fingerprints
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what is a fingerprint
an impression of the pattern of ridges on the last joint of a person’s finger
Dactyloscopy
study of fingerprints
Edward Richard Henry
in collaboration with Galton, instituted a numerical classification system
Fingerprints are ___ evidence
individual
What permits fingerprints to be classified
characteristic ridge patterns
Do fingerprints change during your life
no
How are fingerprints formed
formed during fetal development in the dermis, dermal papillae determine the ridge structure
What are the three basic fingerprint patterns
loop
whorl
arch
Loop requirements
one or more ridges which enter from one side of print and exit on the same side, one delta, one core

type of print and characteristics? (left hand)
here: loop, ulnar, one delta, one core

types of loops
ulnar (points towards pinky finger, ulnar bone)
radial (points towards thumb, radial bone)
whorl requirements
two deltas and a core, swirly shape
types of whorls
plain whorl (plain swirl, most basic)
central pocket whorl (whorl in a pocket, maybe enclosed in a loop)
double loop whorl (two loops next to each other that form the shape of a whorl)
accidental whorl (a combination of like everything to vaguely resemble a whorl)
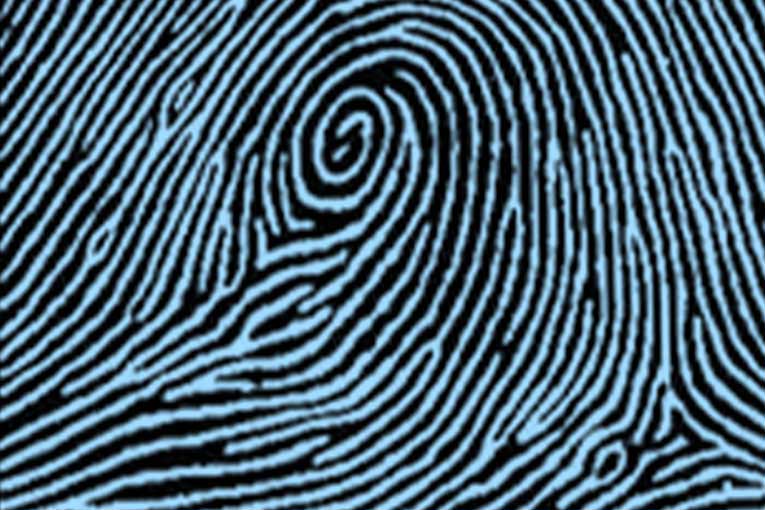

type of print and characteristics
central pocket whorl, two deltas, one core
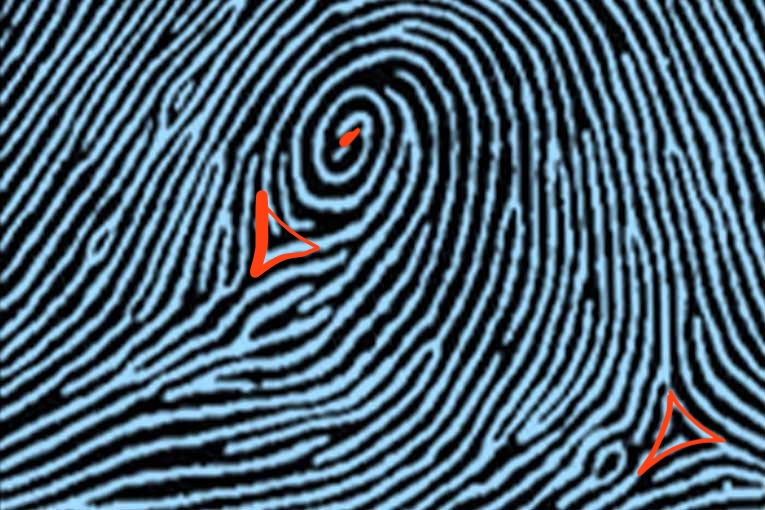


type of print and characteristics
plain whorl, two deltas, one core
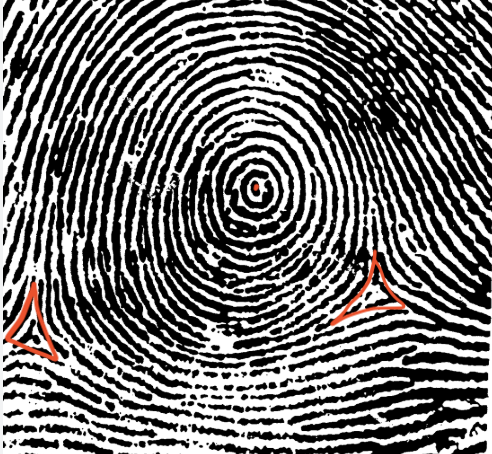


type of print and characteristics
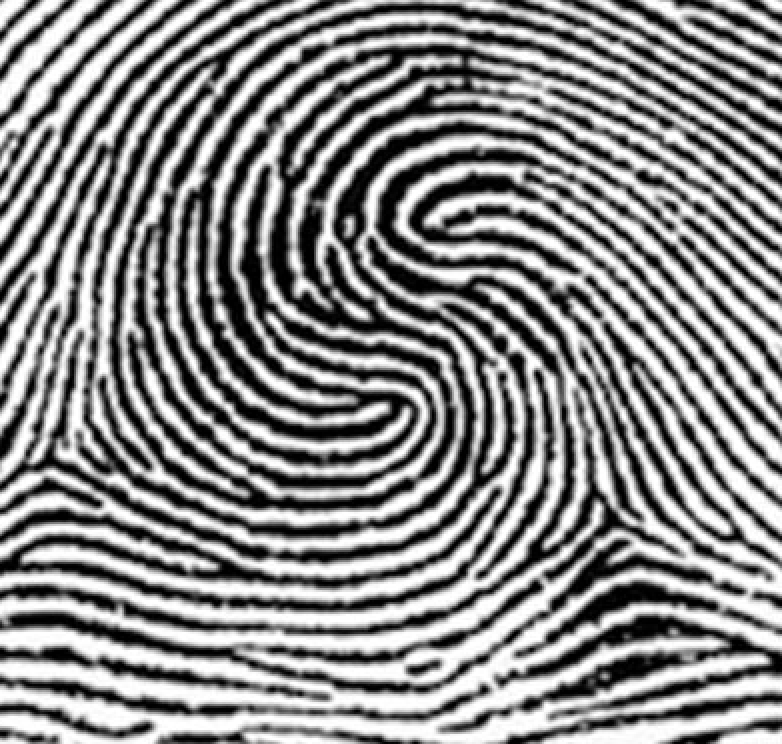
double loop whorl, two deltas, two cores
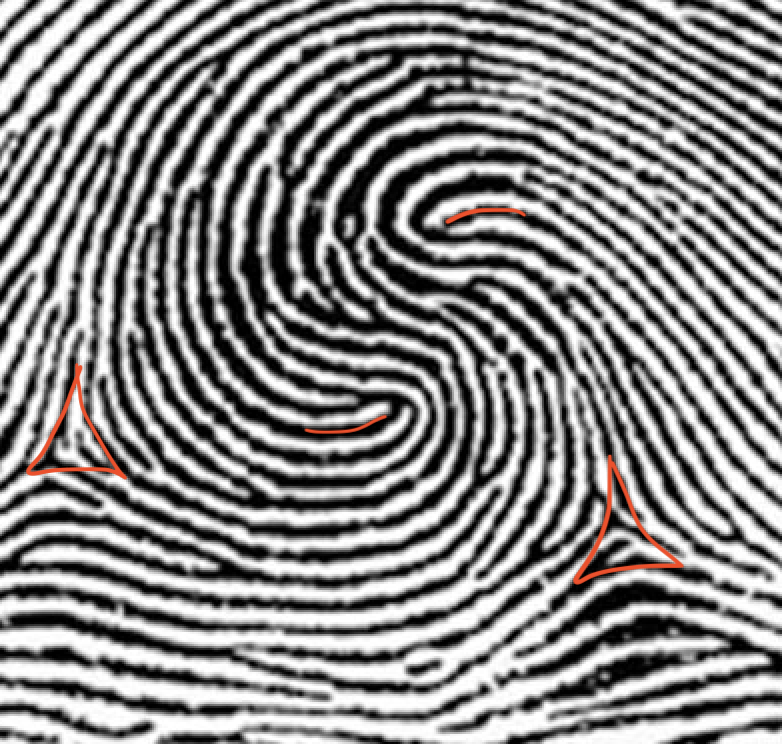


type of print and characteristics
accidental whorl

Arch requirements
ridges enter one side and exit opposite side
types of arches
tented arch (sharp peak in the middle)
plain arch (more subtle)
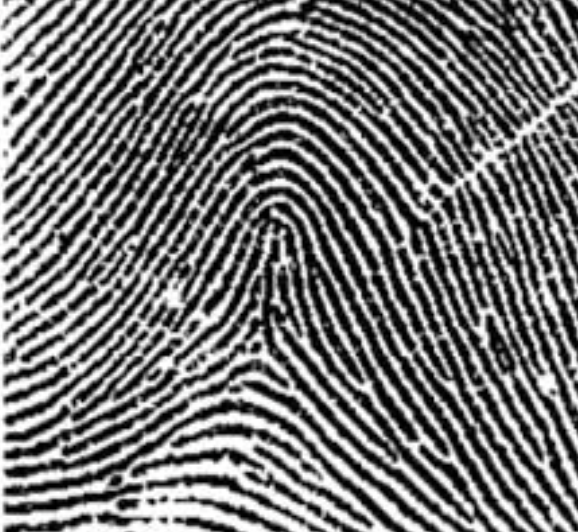

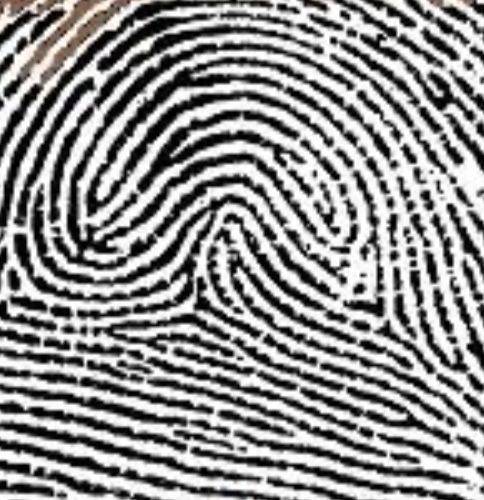
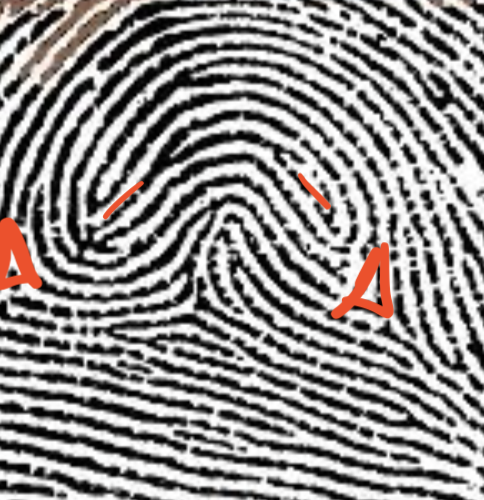
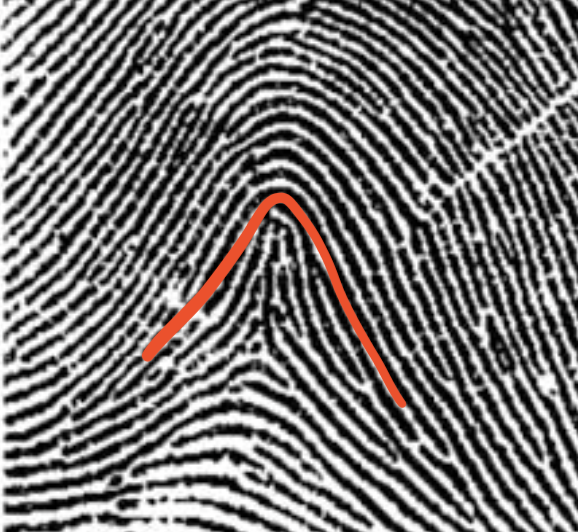
type of print and characteristics
tented arch

type of print and characteristics
plain arch

What are minutiae
specific points on a fingerprint where the ridge pattern changes
types of minutiae
delta
dot
island
spur
bridge
bifurcation (fork)
double bifurcation
trifurcation
eye
ridge ending
how many points of similarity are good to have between prints for forensics
8-12, but no legal requirements
Before computers, fingerprint analysts would…
manually compare evidence print to known prints which were classified into large books or card catalogs
IAFIS acronym meaning
Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System
IAFIS description
made in the 70s
computer searches files for prints similar to one given (taken from an individual)
compare single print, usually latent print developed from crime scene
Finding a print at the scene
photographed before moved or disturbed
Three types of prints found at a scene
plastic
3d impression (wax, soap)
visible
left by fingers coated with a colored substance (blood)
latent
hidden or relatively invisible (need processing or developing to see)
What is a fingerprint made of?
Moisture, sodium chloride, amino acids, organic/inorganic, dead skin cells
Tools for developing prints
flashlight
powders
magnifying glass
brushes
tape
alternate light source
powder
most common, adheres to moisture
regular or magnetic
brushes —> camel hair, fiberglass, magnetic wand
lifting —> use tape to remove powder, mount on a card
Developing latent prints
Iodine
Silver Nitrate
Ninhydrin
Superglue
Iodine
highly toxic, done in a fume hood
fabric, paper, untreated wood
orangey-brown fingerprints
fumes react with oils and fats
silver nitrate
toxic, not used much
reacts with salt in sweat
paper, wood, fabric
brownish-grayish print
Ninhydrin
reacts with amino acids
purple color
non toxic, easy to use
paper, fabric, wood
Superglue
fumes react with water and sweat
hard, whitish deposit
fixes print to surface
must be dusted and lifted (2 steps)