Physiology Lecture 21 - Heart Physiology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what is the resting membrane potential in the heart?
-90 mV
what happens during depolarization?
positive ions entering cell make membrane charge more positive
what happens during repolarization?
positive ions leaving cell make membrane charge negative again
what are the steps that action potentials in contractile cardiac muscle cells go through?
DPR (depolarization, plateau, repolarization)
what occurs during depolarization for action potentials in contractile cardiac muscle cells?
voltage-gated sodium channels open via voltage change and sodium enters the cell reversing membrane potential which causes sodium channels to inactivate.
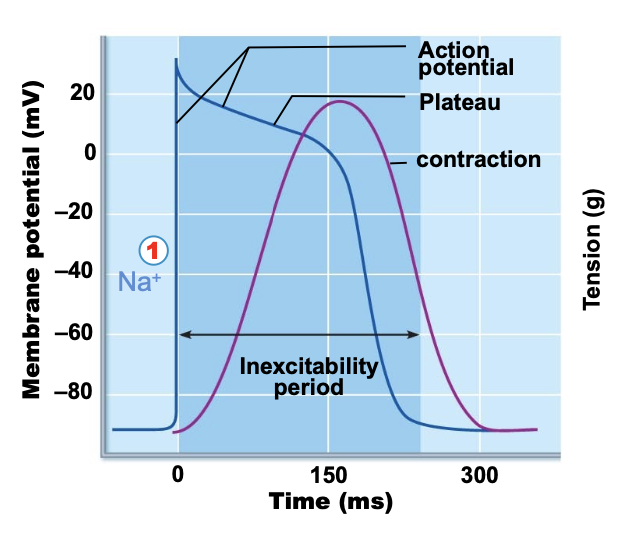
what occurs during the plateau phase for action potentials in contractile cardiac muscle cells?
depolarization causes SR to release calcium and calcium channels also open allowing influx. calcium allows for contraction and calcium bursts prolong depolarization.
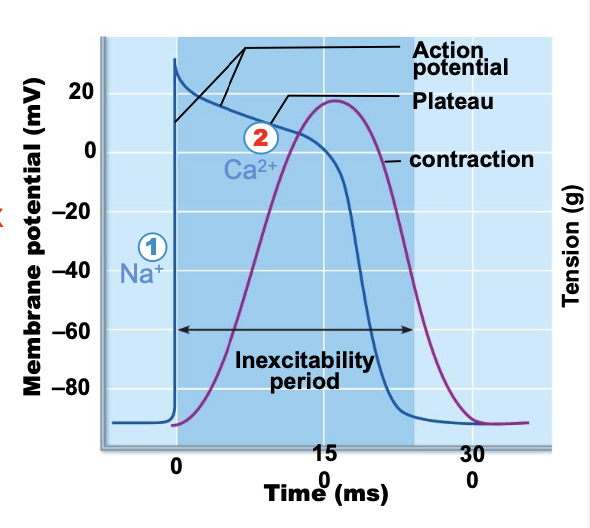
plateau for action potentials in contractile cardiac muscle cells = ______ contraction
sustained contraction
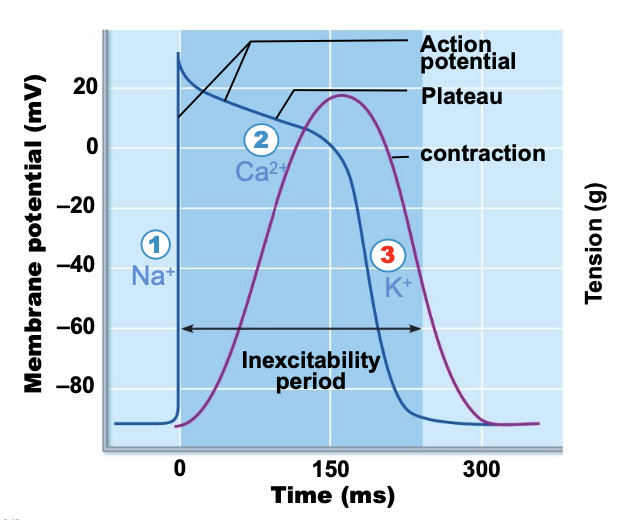
what occurs during repolarization for action potentials in contractile cardiac muscle cells?
calcium channels close and potassium channels open. as potassium leaves the cell, the membrane charge recovers back to -90 mV.
1% of cardiac cells are _______
“self-rhythmic” pacemaker cells that depolarize spontaneously and set the pace of heartbeat, most of the heart responds to these cells
pacemaker cells have an _____ resting membrane potential
unstable
why do pacemaker cells have an unstable resting membrane potential?
they slowly drift towards threshold causing depolarization and spontaneous depolarizations occur
what are pacemaker potentials?
spontaneous depolarizations that spread throughout the heart triggering rhythmic contractions
what are the steps that pacemaker potential go through?
SAP DR (spontaneous action potentials, depolarization, repolarization)
what occurs during spontaneous action potentials for pacemaker potentials?
after repolarization, slow sodium channels stay open and sodium slowly leaks in and the membrane becomes more positive and reaches
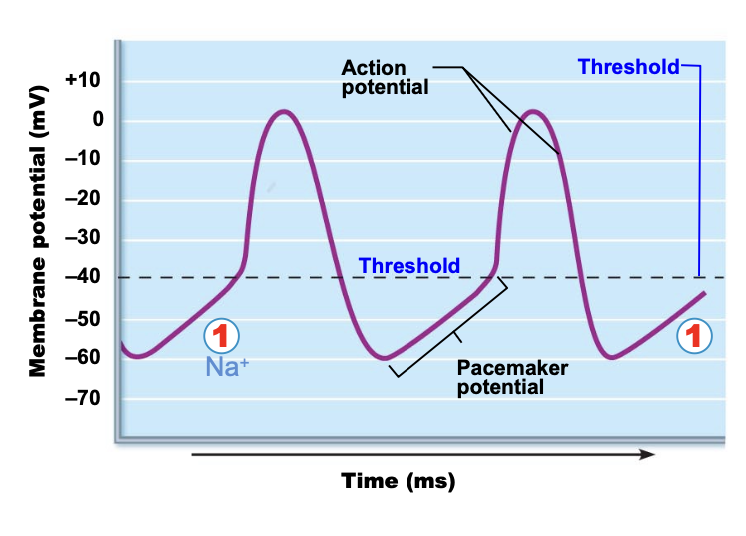
what occurs during depolarization for pacemaker potentials?
at threshold calcium channels open and calcium enters cell which drives depolarization
what occurs during repolarization for pacemaker potentials?
potassium channels open and potassium leaves the cell. the membrane potential returns to negative as sodium slowly leaks in again.
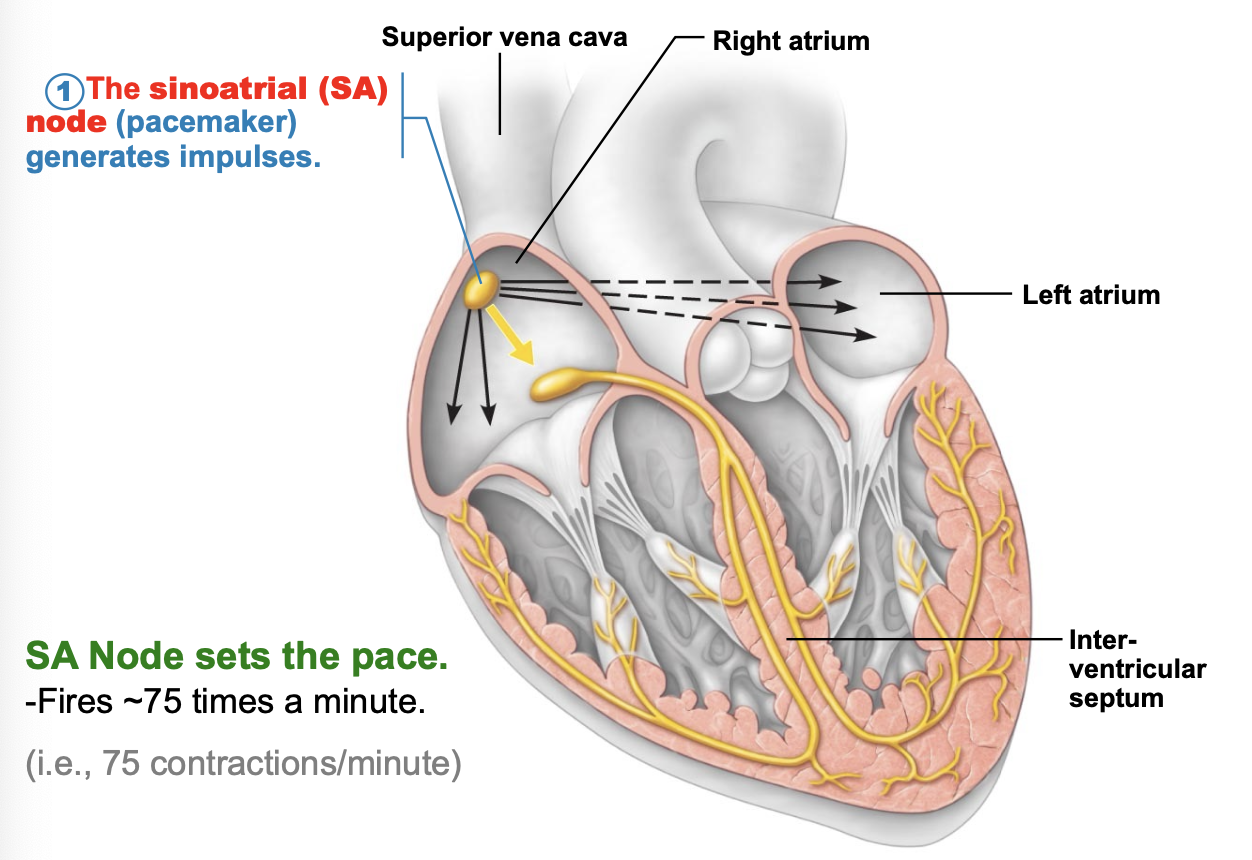
what does the sinoatrial (SA) node do?
the SA node generates impulses and sets the pace
what do atrioventricular (AV) node do?
sends electrical signal to ventricles
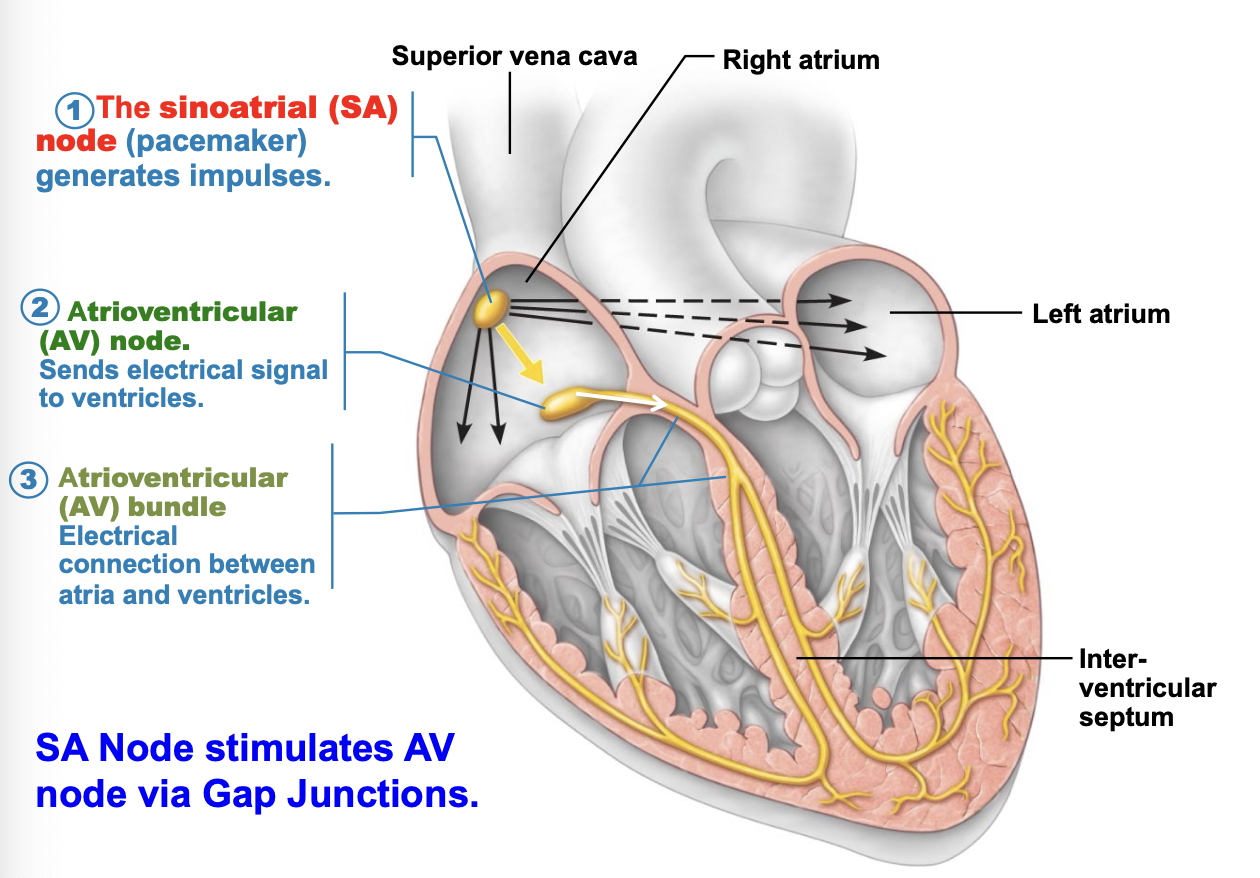
what does the atrioventricular (AV) bundle?
electrical connection between atria and ventricles
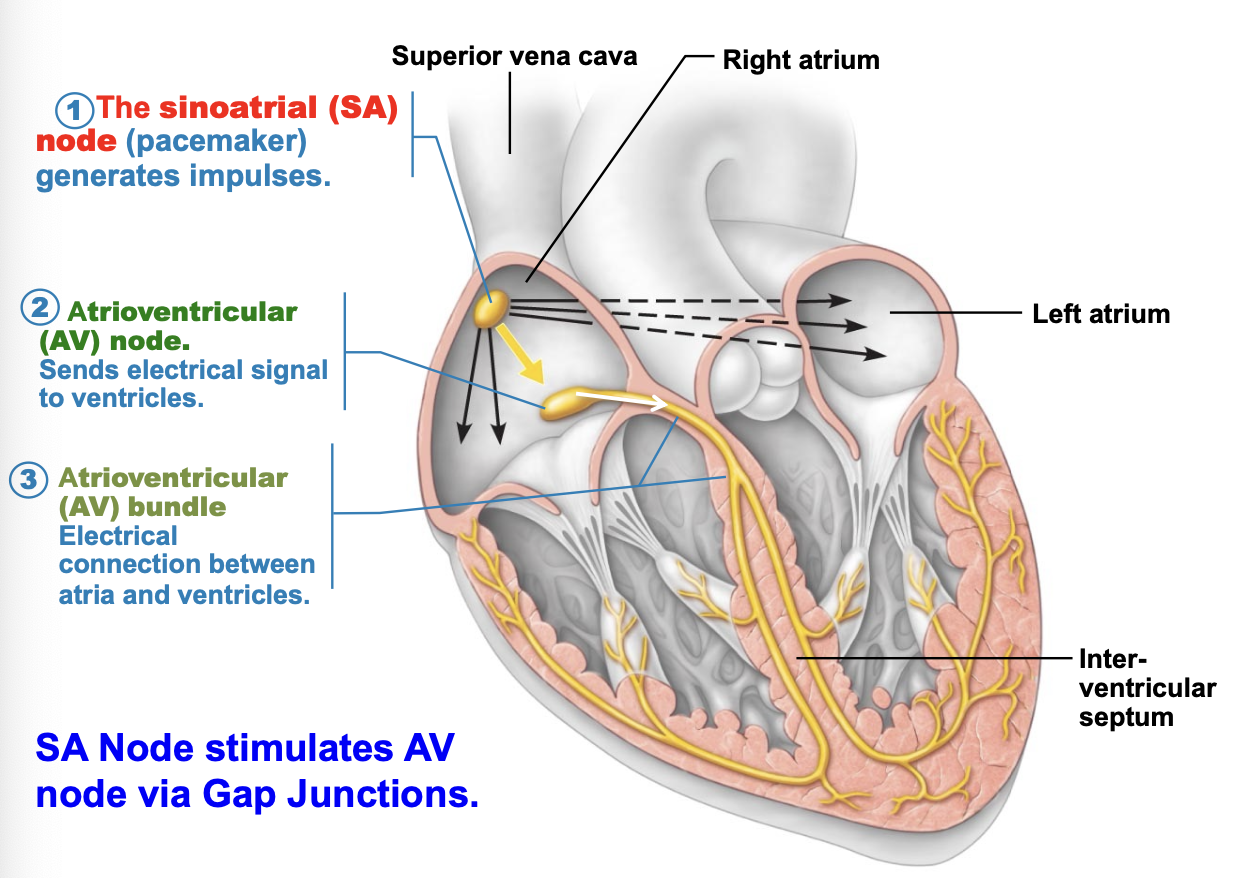
how do SA nodes stimulate AV nodes?
via gap junctions
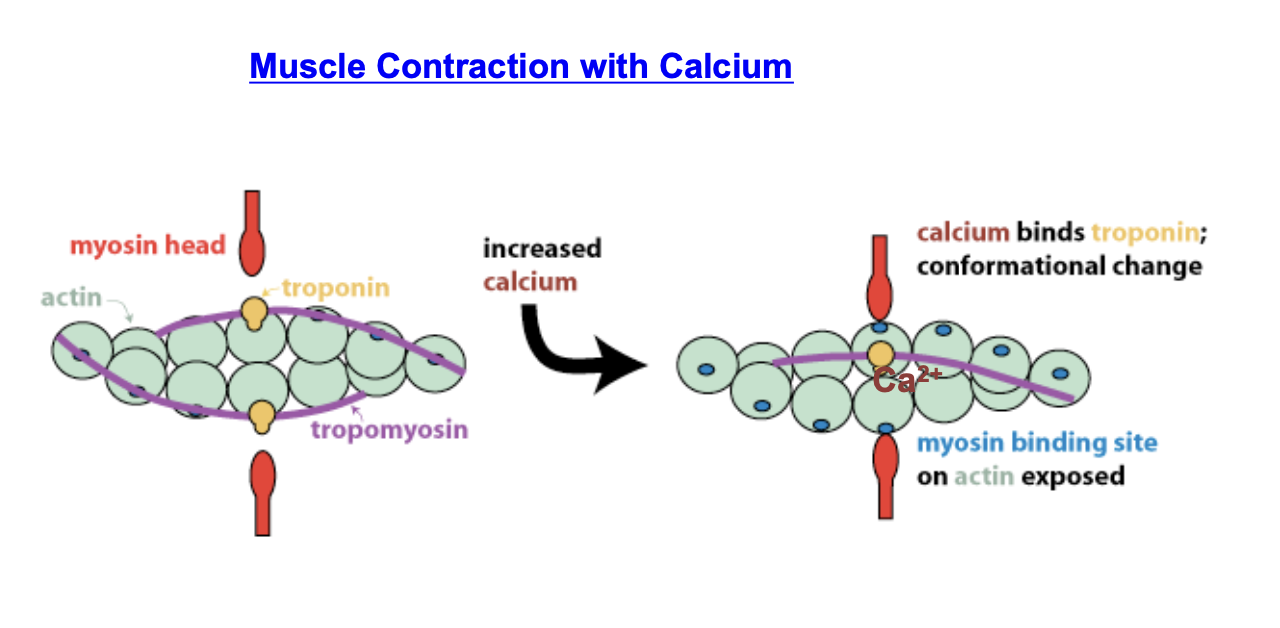
what allows myosin to bind to actin?
calcium allows muscle contractions to occur
what is a pacemaker cell defect?
arrhythmias
what is arrhythmias?
irregular heart rate or rhythms, fibrillation
what is fibrillation?
rapid and irregular out-of-phase contractions
how do the roles of sodium and calcium differ in contractile cardiac cells and pacemaker cells?
Sodium primarily initiates action potentials in pacemaker cells and contributes to the depolarization phase in contractile cells, while calcium primarily triggers muscle contraction in contractile cells and contributes to the upstroke of the action potential in pacemaker cells.
what type of cells makes up 99% of heart muscle?
contractile cardiac cells