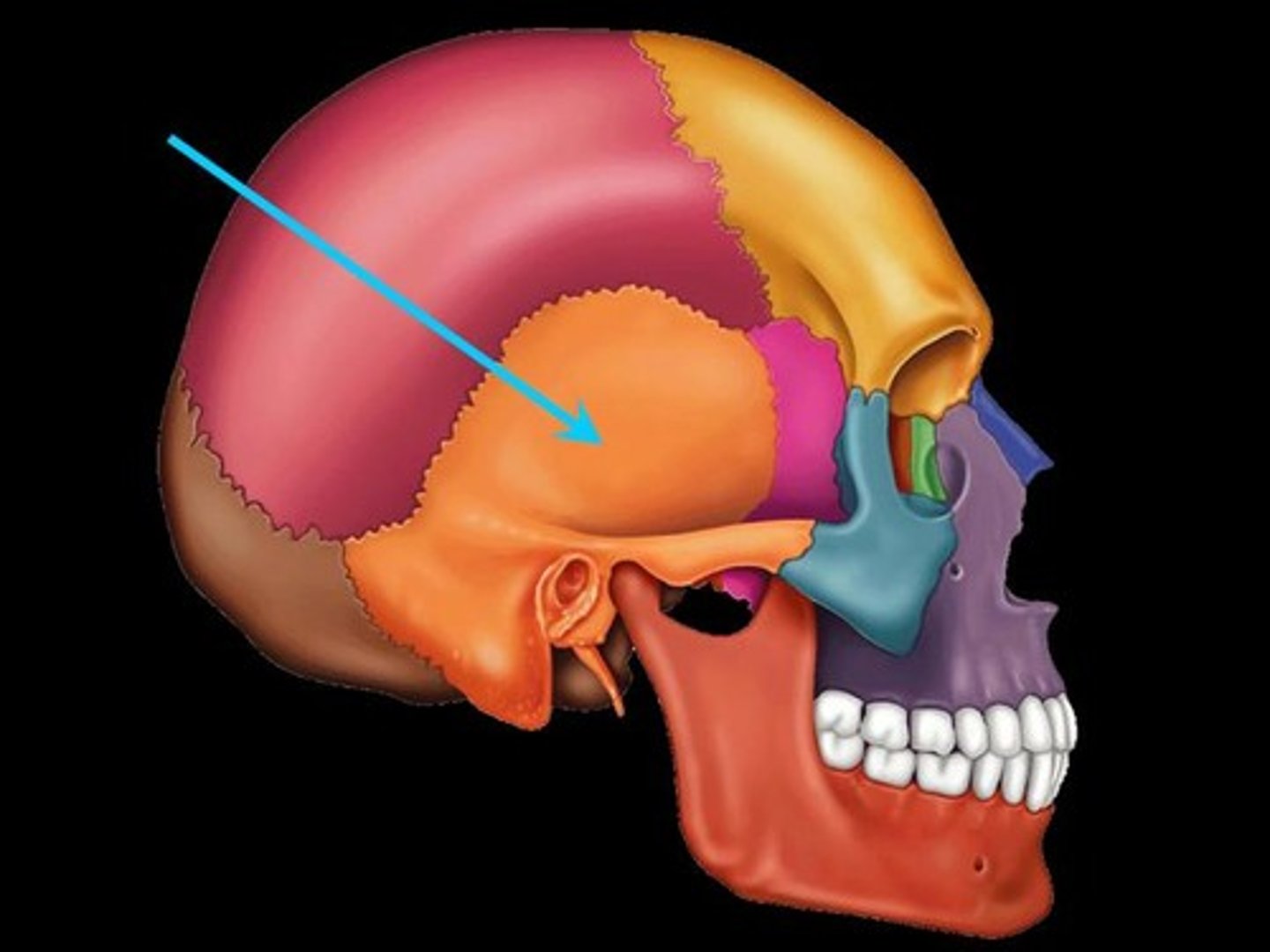
temporal bone
bone that forms parts of the side of the skull and floor of the cranial activity. There is a right and left temporal bone.
styolid process
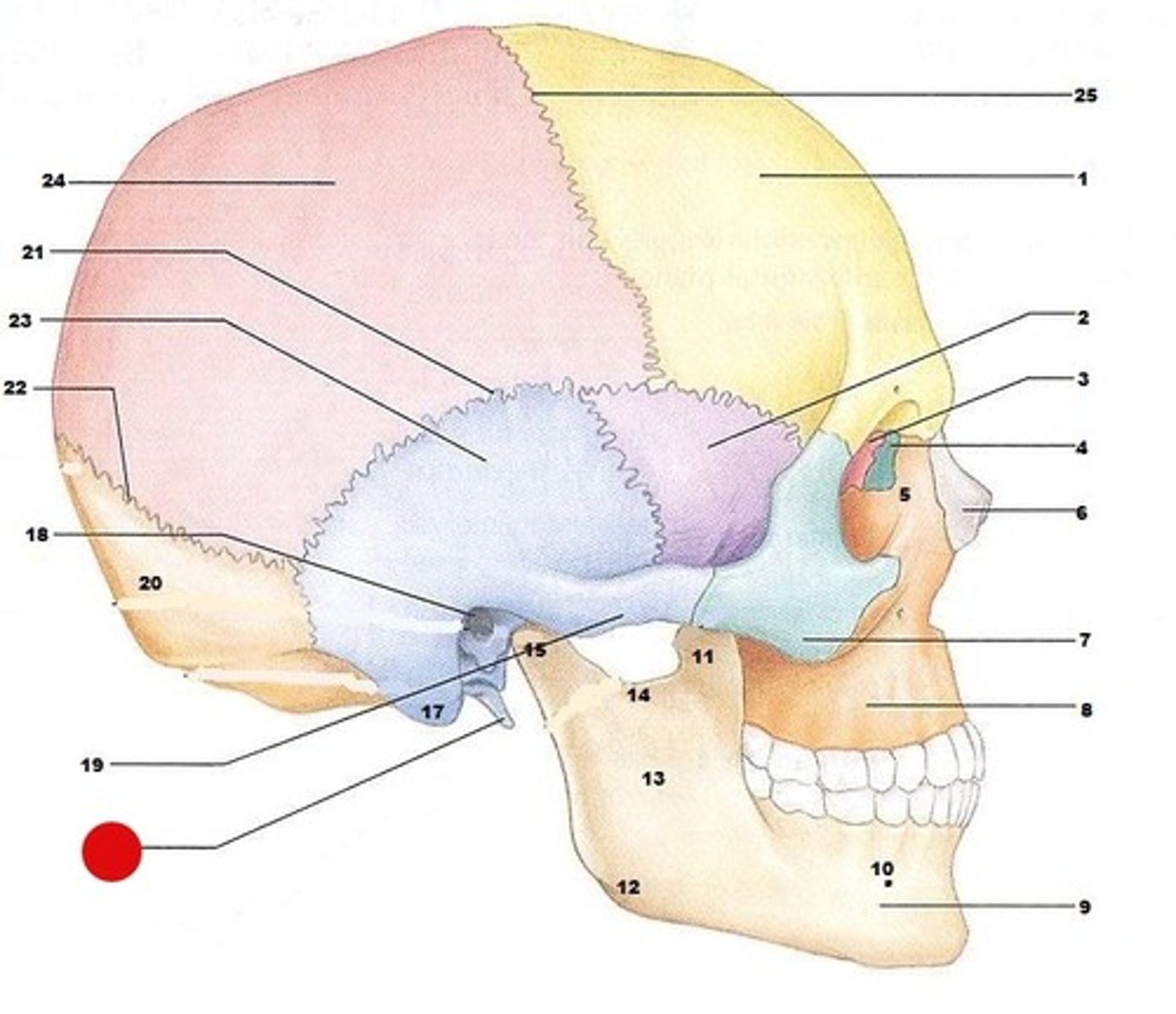
external auditory meatus
makes up the ear canal
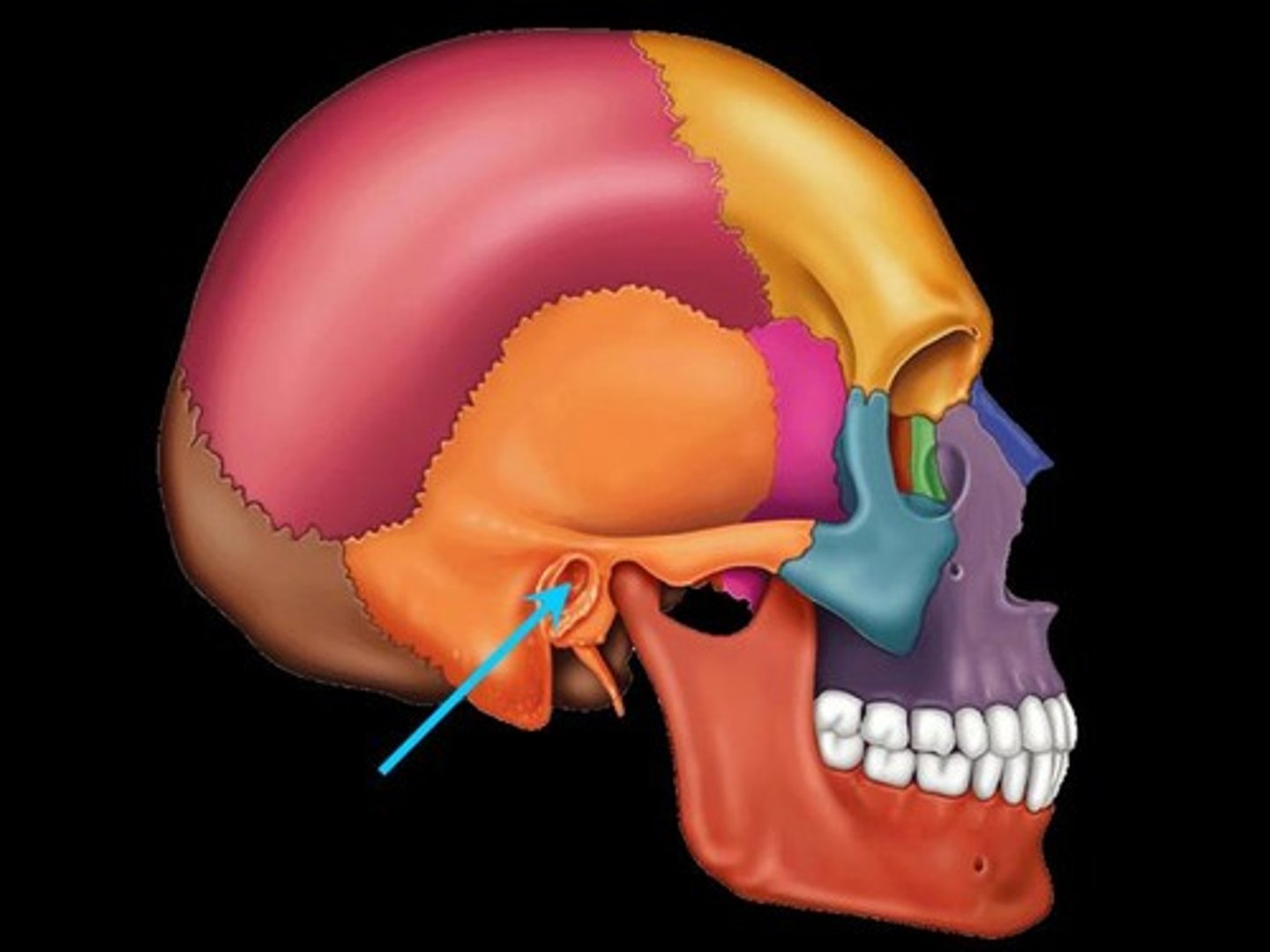
occipital bone
back of head
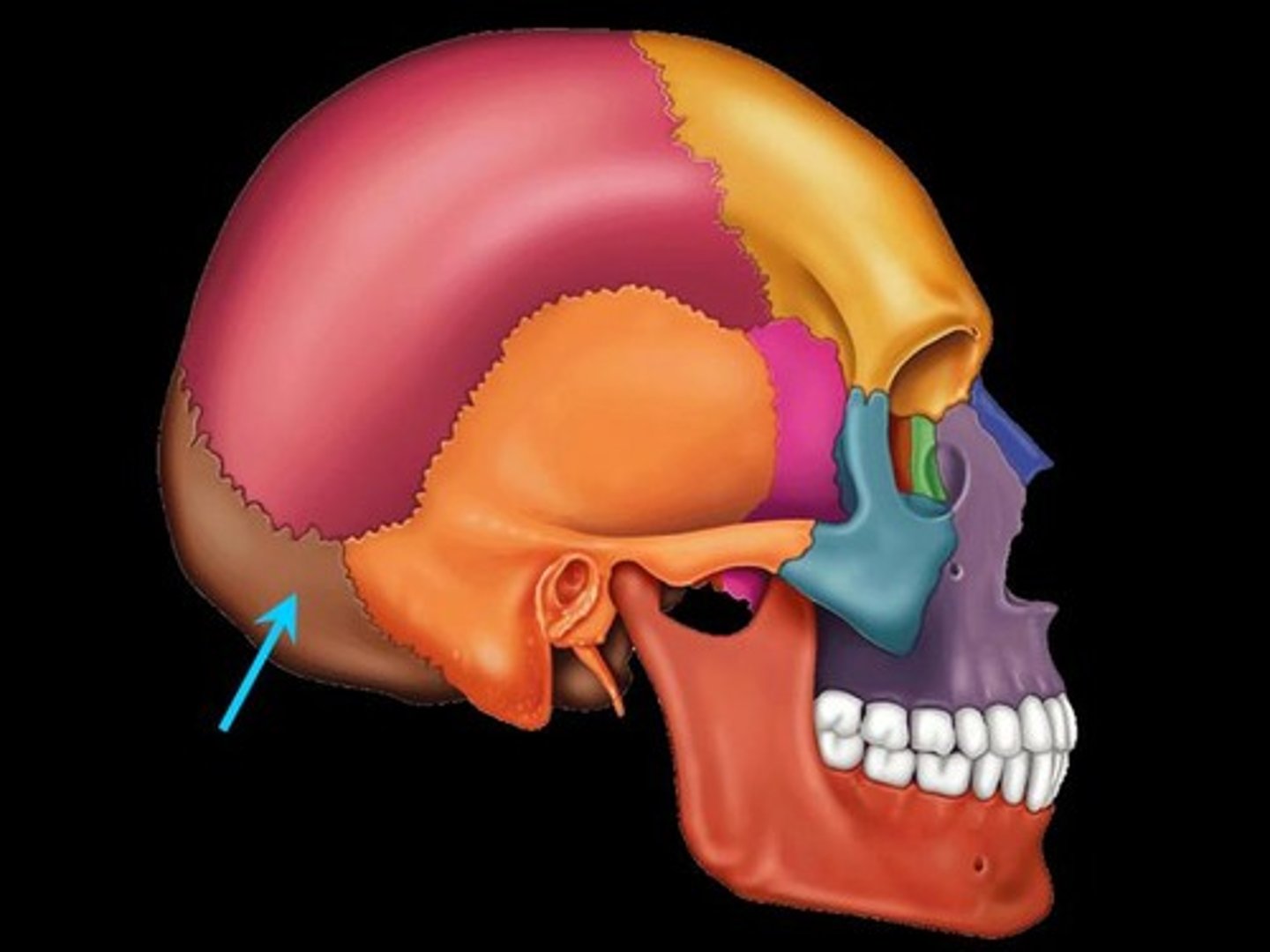
foramen magnum
A large opening at the base of the skull through which the brain connects to the spinal cord.
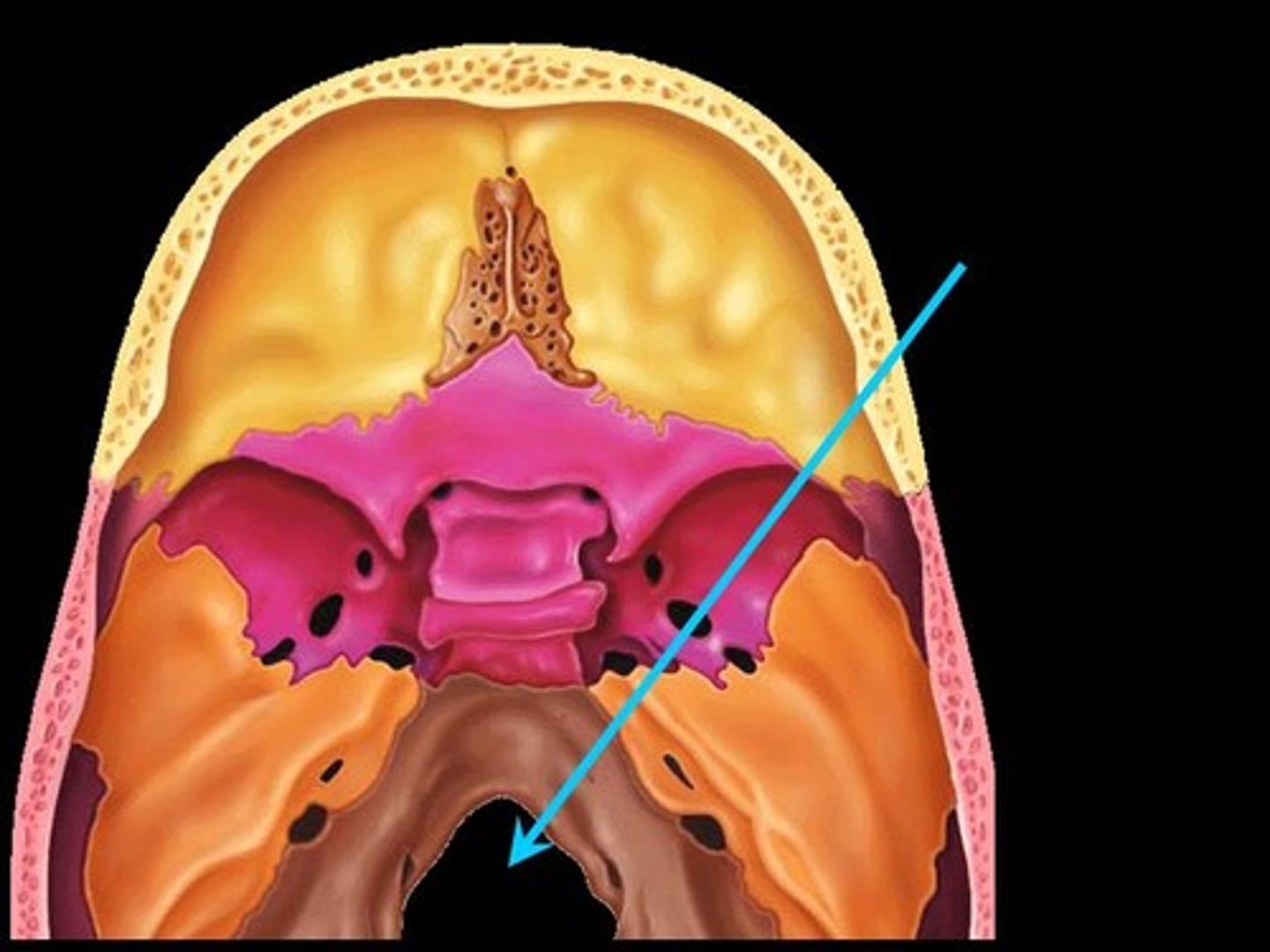
occipital condoyle
each of two rounded knobs on the occipital bone that form a joint with the first cervical vertebra.
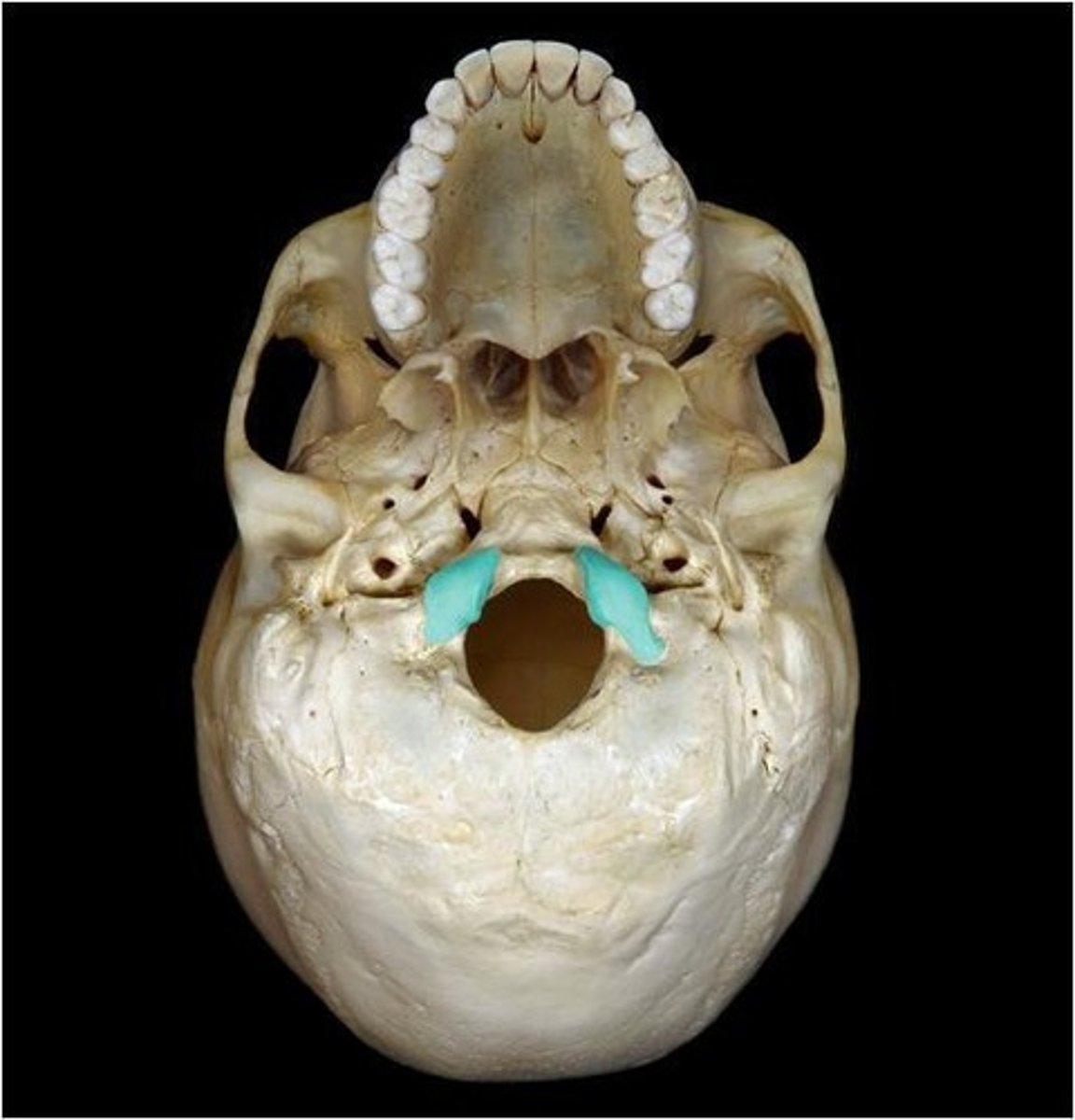
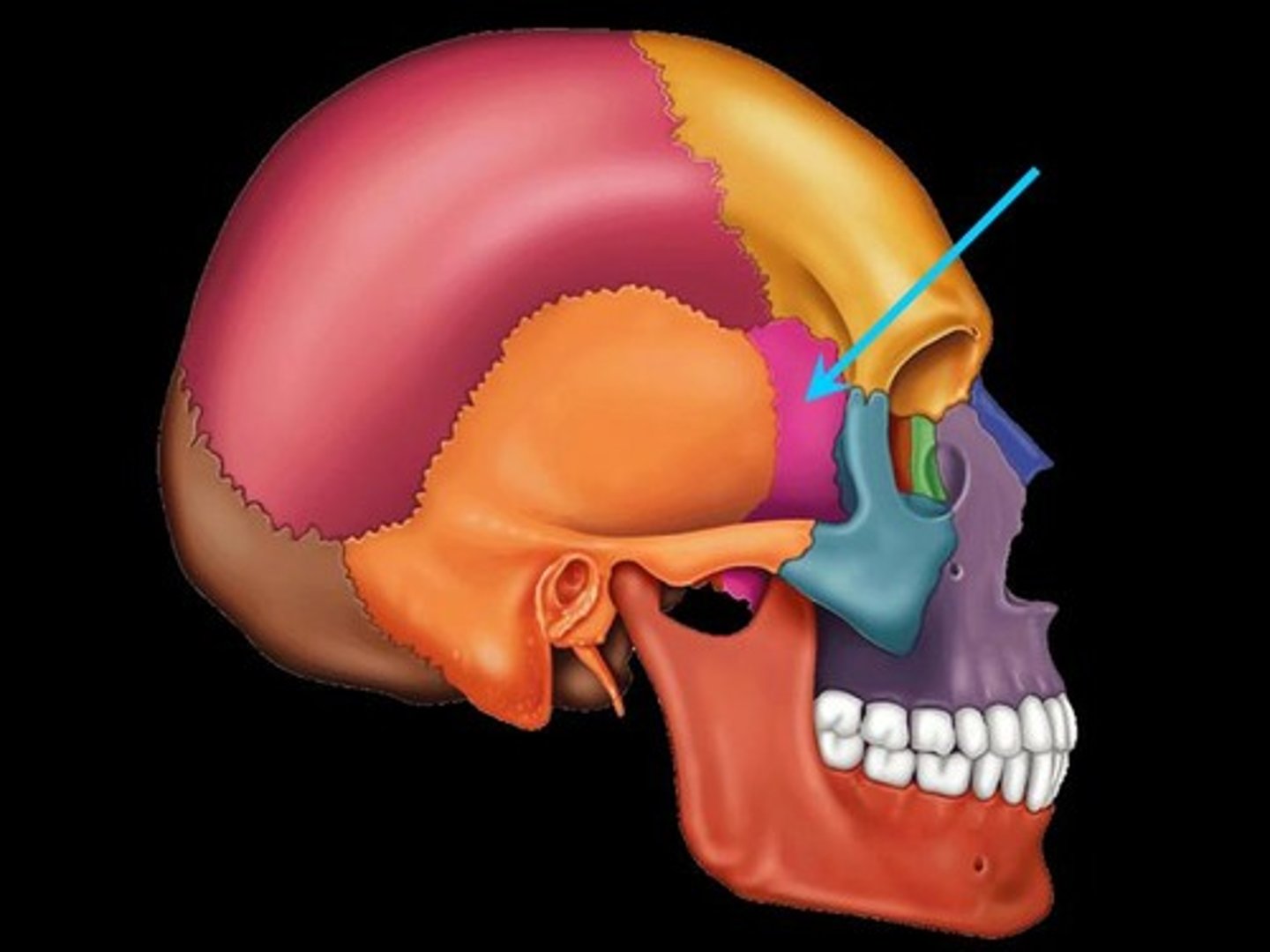
sphenoid bone
forms part of the base of the skull and parts of the floor and sides of the orbit
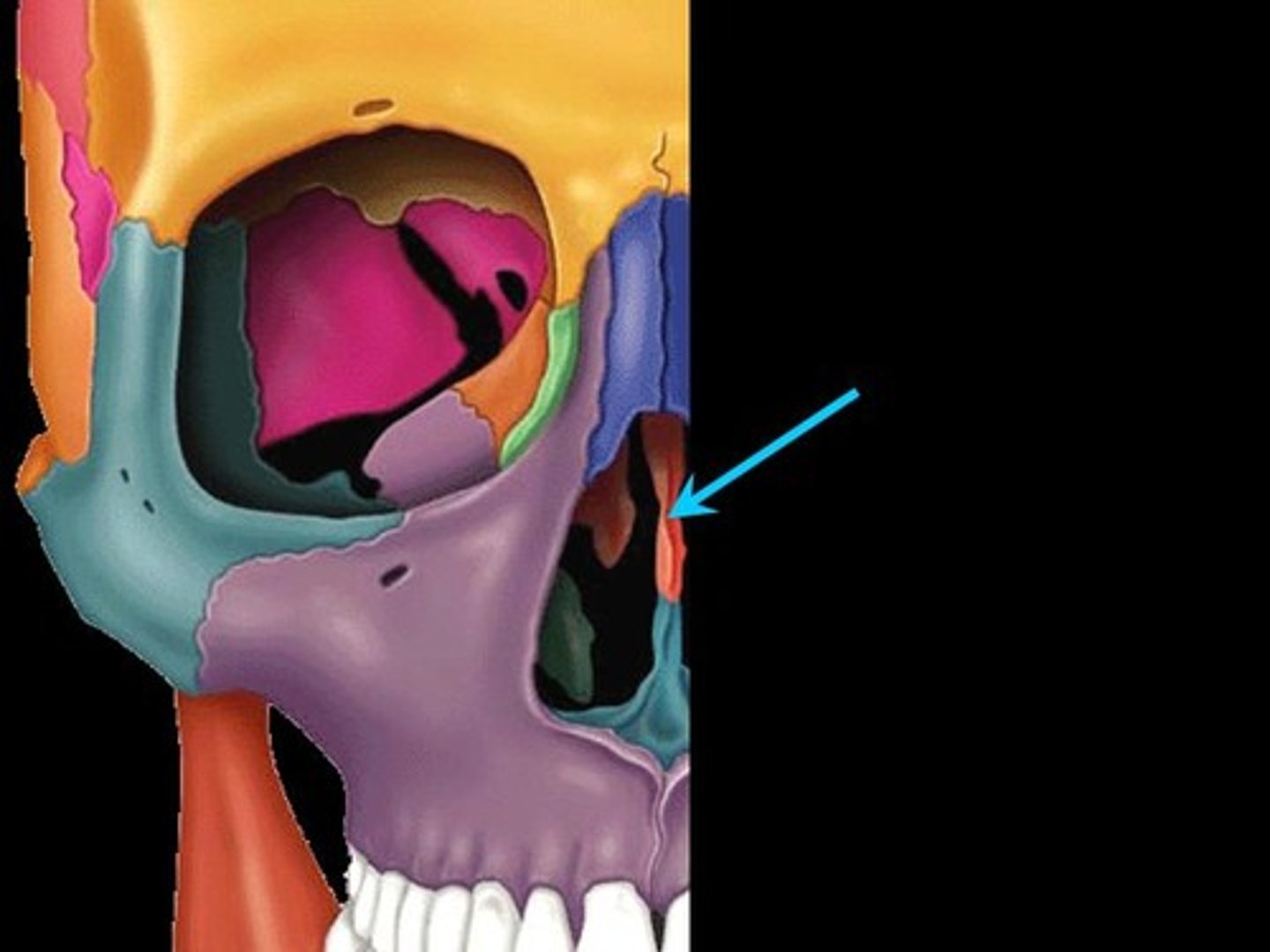
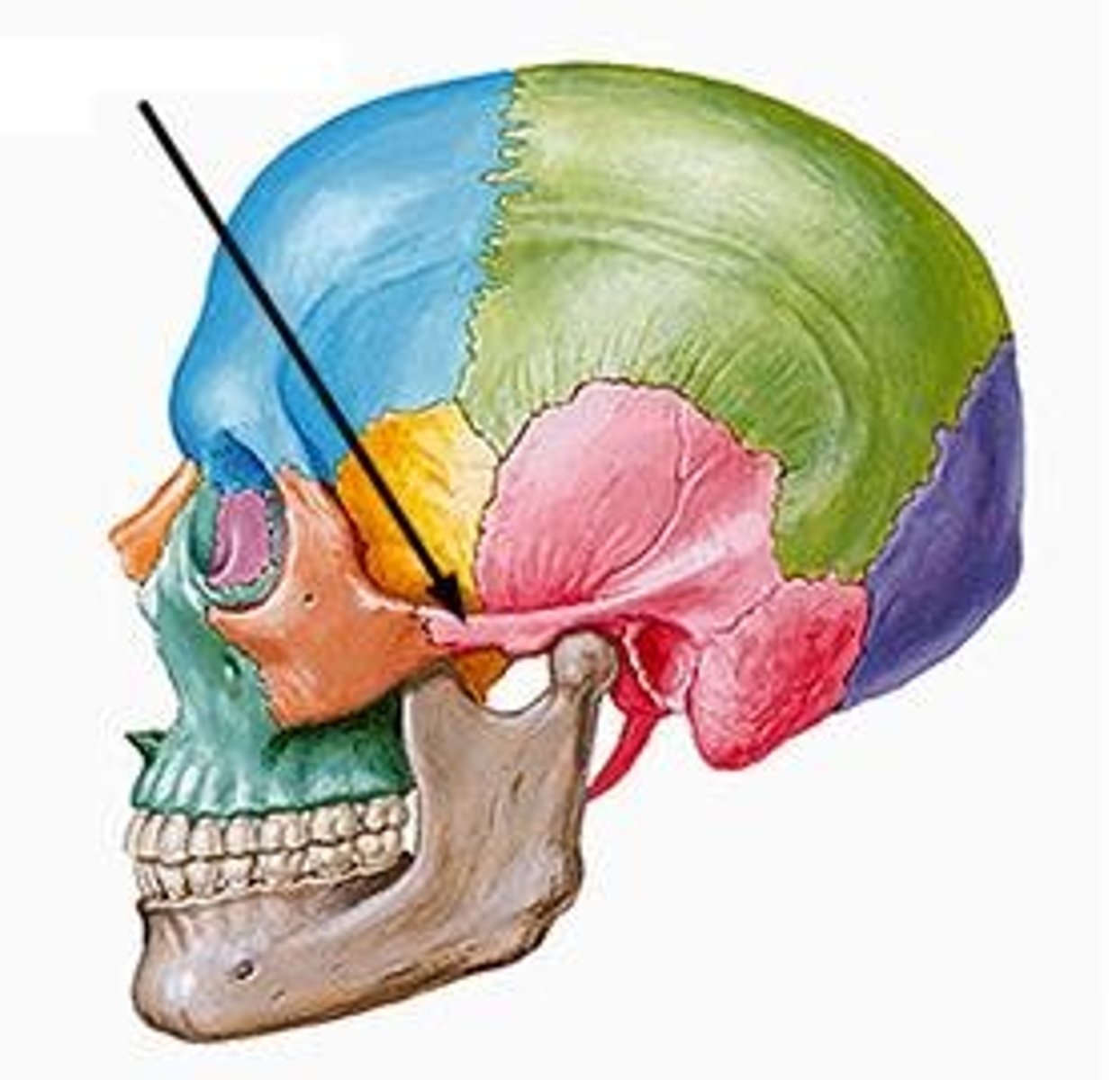
ethmoid bone
forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium
zygomatic process
lacrimal bone
small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal (tear) ducts
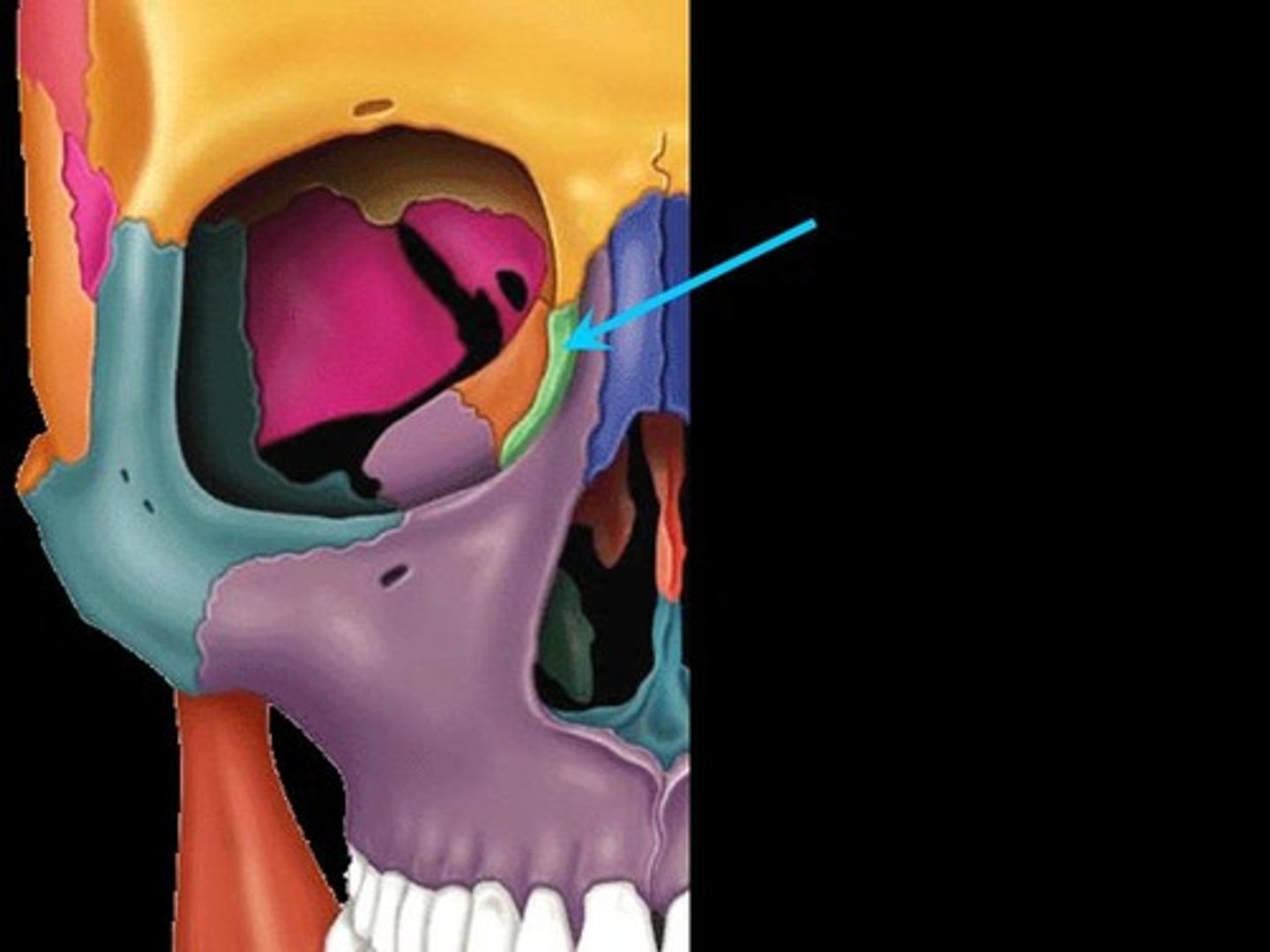
maxilla
upper jaw bone
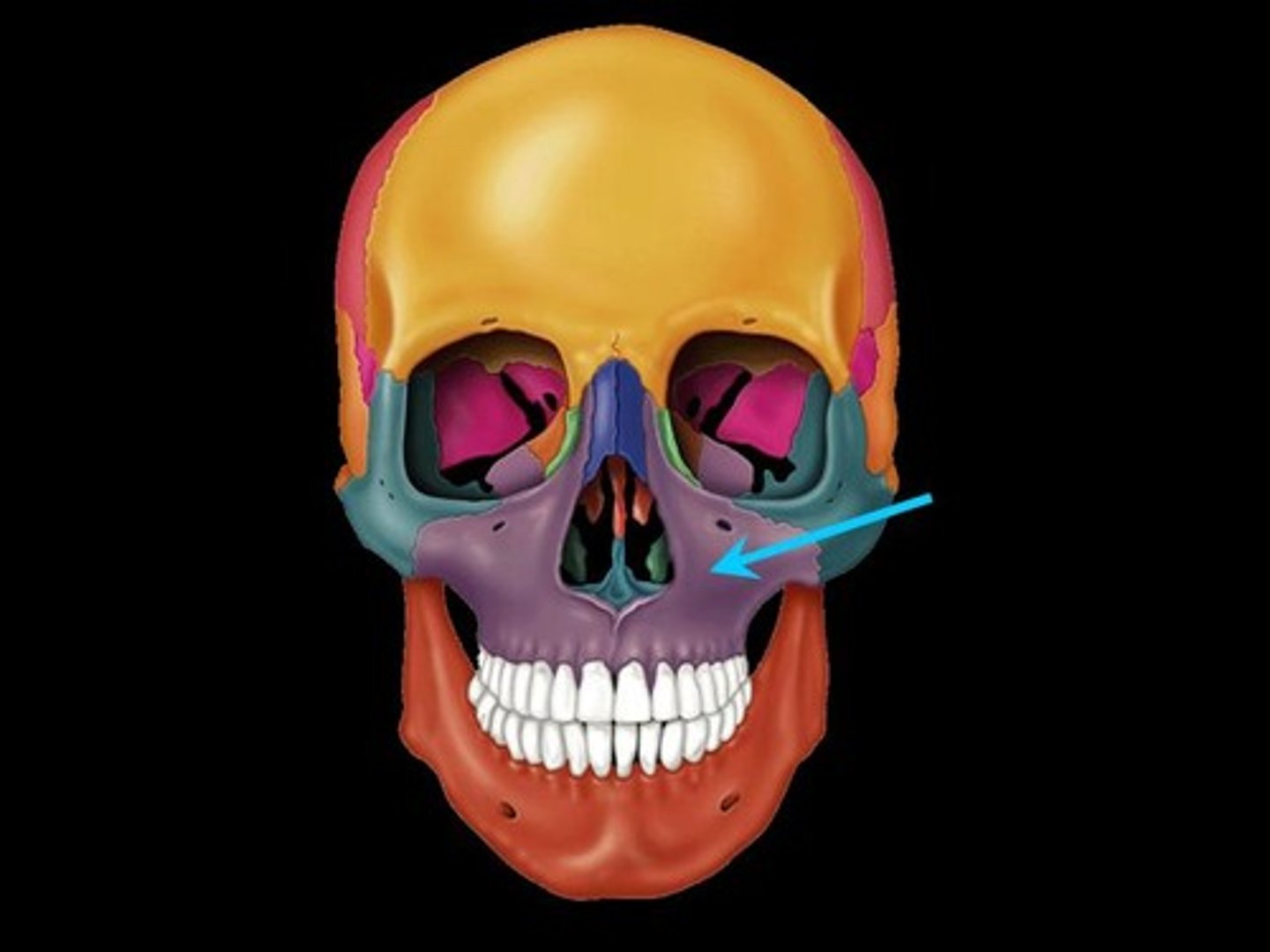
mandible
lower jaw bone
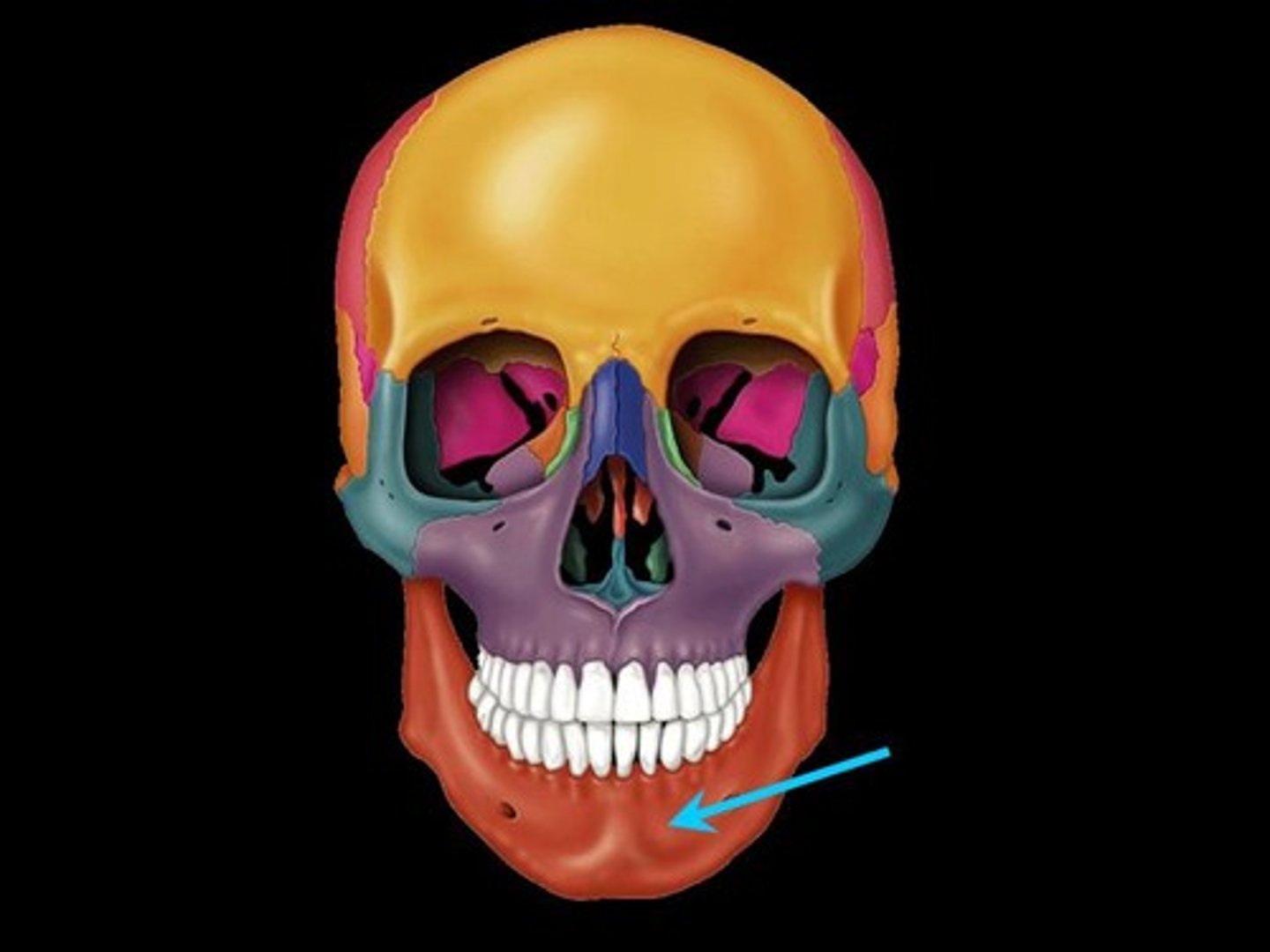
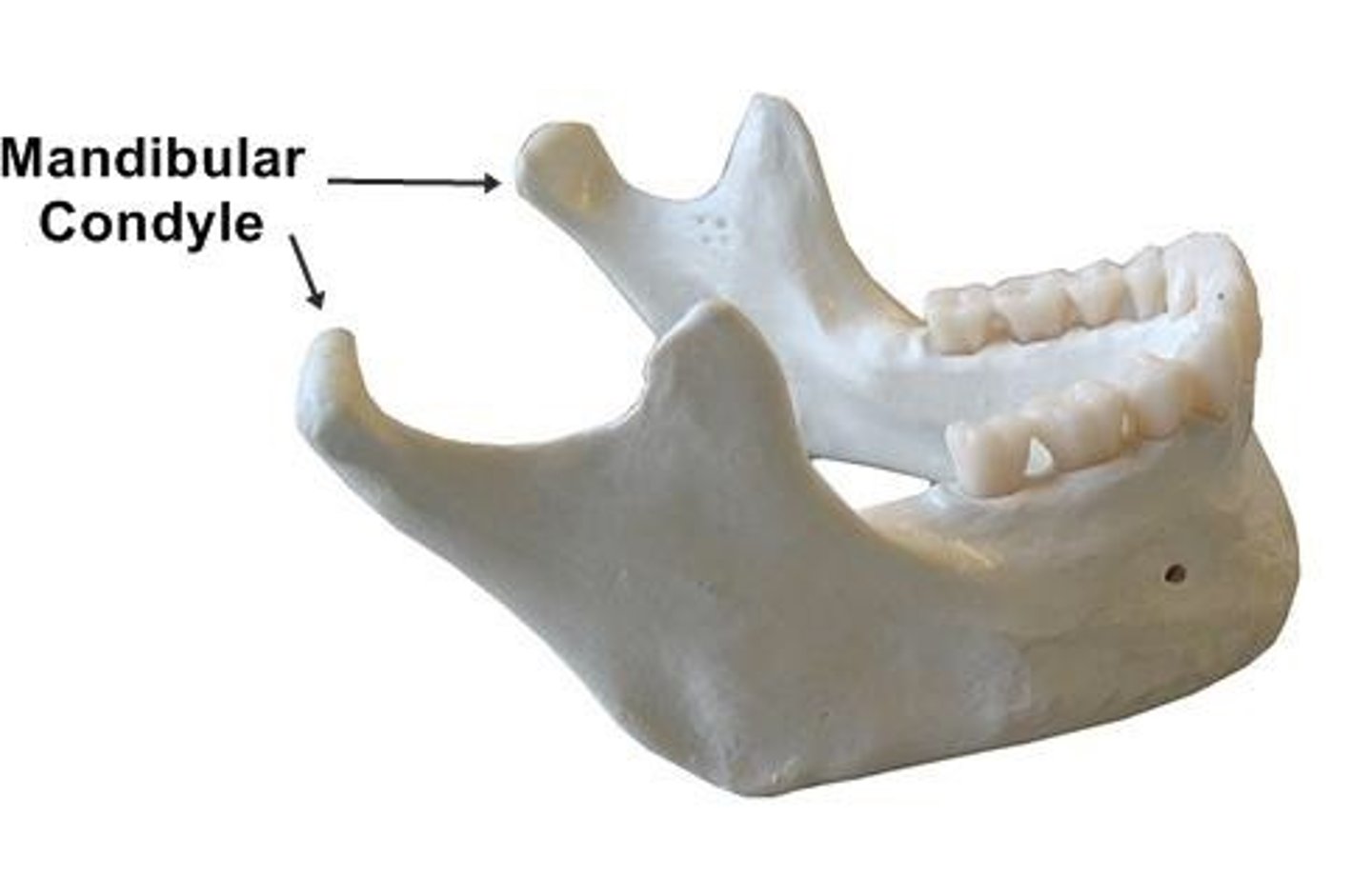
mandibular condoyle
mandibular ramus
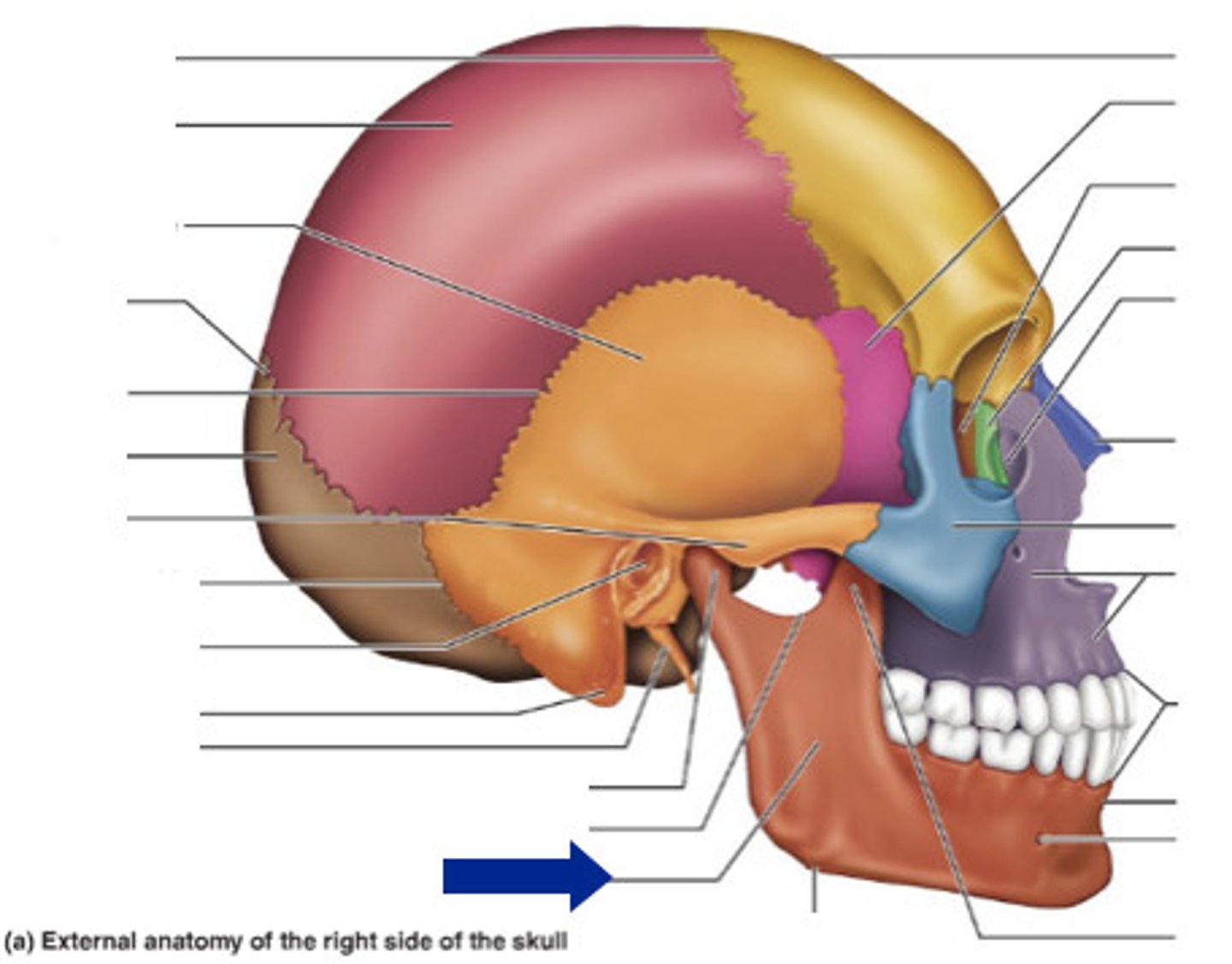
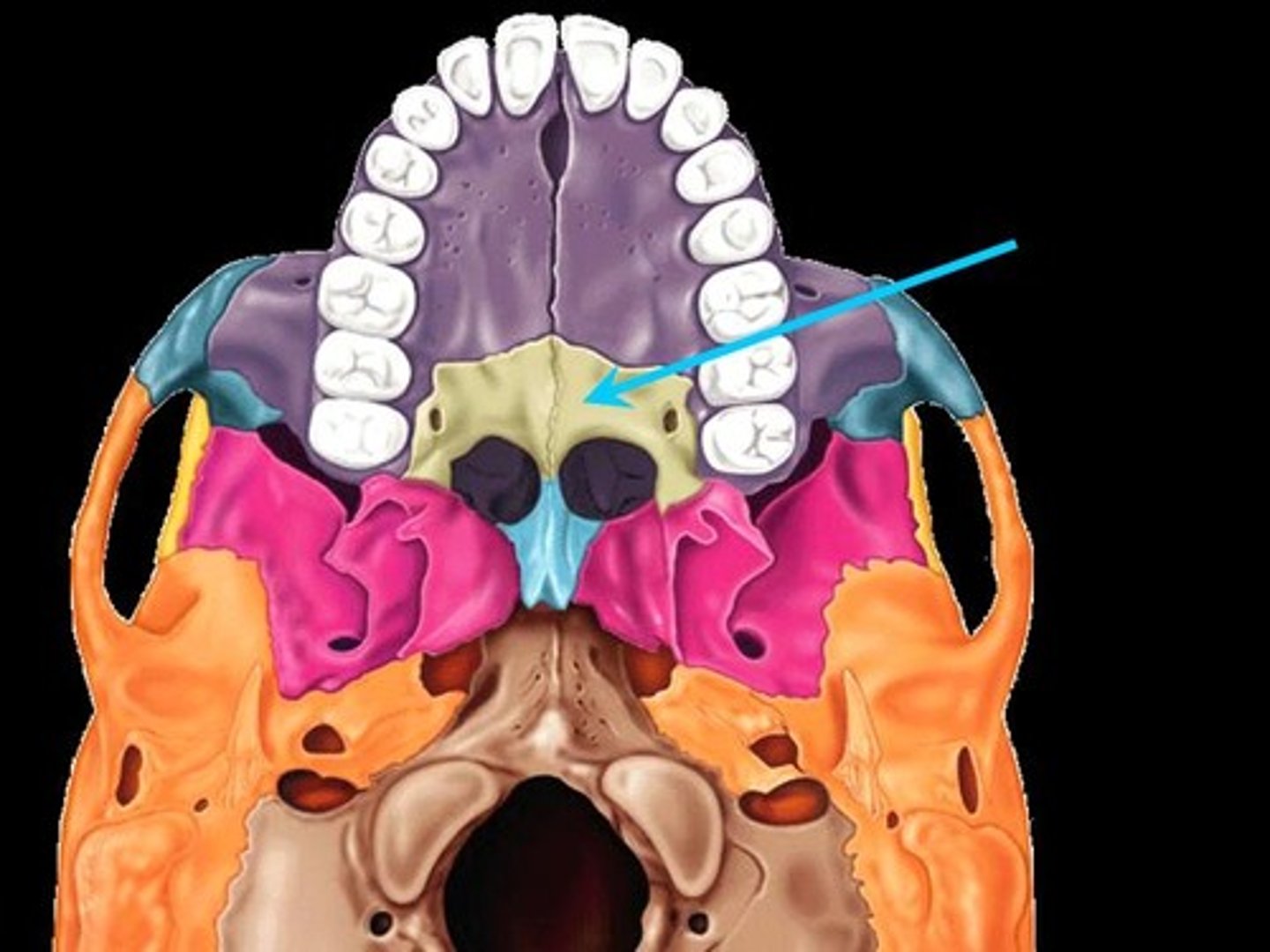
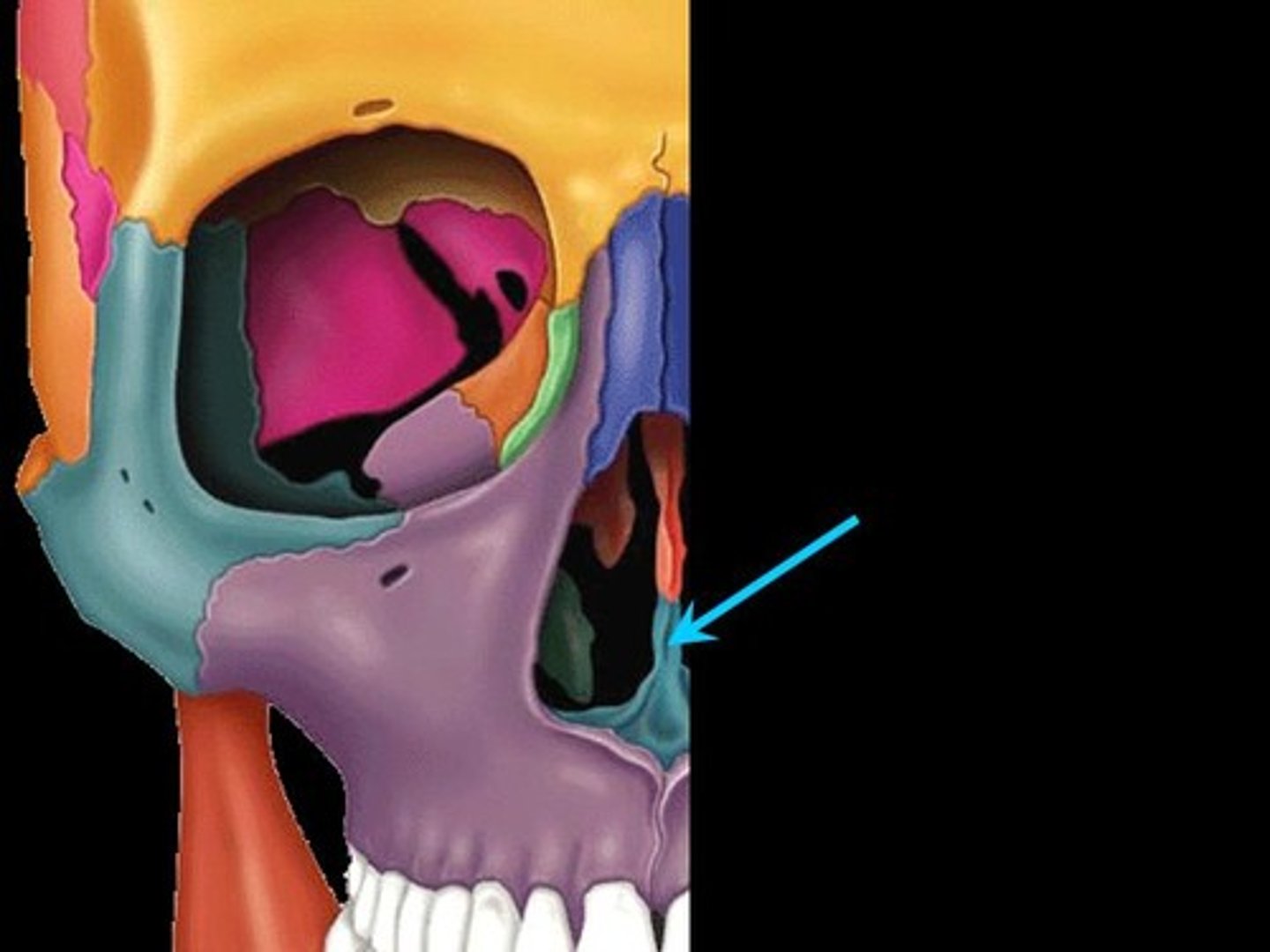
palatine
bone that forms the hard palate and parts of the nose and orbits
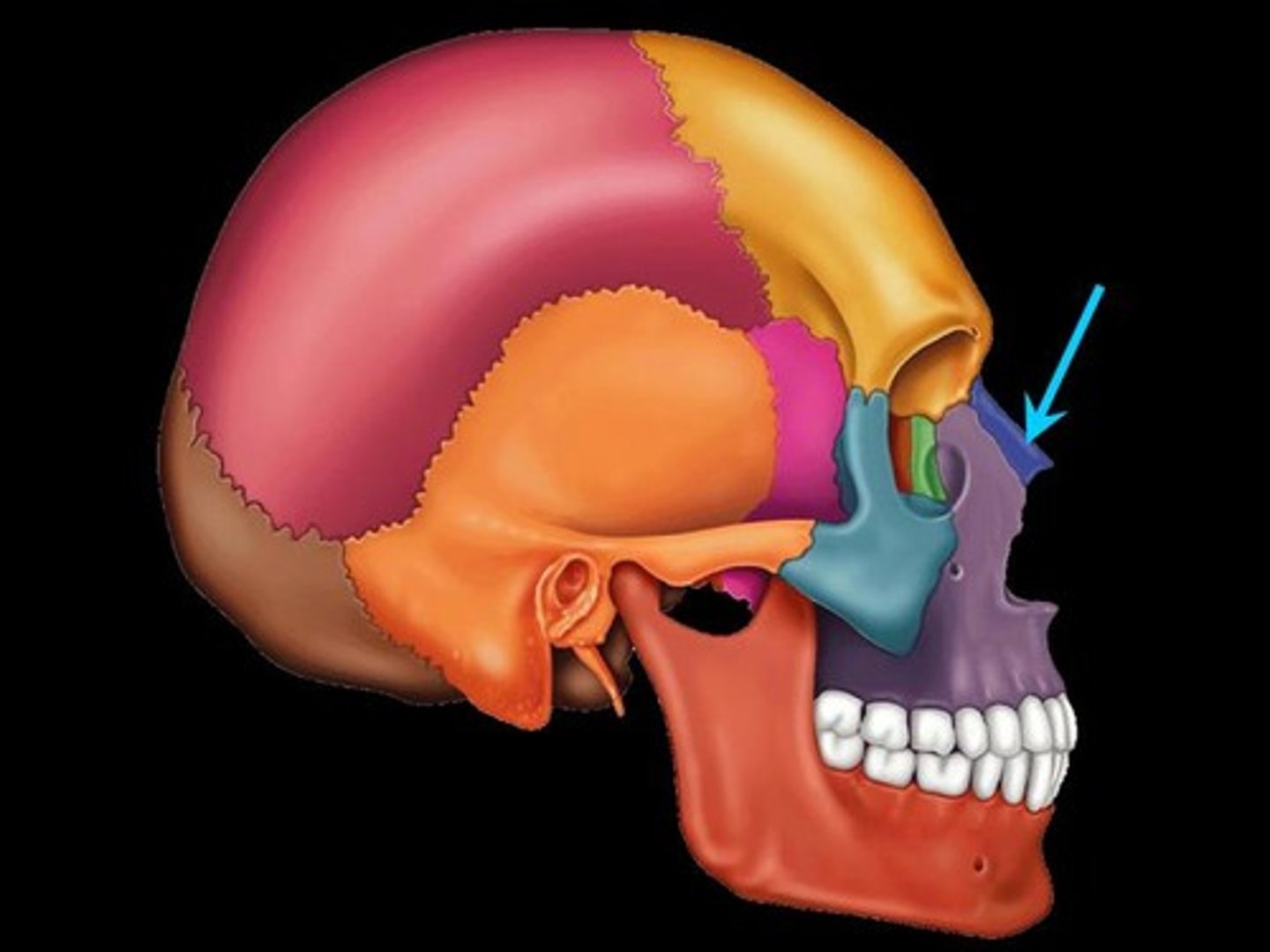
nasal bones
Bones that form the bridge of the nose.
vomer
forms the inferior portion of the nasal septum
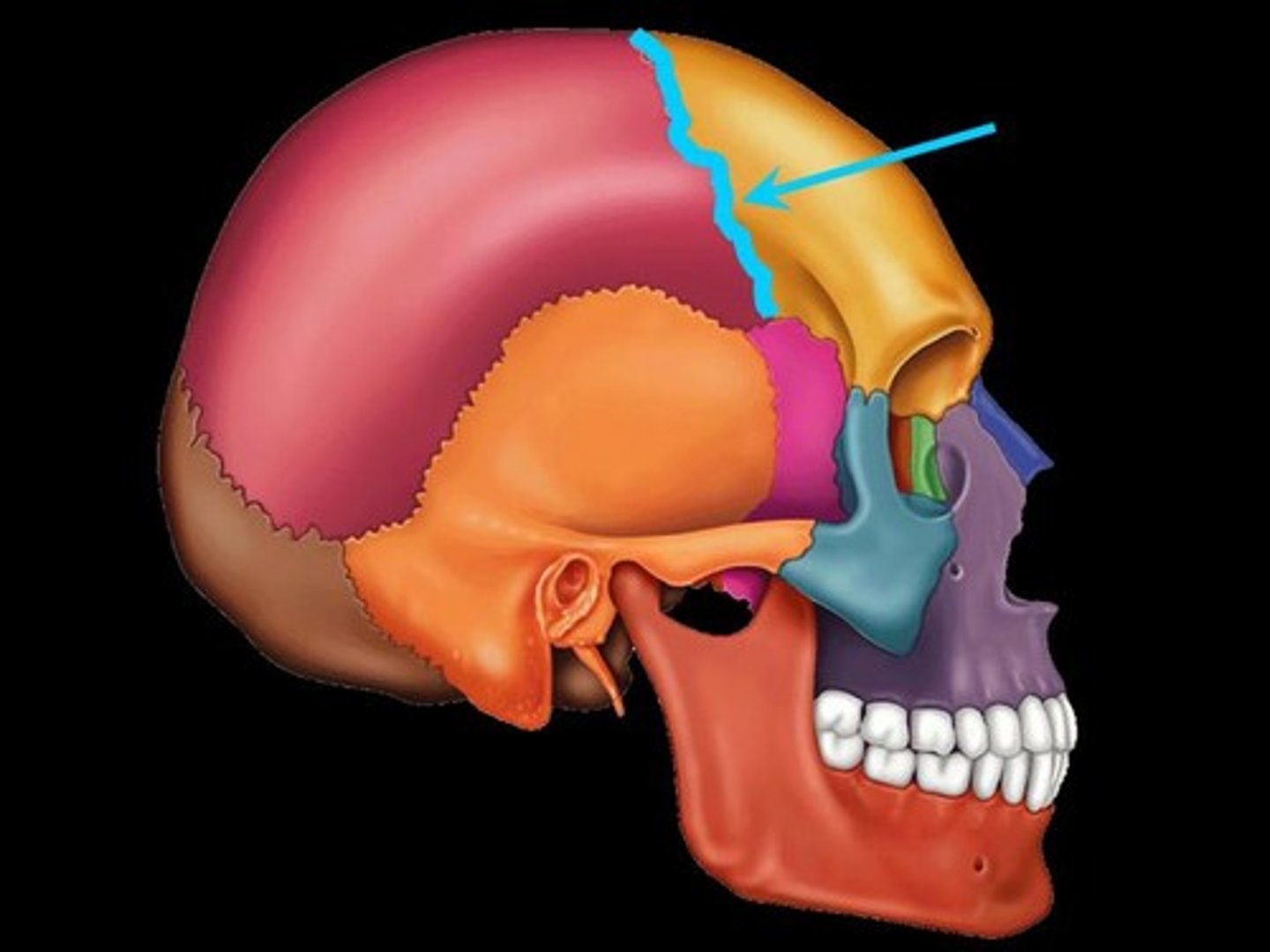
coronal suture
the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
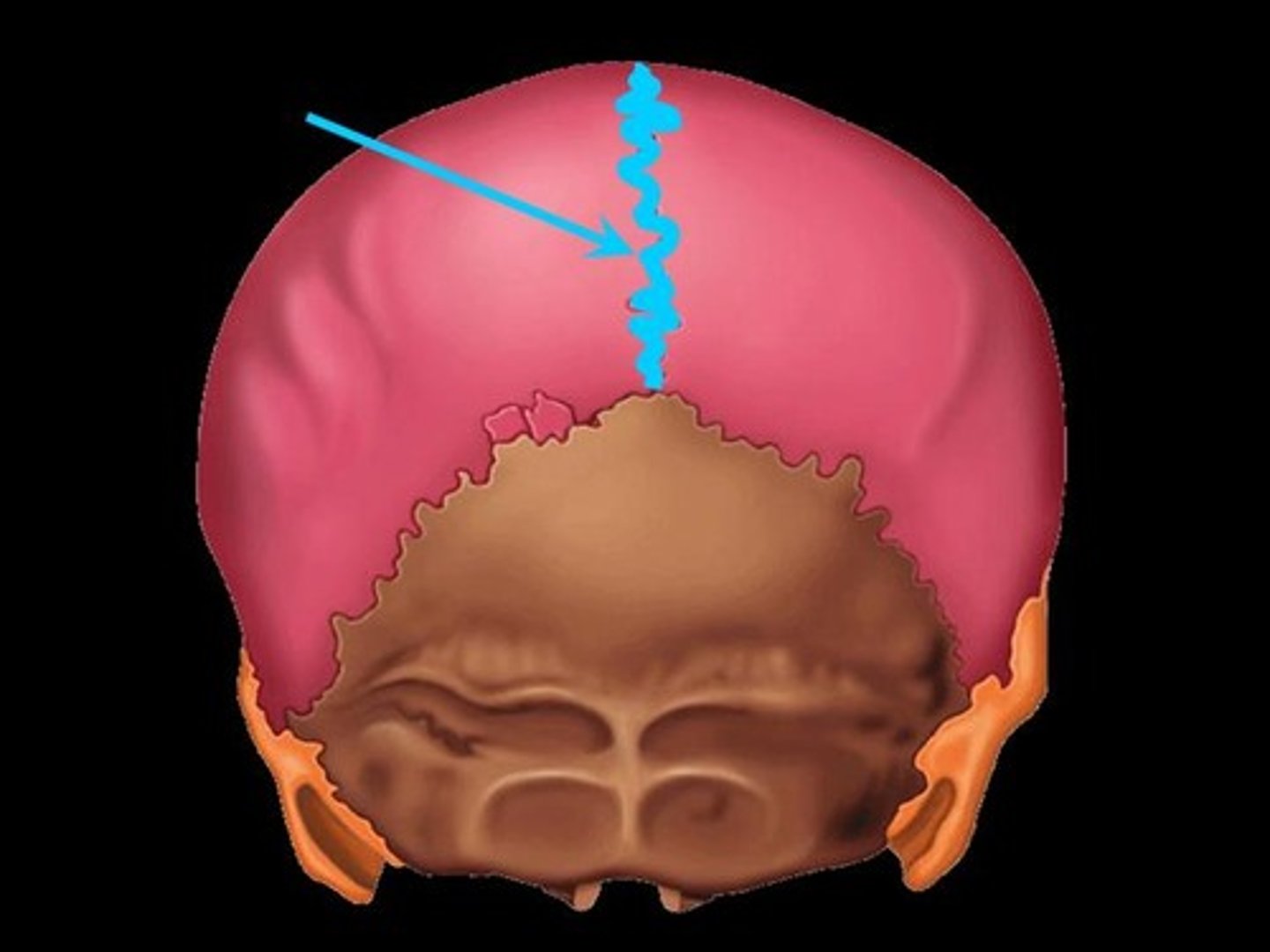
sagittal suture
the suture between the right and left parietal bones
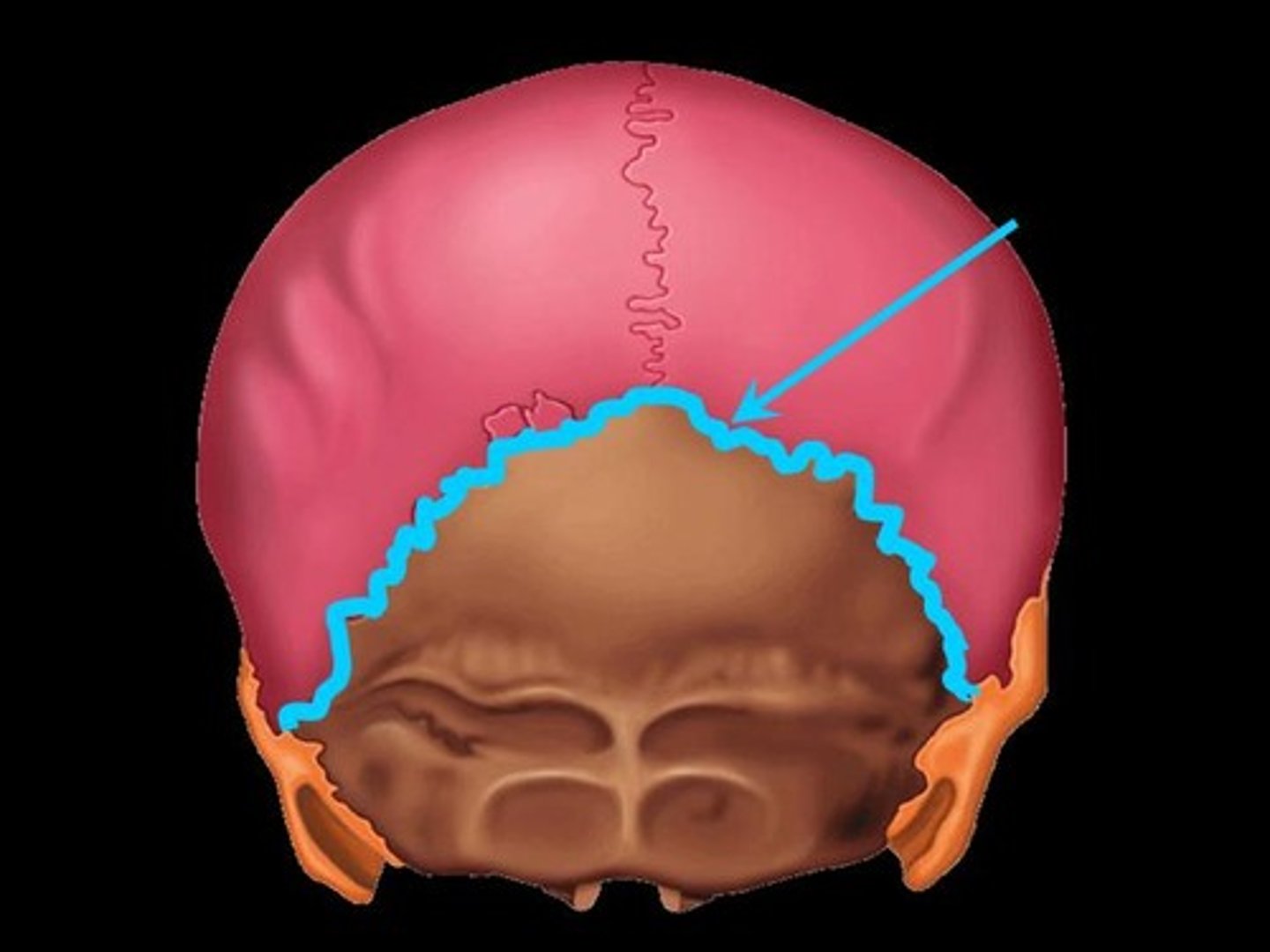
lambdoid suture
between parietal bones and occipital bone
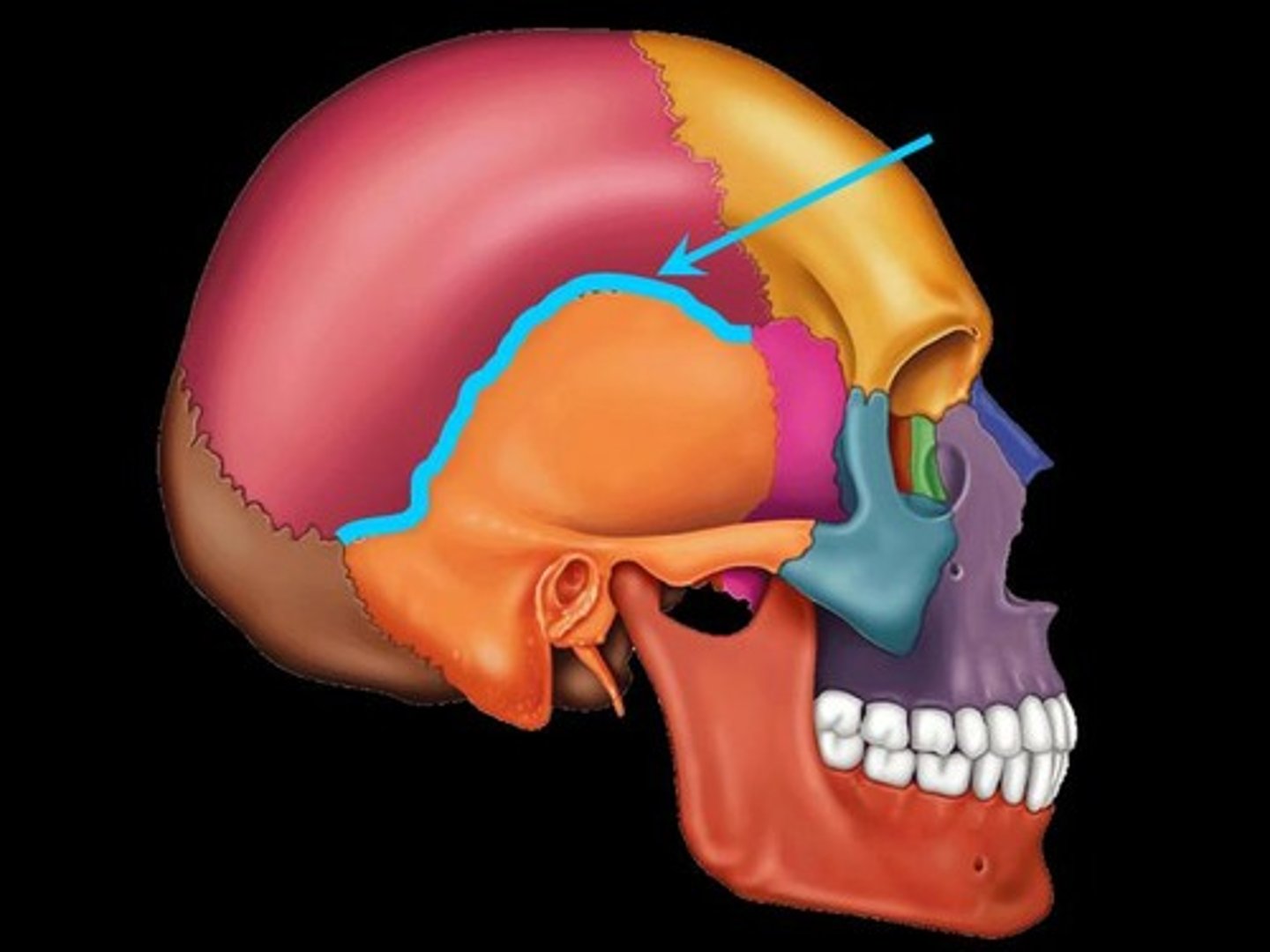
squamous (squamousal) suture
suture between the parietal and temporal bones
vertebrae
spine
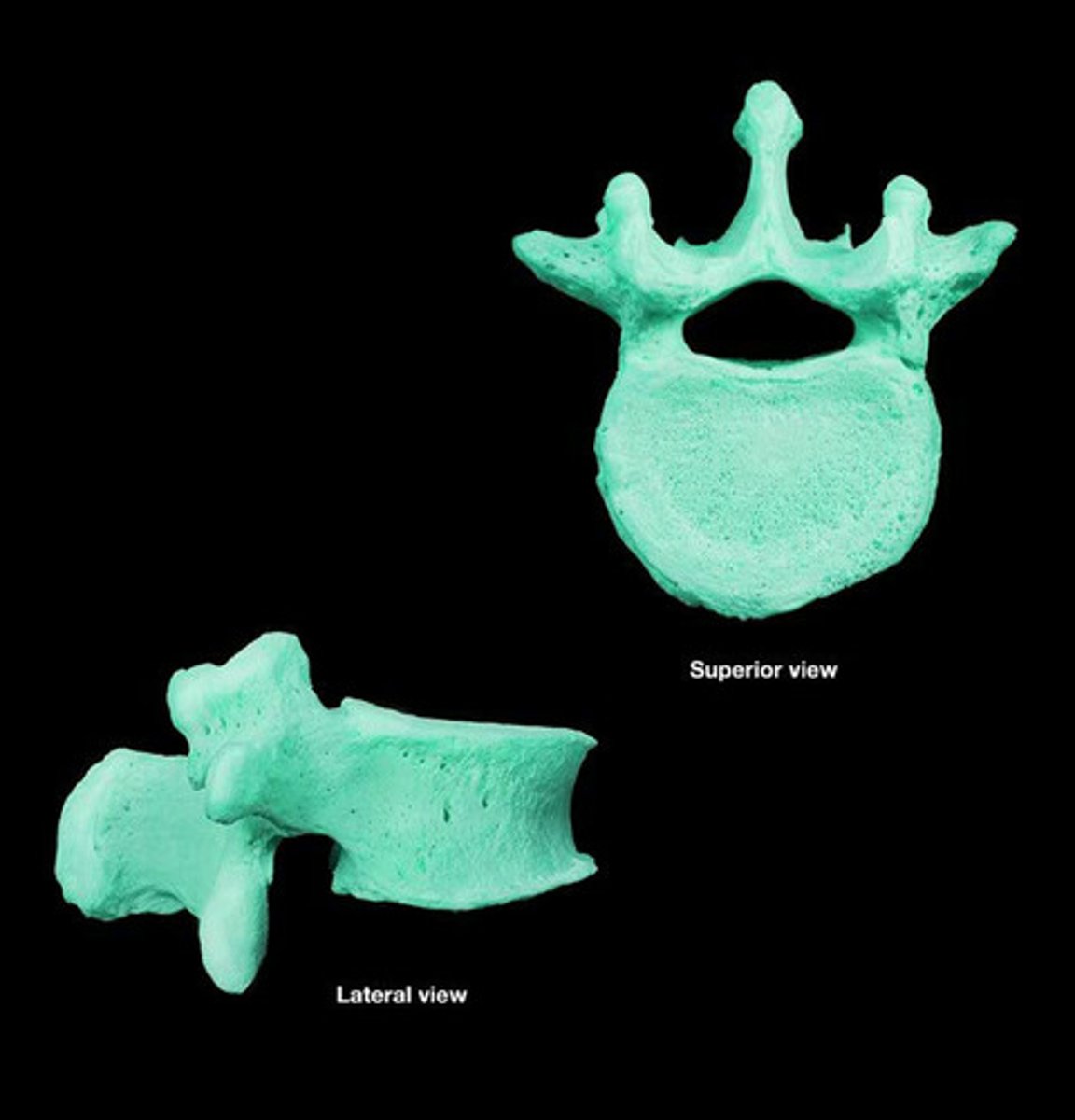
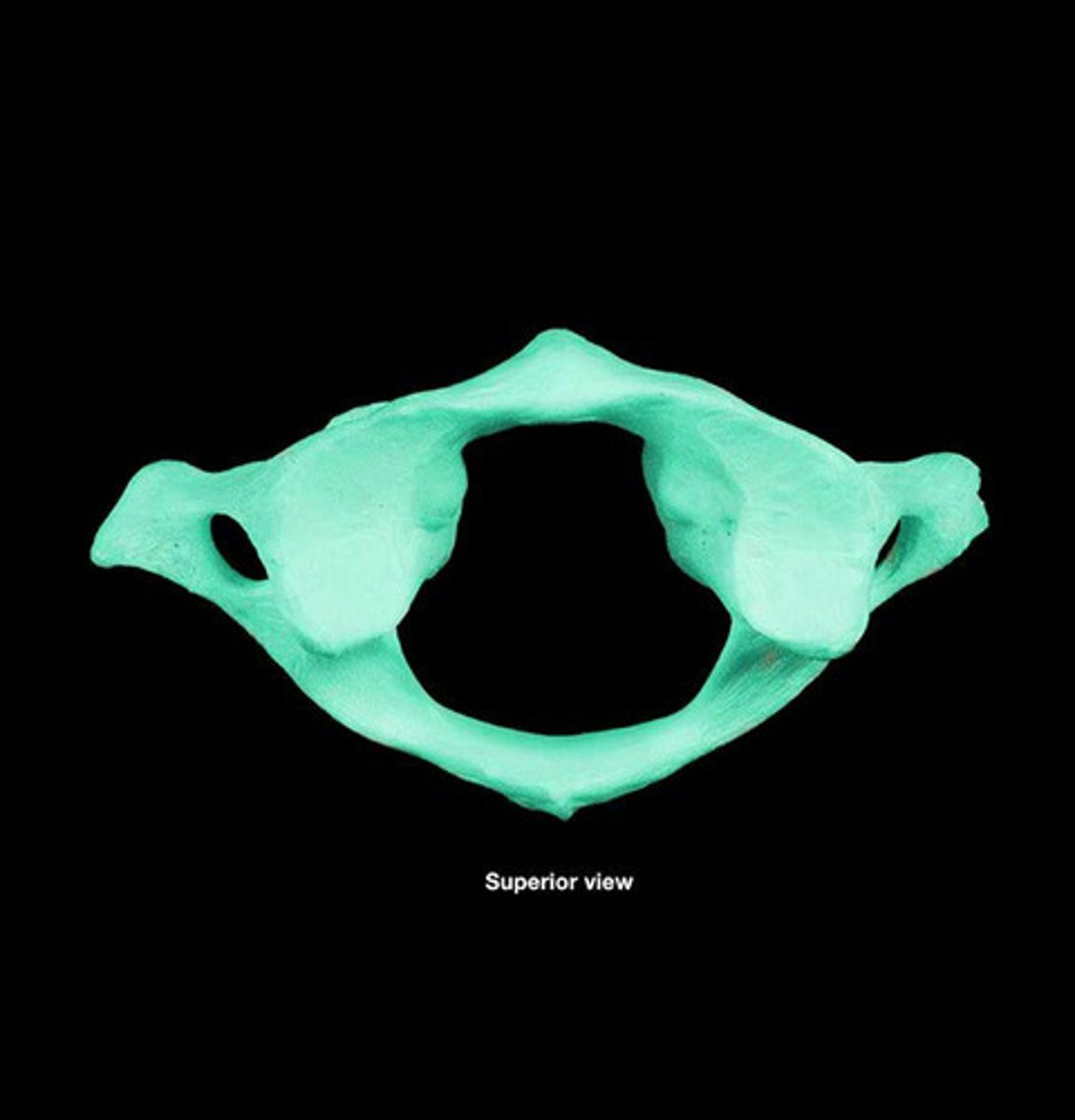
atlas
first cervical vertebra (C1), jointed with the occipital bone allowing the head to nod
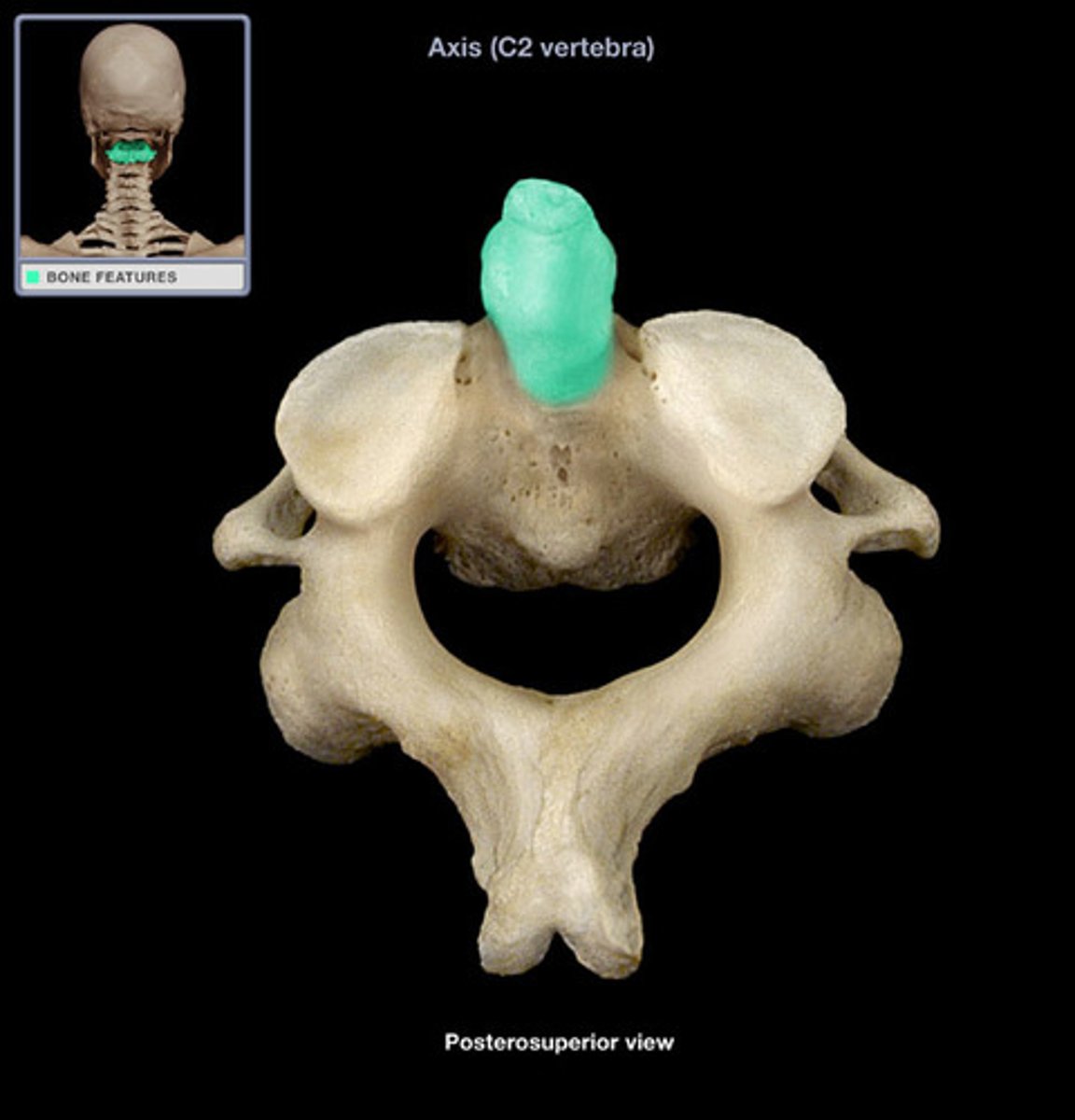
axis
the second cervical vertebrae (C2), allows the head to shake "no"
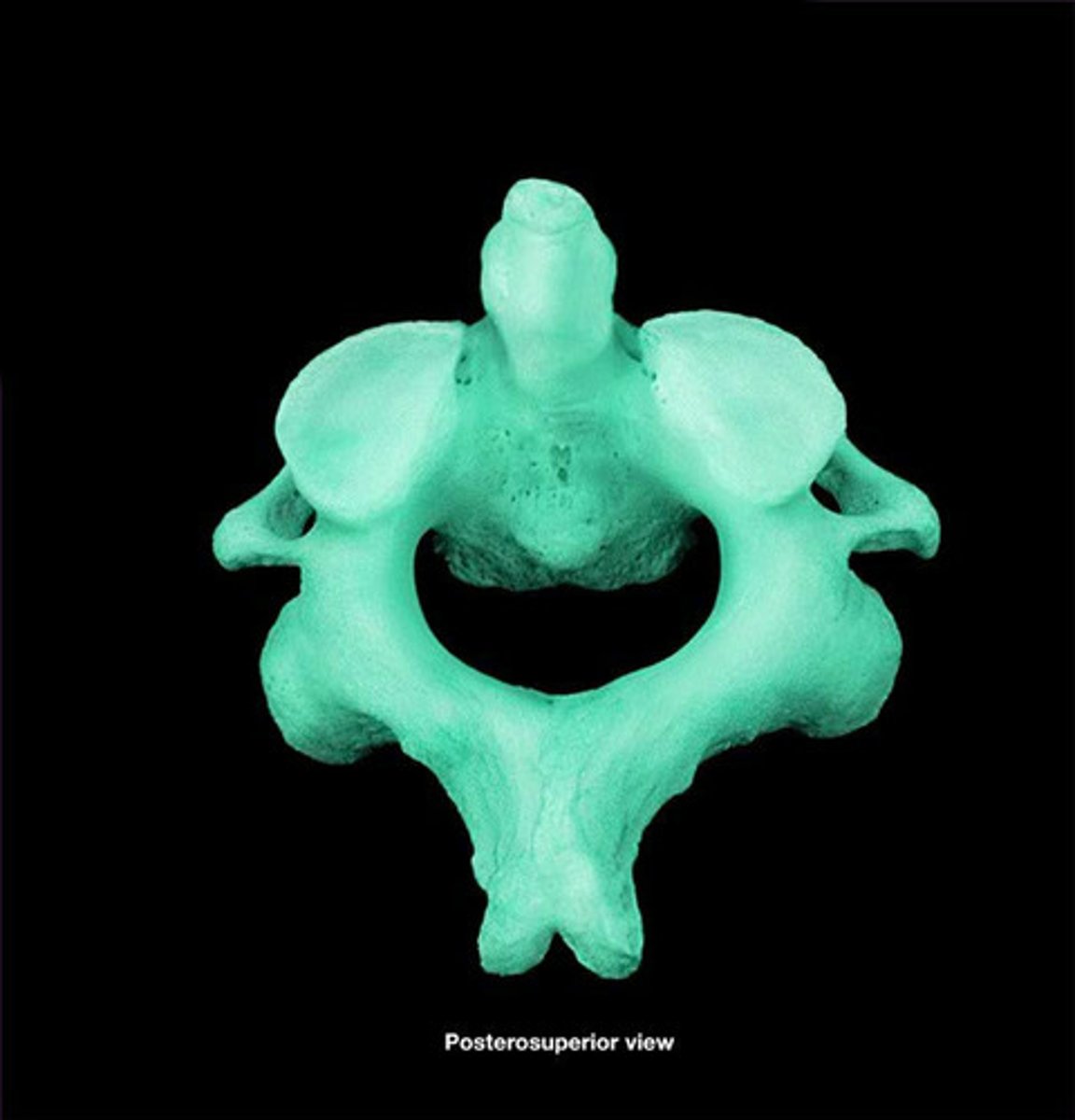
odontoid process (dens)
process of the axis which passes through the vertebral foramen of the atlas
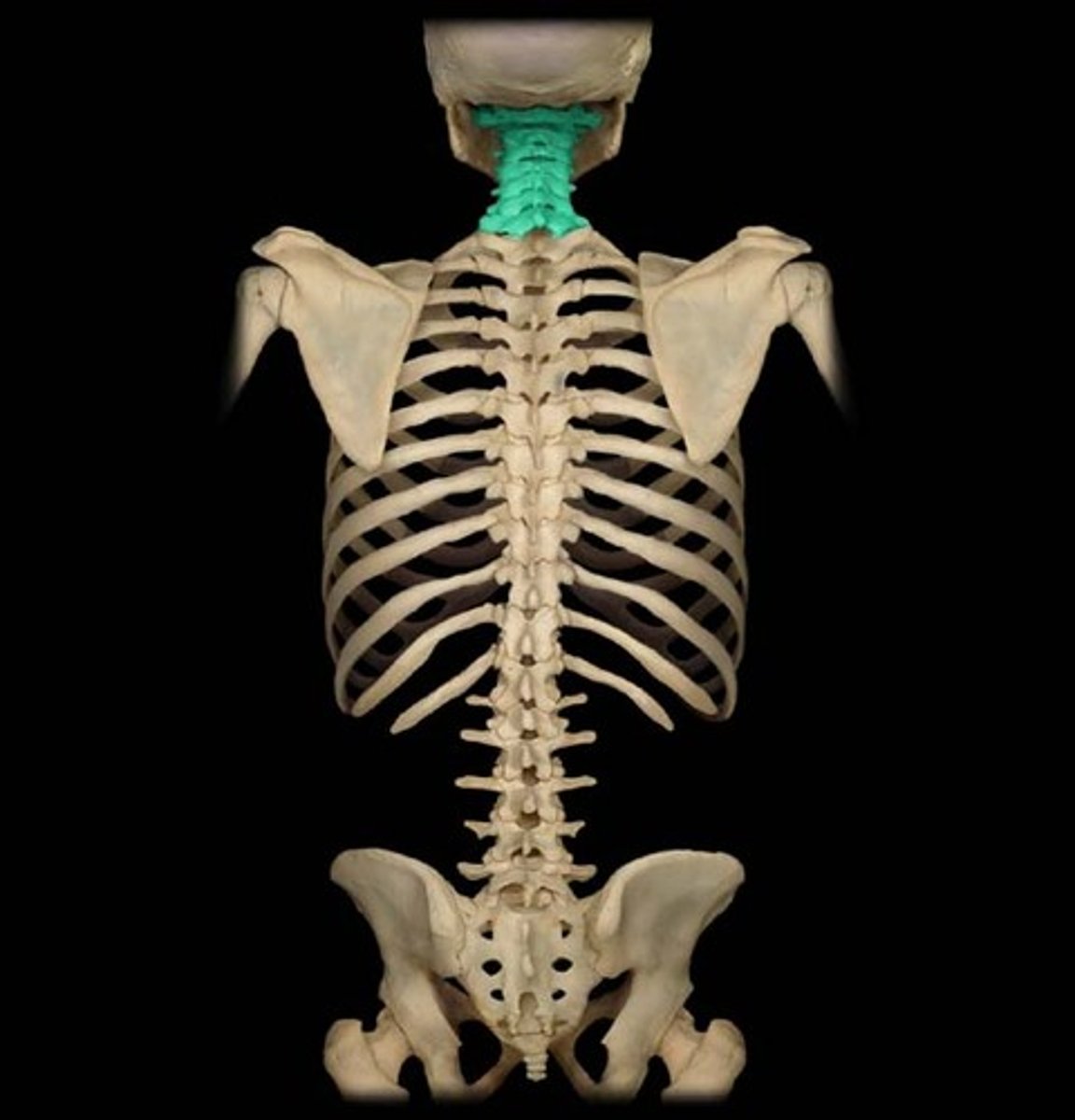
cervical
neck region of the spine (C1 - C7)
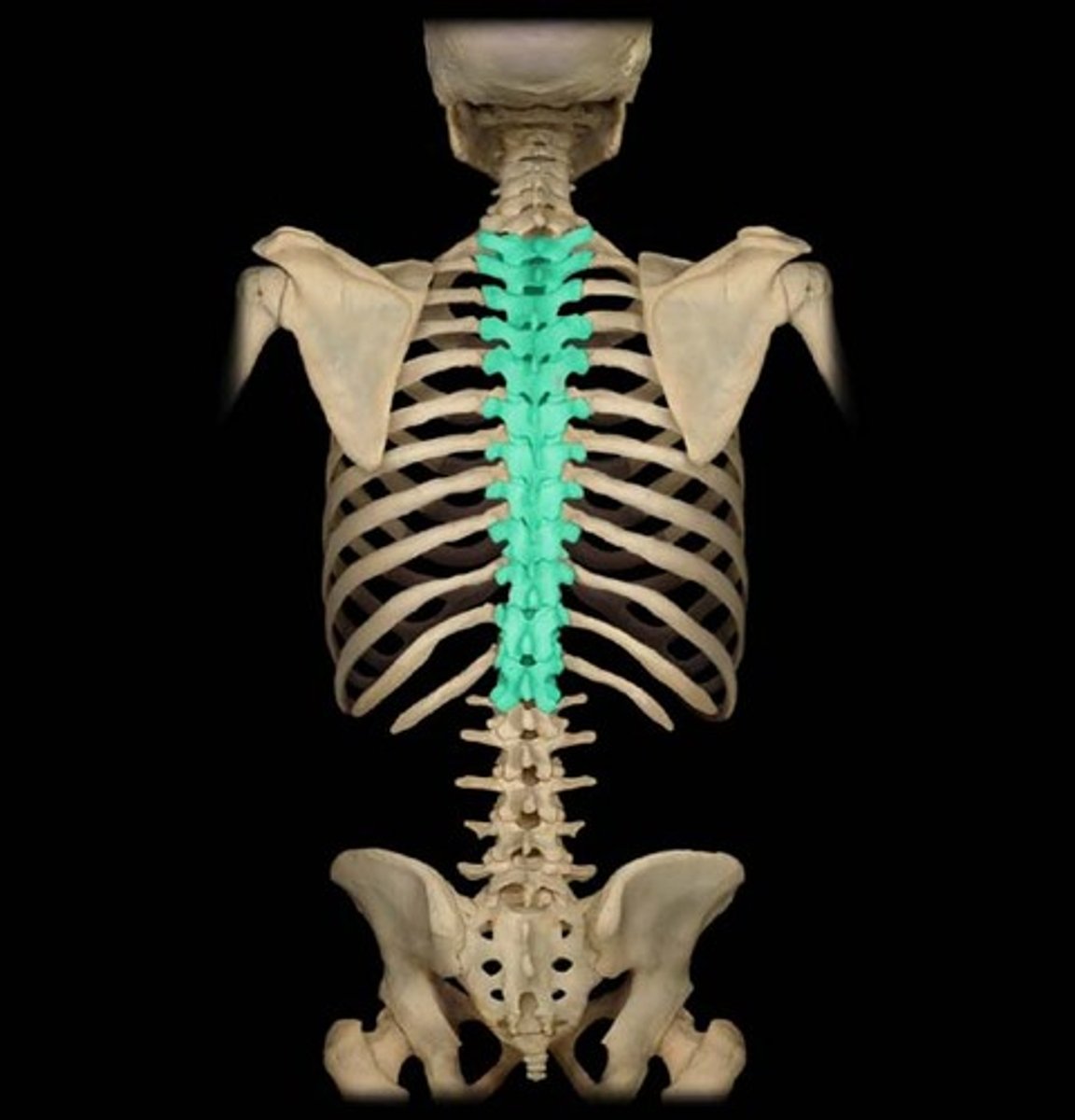
thoracic
chest region of the spine (T1 - T12). Characterized by long, sharp spinous processes and rib facets
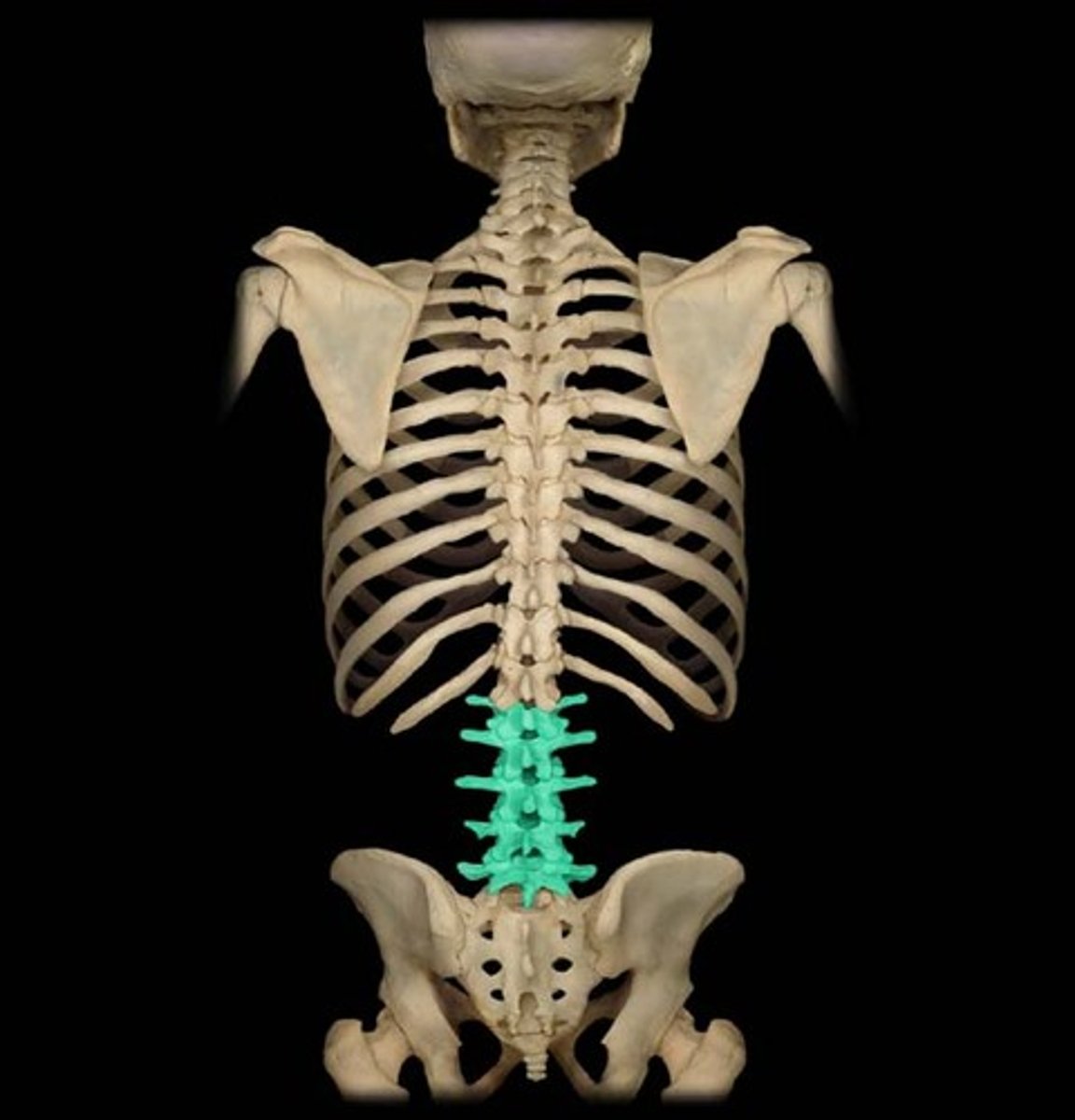
lumbar
back region of the spine (L1 - L5). Characterized by short, blunt spinous process and large body.
spinous process
sharp, slender projection
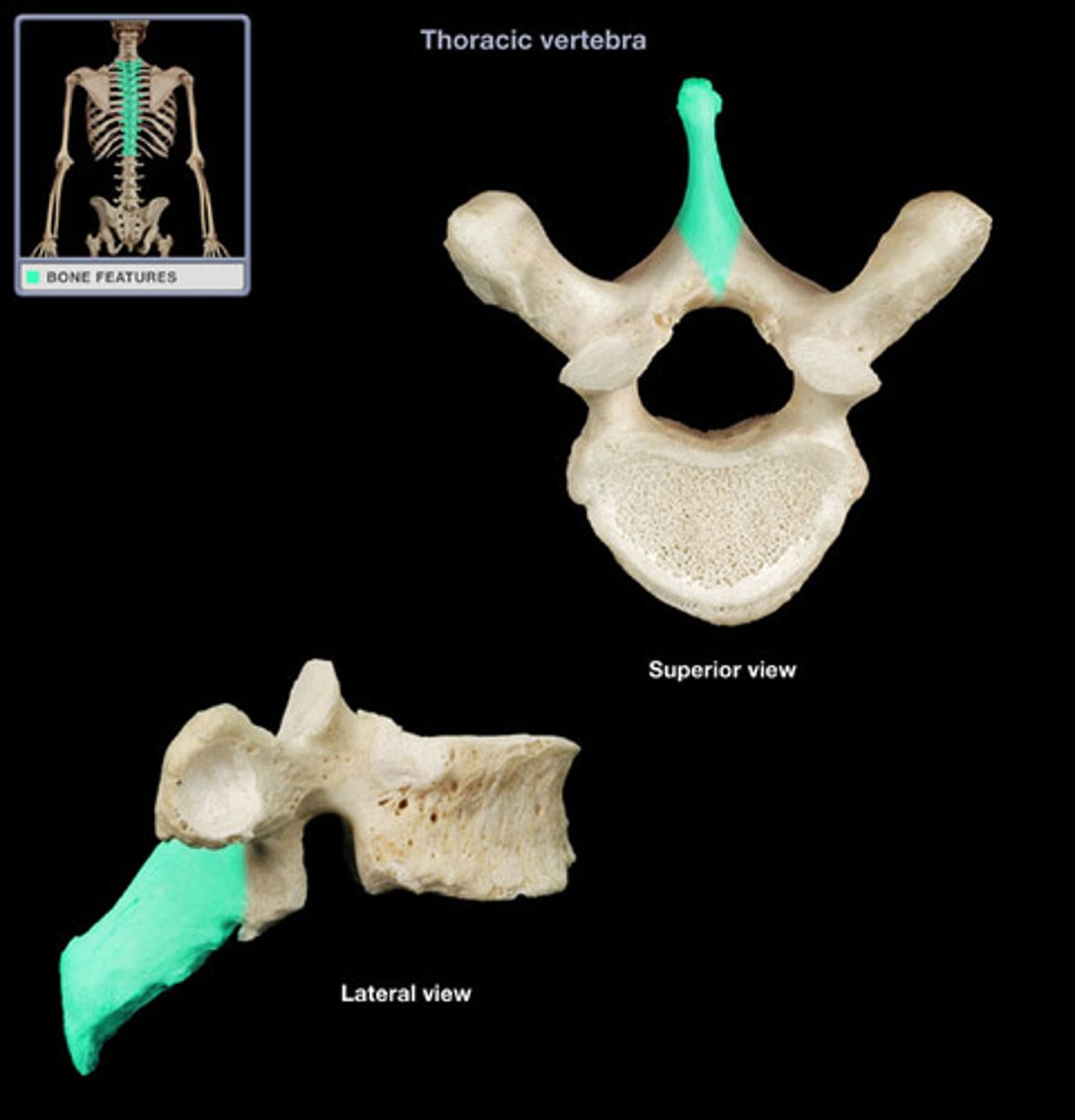
transverse process
two lateral projections from the vertebral arch
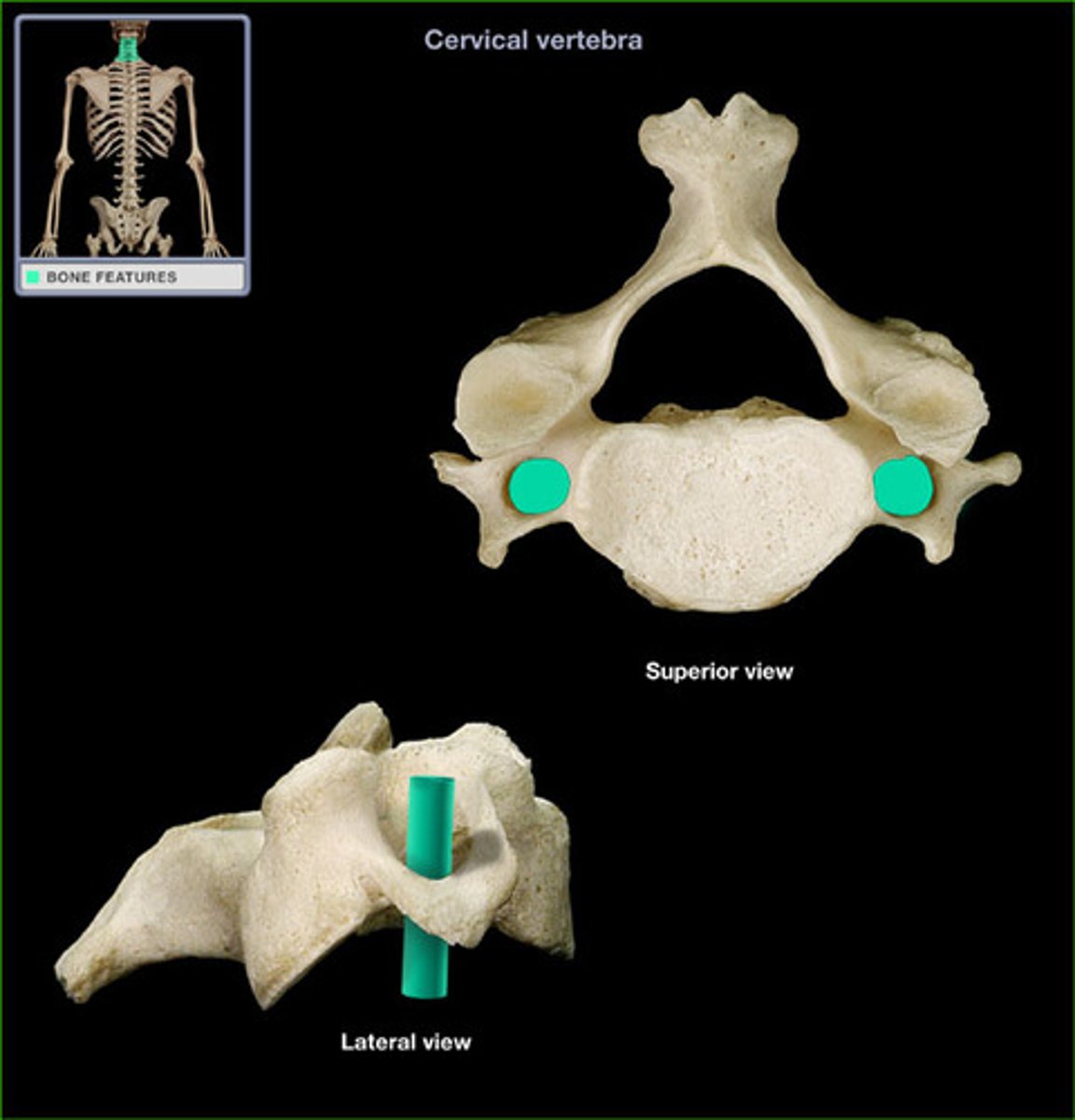
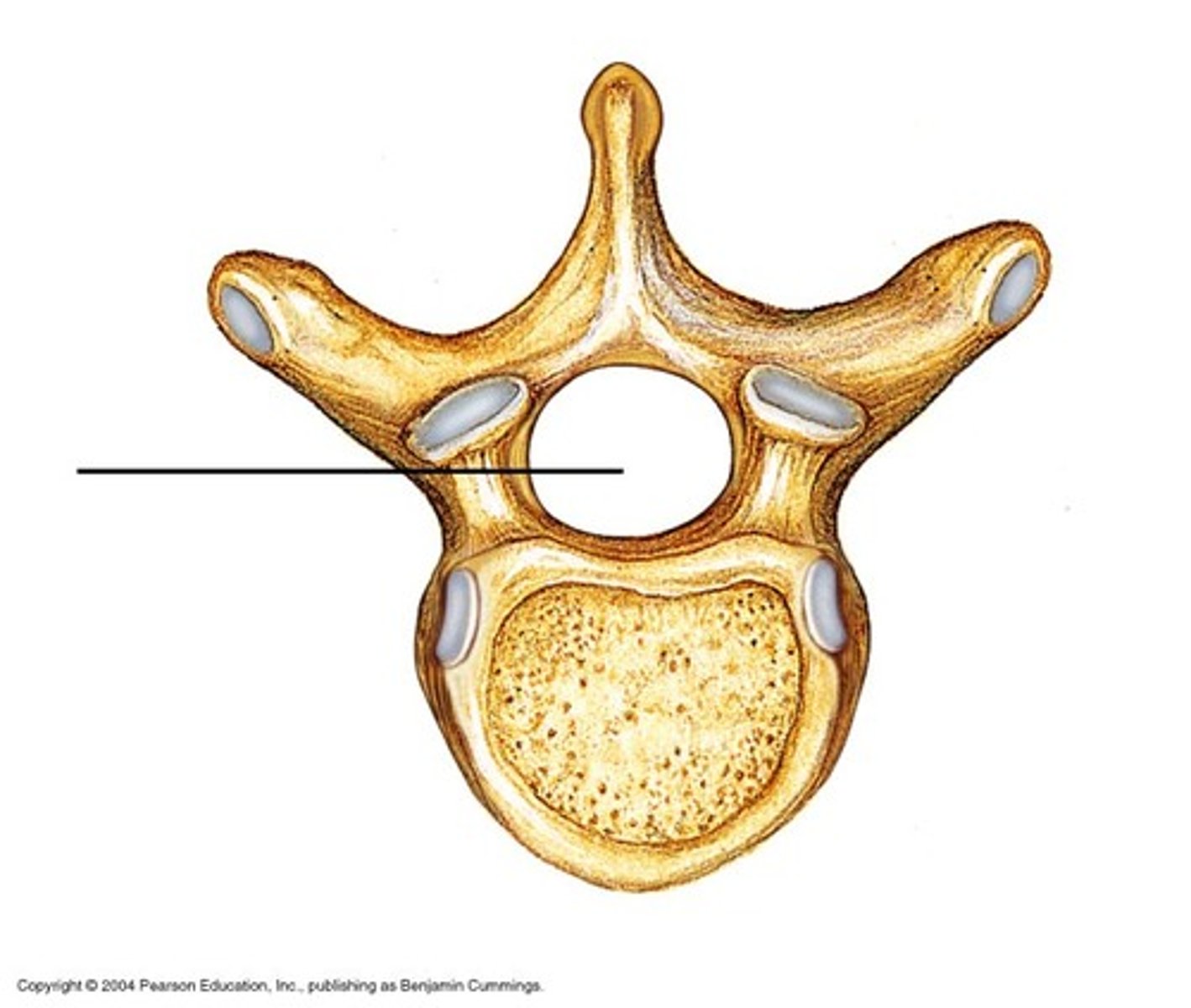
vertebral foramen
canal through which spinal cord passes
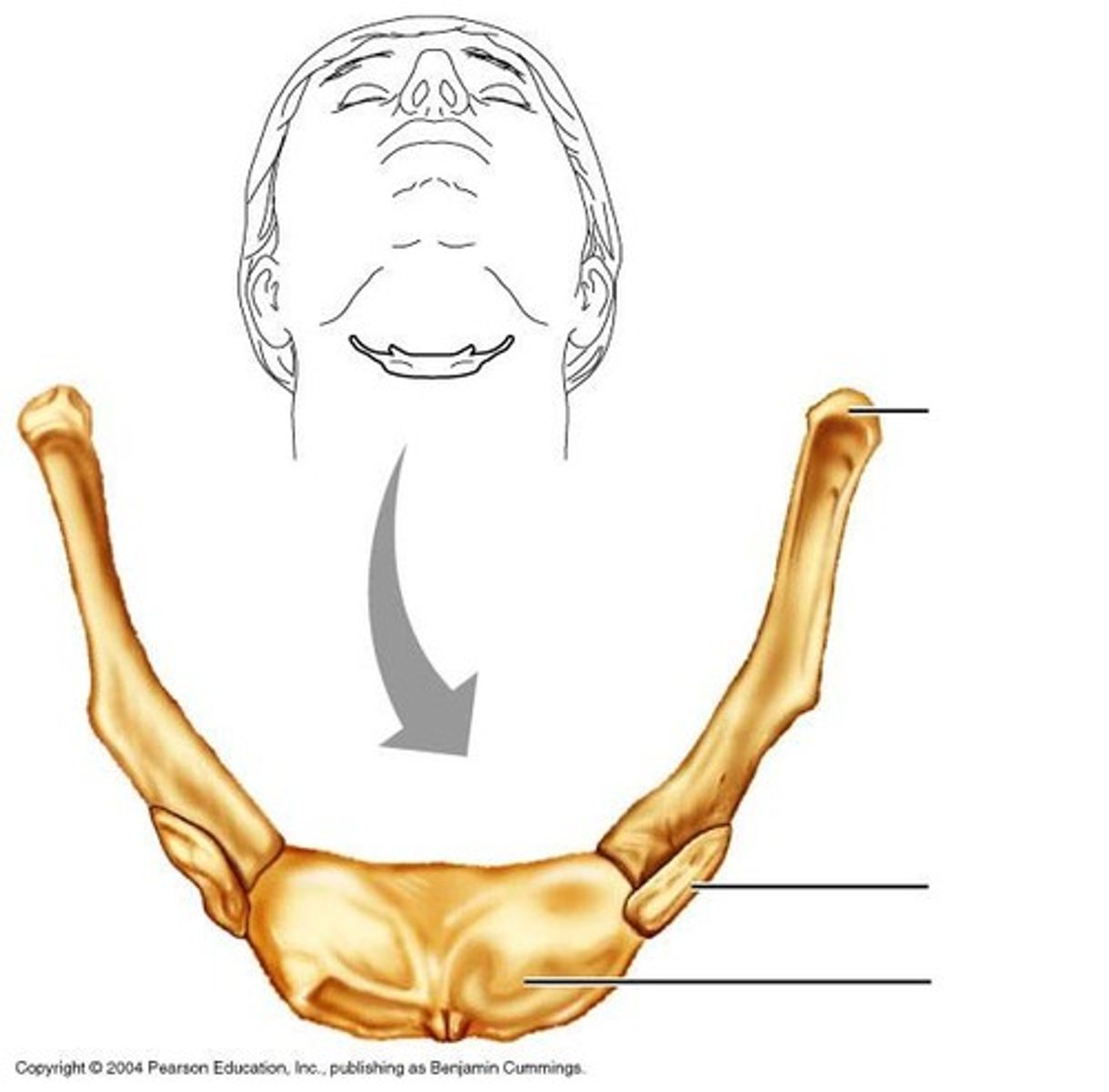
hyoid bone
U-shaped bone at the base of the tongue that supports the tongue and its muscles.
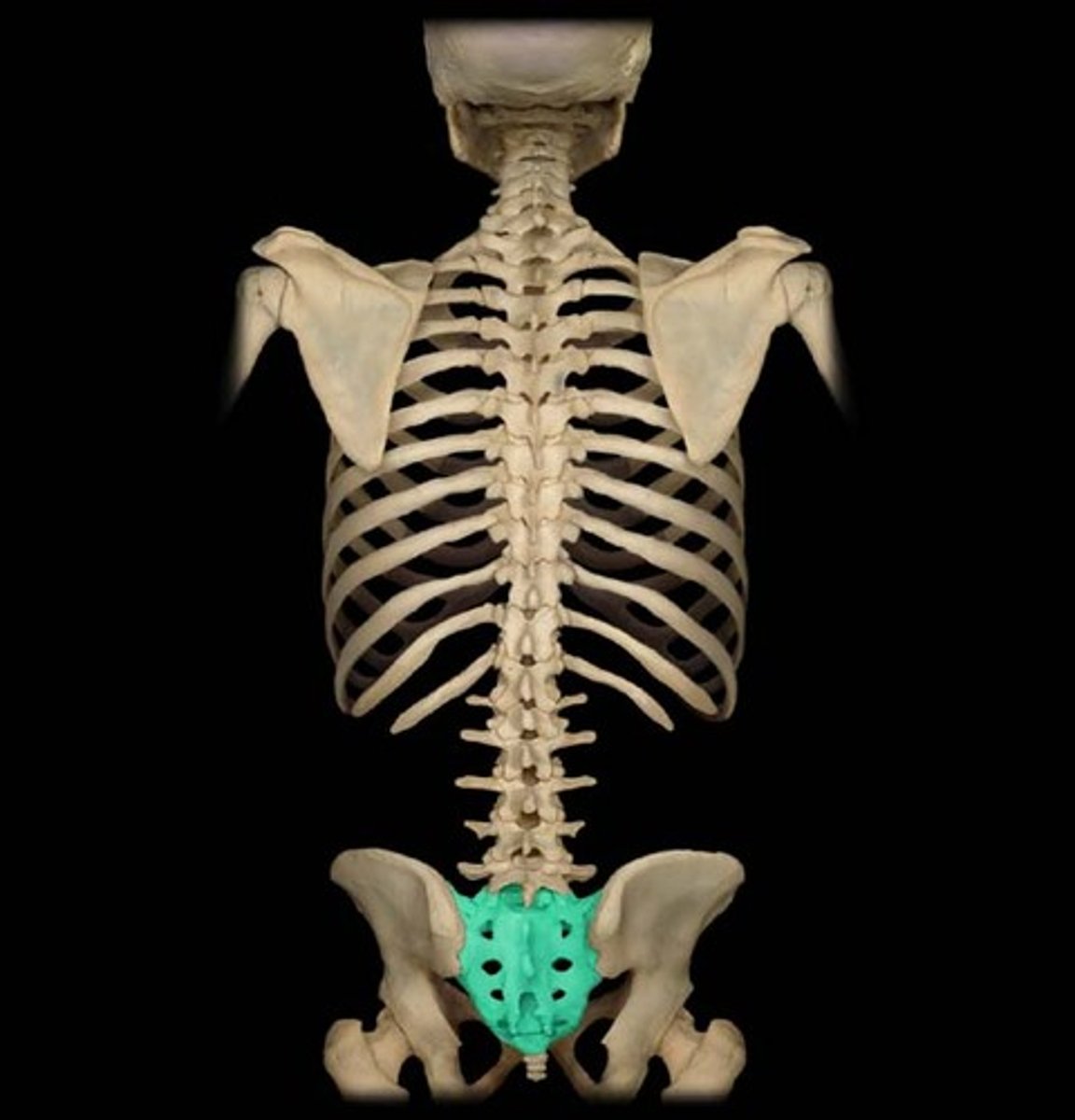
sacrum
bone formed from five vertebrae fused together near the base of the spinal column
coccyx
four vertebrae fused together to form the tailbone
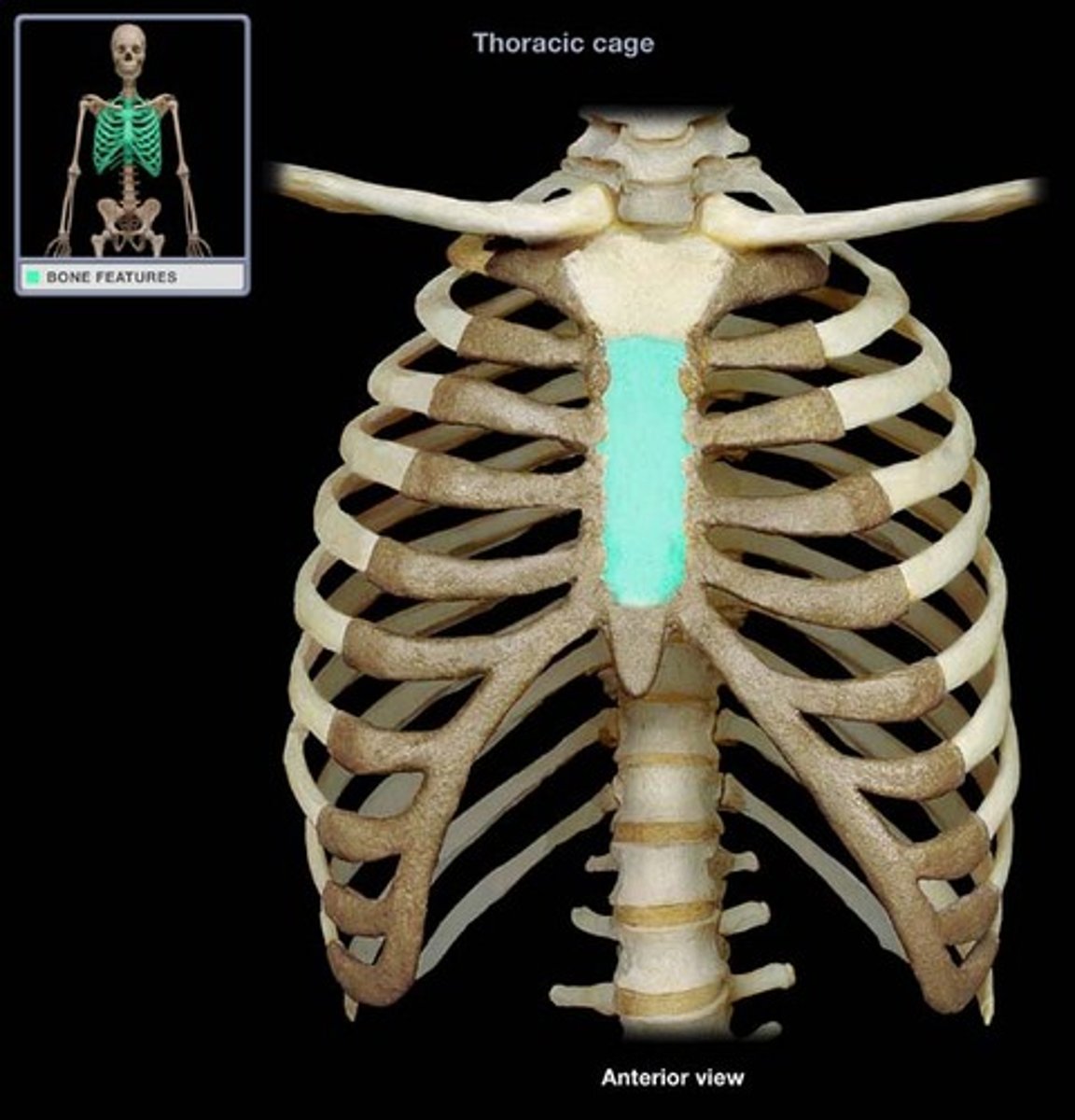
sternum
breastbone
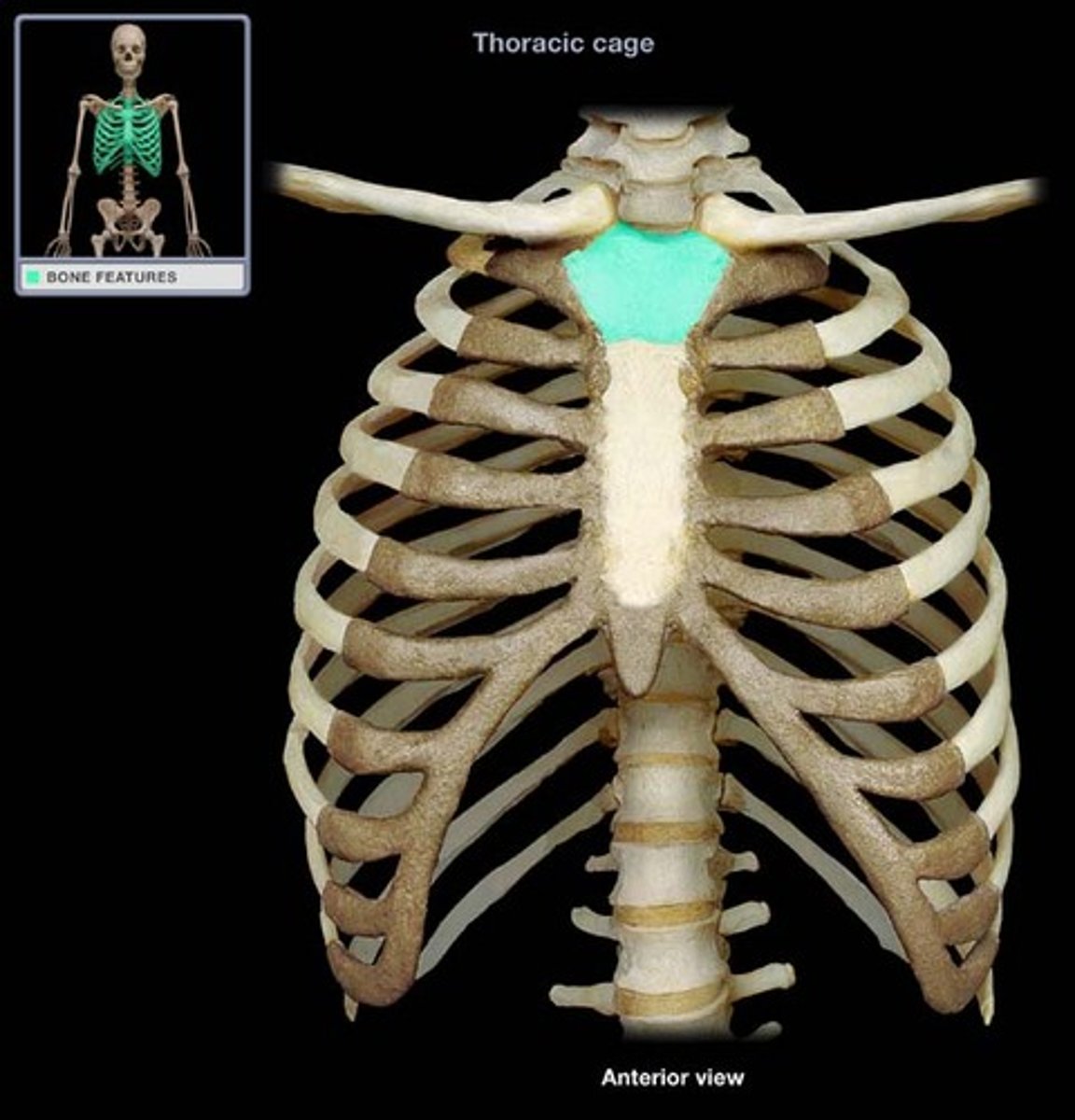
manubrium
the superior portion of the sternum
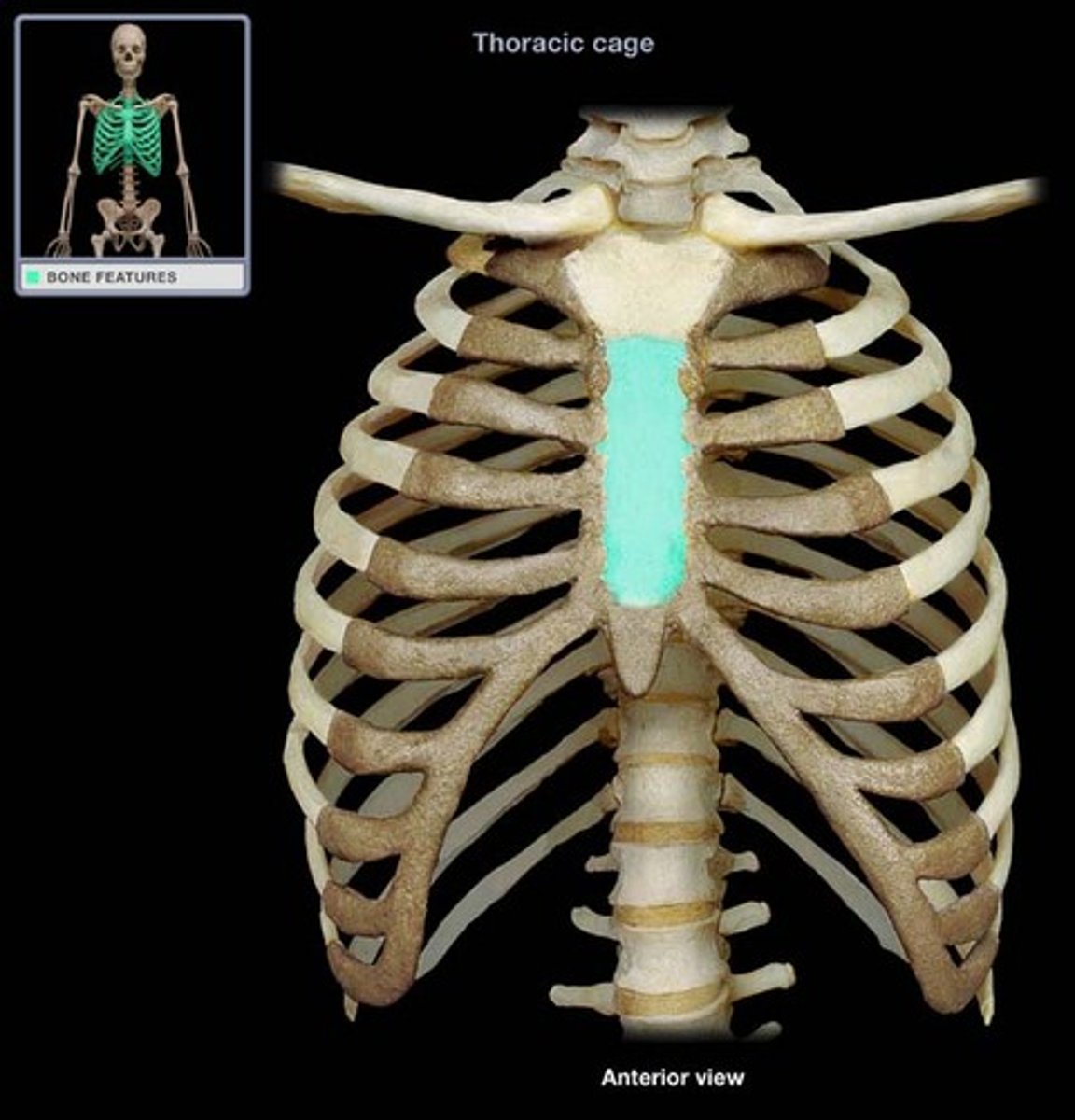
sternum body
main long part of sternum
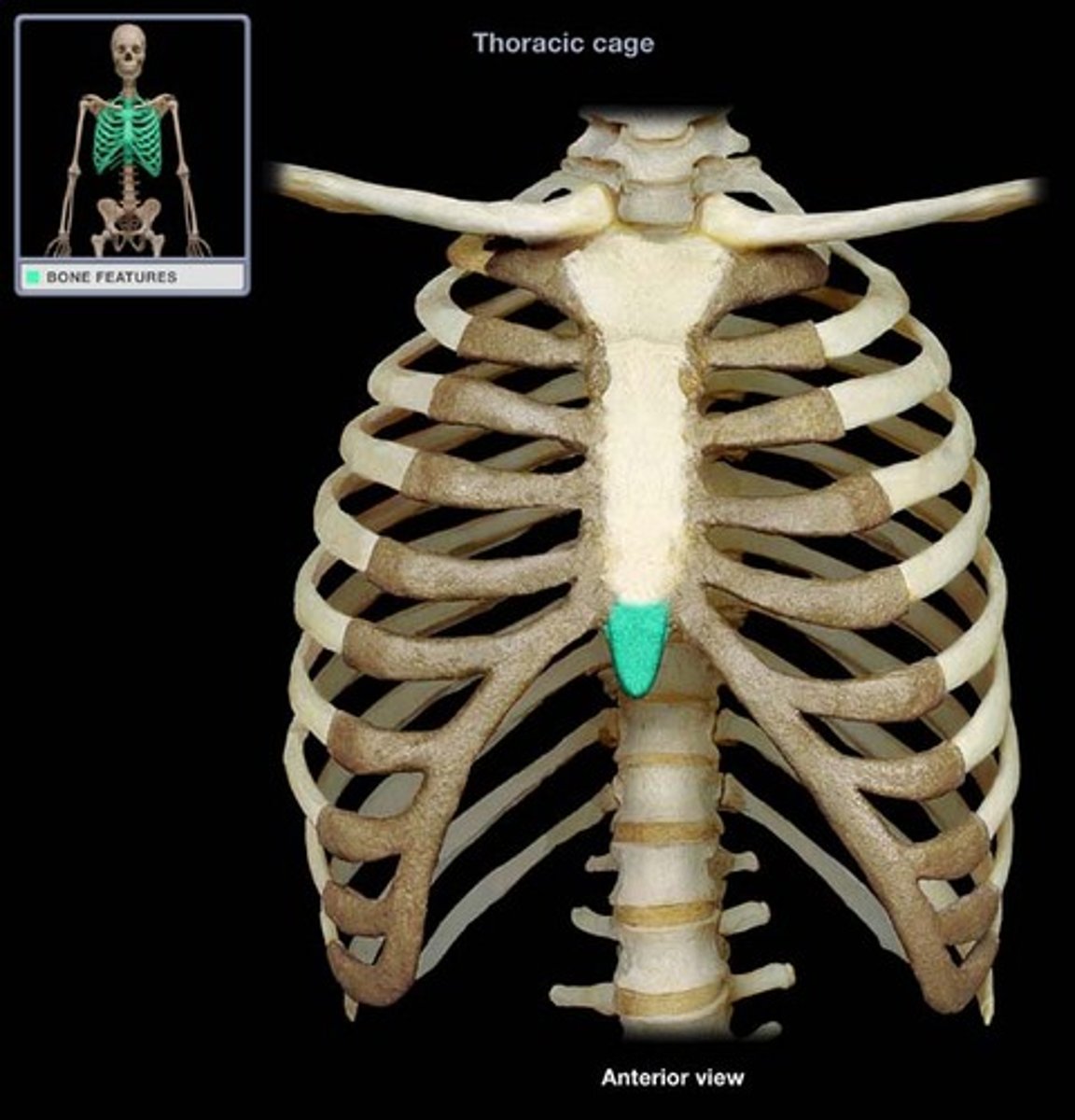
xiphoid process
inferior portion of the sternum
rib
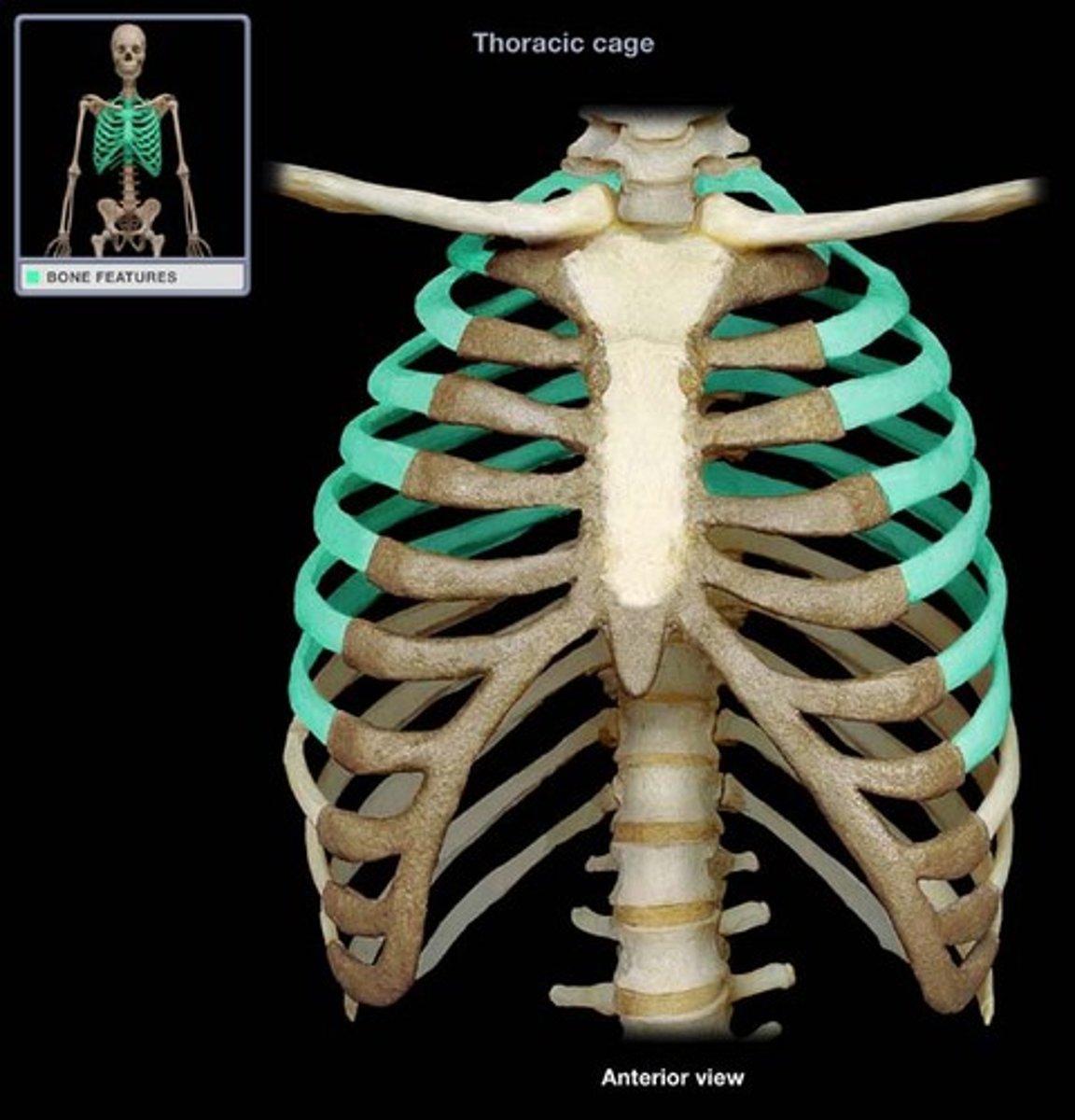
true ribs
1-7 attach directly to sternum
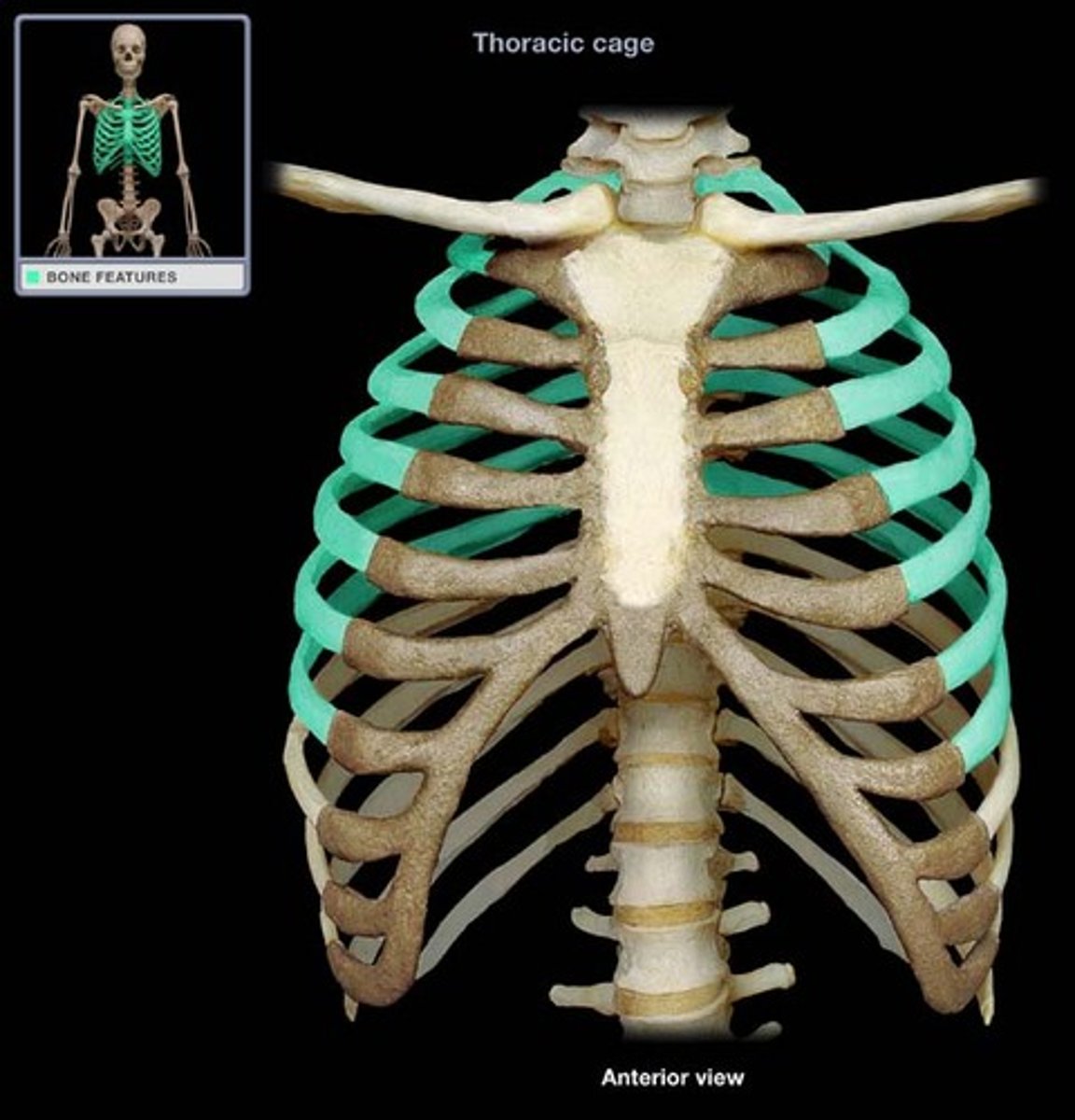
false ribs
8-12 do not attach directly to sternum
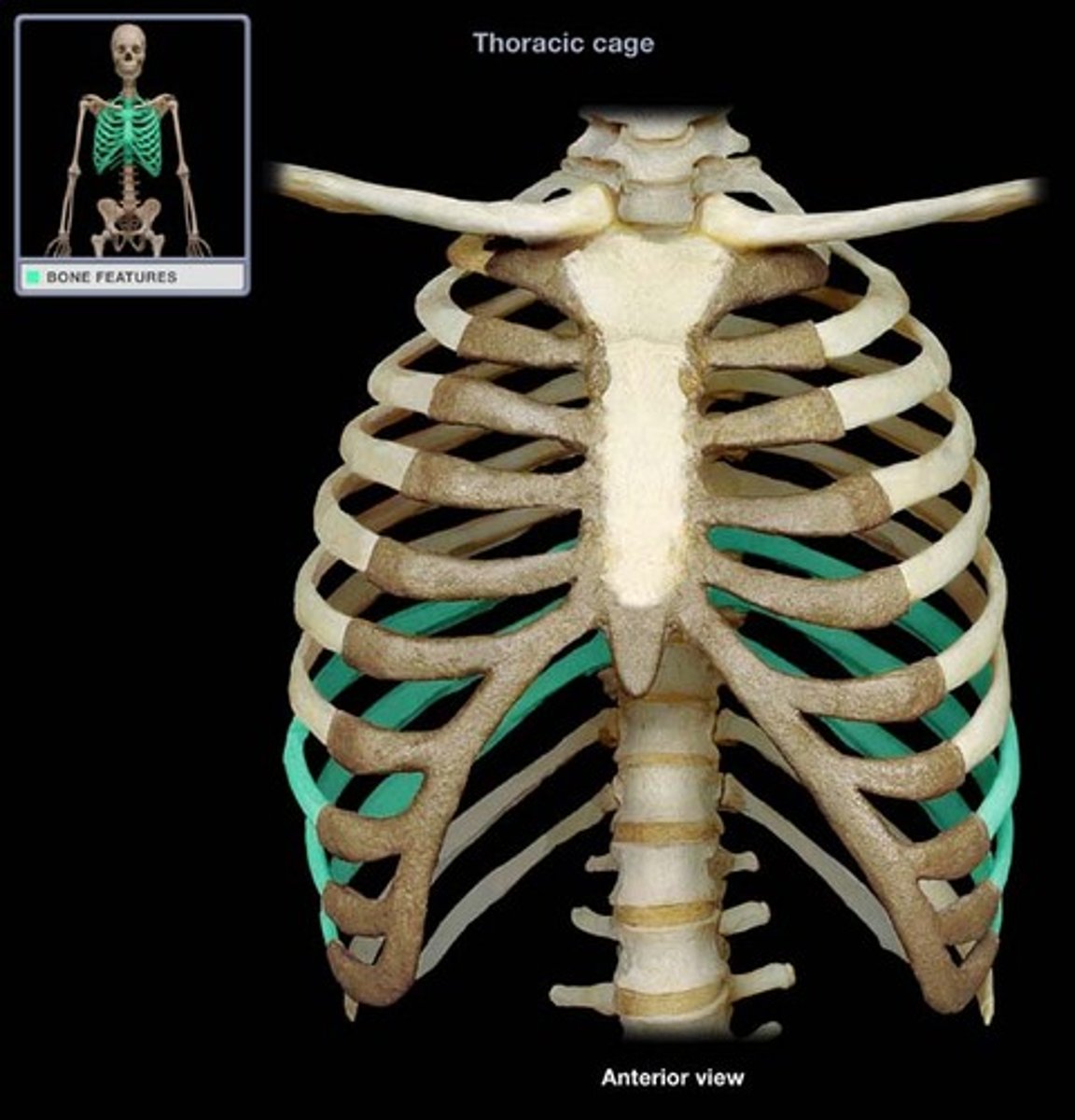
floating ribs
11-12 do not attach to sternum
scapula
shoulder blade
spine
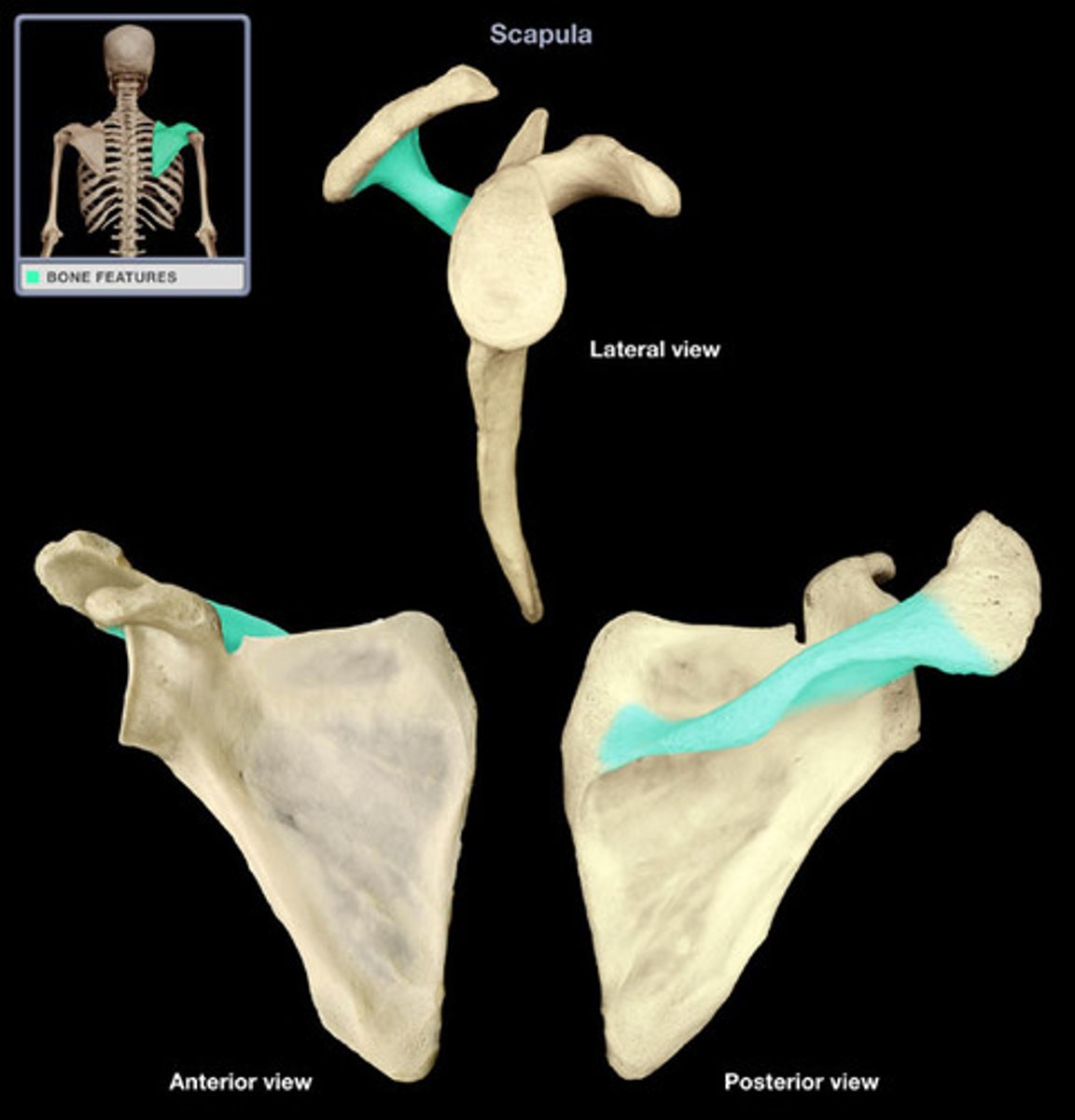
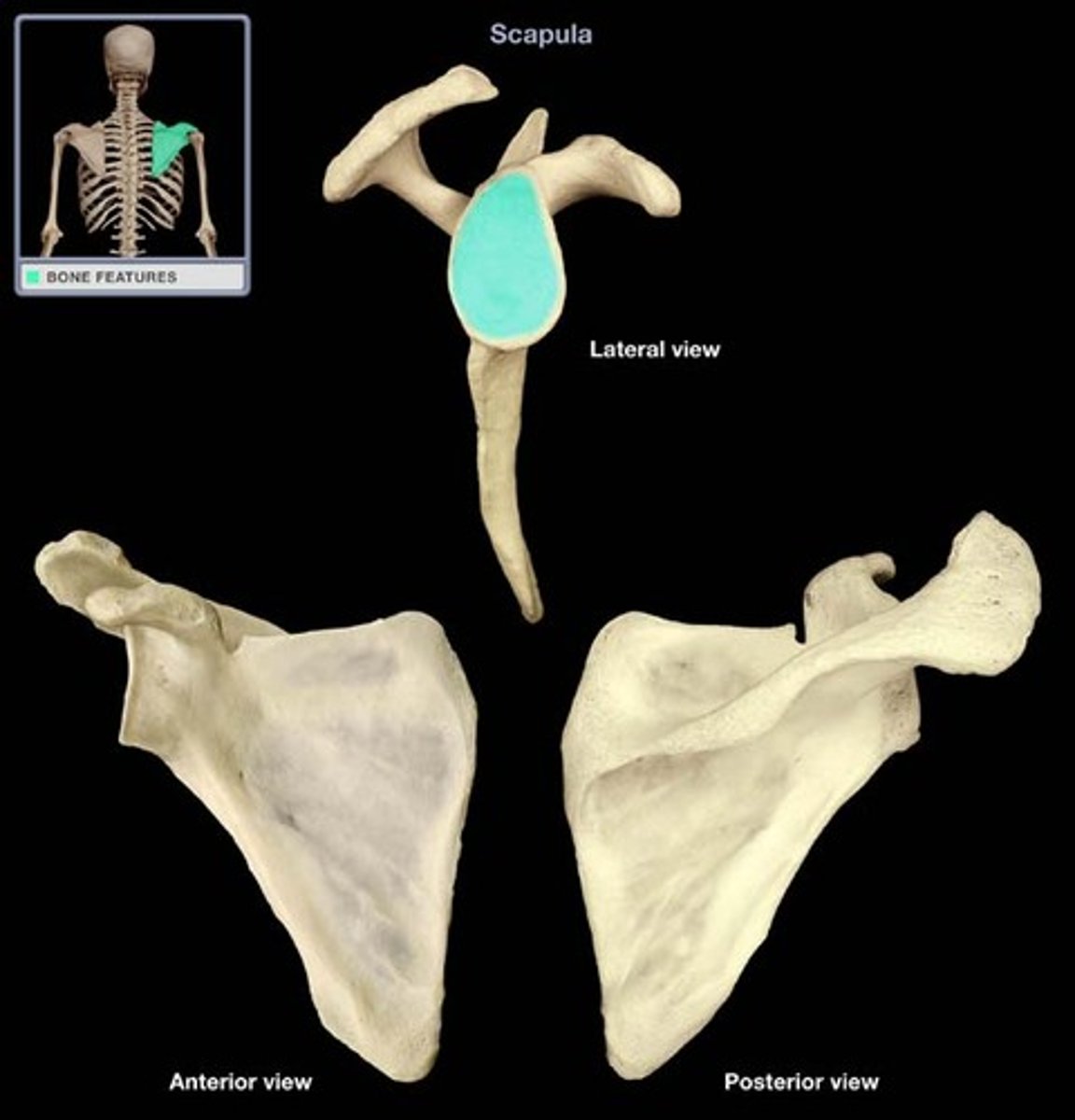
glenoid cavity
socket in scapula that receives head of humerus
coracoid process
process above the glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment
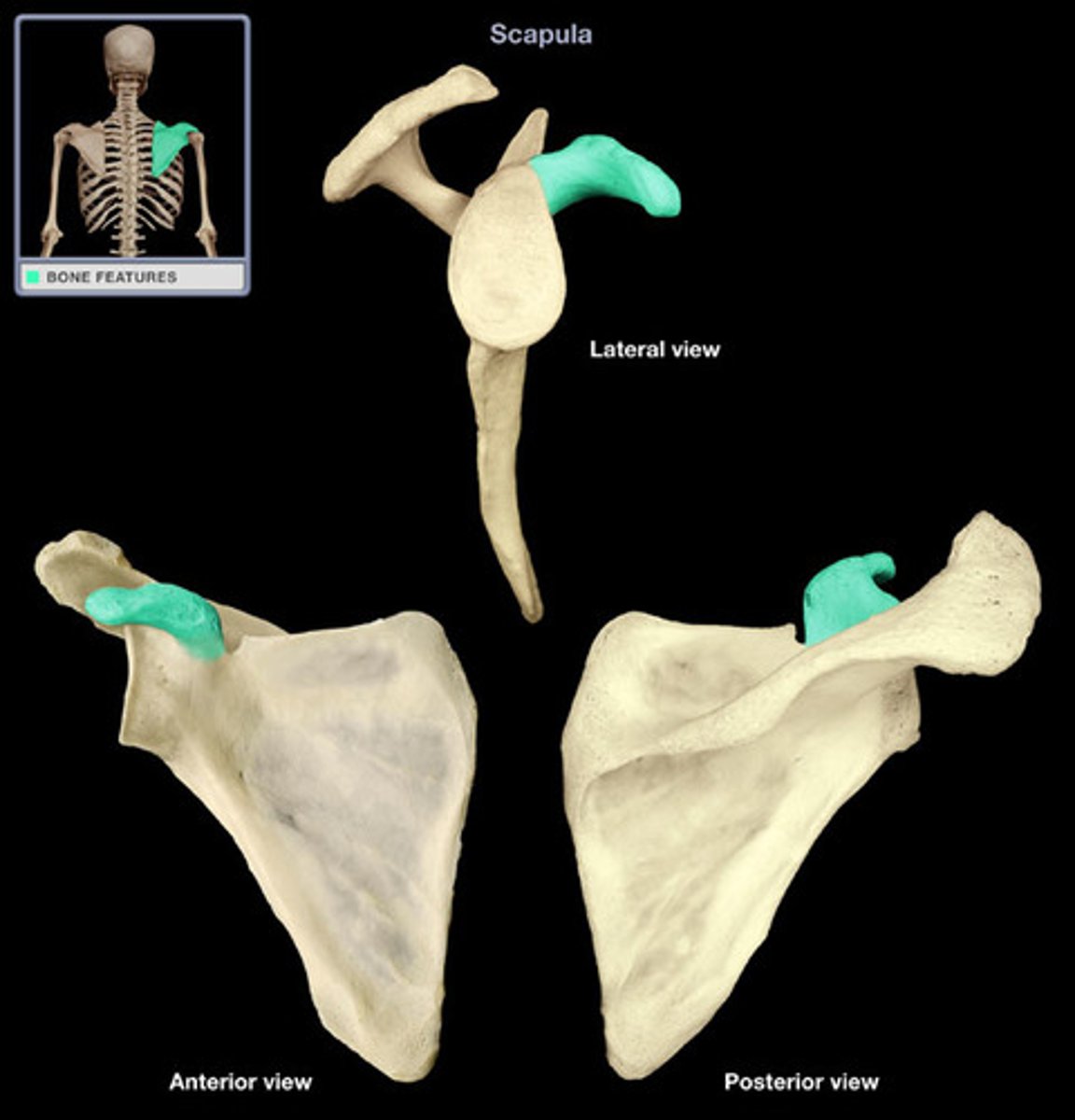
acromion
Outward extension of the shoulder blade forming the point of the shoulder.
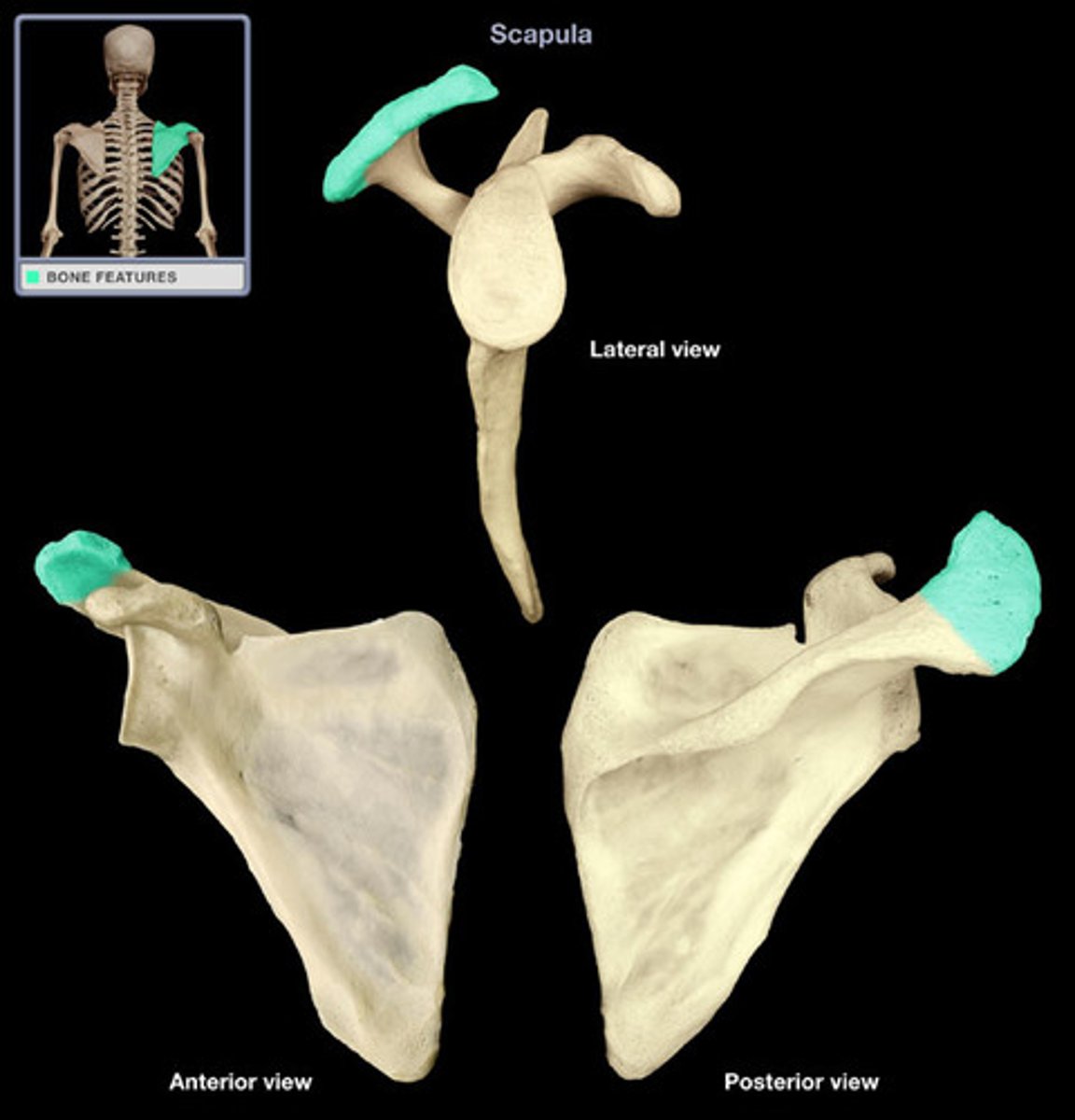
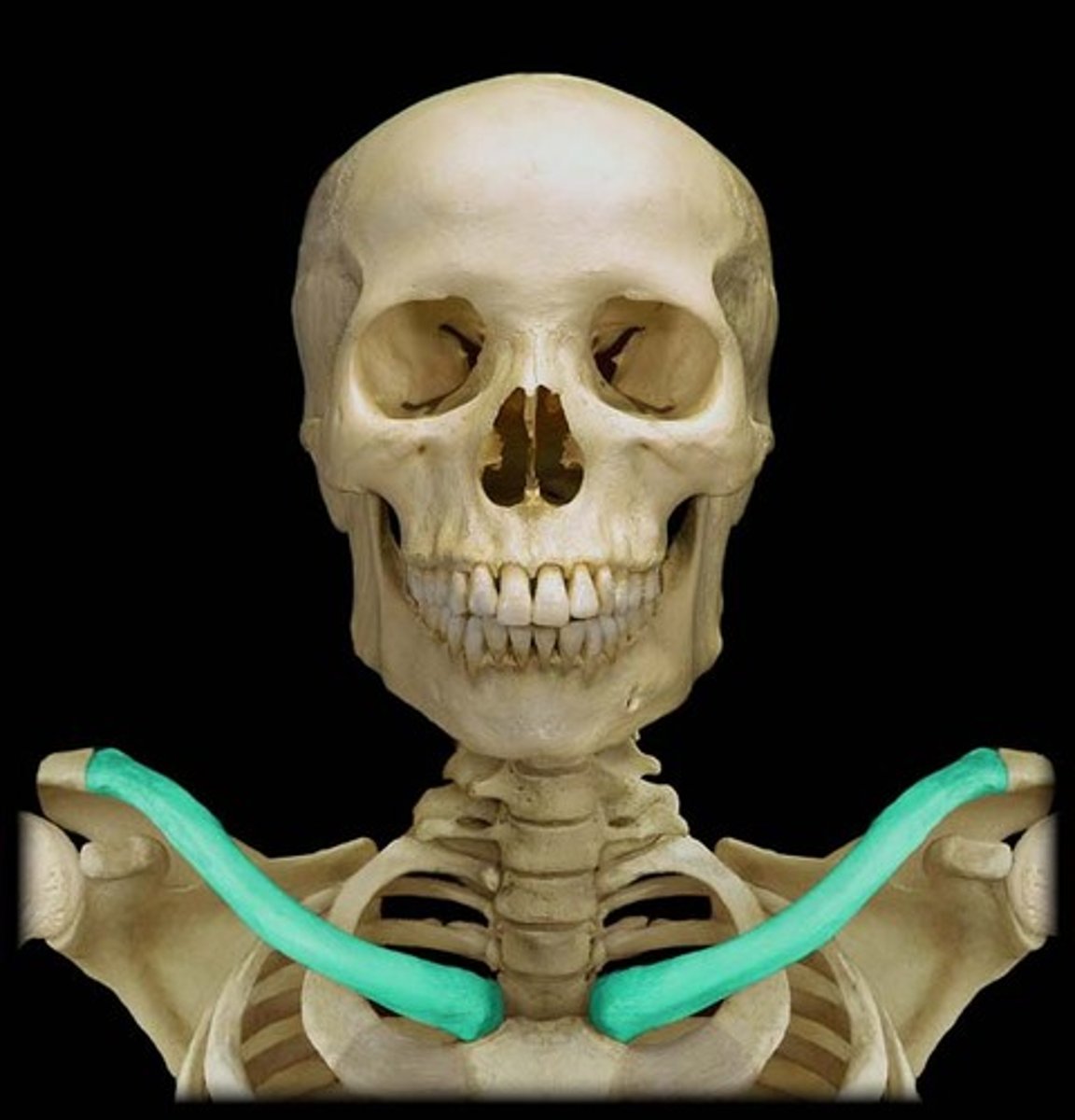
clavicle
collar bone
humerus
arm
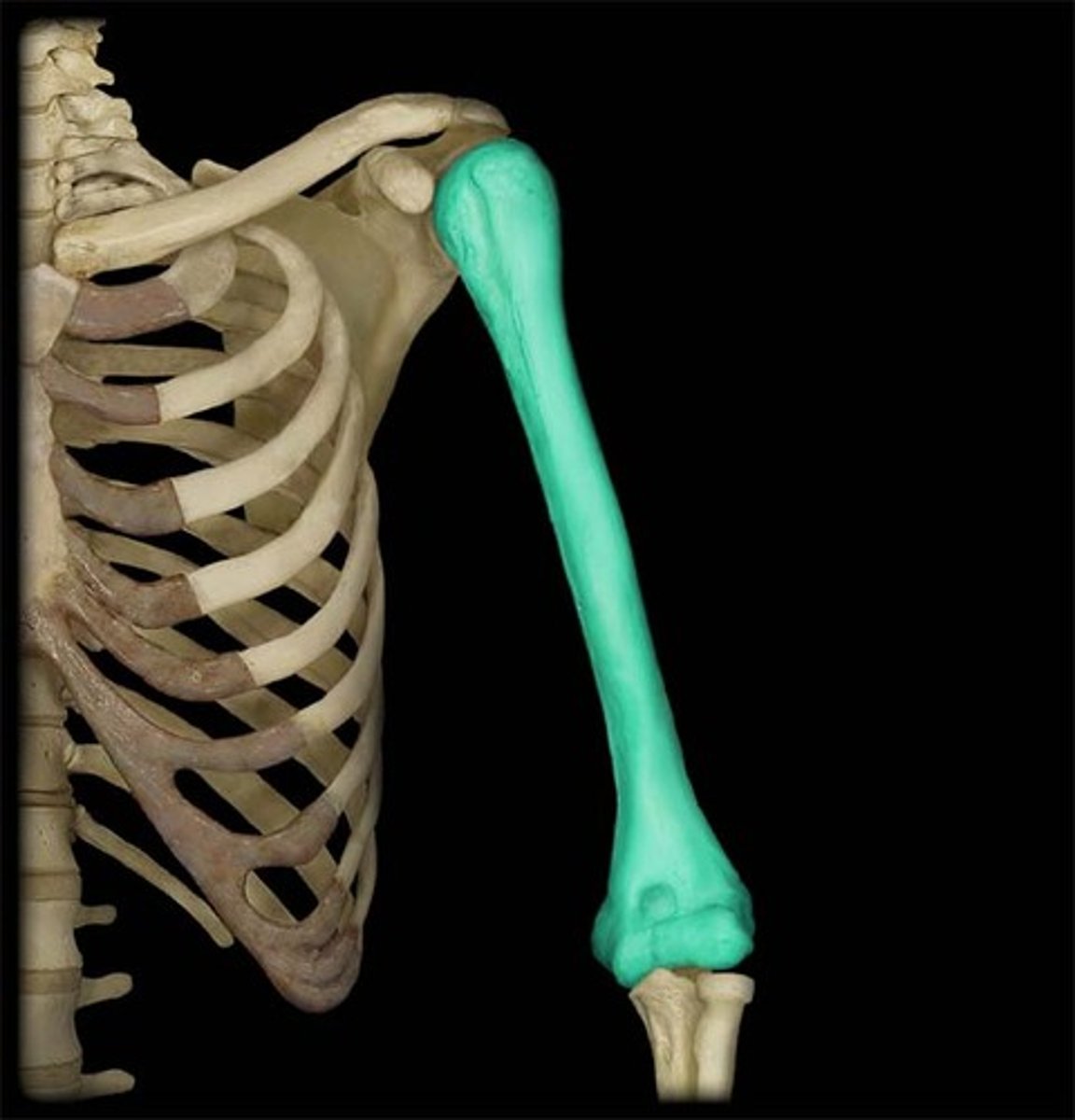
humerus head
rounded section of the humerus that articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula
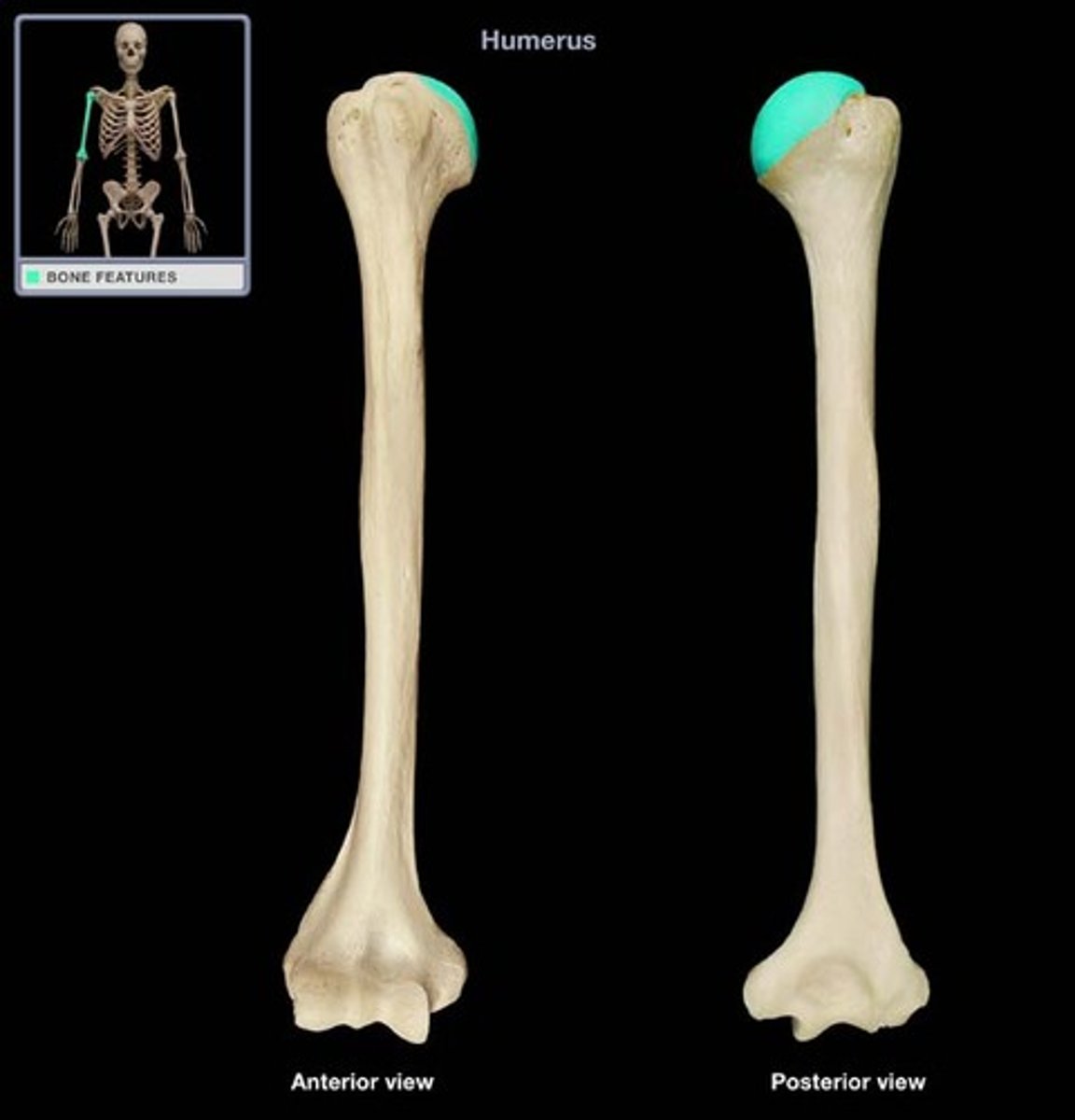
surgical neck
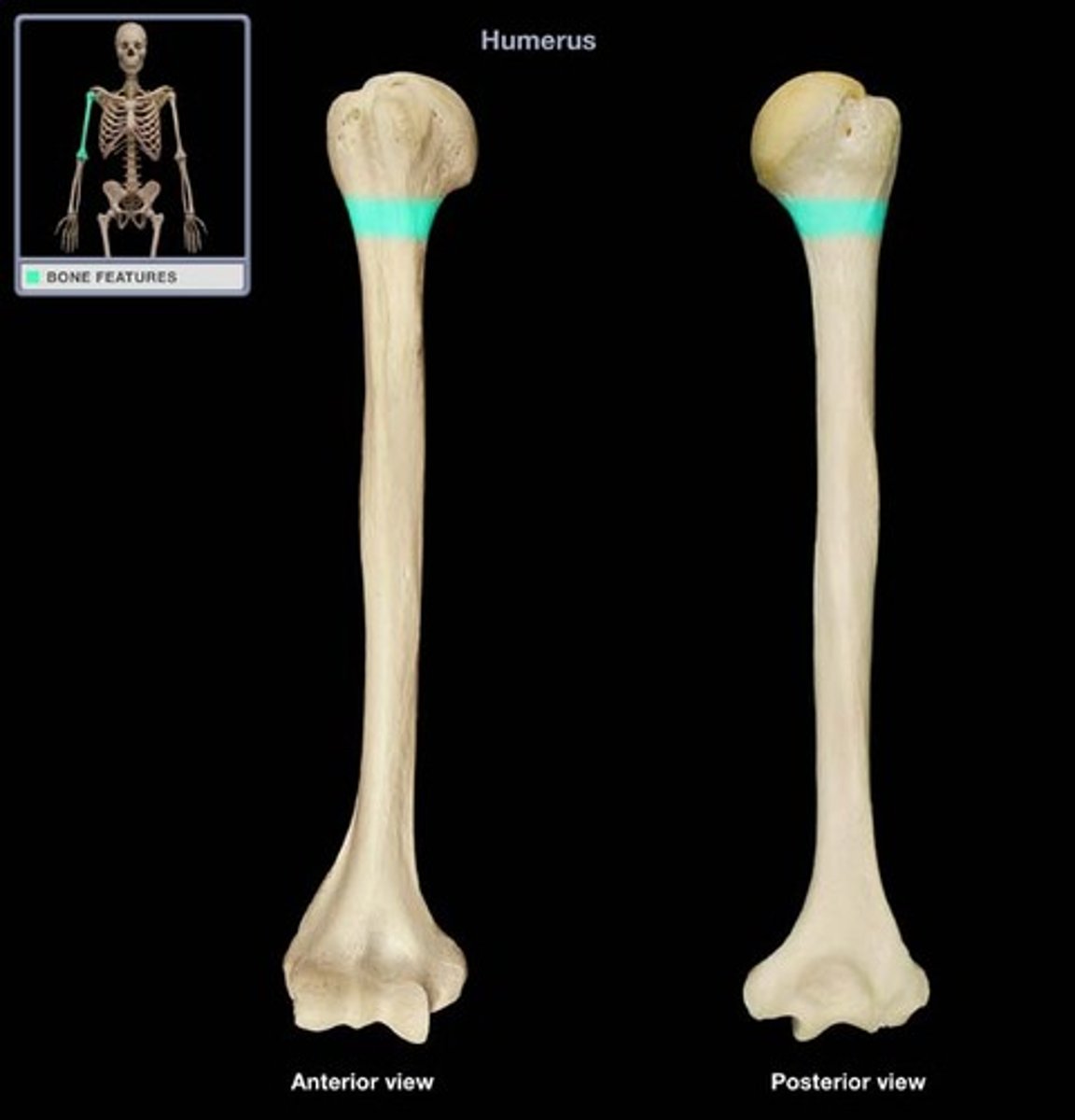
greater tubercle
Large lateral prominence on humerus
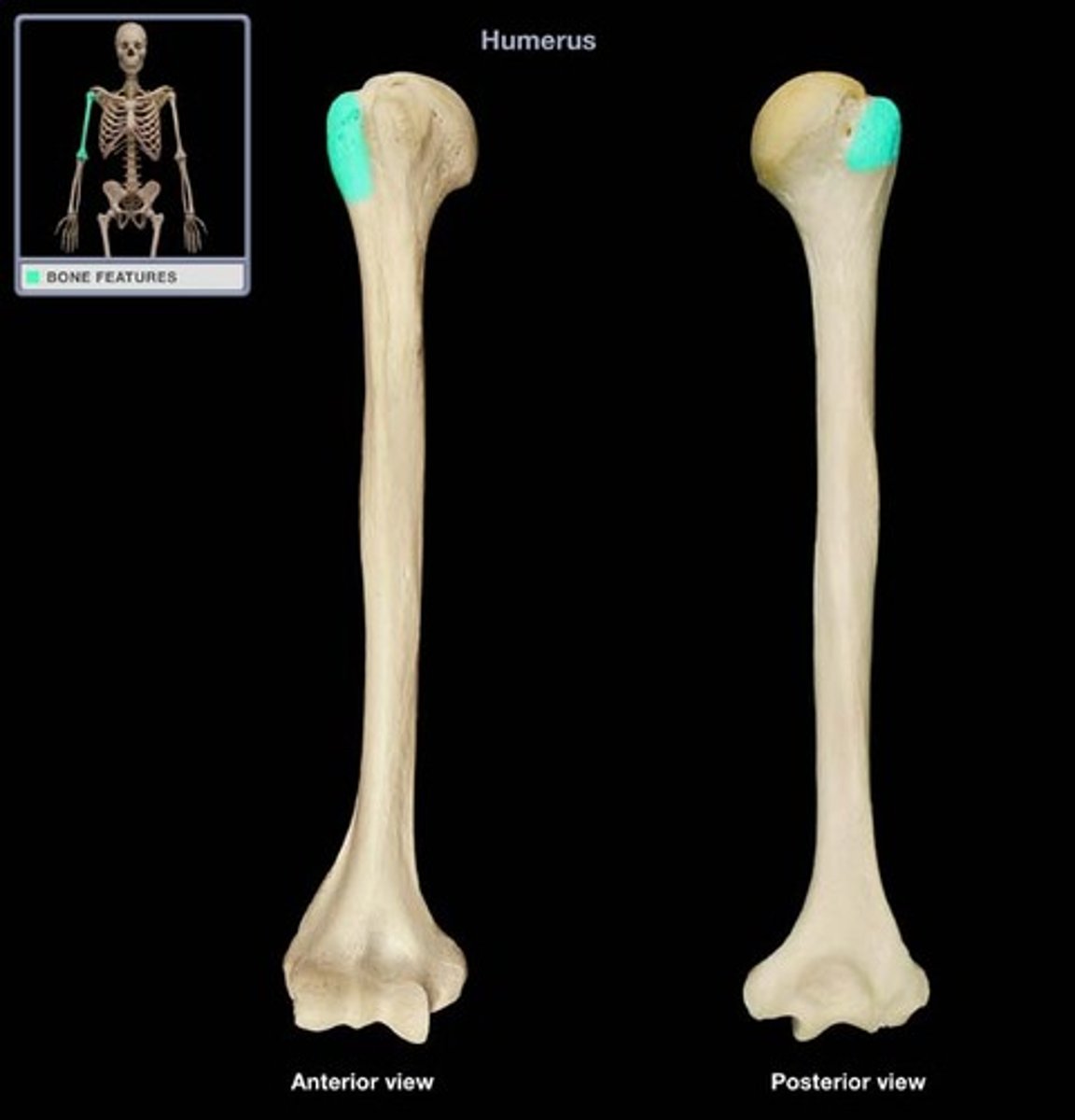
lesser tubercle
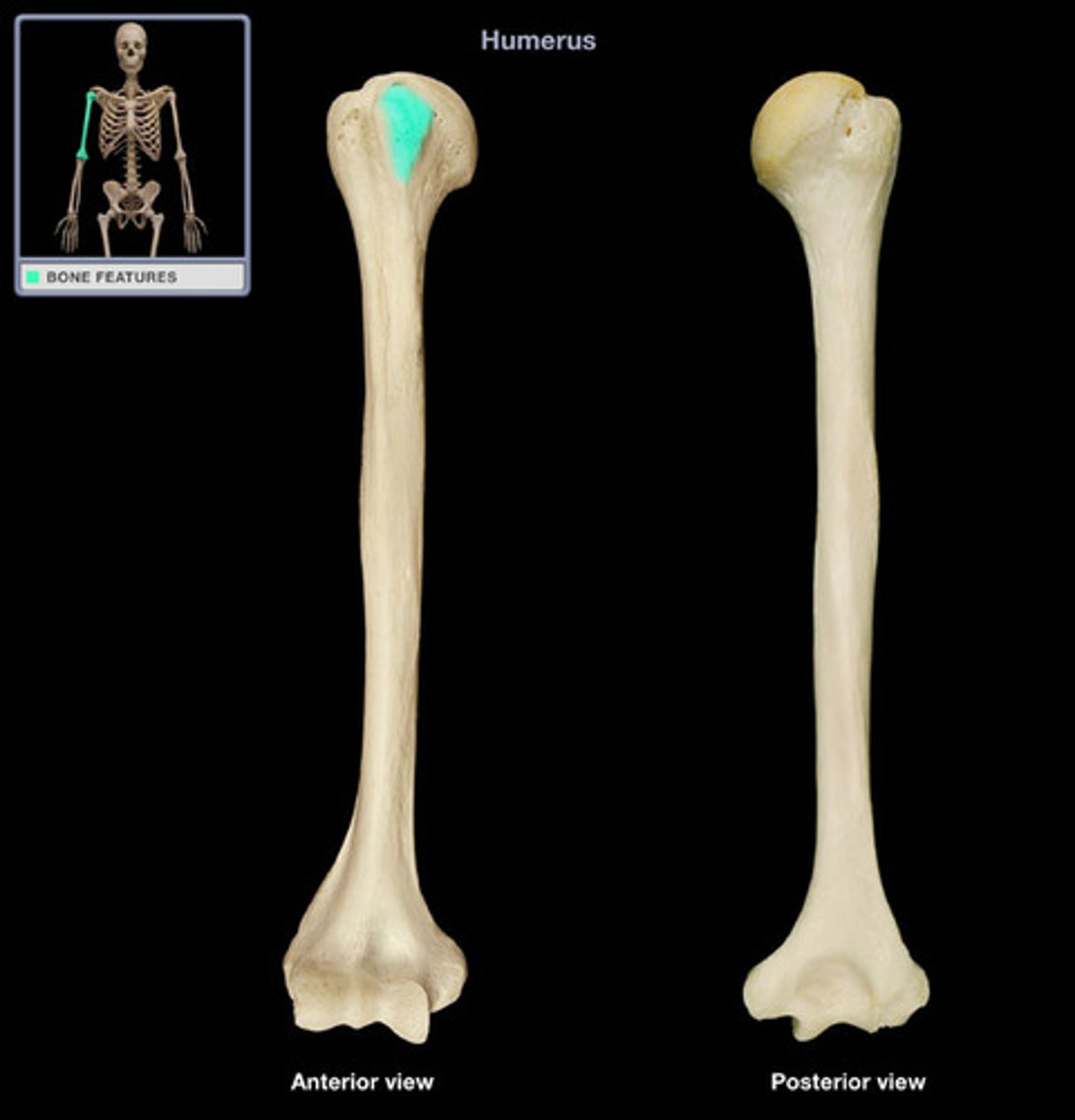
deltoid tuberosity
raised area on lateral surface of humerus to which deltoid muscle attaches
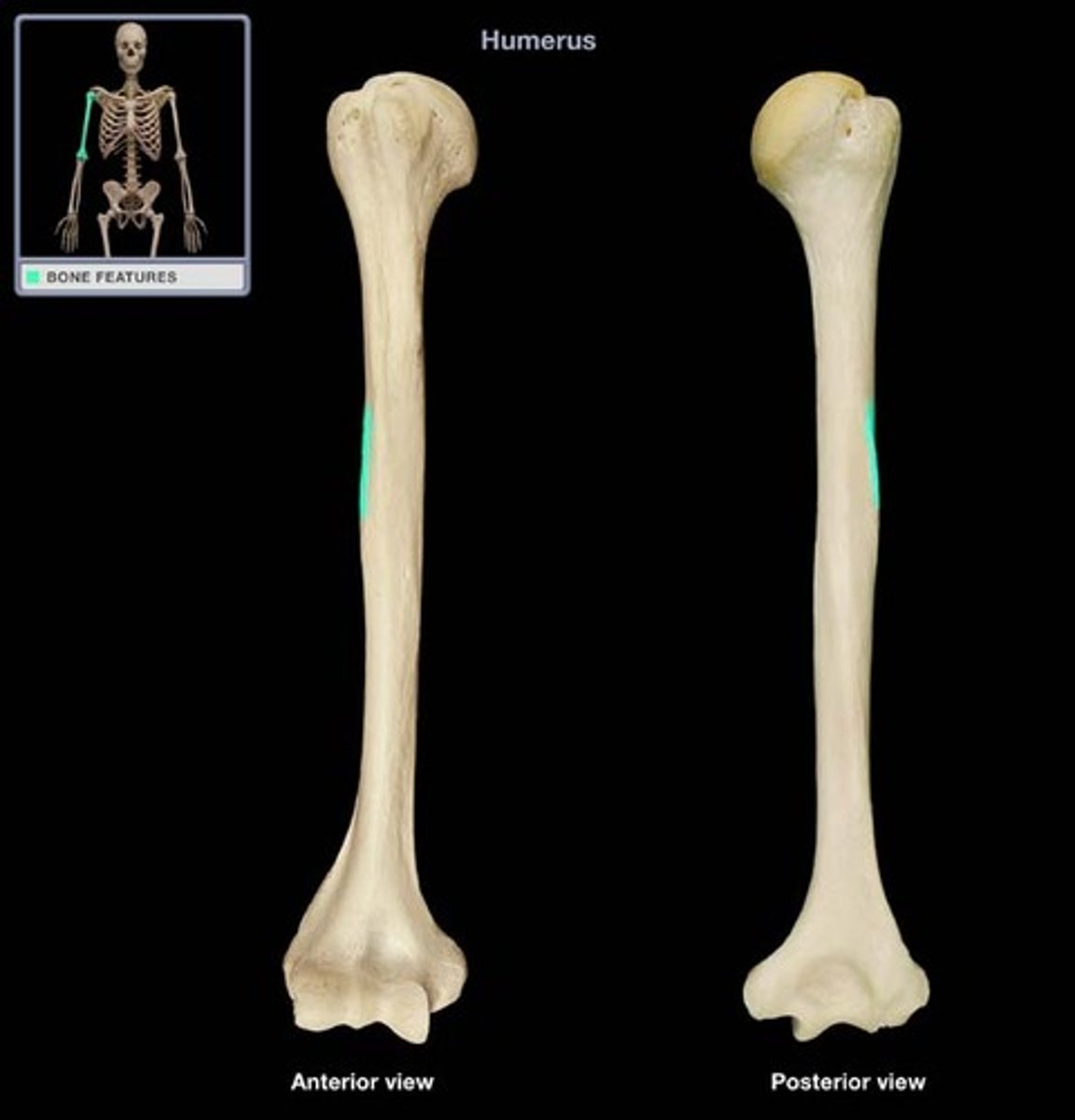
medial epicondyle (humerus)
lateral epicondyle (humerus)
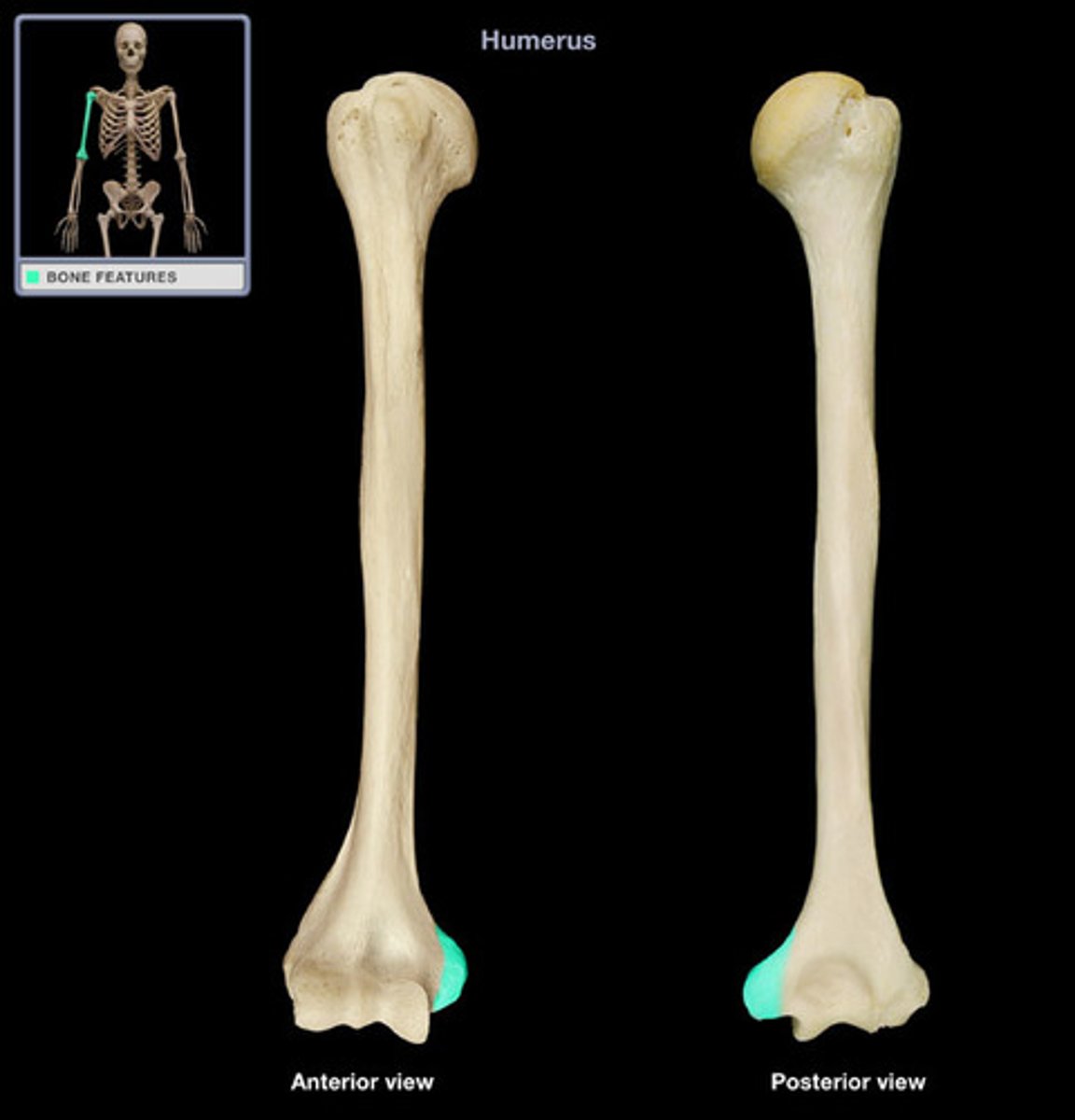
olecranon fossa
located on the posterior side of the distal end of the humerus superior to the trochlea and articulates with the olecranon process of the ulna
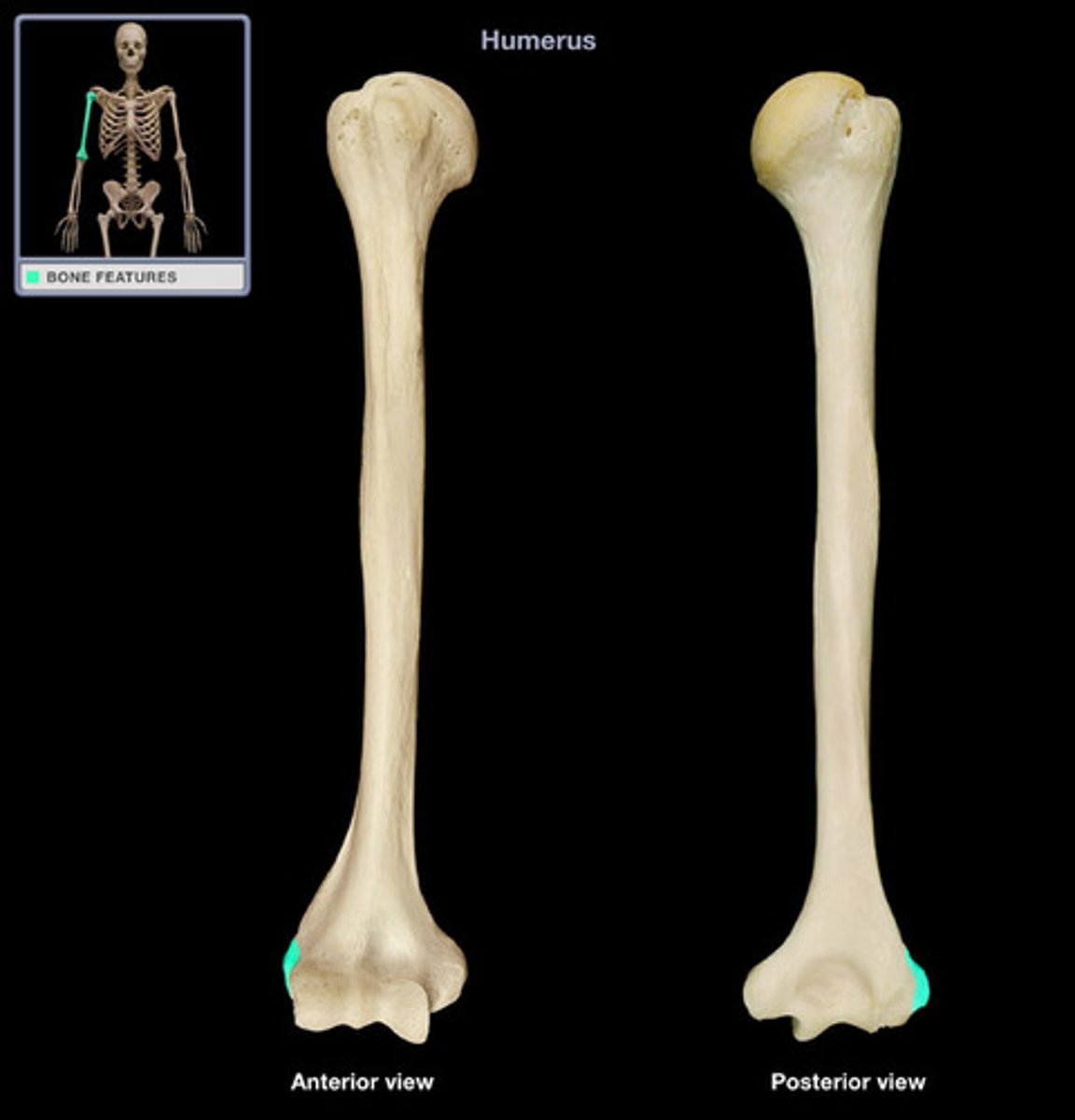
coronoid fossa
anterior depression that receives the coronoid process of the ulna
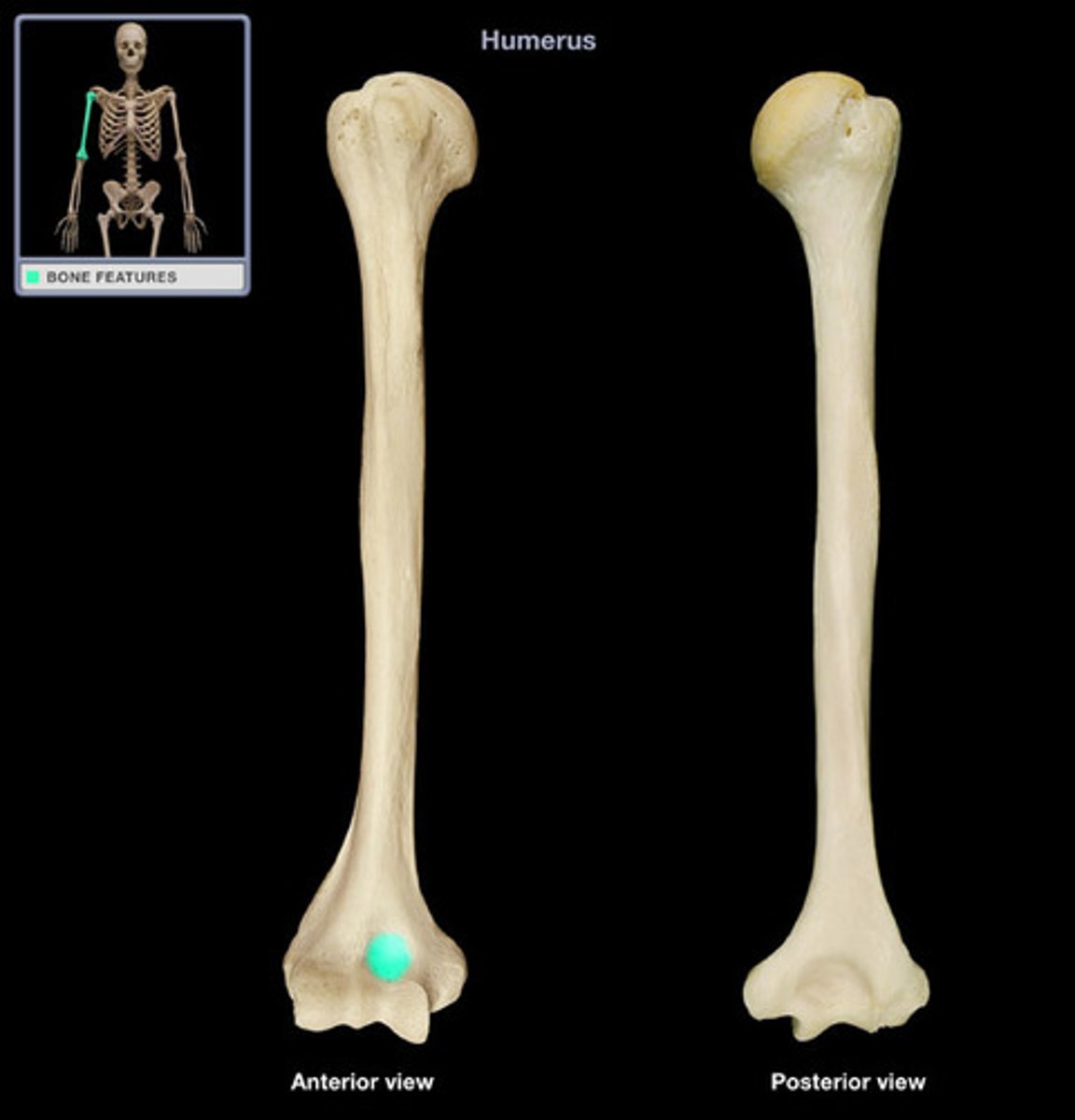
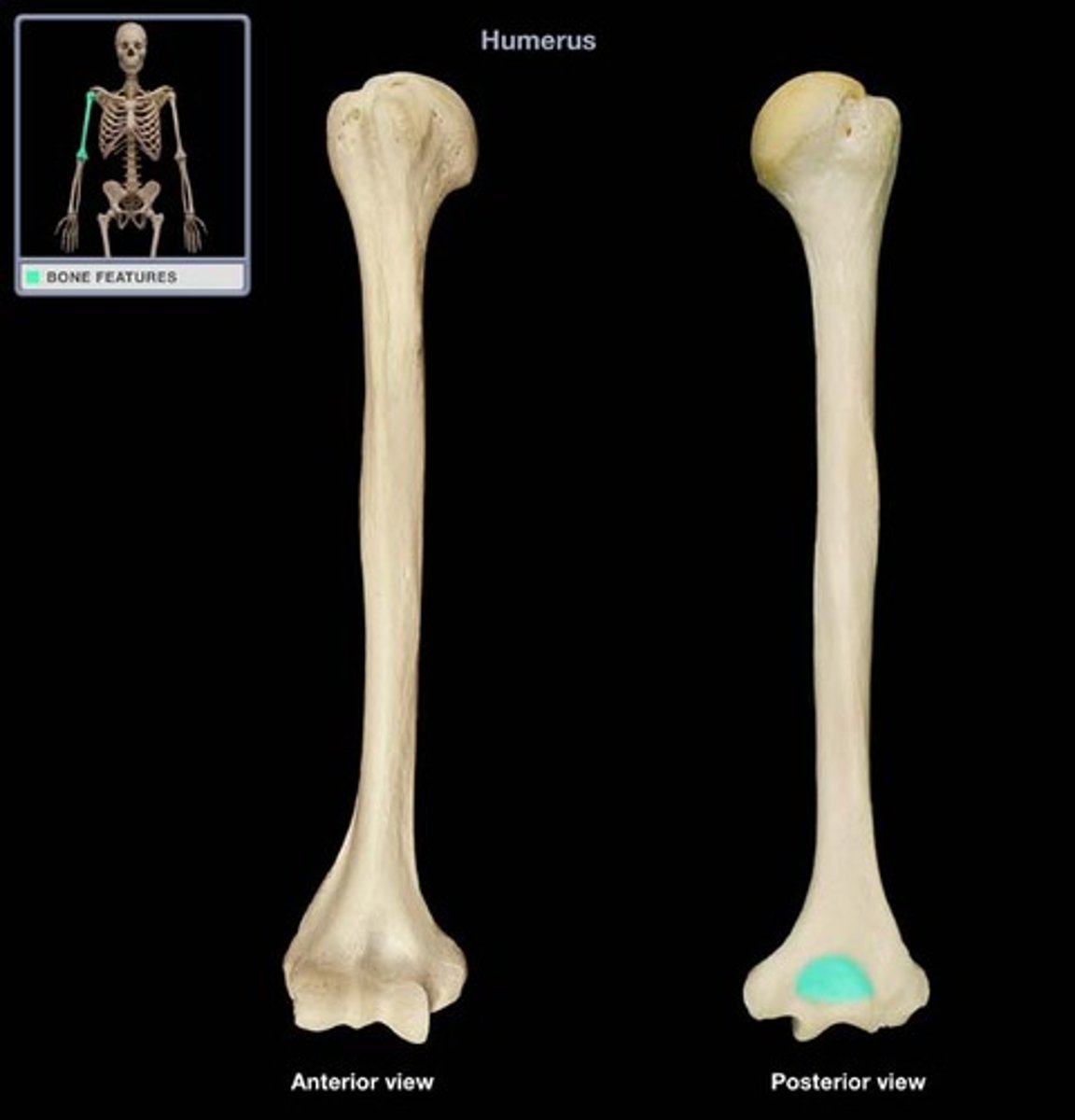
trochlea
a smooth, grooved articular process shaped like a pulley
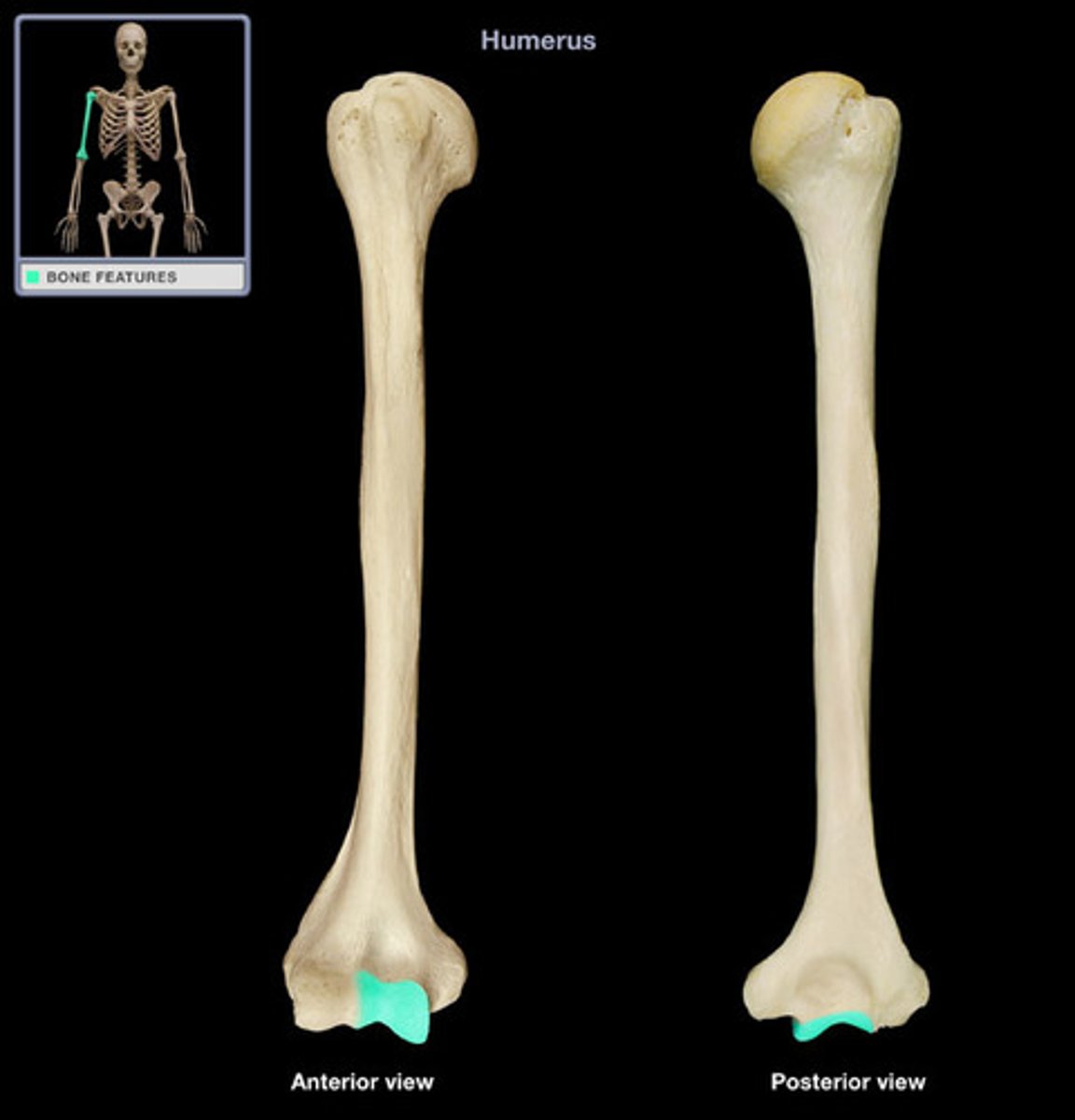
capitulum
ulna
medial bone of the forearm
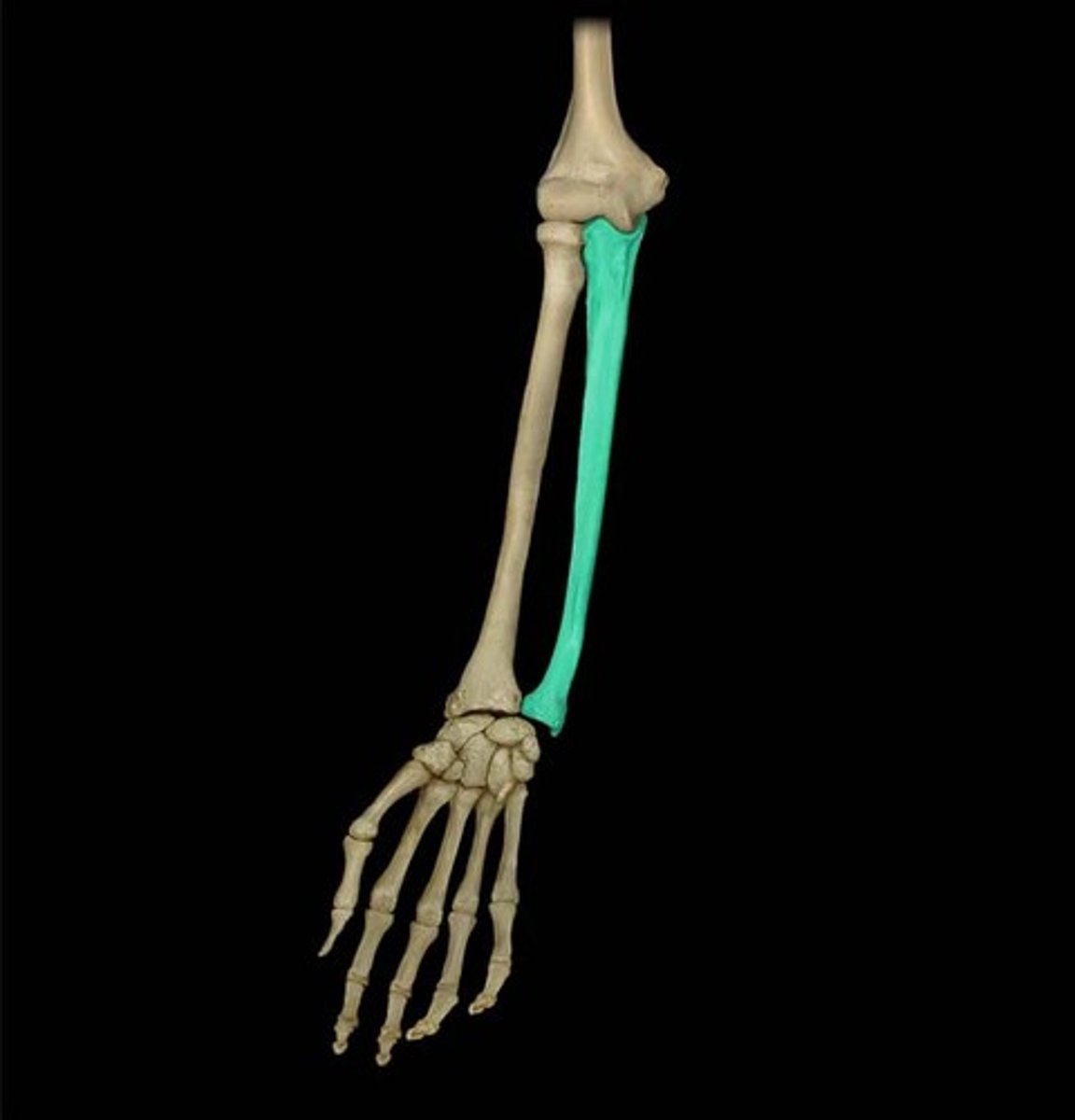
ulna coronoid process
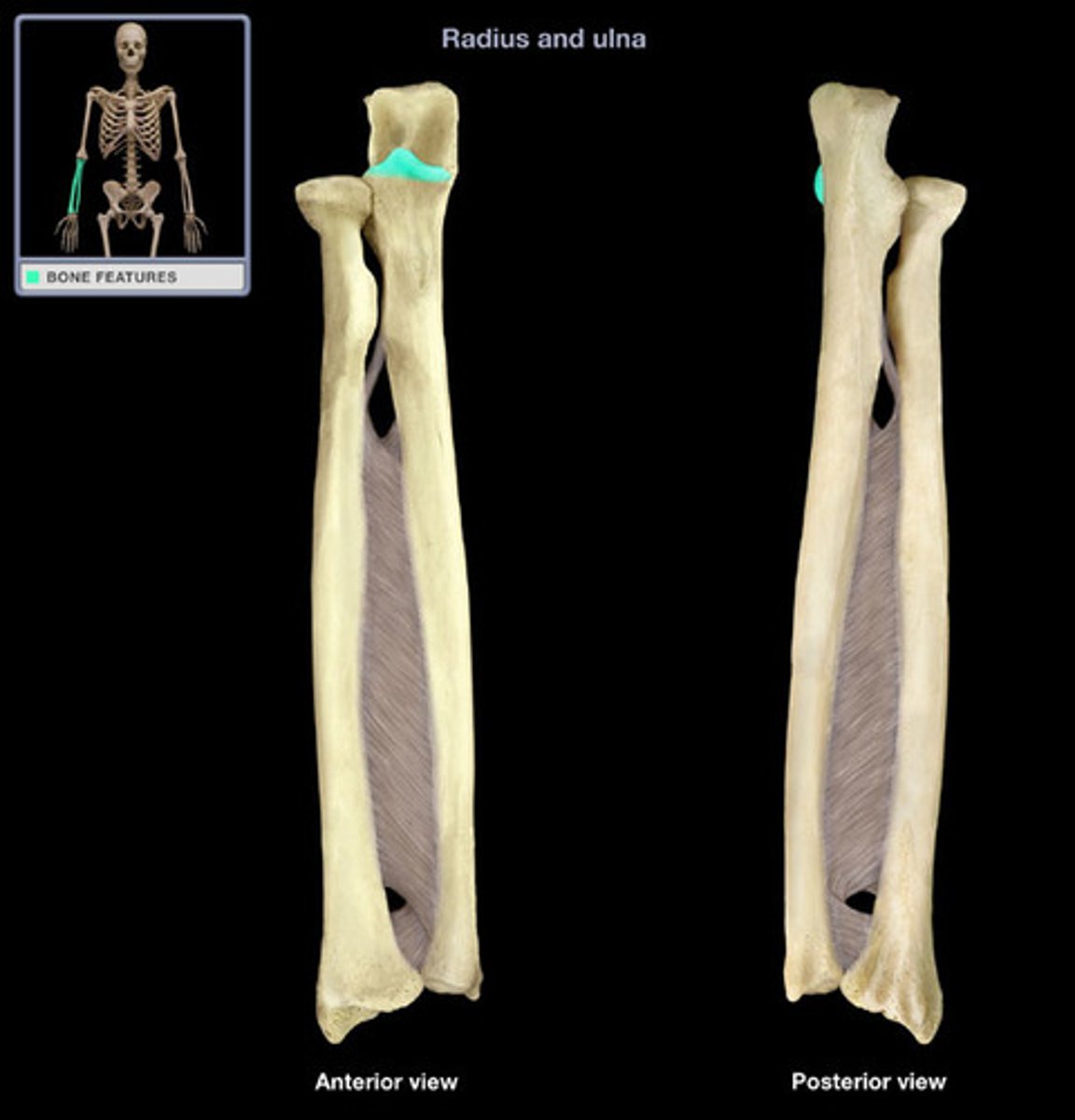
ulna olecranon process
elbow
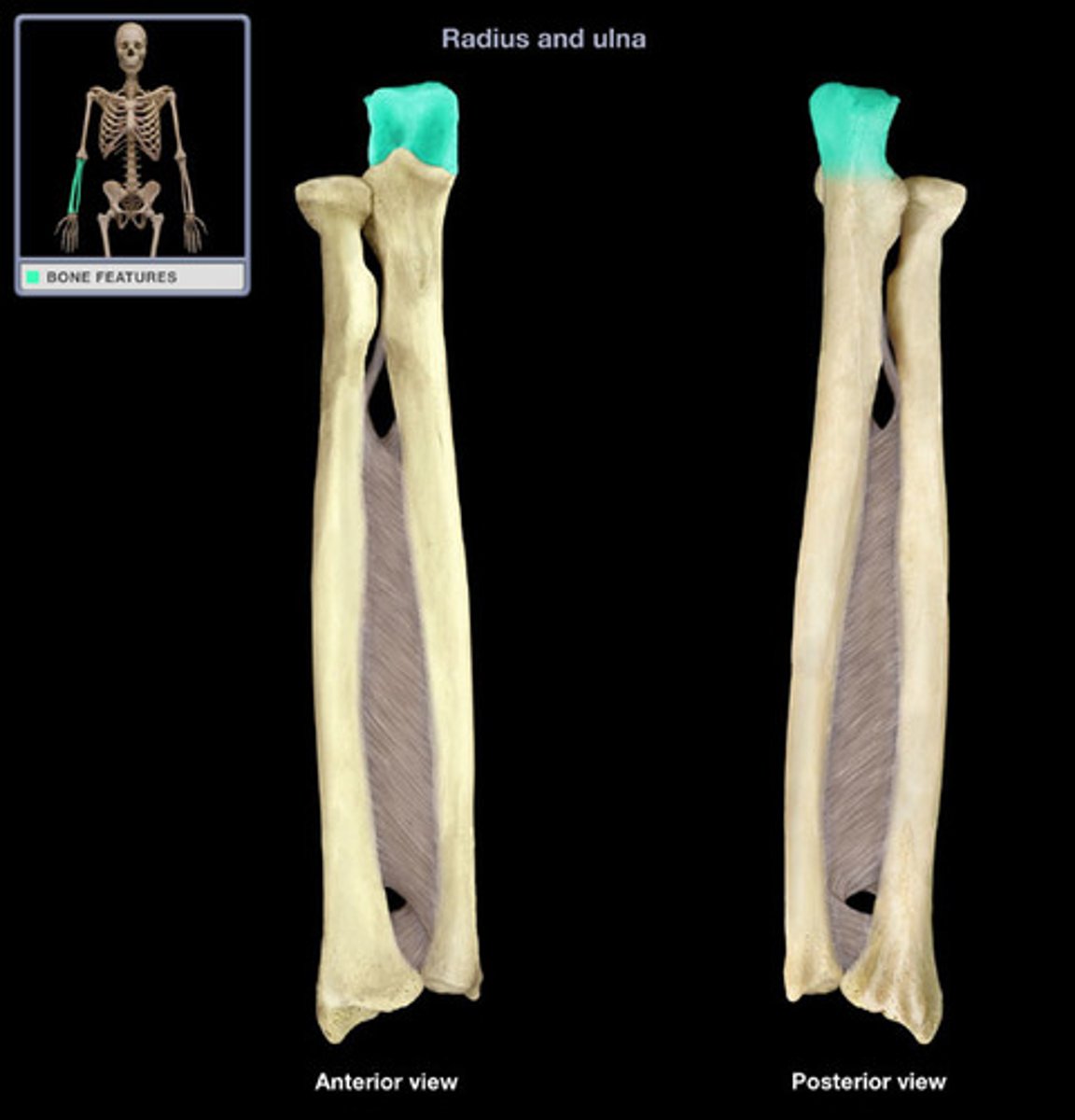
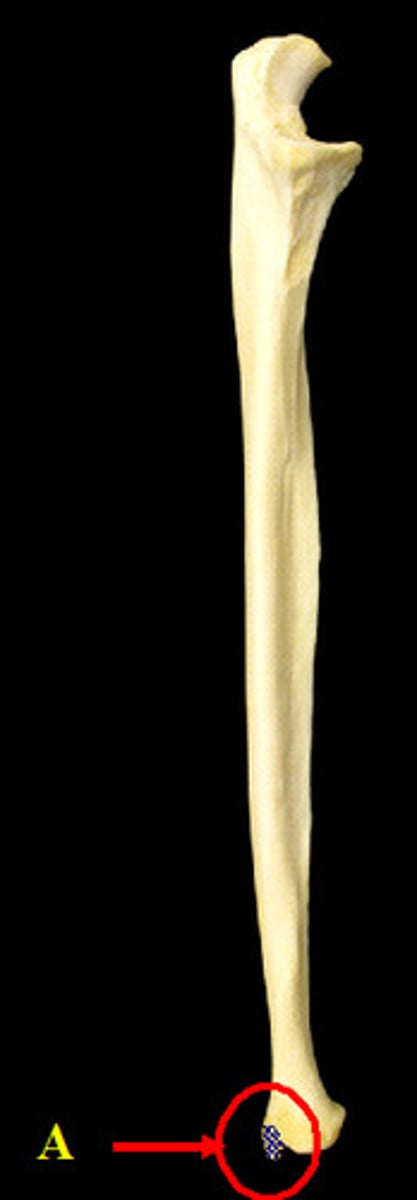
ulna styloid process
pointy projection on the distal end of ulna
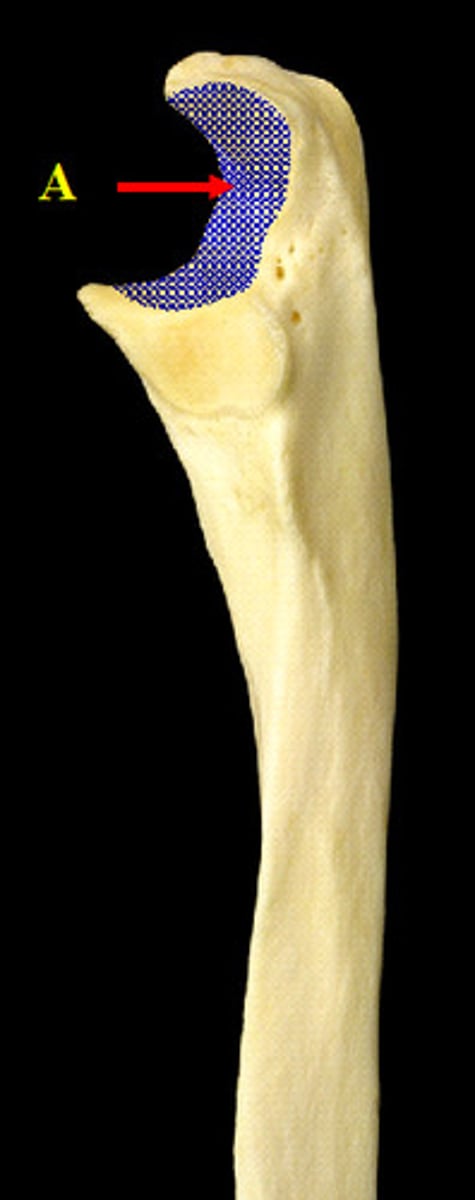
ulna trochlear notch
deep notch that separates the olecranon and the coronoid process; articulates with the trochlea of the humerus
radius
lateral bone of the forearm
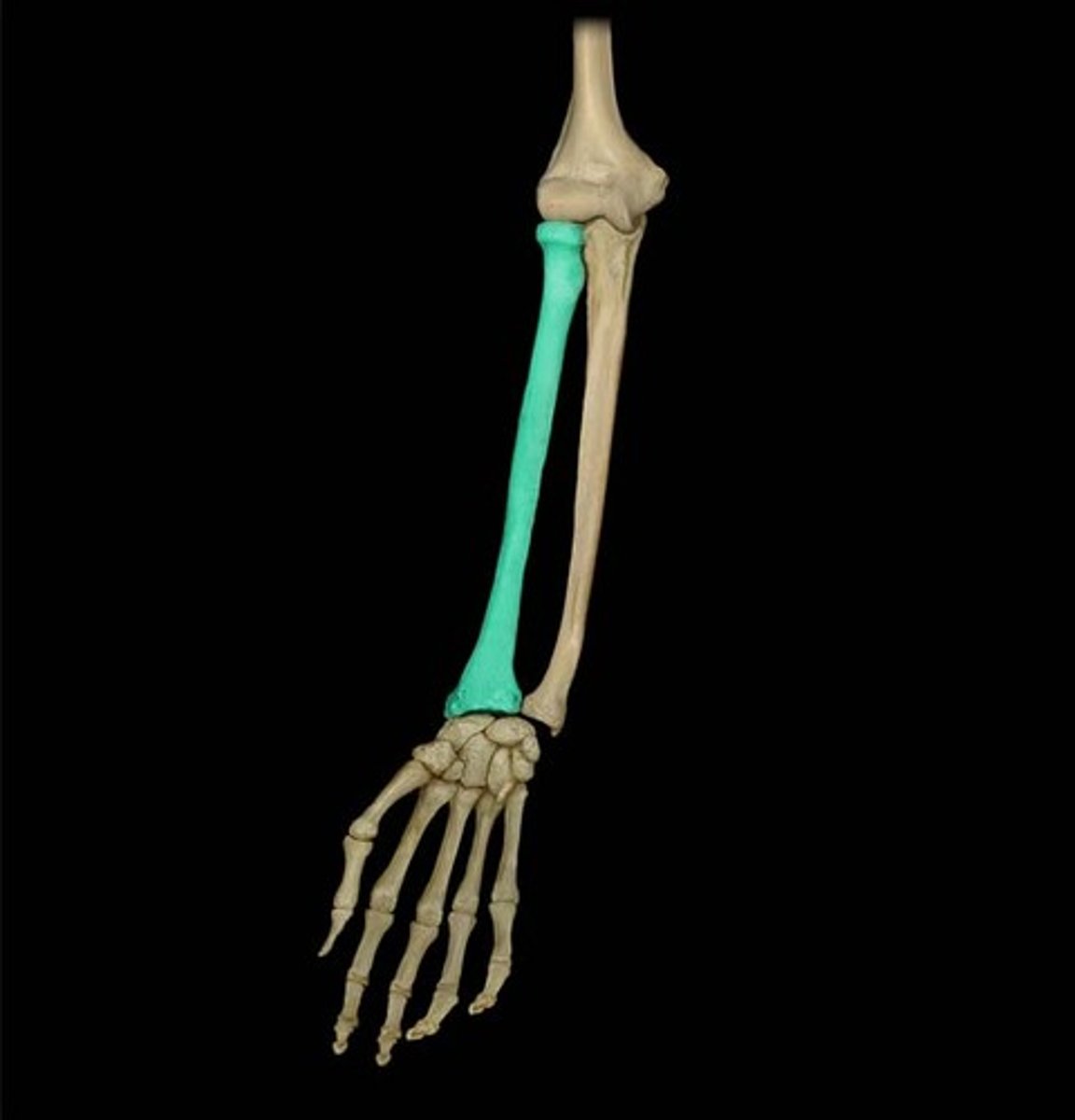
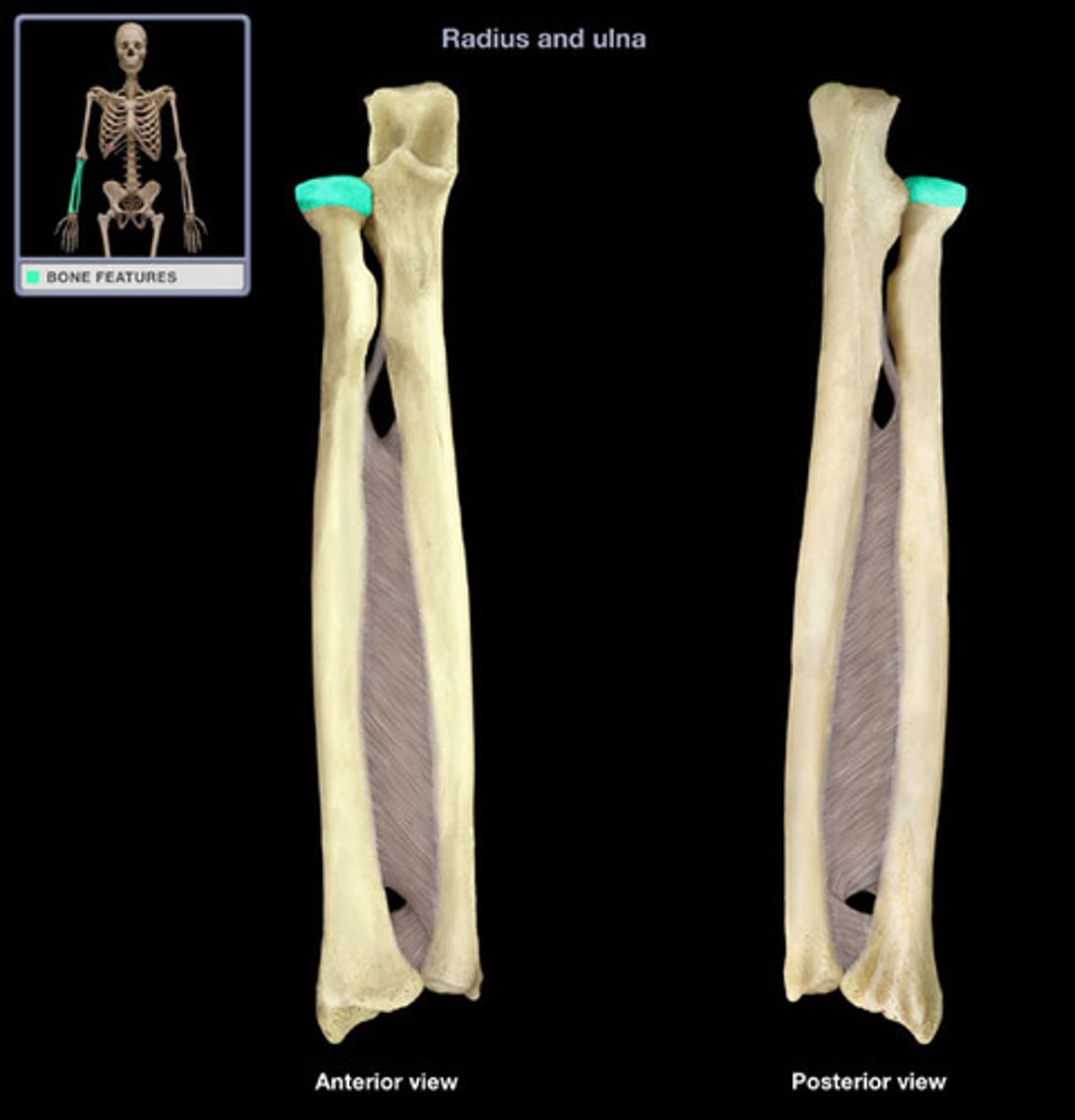
radius head
A round, articular structure on the proximal end of the radius.
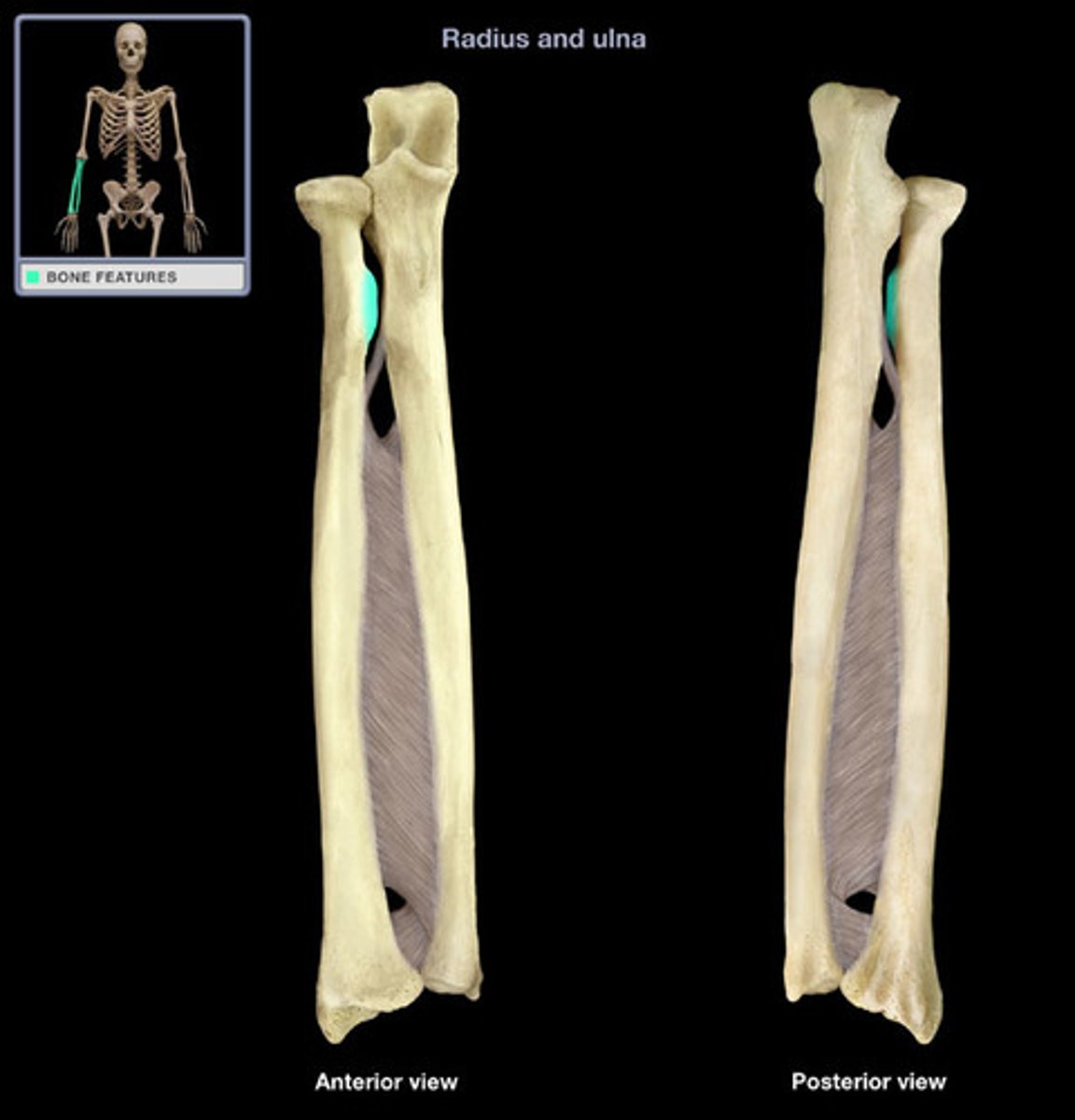
radial tuberosity
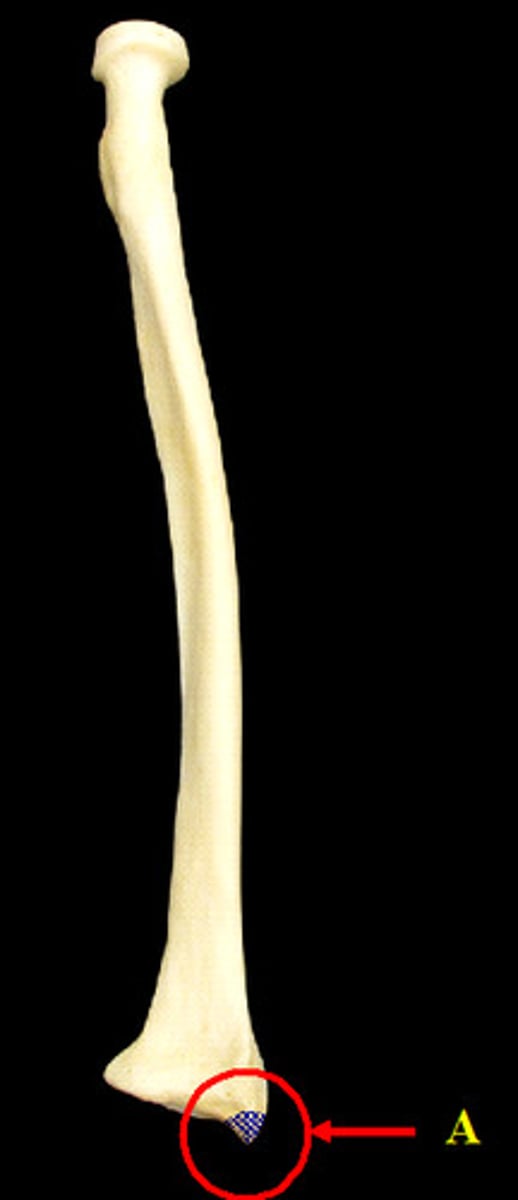
radius styloid process
projection of bone on the lateral surface of the distal radius bone
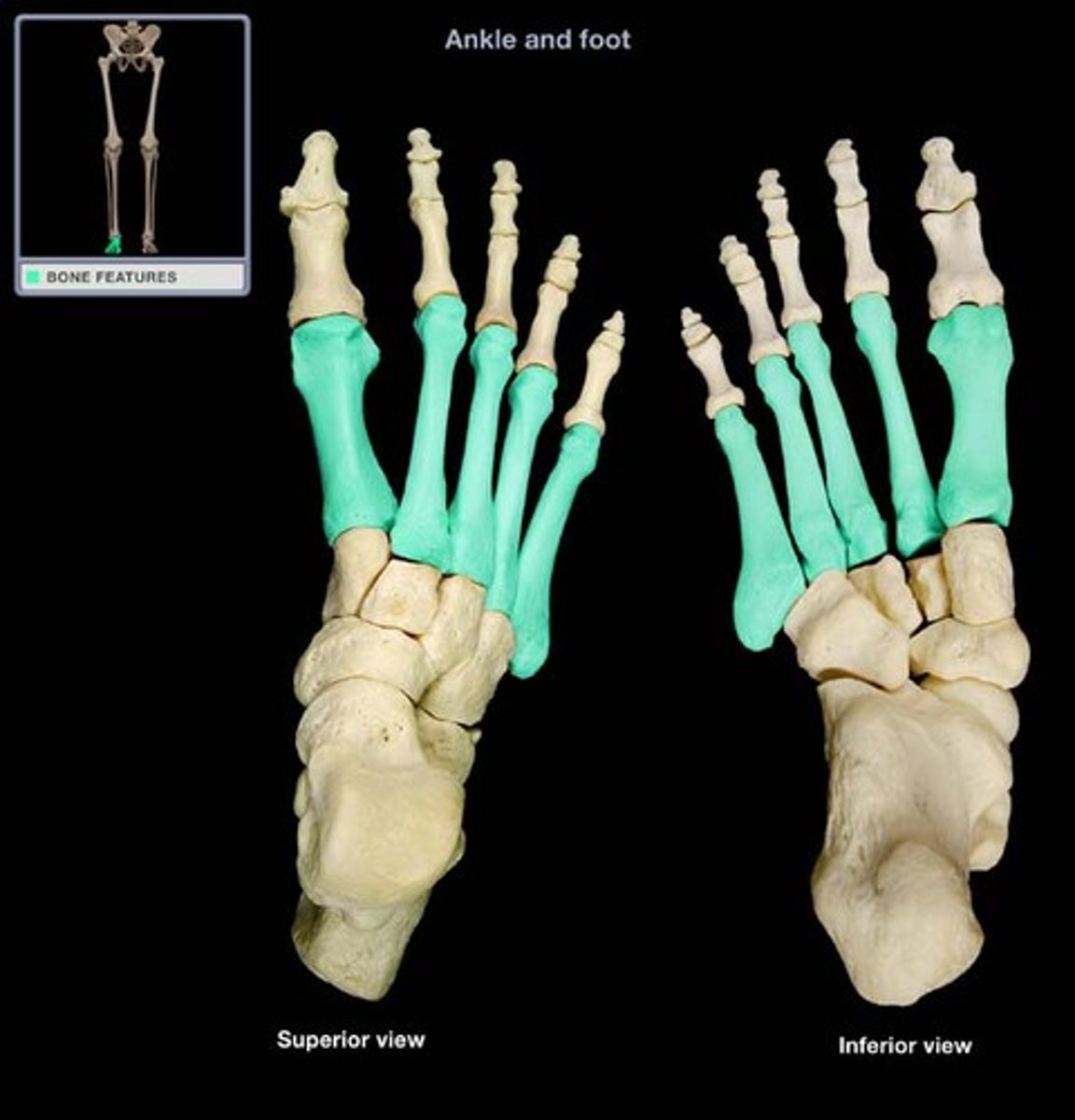
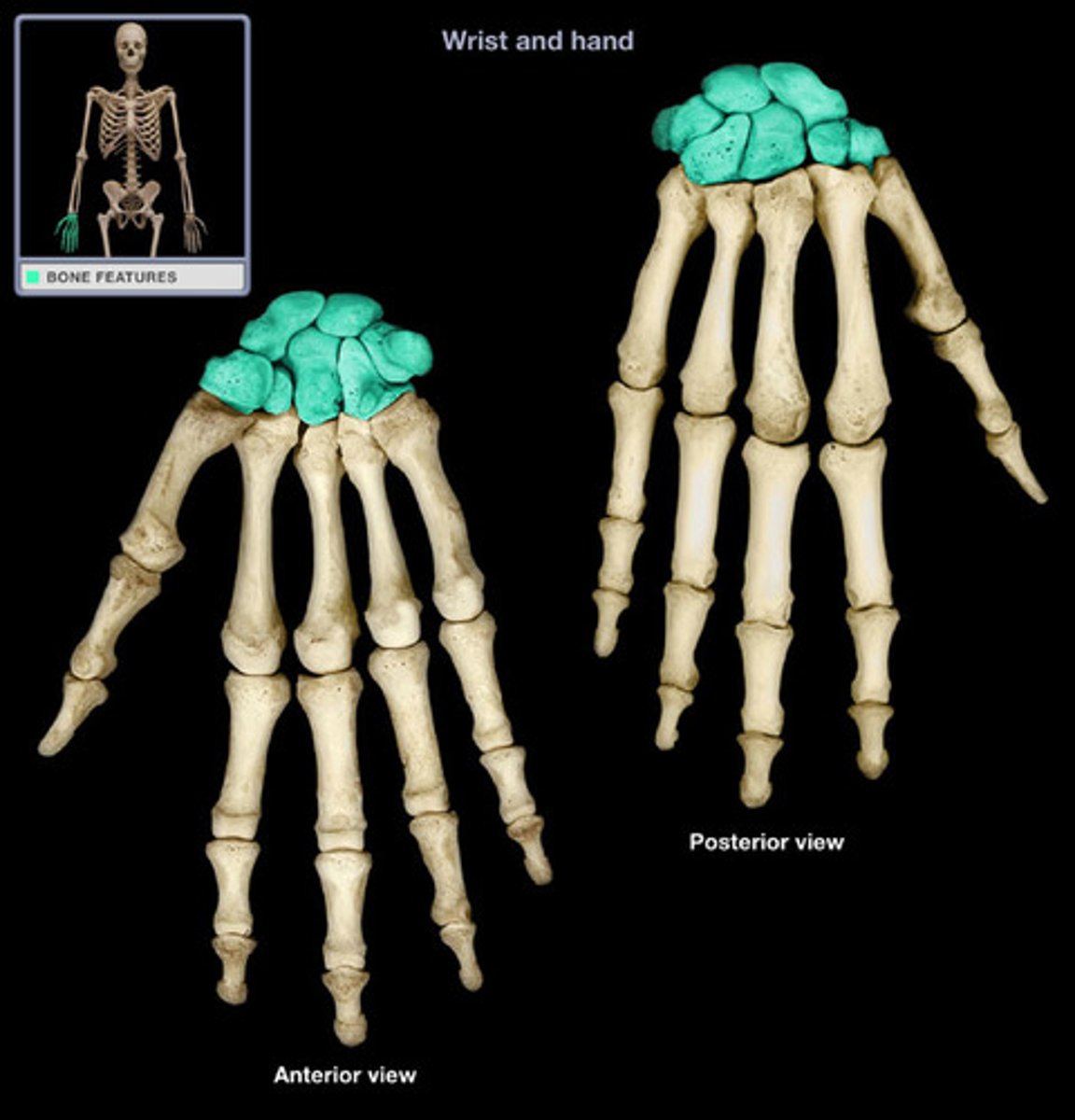
carpals
bones of the wrist
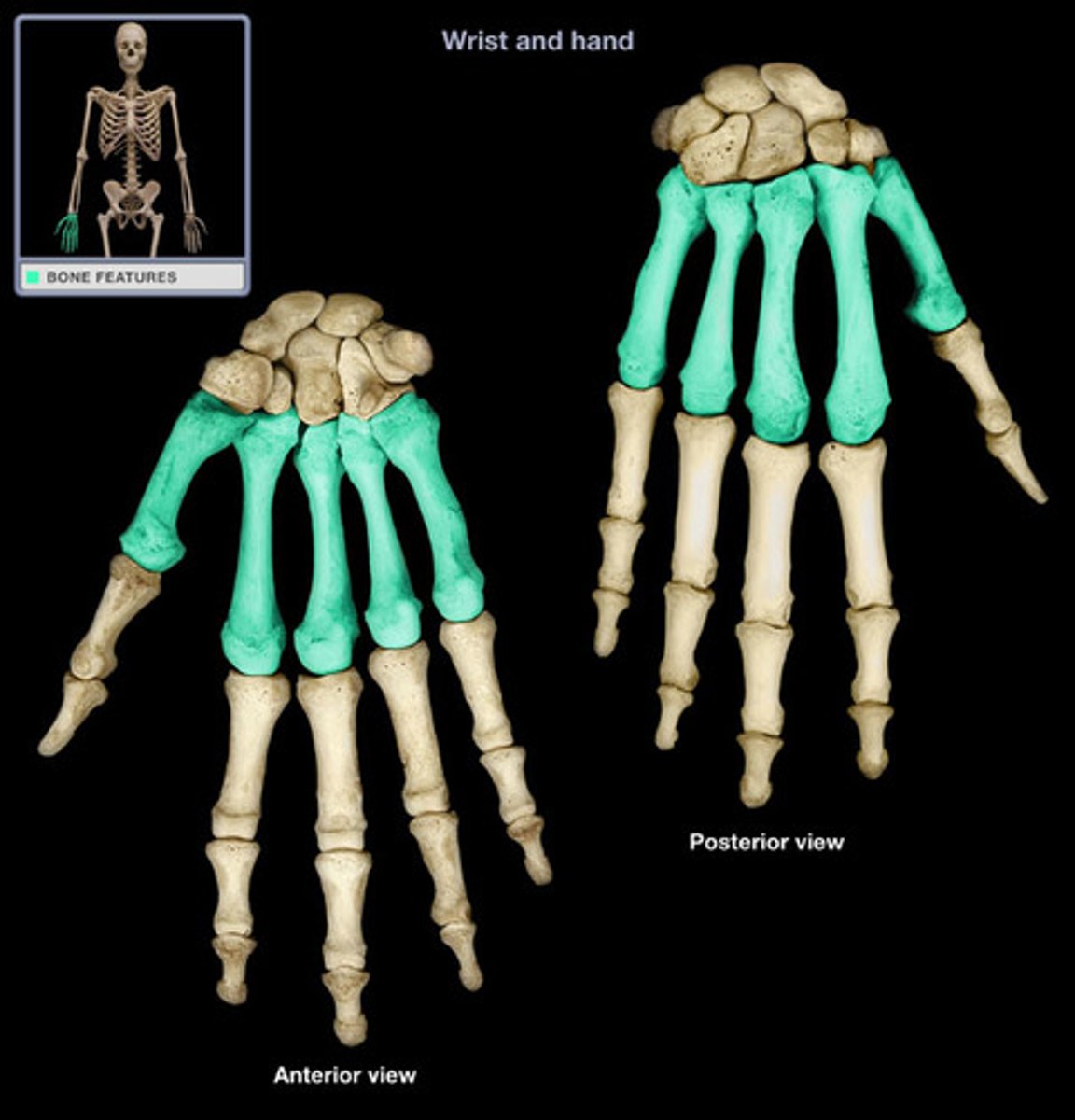
metacarpals
the five bones that form the palms of the hand
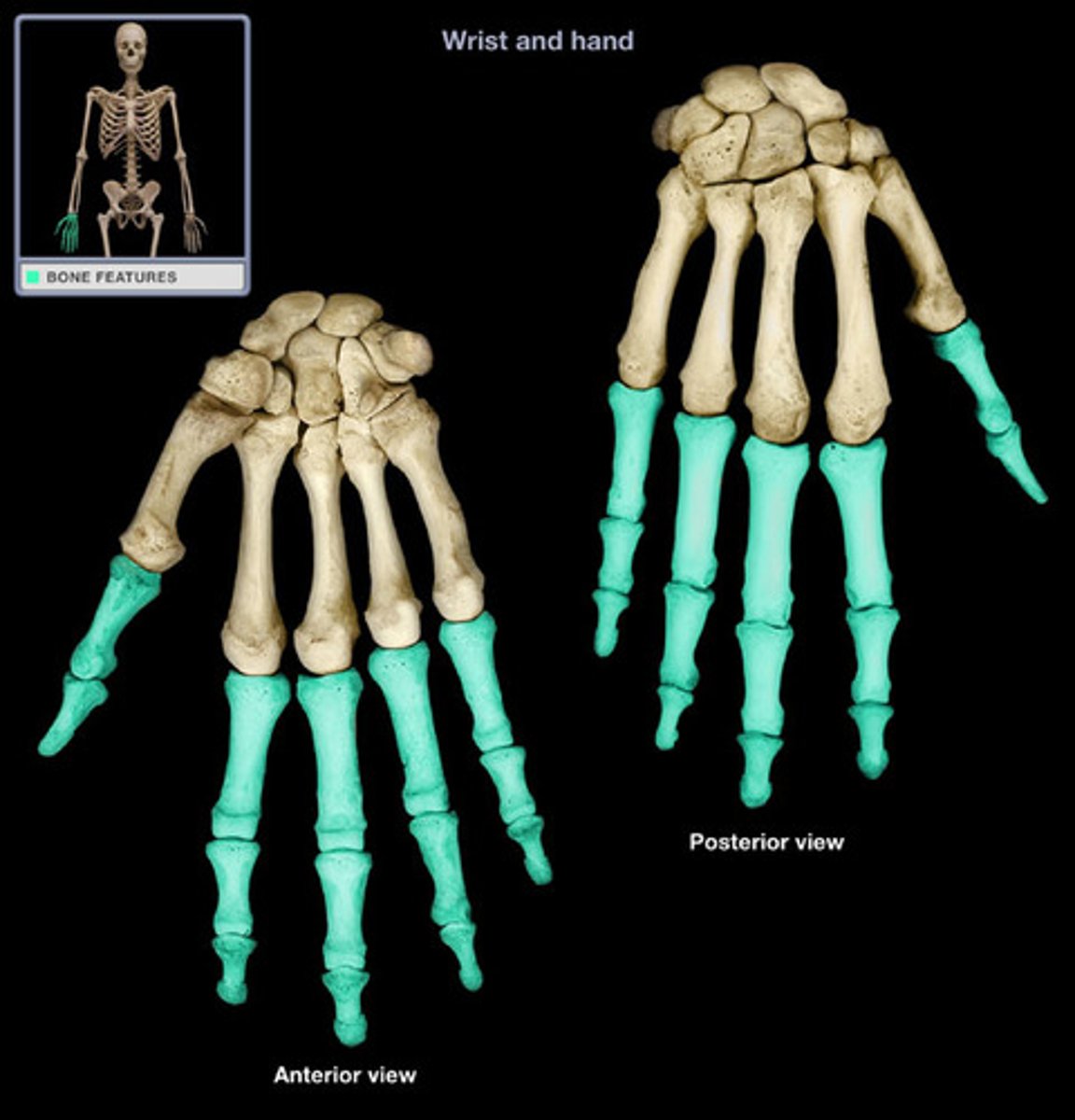
phalanges
bones of the fingers and toes
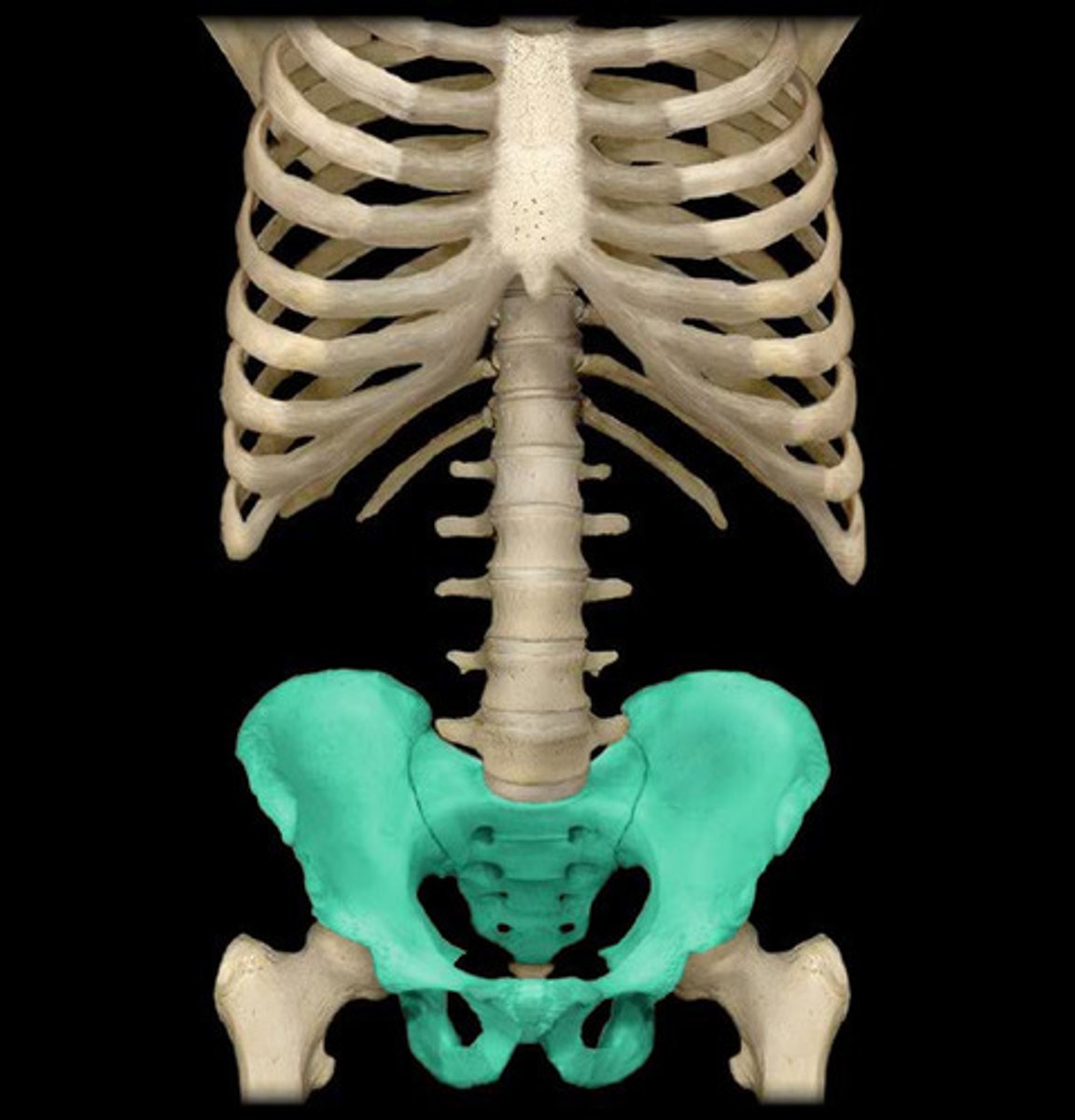
pelvic girdle
coxal bones and sacrum
ilium
the superior and widest portion of the pelvis
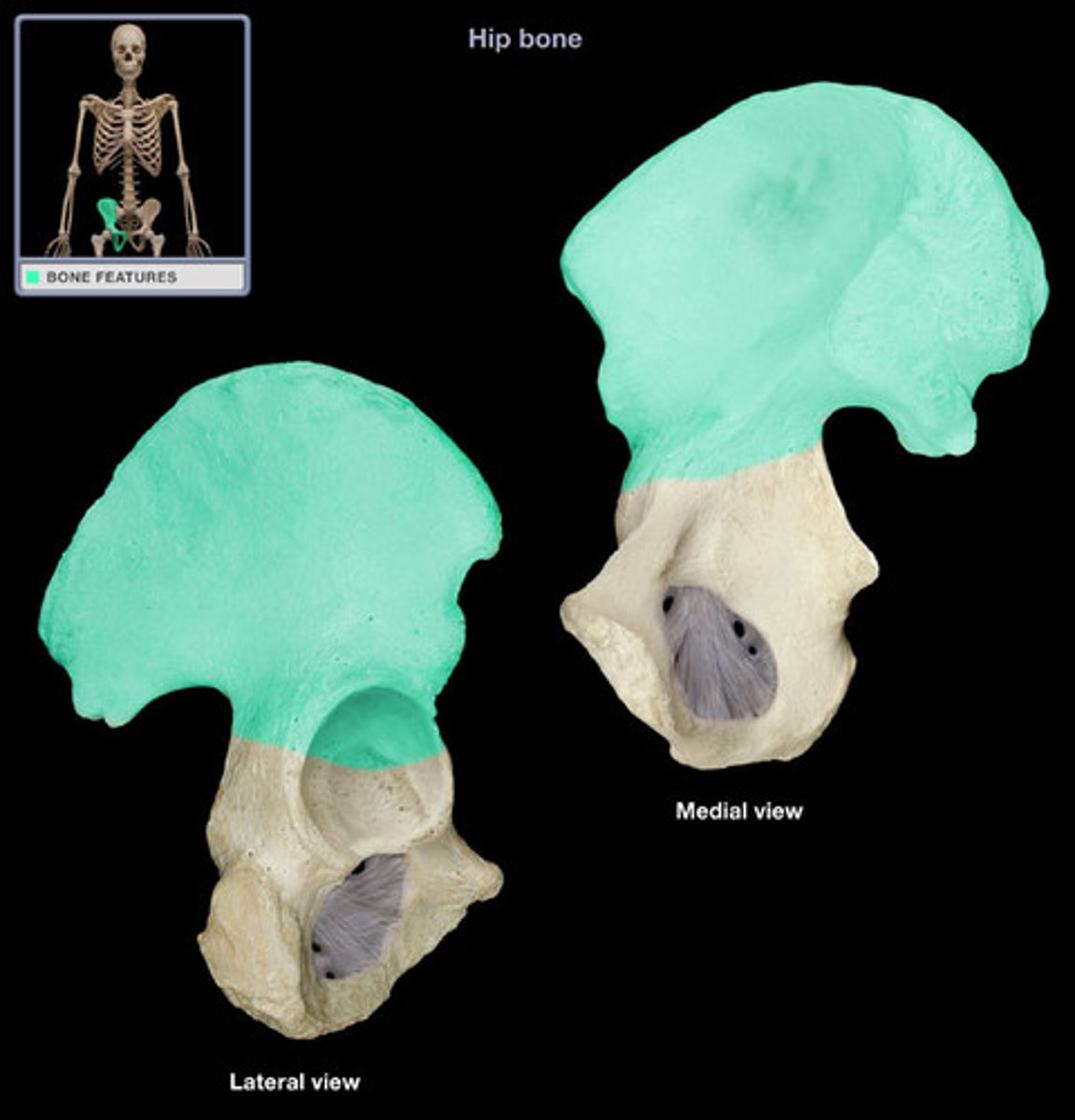
pubis
The medial anterior portion of the pelvis
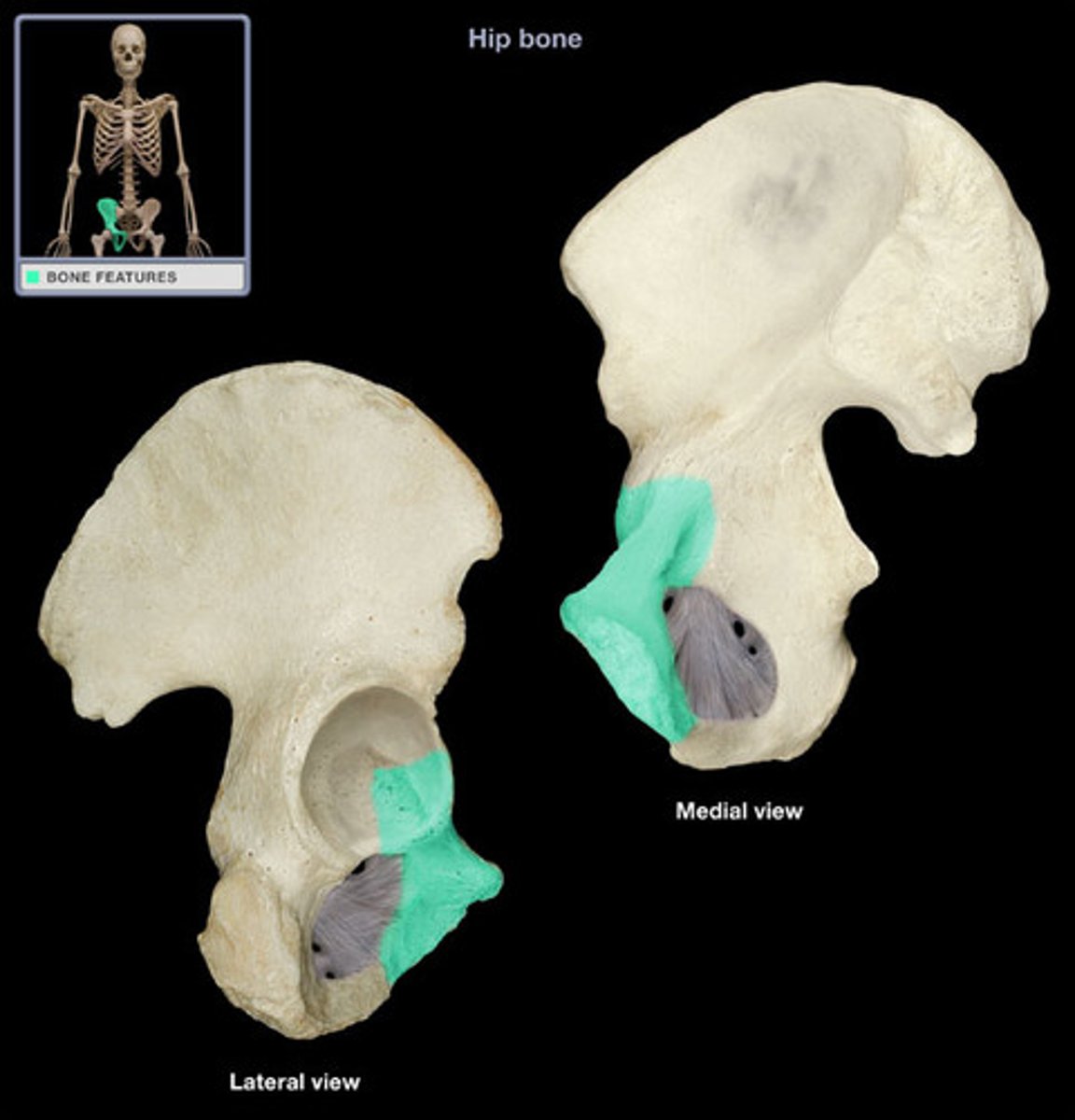
ischium
the lower, posterior portions of the pelvis
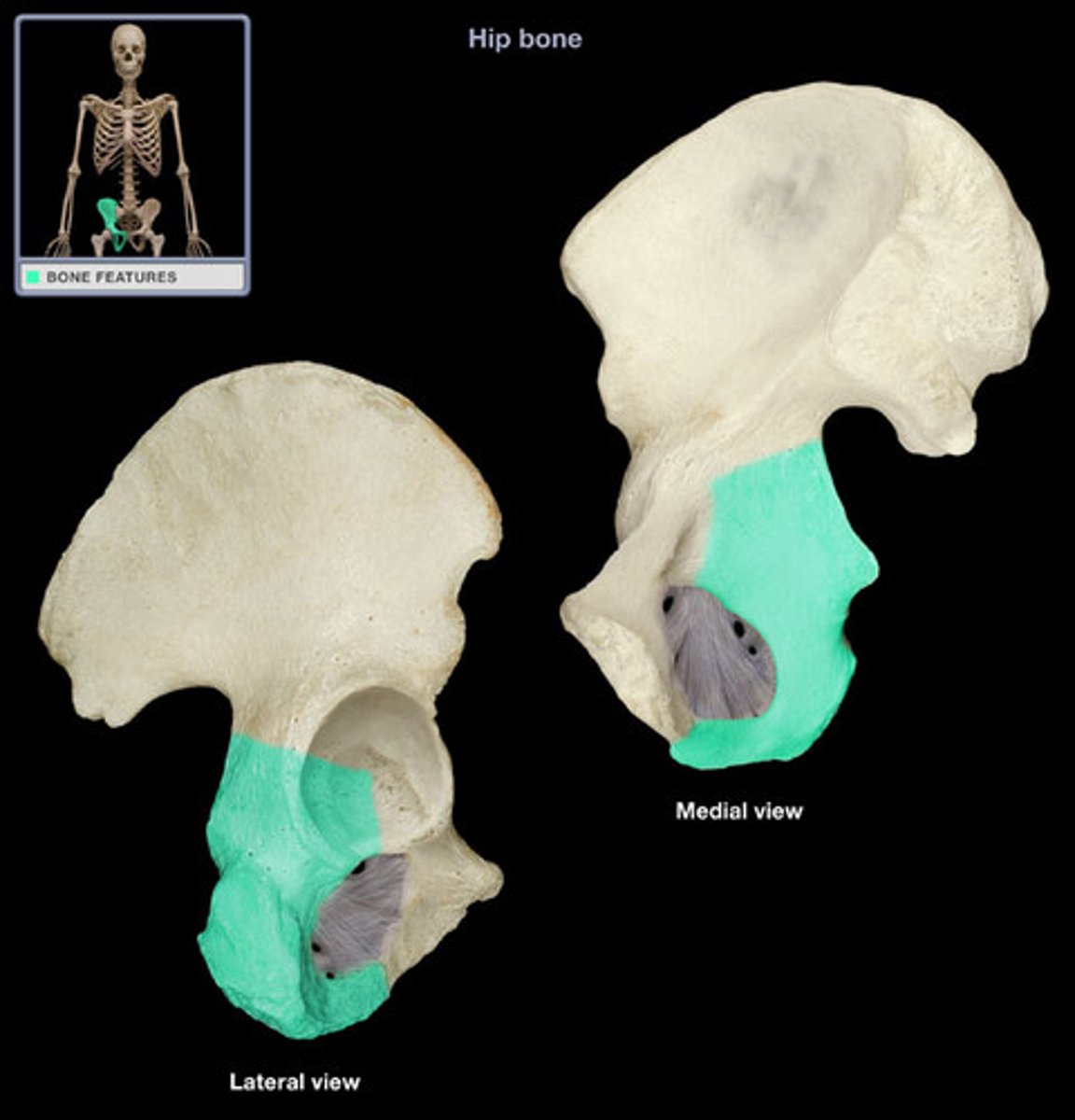
iliac crest
superior border of ilium
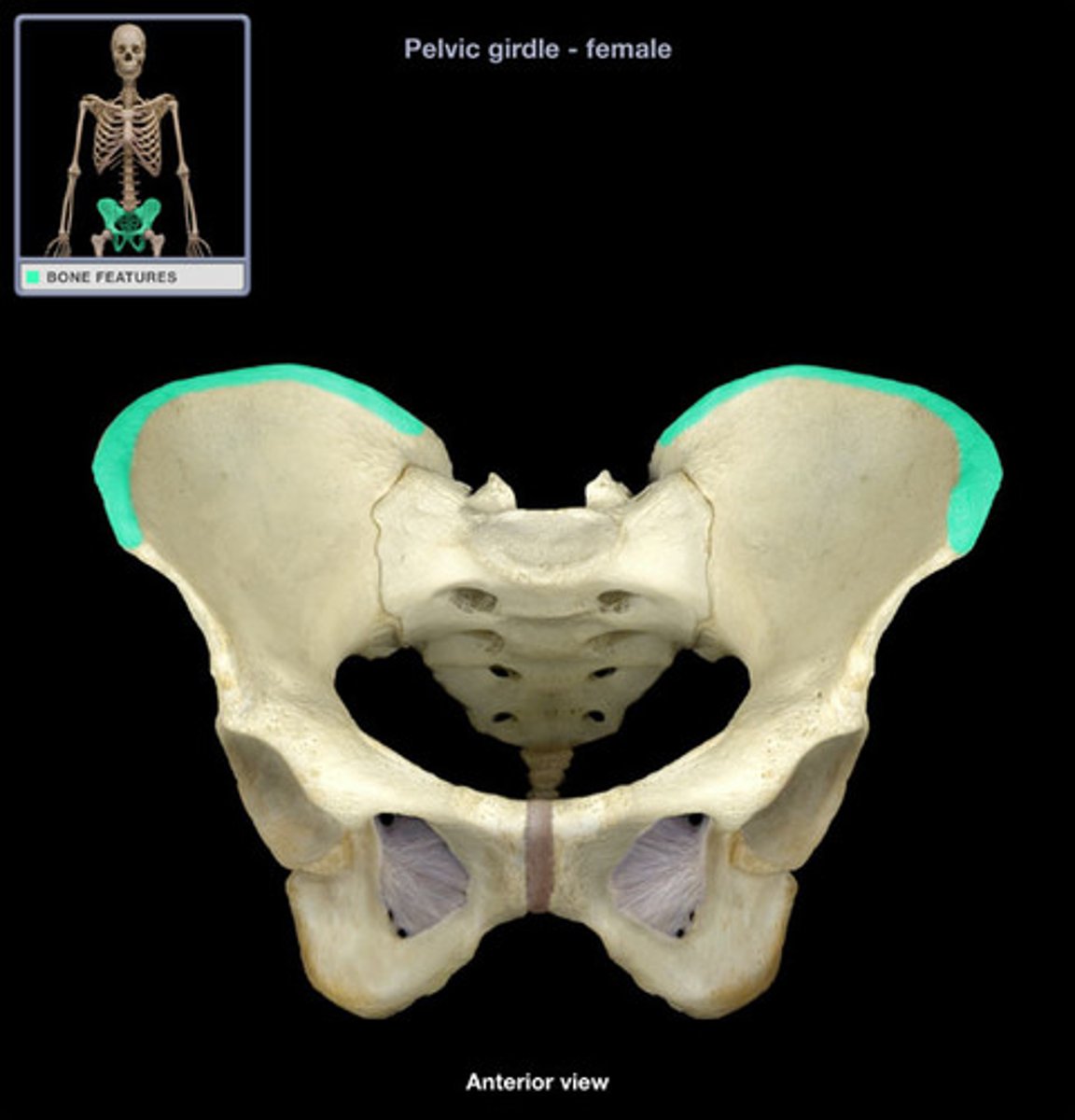
acetabulum
where the ischium, ilium, and pubis unite, creating the socket for the head of the femur
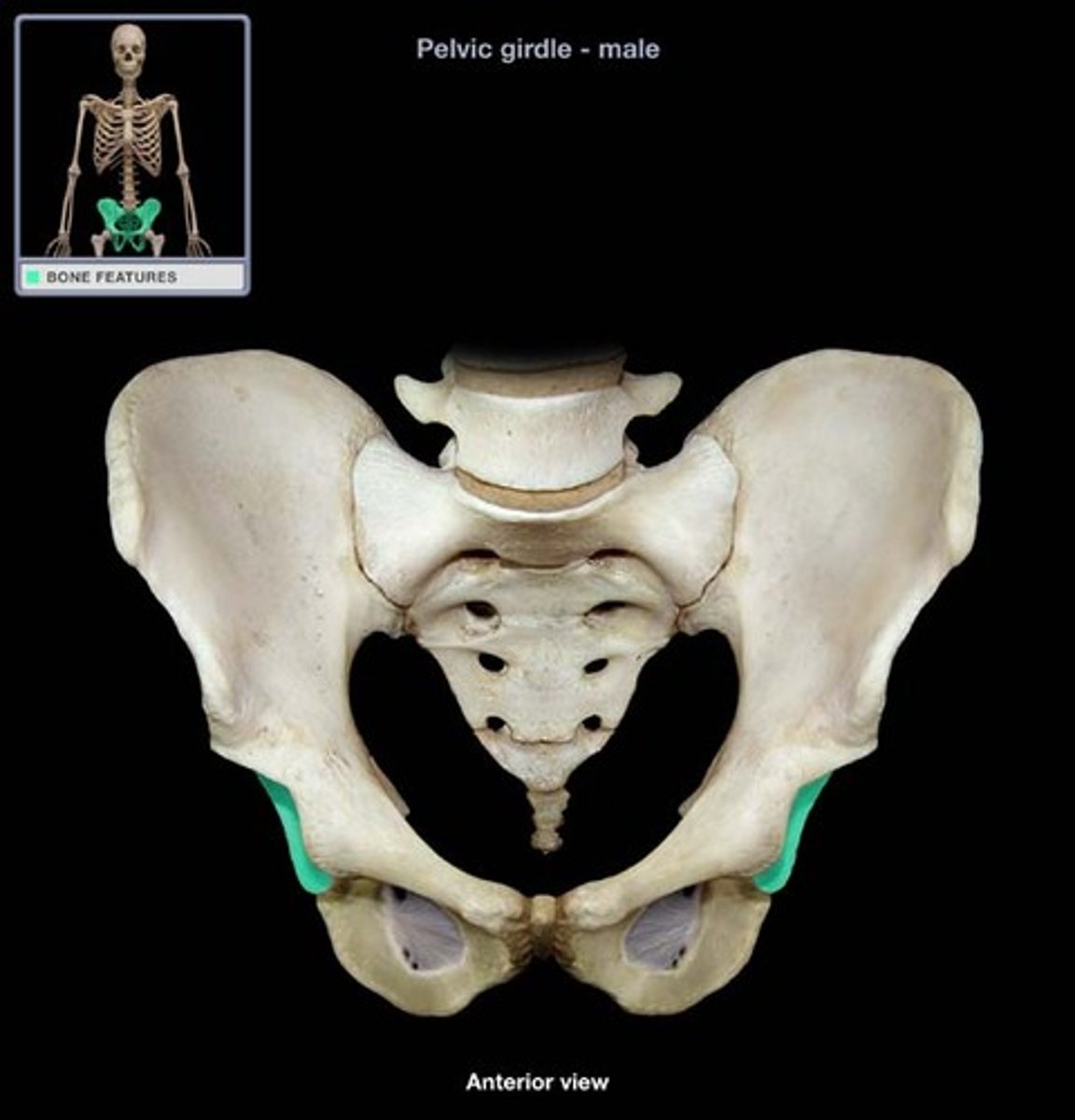
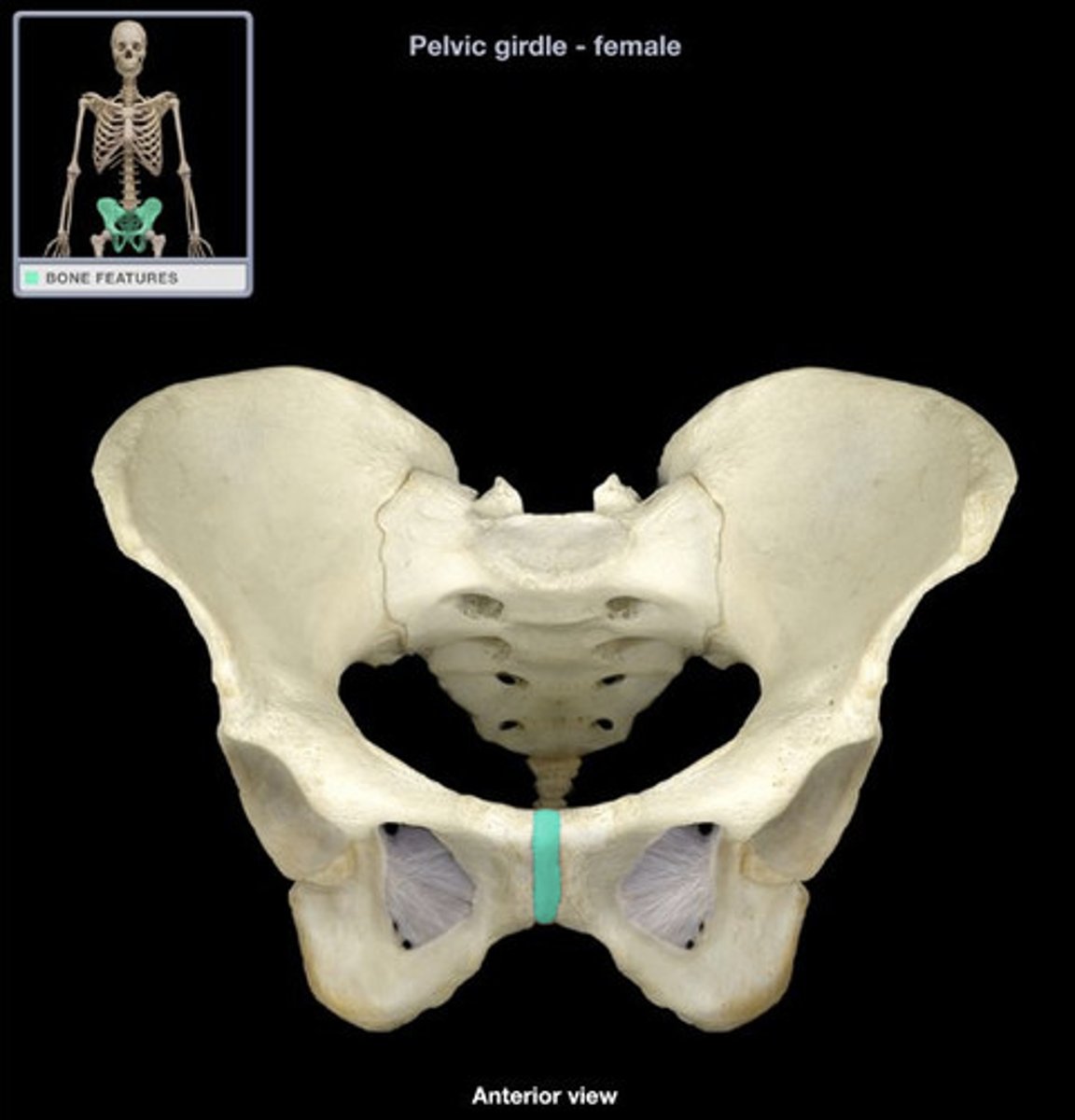
pubic symphysis (symphyseal surface)
the anterior joint where the two pubic bones meet
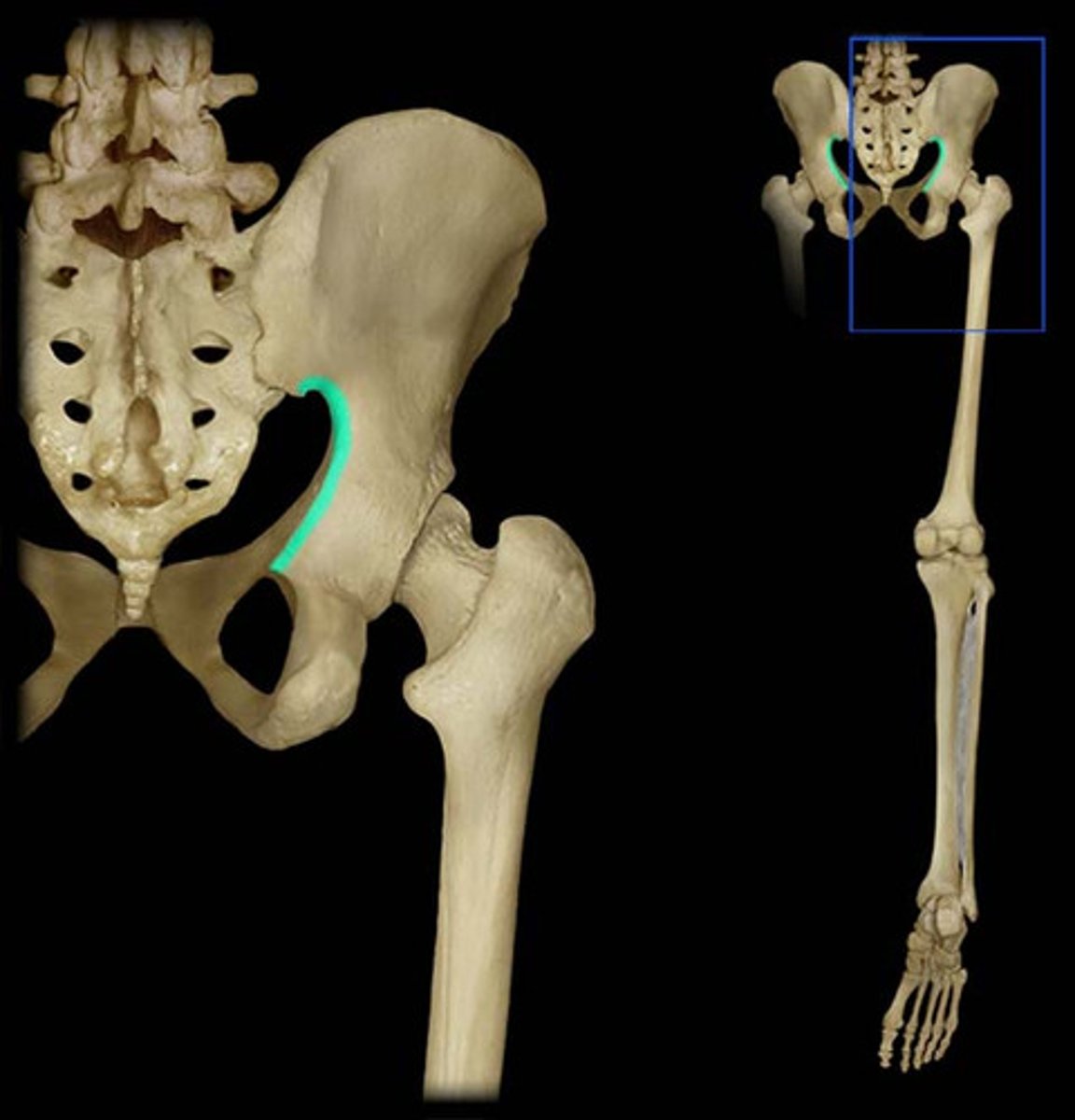
greater sciatic notch
allows blood vessels and the large sciatic nerve to pass from the pelvis posteriorly into the thigh
femur
thigh bone
head (femur)
articulates with the acetabulum (hip socket)
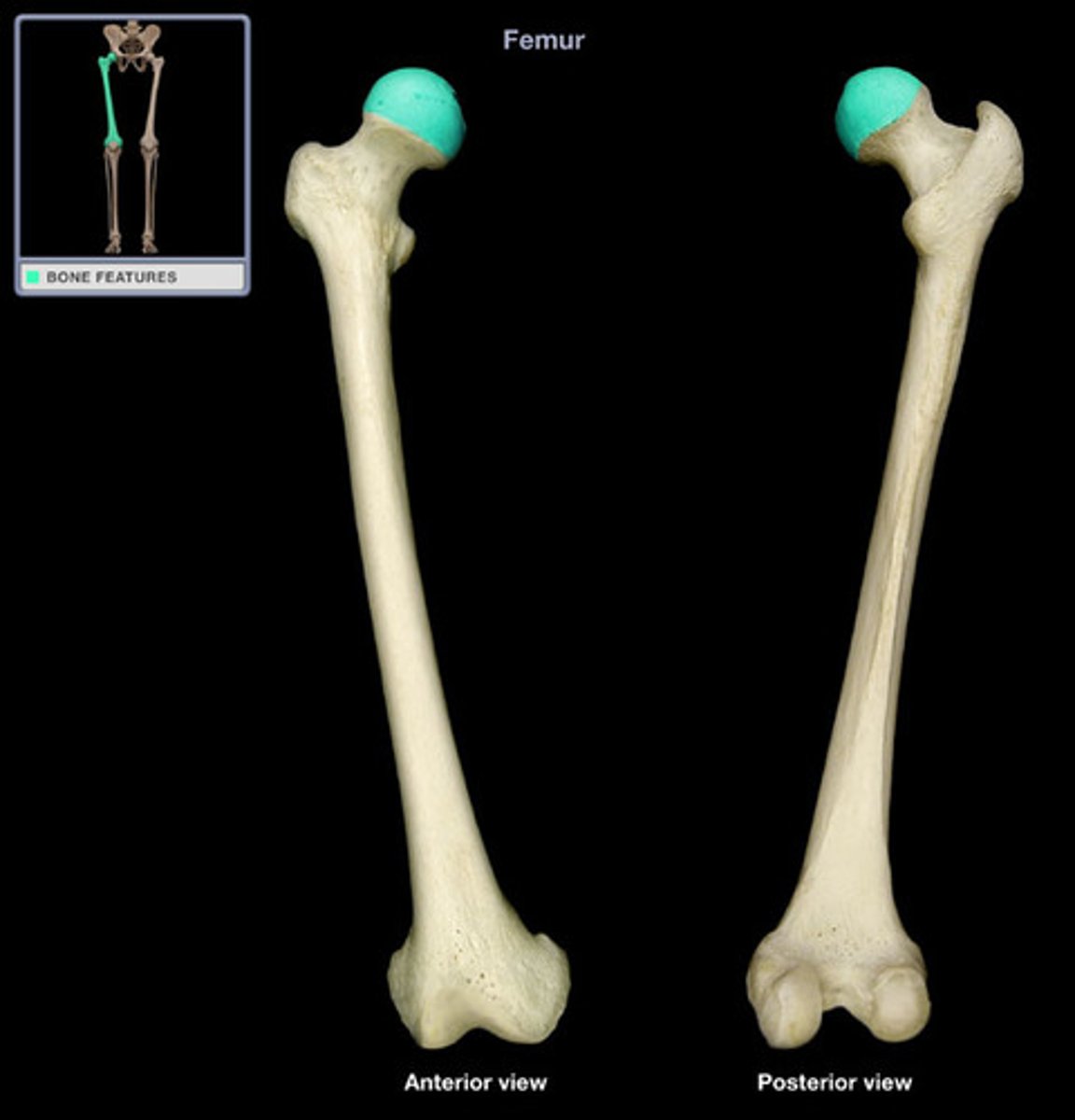
neck (femur)
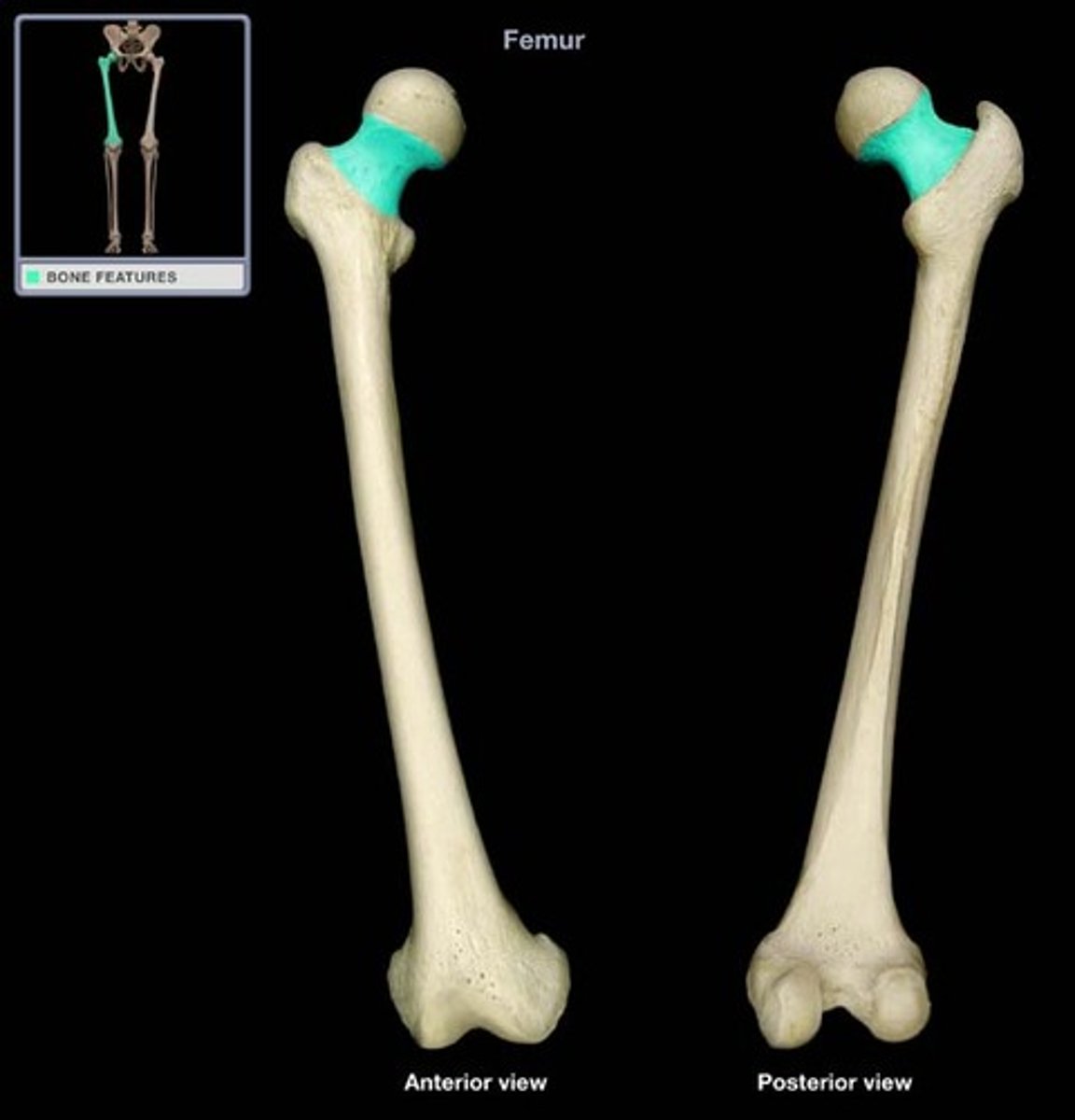
greater trochanter
A bony prominence on the proximal lateral side of the thigh, just below the hip joint.
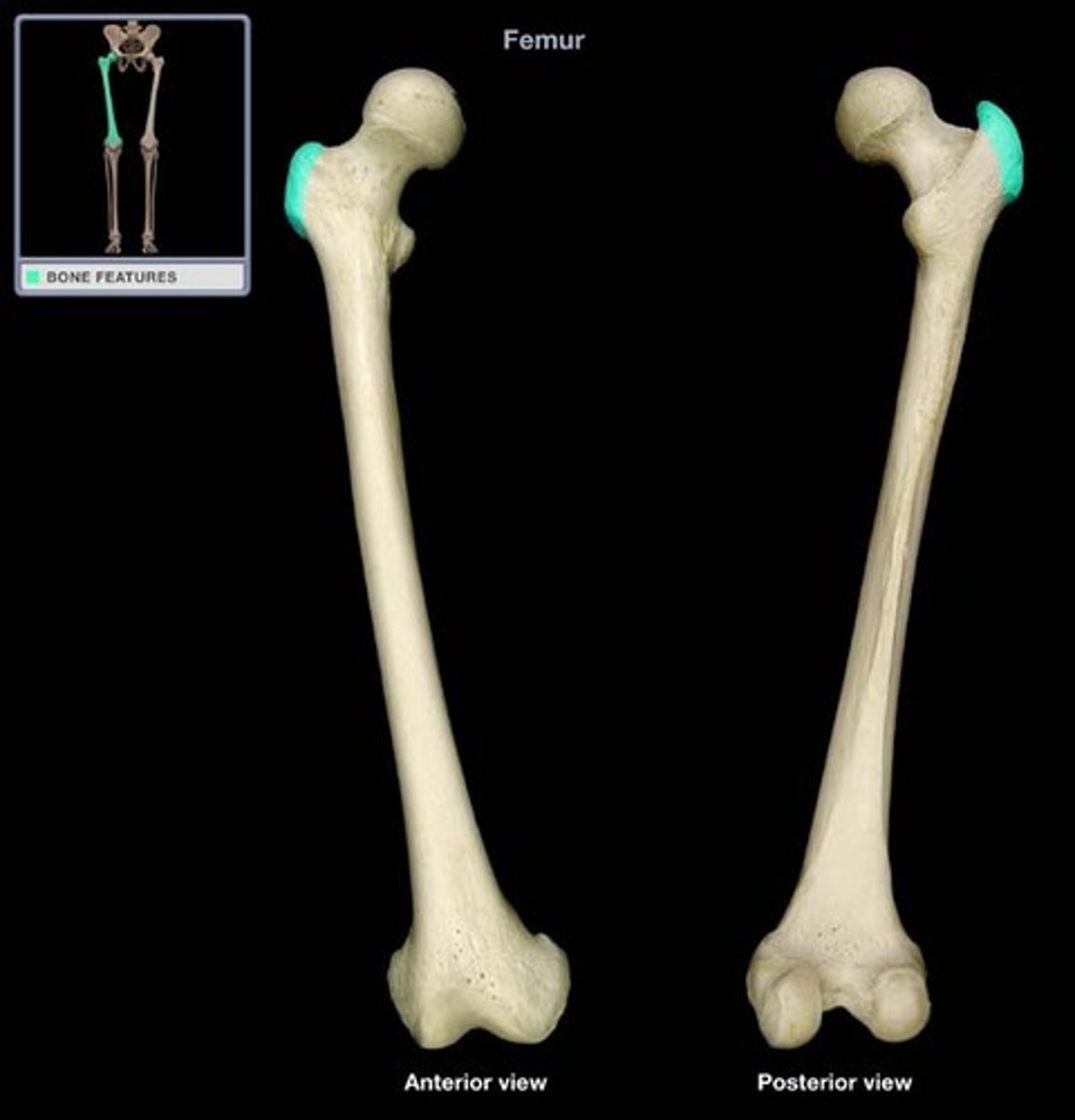
lesser trochanter
The projection on the medial/superior portion of the femur.
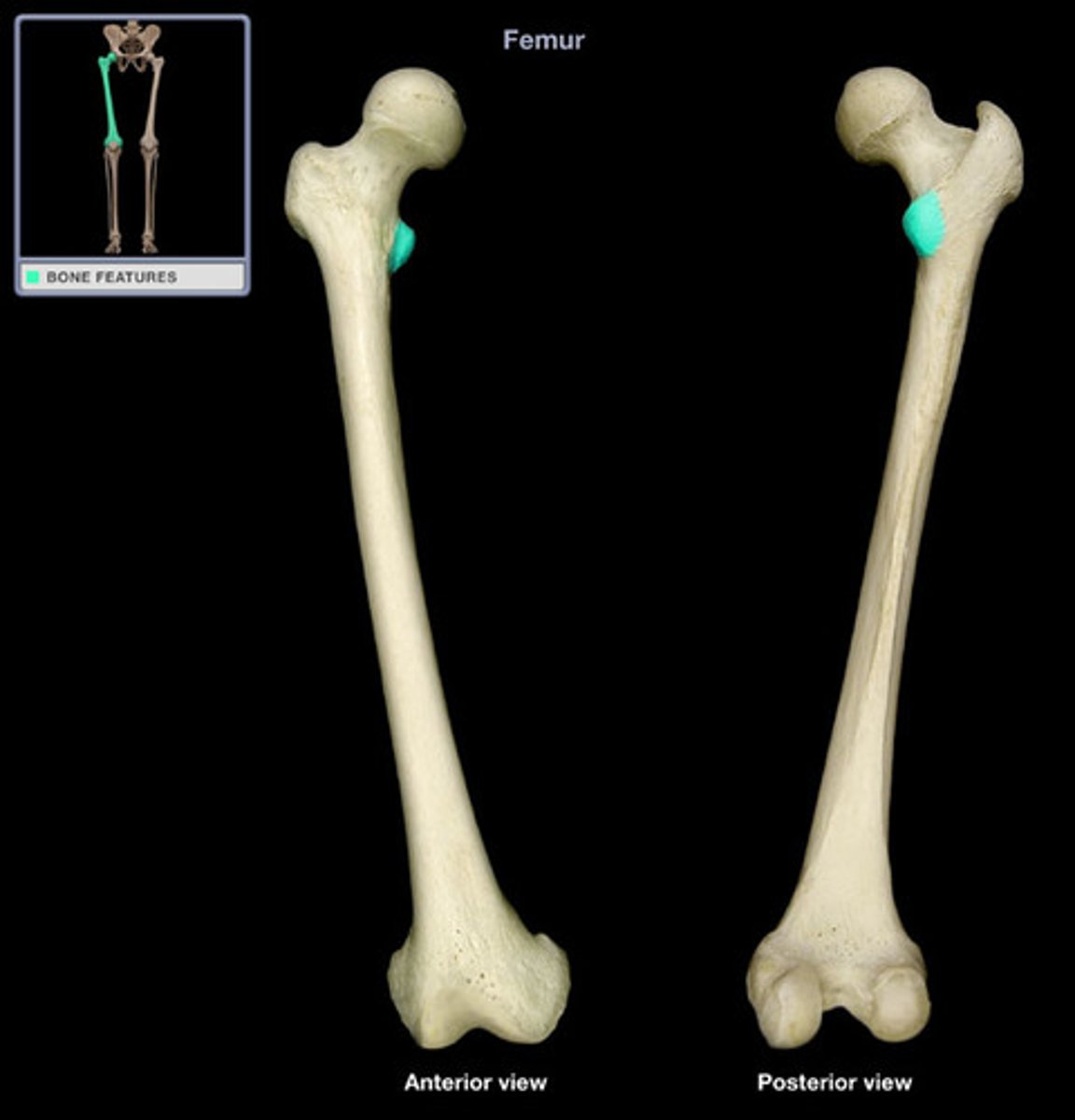
medial condyle (femur)
articulates with the medial condyle of the tibia
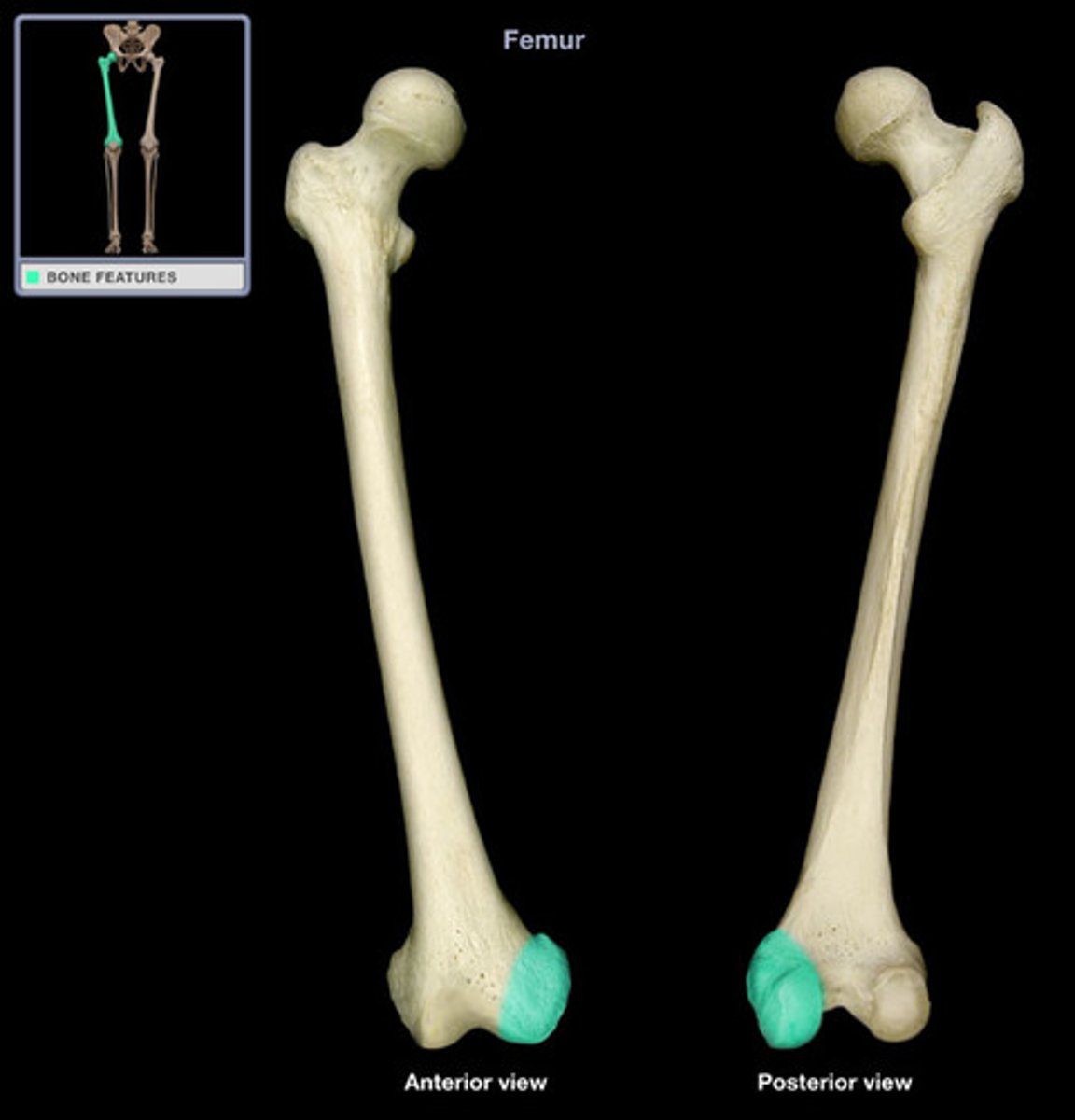
lateral condyle (femur)
articulates with the lateral condyle of the tibia
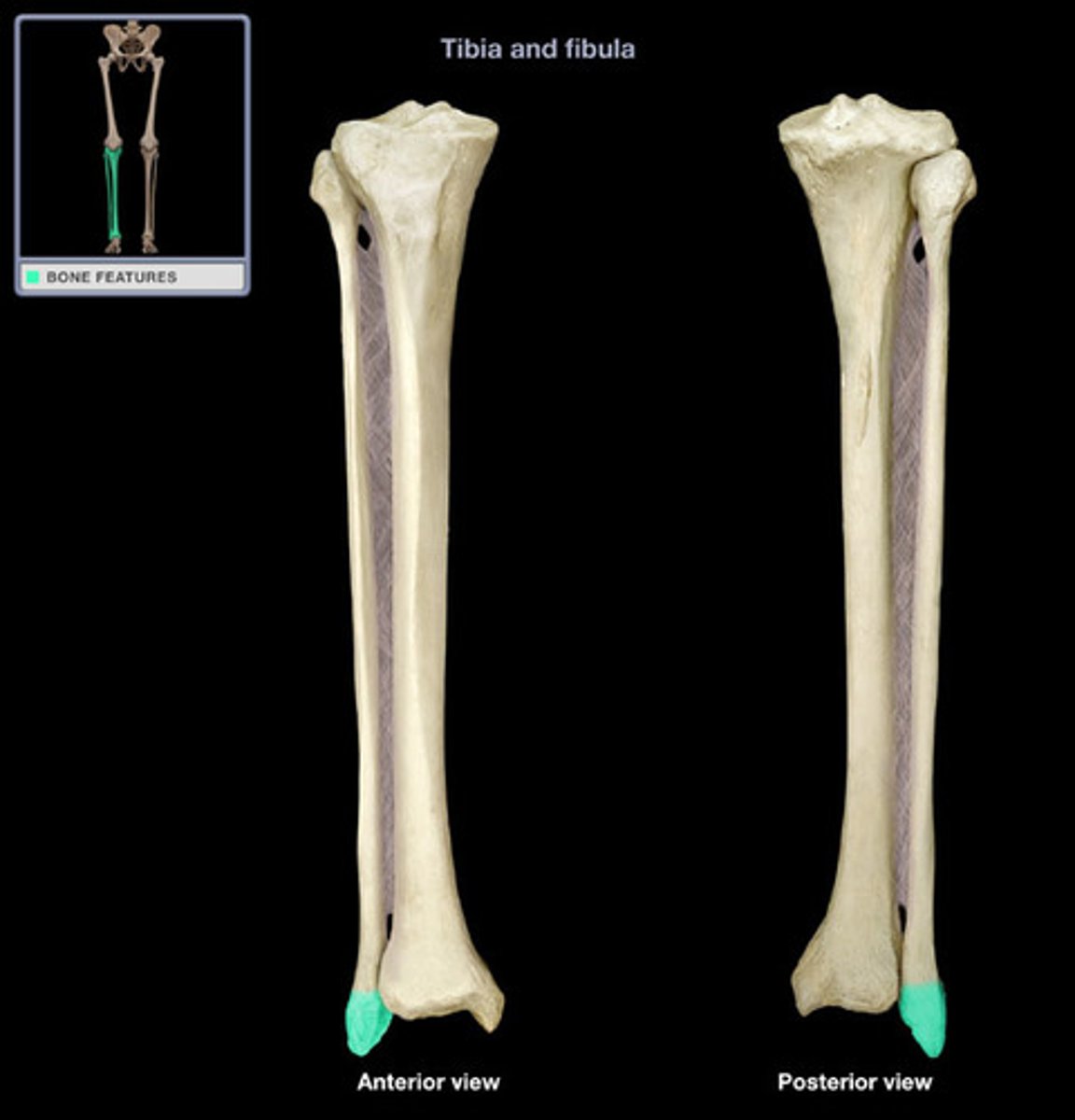
tibia
The shin bone, the larger of the two bones of the lower leg.
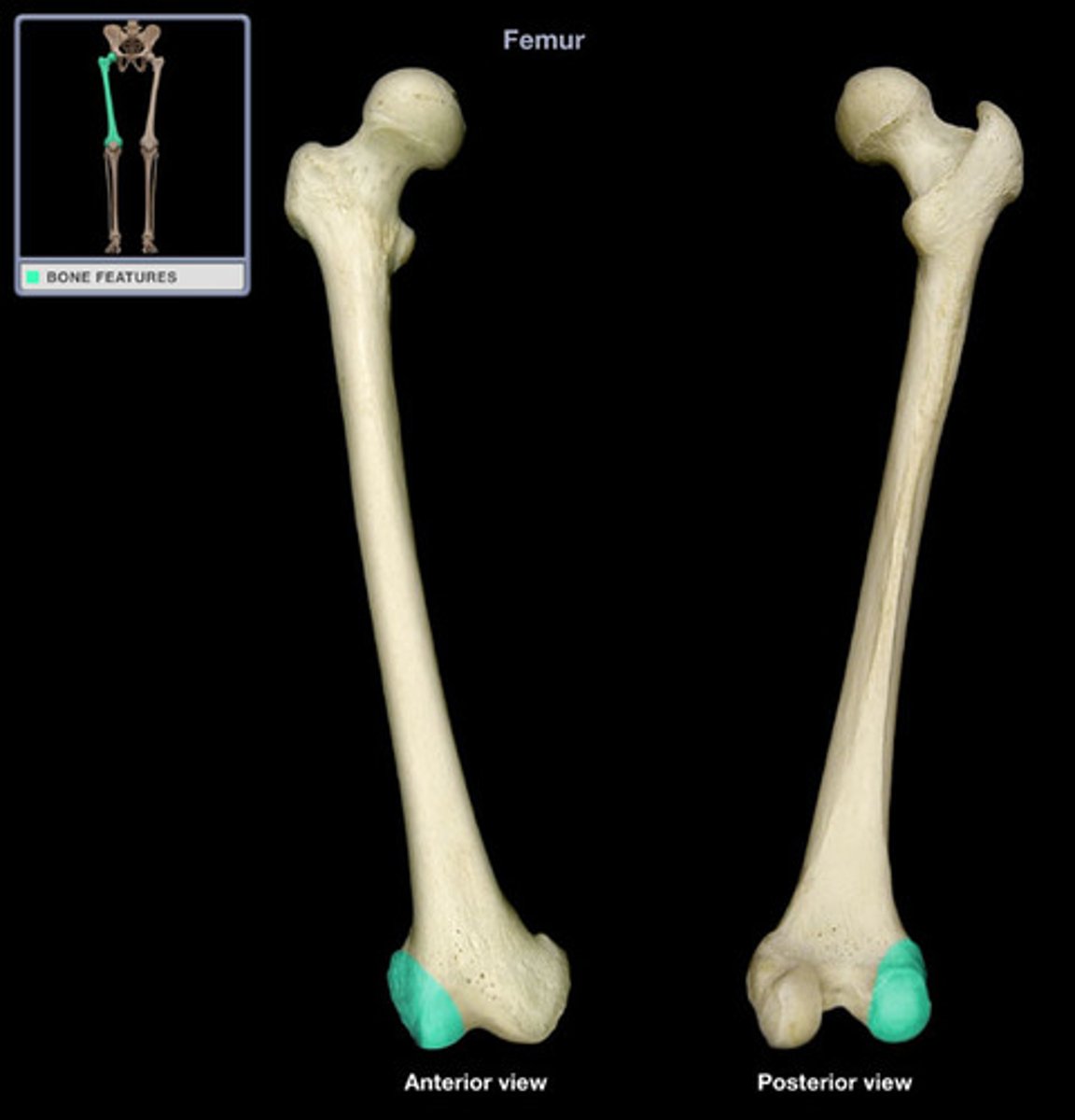
medial condyle (tibia)
articulates with medial condyle of femur
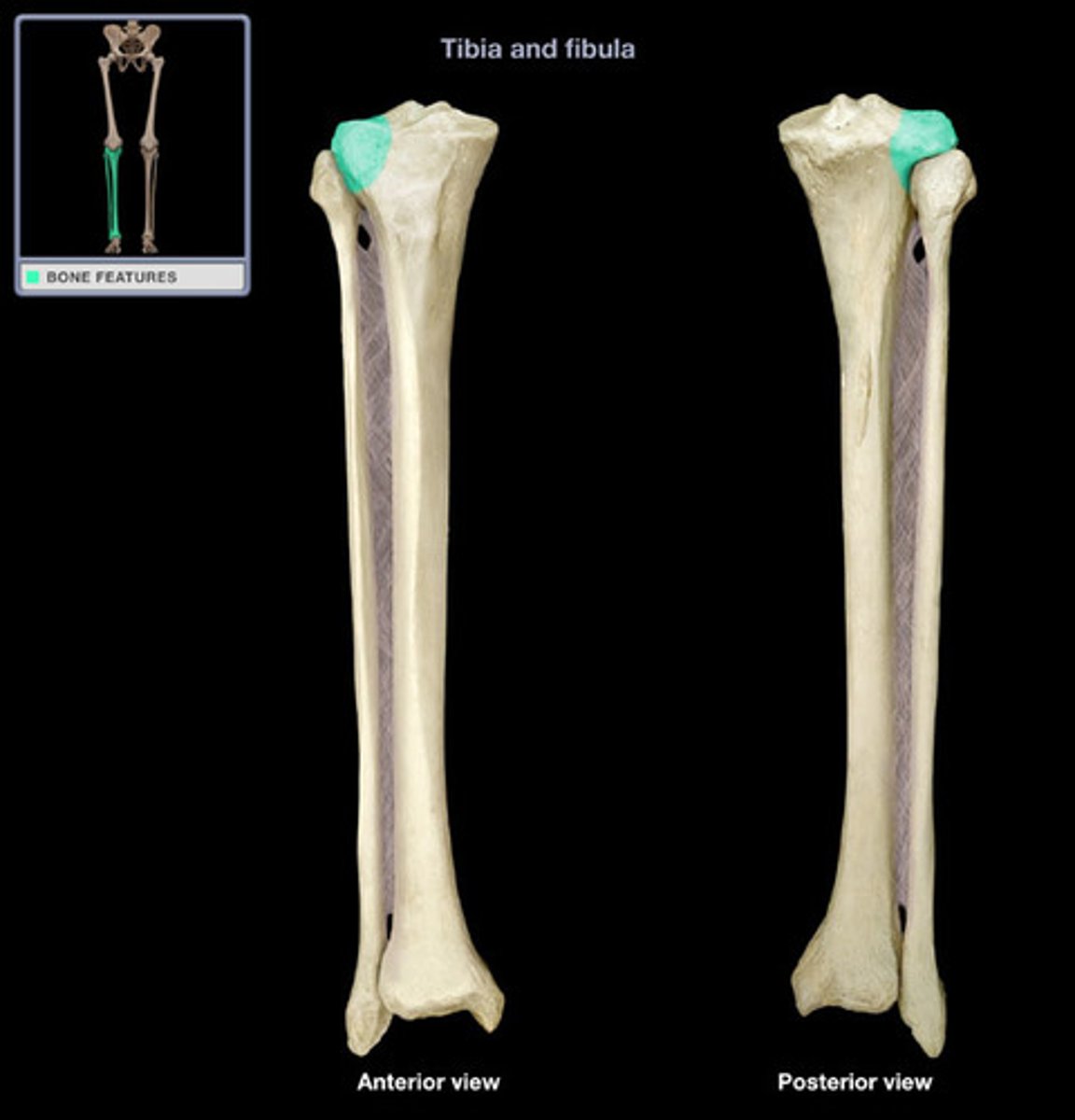
lateral condyle (tibia)
articulates with lateral condyle of femur
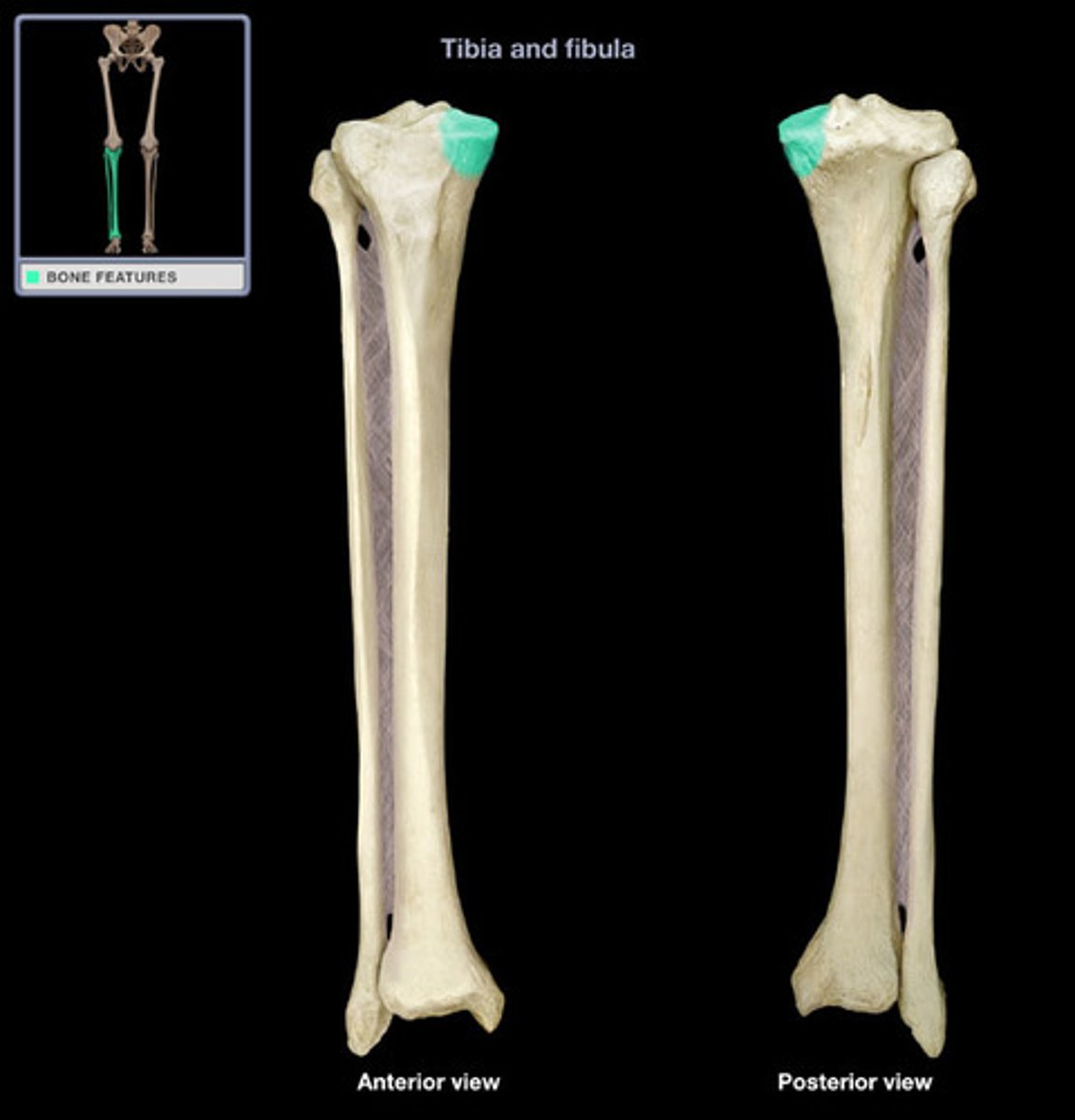
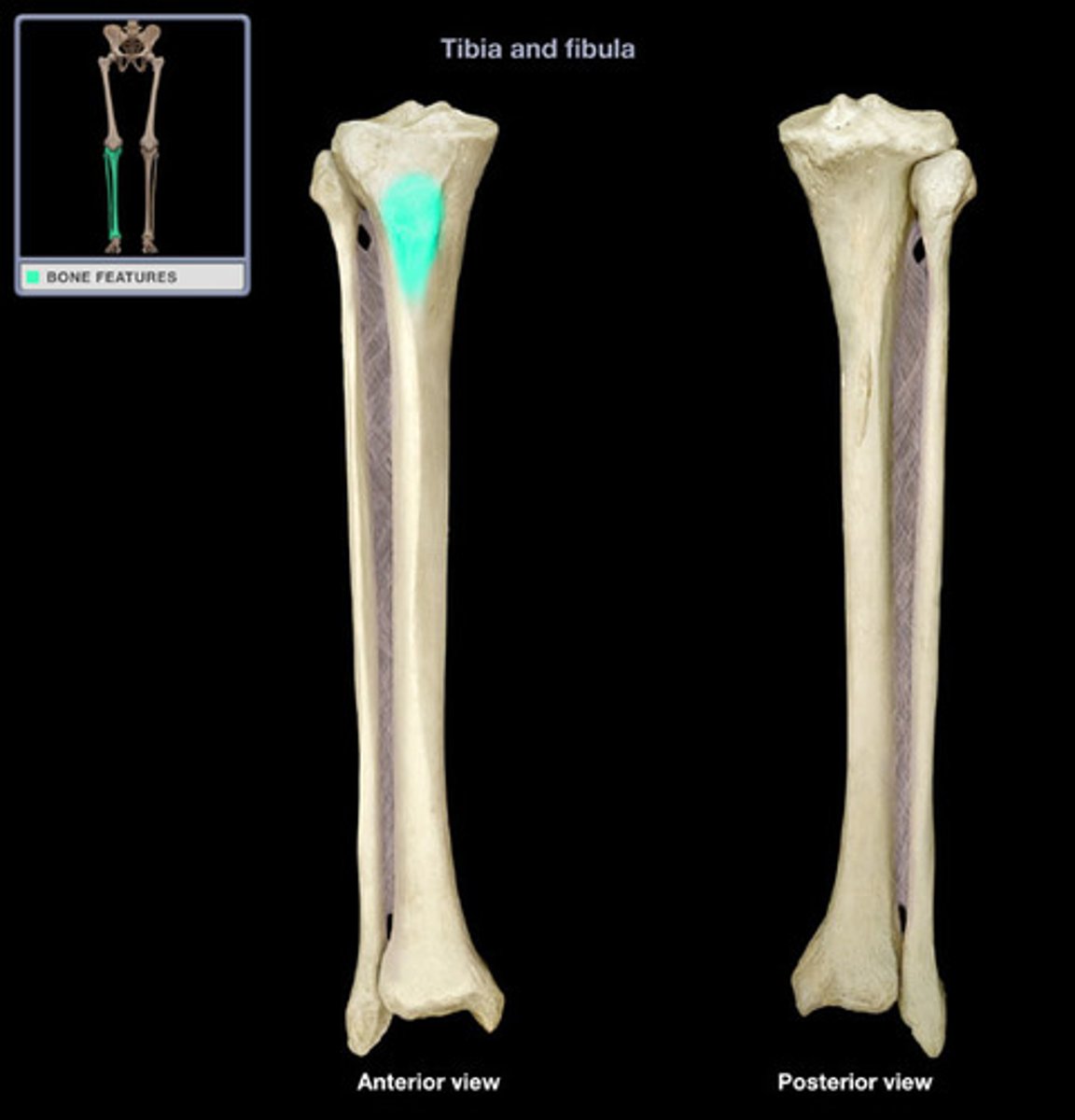
tibial tuberosity
point where the patellar ligament attaches
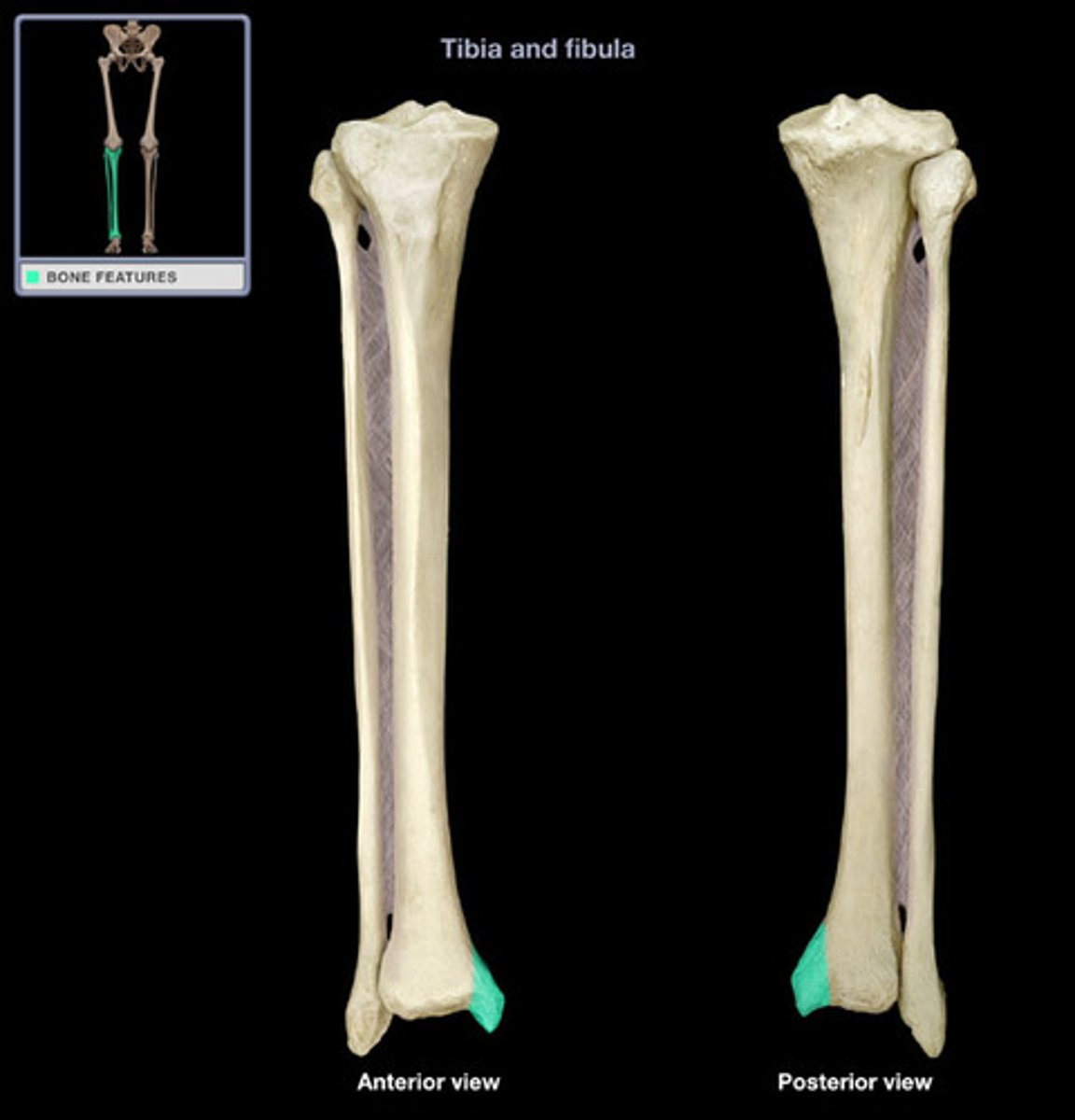
medial malleolus
distal process on medial tibial surface
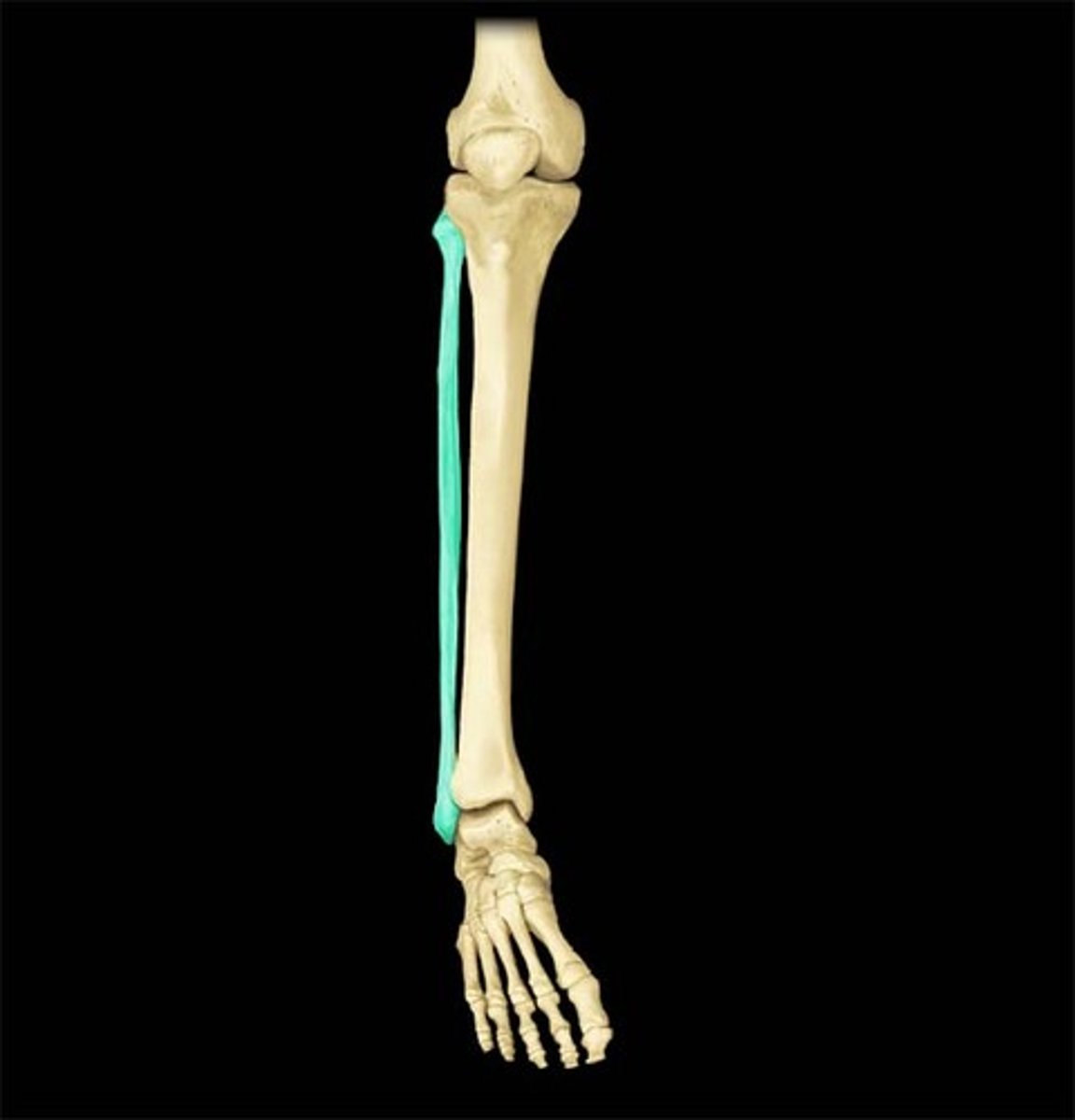
fibula
calf bone; the lateral and smaller bone of the lower leg
head (radius)
articulates with the capitulum and radial notch
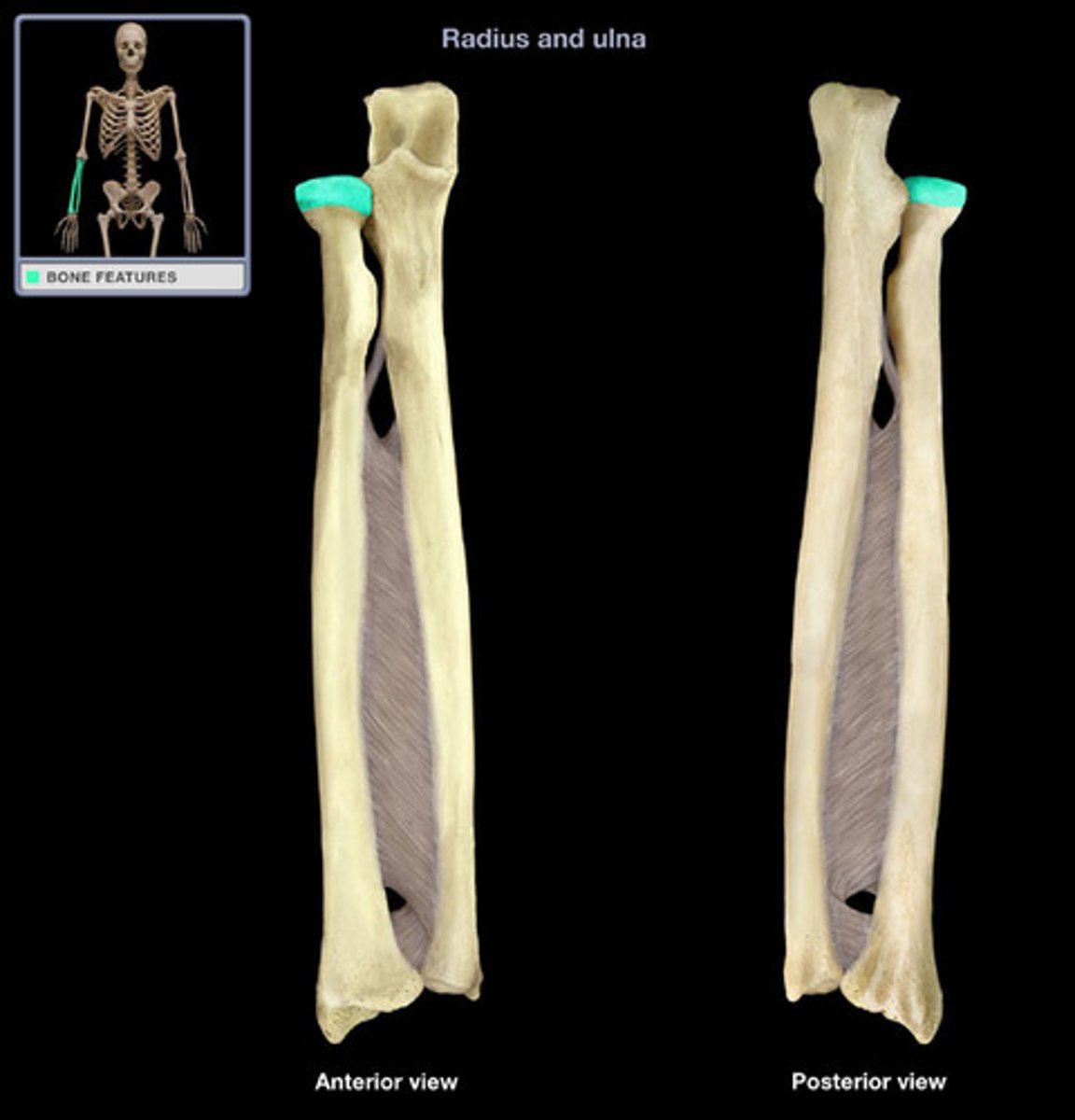
lateral malleolus
process forming the outer (lateral) ankle
tarsals
bones of the ankle
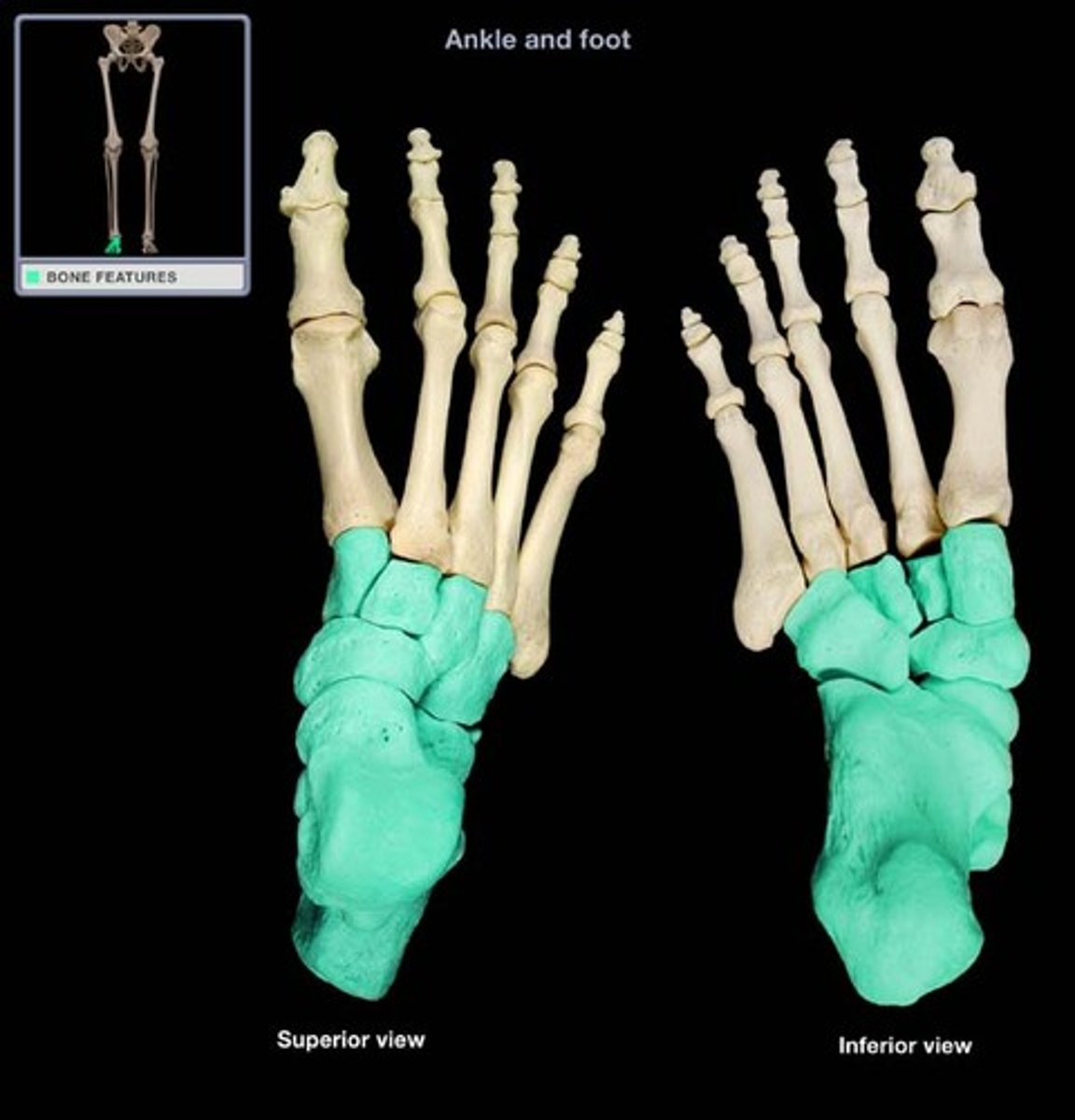
metatarsals
bones of the foot between ankle and toes