A.1.2 Nucleic Acids
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
All living things have three cellular features in common:
•Cell membrane
•Cytoplasm
•Genetic material in the form of DNA
How is genetic material present in prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells have circular DNA in an area referred to as nucleoid.
How is genetic material present in eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have DNA in the linear form of chromosomes inside a membrane bound nucleus.
What are viruses, and do they have genetic material?
Viruses are not living things, but they also can have DNA as genetic material. Commonly, viruses have either RNA (ribose nucleic acid) or DNA inside their viral capsids to carry genetic information.
what are the four major types of biological molecules life is based on?
Lipids, Nucleic acids, Carbohydrates and proteins
Where is DNA found?
Nuclear DNA
Organelle DNA: mitochondria and chloroplasts
What are the different types of RNA
Lipids, Nucleic acids, Carbohydrates and proteins
What are the two primary functions of Nucleotides?
1- gene expression
2-Dna replication
Explain Gene Expression
DNA is first copied (transcribed) into RNA, and then translated into proteins.
Explain DNA replication
Through DNA replication, the information stored in DNA is passed from cell to cell through generations.
What are the components of a nucleotide
•A sugar with 5 carbon atoms (pentose sugar)
•An acidic phosphate group, negatively charged.
One of 4 - 5 different bases that contains nitrogen
How are the components of DNA and RNA similar?
•Both have a phosphate group, sugar and nitrogenous base
•But RNA has a ribose sugar, while DNA has a deoxyribose.
•RNA has the nitrogenous base Uracil instead of Thymine
Both nucleotides have the bases Cytosine, Adenine and Guanine
How are these components of a nucleotide bonded together? Explain
The phosphate group is bonded to 5’ Carbon of sugar. The nitrogen base is bonded to 1’ carbon of sugar.
what are pyrimindines?
cytosine, uracil (rna), thymine (dna)
what are purines?
guanine, adenine. Purines are larger than pyrimidines.
what reaction takes place when the sugar phosphate backbone forms?
The individual nucleotides (the monomers) of a DNA or RNA strand are linked together to polymers in long chains through a condensation reaction (releasing water).
This reaction forms covalent bonds between nucleotides and long continuous strands with a characteristic sugar-phosphate backbone.
define a condensation reaction
A condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, with the loss of a water molecule.
what happens specifically in the condensation reaction in the nucleotide?
In the condensation reaction, the phosphate group attached to the 5’ carbon atom on one nucleotide forms a new covalent bond with the 3' carbon on the pentose of the next nucleotide.
how are the bases in nucleic acids important?
In a strand of a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) the sequence of the nitrogenous bases forms the basis of the genetic code. Specifically, The order of bases in the DNA of a gene codes for the order of amino acids in a protein.
how is dna structured?
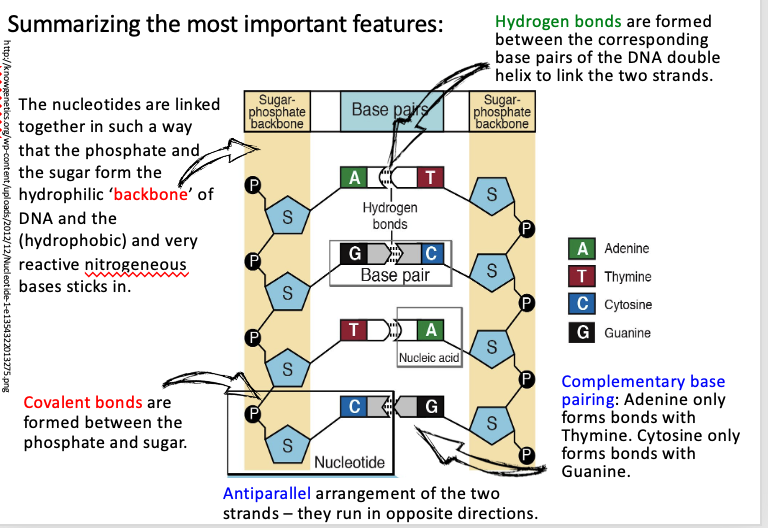
-double helix, two strands that twist around each other in antiparallel way.
-Each strand is made of single units called nucleotides
-Nucleotides have a sugar-phosphate backbone.
-The nitrogen bases join the two strands by hydrogen bonds.
how do the two stands run?
The two strands run antiparallel. They run in opposite directions. (One from 5’ à 3’, and the other from 3, à 5, with the respective numbers connotating the numbered carbon atom in the deoxyribose sugar ring.
how many bonds are between bases a and t
2 hyrdogen bonds
how many bonds are between c and g
3 hydrogen bonds
summarize the important features of DNA
What are complementary base pairings? What’s the role of complementary base pairing
-describes the manner in which the nitrogenous bases of the DNA molecules align with each other. Adenine always pairs with Thymine, Guanine always pairs with Cytosine.
-Complementary base pairing ensures regular arrangement and geometry within the double helix and allows an exact copy to be made in a process called replication.
What do complementary base pairings depend on?
hydrogen bonding between matching bases.
define hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is an electrostatic force of attraction between the hydrogen which is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (N, O, F) and an electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons.
what are hyrdogen bonds formed between?
Hydrogen bonds are forming between complementary base pairs only, that is between Guanine and Cytosine (3 H-bonds) and Adenine and Thymine (2 H-bonds), respectively.
differences between dna and rna
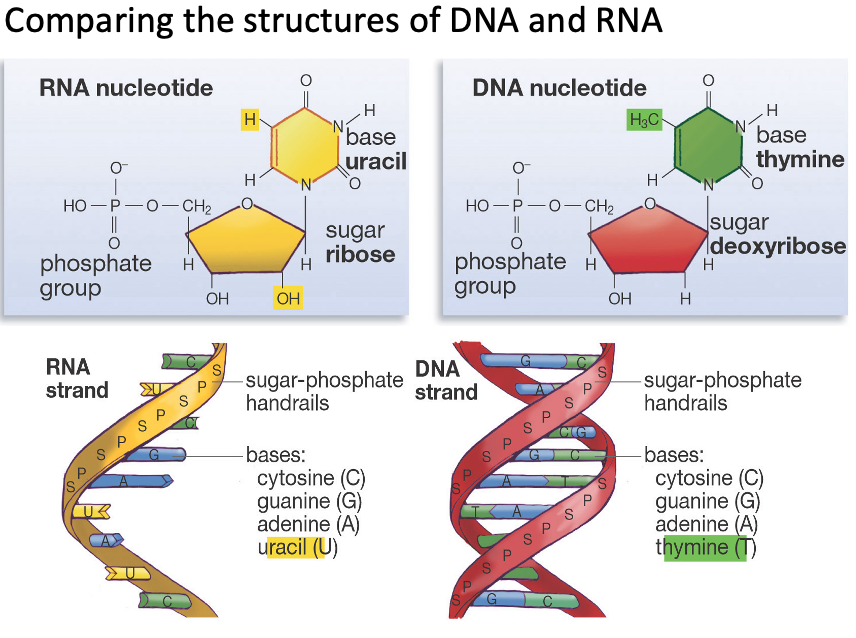
compare and contrast dna and rna
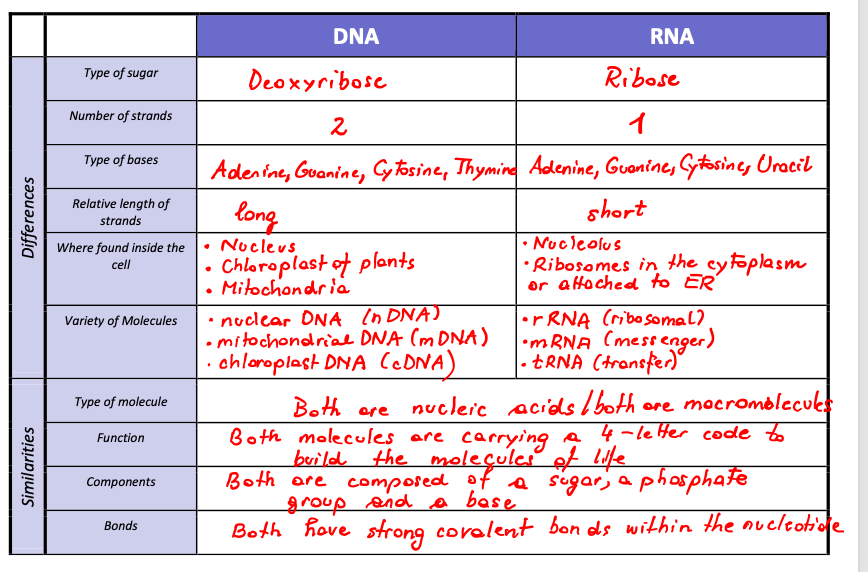
How is genetic information stored
Genetic information is stored in the base sequence of one of the two strands of a DNA molecule. Any sequence of bases is possible. There are 4 different bases which can be arranged in any order: A, C, G, T
•How many different possibilities is there for a sequence of two bases? (e.g. AC, AT, AG…)
16 —→ 4² —→ n^k formula
•How many different possibilities are there for a sequence of 3 bases? (e.g. ACT, AGG, ACC…)
64how
how much is the dna storage in the body
150,000,000,000
compare the dna storage in body with something else
every movie released in the 21st century —> 48 terabytes of dna
dna storage of a human body —> 150,000,000,000 terabytes of dna
how is dna evidence of universal common ancestory
The sequence of bases in DNA or RNA contains information in a coded form. The information is decoded during protein synthesis. Groups of three bases are called codons and code for one specific amino acid. Because nearly all organism (bacteria, plants, animals, fungi…) have the same genetic code, it is said to be universal and most like the basis of common ancestry.
examples of how scientists used dna to create other new stuff
Scientists have genetically engineered plants which can glow by transferring genes from a firefly, which are subsequently expressed by the plant.