Computer Networking flashcards
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Data Communication
Data communicates from host-to-host
Computer Network
Internet is the “network of networks”
How do hosts communicate?
Hosts communicate using protocols
Protocols are the format, order of messages, actions taken,
Inter-networking principles
Minimalism, autonomy, best-effort service model, stateless routing, decentralized control
Characteristics of the Internet
host-to-host communication
packet switching
best-effort service
stateless routing
autonomy
circuit switching
continuous connection
end-end resources are reserved
packet switching
simpler, great for bursty data → can support more users
only when you need it
on-demand resource allocation (resources are allocated only when necessary)
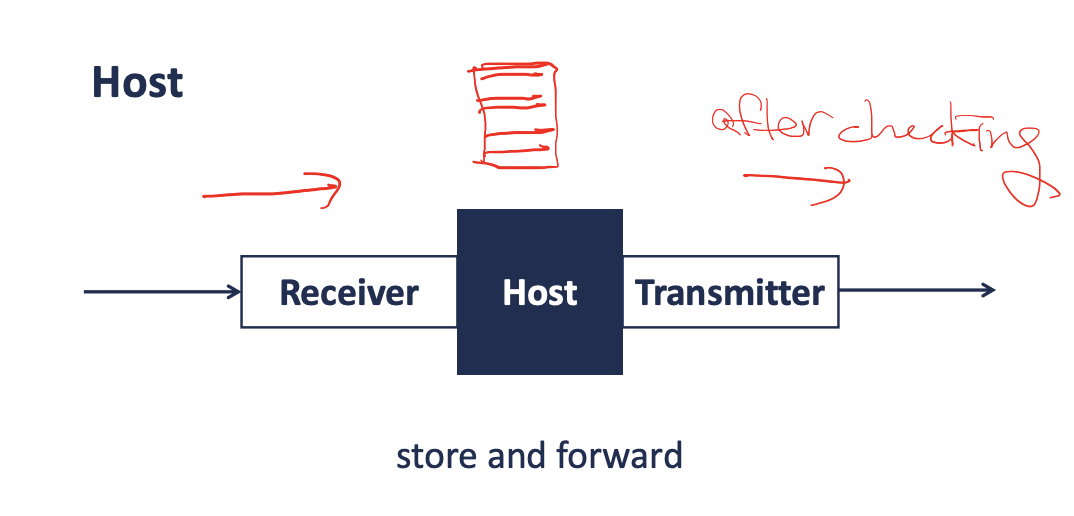
message → multiple packets (messages into smaller chunks → packets)
store and forward
can lead to packet queuing and loss
Best-effort service
In the event of packet queuing and loss
the best-effort service approach is to → Do NOTHING
Autonomy
each network has complete control over itself
network structure
network edge
- hosts: clients and servers
network core
- interconnected routers
- network of networks
Network core
mesh of interconnected routers
packet switching
- forward packets from one router to the next, across links on path from source to destination
- each packet transmitted at full link capacity
Internet Protocol Stack
application
transport
network
link
physical
Four sources of packet delay
transmission, propagation, nodal processing, queueing
Transmission delay
