final exam (1)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
When applying chest leads, V6 is placed
a.at the fourth ICS, right sternal border
b. at the fourth ICS, left sternal border.
c.in the line with V4 on the midaxillary line
d.at the fifth ICS, left midclavicular line
c.in the line with V4 on the midaxillary line
PVCs occurring in a pattern of every other beat are referred to as ---
a.trigeminy
b.bigeminy
c.runs
d. quadrigeminy
b.bigeminy
On the ECG graph paper _
big boxes equal a 6-second section.
a.twenty
b.thirty
c.ten
d. fifteen
b.thirty
The rhythm in which there is a series of Atrial waves with a Saw toothed appearance is called -----
a. Atrial Fibrillation
b.Premature Atrial Contraction
c.Atrial Flutter
d.Atrial Tachycardia
c.Atrial Flutter
Your patient's heart rate changed from 66 to 110. You note regular, upright, matching P waves. The rhythm has changed from -
a.normal sinus rhythm to sinus Tachycardia
b.normal sinus rhythm to sinus Bradycardia
c.sinus Bradycardia to normal sinus rhythm
d.normal sinus rhythm to sinus arrhythmia
a.normal sinus rhythm to sinus Tachycardia
EKG Strip showing PR interval prolonged (more than normal), without dropping a QRS complex.
a.second degree AV block, Mobitz II
b.third degree or complete heart block
c.second degree AV block, Mobitz I
d.first degree AV block
d.first degree AV block
To obtain 12-lead EKG, you must apply -
- electrodes to the patient.
a.10
b.8
c.12
d.3
a.10
The ECG complexes are determined to occur in a regular pattern. What method do you use calculate most accurate heart rate?
a.1500 method
b.Any of these method
c.300 method
d. 6-second method
a.1500 method
Together, the contraction and relaxation of the heart make up:
a.Coronary circulation
b.Diastole
c.Systole
d.One cardiac cycle
d.One cardiac cycle
If the patient has amputated left lower leg, electrodes should be placed as
a.LL on left lower leg, RL on the right upper leg
b.LL on left lower abdomen, RL on the right lower abdomen
c.LL on left lower abdomen, RL on the right lower leg
d.LL on left upper leg, RL on the right lower leg
b.LL on left lower abdomen, RL on the right lower abdomen
Vertically, 10 mm represent electrical voltage which is about
a.10 mV
b.0.01 mV
c.0.1 mV
d.1 mV
d.1 mV
Premature Atrial Contraction is a.
a.A premature beat from the sinus node
b.A premature beat from the atrium
c.An premature beat from the AV Junction
d.An premature beat from the ventricle
b.A premature beat from the atrium
Using the (big box - 300) method, if there are four big boxes between two successive R-R (QRS complexes), the heart rate is - a.
a.300 bpm
b.75 bpm
c.100 bpm
d.150 bpm
b.75 bpm
14. An electrocardiogram is a recording of -
a.ability of the heart to pump blood to the body.
b.electrical activity traveling through the heart
c.electrical activity traveling through the body
d. ability of the heart muscles to
b.electrical activity traveling through the heart
You are working as an EKG technician. Your favorite uncle says to you "will you do EKG on me
I come by where you work?" You should tell your uncle that--
a.you need to give detail of your insurance
b.yes, why not, you are welcome
c.you need doctor's order to perform an EKG
d.I am sorry, still I am on part time position.
c.you need doctor's order to perform an EKG
Lead wire color for Left Leg is --
a.red
b.green
c.black
d.white
a.red
atrial dysthythmia has at least three clearly changing P wave and a heart rate of 101 to 150 beats per minute.
a.Wandering atrial pacemaker (WAP)
b.Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
c..Atrial fibrillation
d.Atrial flutter
b.Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
The usual speed at which the EKG machine runs out of EKG machine and records EKG at
a.2.5 mm per minute
b.0.25 mm per second
c.25 mm per minute
d.25mm per second
c.25 mm per minute
Which of the following artifacts can be corrected by having the patient relax and stay still?
a. somatic tremor
b.AC interference
c.Wandering baseline
d.Interrupted baseline
c.Wandering baseline
Your patient's heart rate changed from 110 to 37. You note regular, upright, matching P waves. The rhythm has changed from ---
a.sinus Bradycardia to normal sinus rhythm
b.sinus Tachycardia to sinus Bradycardia
c.normal sinus rhythm to sinus arrhythmia
d. normal sinus rhythm to sinus Tachycardia
b.sinus Tachycardia to sinus Bradycardia
You should place the limb electrodes before the chest electrodes because:
a.The limb leads rarely require a skin prep or cleansing
b.The ECG will not run at all without the limb leads attached
c.They are closest to you and easiest to reach
d.They don't fall often
b.The ECG will not run at all without the limb leads attached
For adult performing a stress EKG test, which of the following is an indication to stop the test?
a.Diaphoresis
b.Hypertension
Rapid breathing
d. Tachycardia
a.Diaphoresis
You walk by a room where a co-worker is performing an EKG on a female patient. The door is open and the patient is not covered. You should --
a.inform your supervisor about the incident
b.ask your coworker not to forget to close the door and/or curtain
c.say sorry, and just go back to your room
d.quietly close the door and/or curtain
d.quietly close the door and/or curtain
Following are the ways to correct the somatic tremors ----
a.unplug electrical equipments, move bed away from the wall
b. replace loose electrodes and have the patient turn slightly to the side.
c.have patient place hands under his or her buttocks, remind patient not to move
d.apply electrodes securely, remove tension from lead wires
d.apply electrodes securely, remove tension from lead wires
PVCs that occur in different shapes and forms are called
- PVCs.
a.Coupling
b. Unifocal
c.Trigeninal
d.Multifocal
d.Multifocal
Sinus rhythm with a rate more than 100 bpm is.--
a.sinus Bradycardia
b.normal sinus rhythm
c.sinus dysrhythmia
d.sinus Tachycardia
d.sinus Tachycardia
The correct sequence for the conducting system is:
a.SA node, AV node, AV bundle, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers
b.SA node, bundle branches, bundle of His, AV bundle, Purkinje fibers
c.SA node, AV bundle, Purkinje fibers, bundle branches, bundle of His
d.SA node, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers, AV bundle, AV node
a.SA node, AV node, AV bundle, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers
Which of the following EKG changes is a sign of cardiac ischemia?
a.ST segment depression
b.ST segment elevation
c.Wide QRS duration
d.Long PR interval
d.Long PR interval
Usual rate for Wandering Atrial Pacemaker rhythm is - a.
a.100 to 150 bpm
b.60 to 100 bpm.
c.50 to 90 bpm
d. 60 to 80 bpm
b.60 to 100 bpm.
Deoxygenated blood from the body is drained back to -
a. left ventricle
b.right atrium
c.right ventricle
d.left atrium
b.right atrium
When applying chest leads, V1 is placed
a. midway between V3 and V5
b.at the fifth ICS, left midclavicular line
c.at the fourth ICS, right sternal border
d. at the fourth ICS, left sternal border
c.at the fourth ICS, right sternal border
When performing posterior 12 leads EKG, V7 is positioned at -----
a.Right posterior axillary line
b.Left posterior axillary line
c.Right para-spinal line
d.Left para-spinal line
b.Left posterior axillary line
Premature Ventricular contraction is a/an
a.premature beat from sinus node
b.premature beat from AV Junction tissues
c.premature beat from Atrial pathway
d. premature beat from ventricular tissue
b.premature beat from AV Junction tissues
What are common symptoms of low cardiac output?
a.Shortness of breath, hypotension
b.Chest pain, palpitations
c.Dizziness, confusion
d.All of these
d.All of these
During normal cardiac cycle, the electrical impulse representing Atrial depolarization, recorded on the EKG paper as ---------a.
a.T wave
b.QRS complex
c.P wave
d.U Waves
c.P wave
The rate for Accelerated Idio-ventricular rhythm is-
a.20 - 40
b.40 - 100
c60 - 100
d. 100 - 150
b.40 - 100
Which lead is considered ideal for P wave morphology check?
a.I
b.II
c.III
d.V1
b.II
The Einthoven triangle is formed by using the following placement sites
a.right arm, left arm, right leg
b.right arm left arm, left leg
c.right arm, left leg, right leg
d. any one of the above
b.right arm left arm, left leg
The ways to correct the AC interference is/are a.
a.replace loose electrodes and have the patient turn slightly to the side.
b. have patient place hands under his or her buttocks, remind patient not to move
c.apply electrodes securely, remove tension from lead wires
d.unplug electrical equipments, move bed away from the wall
d.unplug electrical equipments, move bed away from the wall
The innermost layer of the heart is called the:
a.epicardium
b.endocardium
c.visceral pericardium
d. Pericardium
b.endocardium
A patient using a diary with Holter monitoring should include all of the following except:
a.Sexual activity
b.Dizziness sensation
c.Exercising
d.Reading
d.Reading
Sinus rhythm with heart rate increasing during inspiration and decreasing during expiration is-
a.sinus Tachycardia
b.sinus dysrhythmia
c.sinus Bradycardia
d. normal sinus rhythm
b.sinus dysrhythmia
Which of the following EKG settings requires patient's informed consent?
a.Holter monitor
b.Stress EKG test
c.Posterior 12 lead EKG
d. Telemetry monitor
b.Stress EKG test
The three types of leads that make up a 12-lead ECG consist of:
a.4 augmented limb, 4 standard bipolar, and 4 chest leads
b.3 standard bipolar, 3 augmented limb, and 6 chest leads
c.6 standard bipolar, 3 augmented limb, and 3 chest leads
d. 6 augmented limb, 3 standard bipolar, and 3 chest leads
b.3 standard bipolar, 3 augmented limb, and 6 chest leads
V1 - V2 - V3 - V4 - V5 - V6 are known as: a.
a.Standard leads
b.Precordial leads
c.Bipolar leads
d.Augmented limb leads
b.Precordial leads
note: V1 - V2 - V3 - V4 - V5 - V6
Measurement of PR interval is ----
a.beginning of P wave to beginning of QRS complex
b.beginning of P wave to the end of P wave
c.end of P wave to the end of QRS complex
d.beginning of P wave to end of QRS complex
a.beginning of P wave to beginning of QRS complex
The heart's ability to initiate its own electrical impulse is known as
a.Conductivity
b.Contractility
c.Excitability
d.Automaticity
d.Automaticity
Deplarization of the cells causes the heart muscle to .--.
a. refill the chambers of the heart
b.relax (lengthen)
c.contract (shorten)
d.None of the above
contract (shorten)
The heart block dysrhythmia which is characterized by complete atrio-ventricular dissociation is
a.Third degree AV block b.Second degree AV block, type I c.Second degree AV block, type II d.First degree heart block |
a.Third degree AV block
The superior vena cava carries
a. oxygen-rich blood to the left atrium
b.oxygen -rich blood to the right atrium
c.oxygen-poor blood to the right atrium
d.oxygen-poor blood to the left atrium
c.oxygen-poor blood to the right atrium
When the EKG paper is read in a horizontal way, it gives the information related to:
a.voltage
b.time(duration)
c.height
d.amplitude
b.time(duration)
What would be the first and the most appropriate thing to say if a patient refuses an EKG
a.may I know why you don't wish to have an EKG done?
b.your doctor has order this test and it must be done
c.don't worry, it only takes a few seconds
d.I will have to report you to my supervisor immediately
a.may I know why you don't wish to have an EKG done?
An ECG tracing showing big waves that doesn't fit in the graph paper with the standard gain, what's the next step?
a.Adjust the gain to 20 mm/mV
b.Adjust the gain to 15 mm/mV
c.Adjust the gain to 10 mm/mV
d. Adjust the gain to 5 mm/mV
d. Adjust the gain to 5 mm/mV
Which of the following statements made by the patient indicates understanding of Event monitor?
a.I should remove the monitor when I go to bed"
b.I should stop my heart medications before using the monitor"
c.I should press on the button once I feel any symptom
d.I should resume my daily activities including my swimming lessons
c.I should press on the button once I feel any symptom
During sinus rhythm (normal heart activity) the primary pacemaker is --
a.AV junction
b.Bundle of HIS
c.AV node
d.SA node
d.SA node
One "small square" when is measured in horizontal axis for duration is equal to:
a. 0.2 sec
b.0.04 sec
c.0.08 sec
d. none of the above
b.0.04 sec
aVR - aVL - aVF are known as:
a.Augmented limb leads
b.Standard leads
c.Precordial leads
d.Bipolar leads
a.Augmented limb leads
Which of the following leads explore the left lateral wall of the left ventricle?
a.V1, V2
b.V3, V4
c.V5, V6
d.II, III
c.V5, V6
Normal QRS complex duration is --
- second.
a.0.12 to 0.20
b.0.22 to 0.26
c.0.06 to 0.10
d. 0.28 to 0.32
c.0.06 to 0.10
What adjustment is needed for recording EKG on a patient with orthopnea?
a.Put the patient on the left side
b.Put the leg electrodes on the abdomen
c.Put V1 and V2 electrodes higher level than normal
d.Put the patient in semi sitting position
d.Put the patient in semi sitting positio
In a normal ECG tracing, the T wave represents the:
a.repolarization of the atria
b.repolarization of the ventricles
c.depolarization of the ventricles
d.depolarization of the atria
b.repolarization of the ventricles
Normal PR Interval is
- second.
a.0.28 to 0.32
b.0.22 to 0.26
c.0.06 to 0.10
d.0.12 to 0.20
d.0.12 to 0.20
Which of the following leads explore the anterior wall of the heart
a.Leads I, II, IlI
b.Leads V3, V4
cLeads V5, V6
d. Leads aVF, aVL
b.Leads V3, V4
note:
Leads | Heart Wall / Area | Main Coronary Artery |
|---|---|---|
V1–V2 | Septal wall | Left anterior descending (LAD) |
V3–V4 | Anterior wall | Left anterior descending (LAD) |
V5–V6 | Lateral wall | Circumflex artery |
Leads I, aVL | High lateral wall | Circumflex artery |
Leads II, III, aVF | Inferior wall | Right coronary artery |
Which of the following EKG changes may indicate the patient suffering from a Myocardial infarction?
a. Absent P wave
b.Wide QRS duration
c.ST segment elevation
d. Short PR interval
c.ST segment elevation
The tricuspid valve is located between the:
a.left atrium and left ventricle
b. right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
c.left ventricle and the aorta
d.right atrium and right ventricle
d.right atrium and right ventricle
Unwanted marks on the EKG tracing caused by other source than myocardium is/are called
a.Asystole
b.standardization marks
c.artifacts
d. conduction marks
c.artifacts
With junctional rhythms P waves may be:
a. Upright and peaked
b.Multiple shapes
c.Having variable PR intervals
d.Absent or inverted
d.Absent or inverted
As you are conducting 12-lead EKG, a red line appears at the bottom of your EKG graph paper. This
means--
a. you have placed an electrode at the wrong place
b.Nothing, this is what occurs with each 12- lead EKG.
c.the EKG paper is running low and needs to be replaced soon.
d.the patient has moved during the procedure and so invalid recording
c.the EKG paper is running low and needs to be replaced soon.
The valve located between the left atrium and left ventricle is the:
a.Mitral (bicuspid) valve
b.Pulmonary valve
c.Aortic valve
d.Tricuspid valve
a.Mitral (bicuspid) valve
The term Dyspnea means:
a.Shortness of breath
b.Fast breathing rate
c.Normal breathing rate
d.Slow breathing rate
a.Shortness of breath
Wenckebach rhythm is a -
-- heart block
a.first degree
b.second degree, Type I
c.third degree
d. second degree, Type II
b.second degree, Type I
Which of the following EKG devices is used as real time monitor in hospital?
a. Holter monitor
b.Loop Memory event monitor
c.Telemetry monitor
d.12 lead EKG
c.Telemetry monitor
Two PVCs back to back are referred to as a a.
a.PVC occurring as multifocal
b. PVCs occurring as trigeminy
c.PVCs occurring as bigeminy
d.PVCs occurring as couplet
d.PVCs occurring as couplet
Leads I - II - IlI are known as:
a.Standard (bipolar) limb leads
b.Precordial leads
c.Unipolar limb leads
d. augmented limb leads
a.Standard (bipolar) limb leads
Diastole is the - phase of the heart
a.ventricular squeezing
b. contraction
c.relaxation
d.blood moving through the heart
c.relaxation
Which of the following is an indication to stop a stress EKG test
a.Respiratory rate of 25/ min
b.Hypertension of 170/90
c.Fatigue
d.Pulse Oximeter 90%
a.Respiratory rate of 25/ min
The right side of the heart (Right Ventricle) -
a.pumps Oxygen-poor blood to the lungs
b.pumps Oxygen rich blood to the lungs
c.pumps Oxygen rich blood to the Aorta
d.pumps Oxygen poor blood to the Aorta
a.pumps Oxygen-poor blood to the lungs
The phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart is pumping blood out to the body, also known as the contraction phase, is:
a.Systole
b.Diastole
c.Conductivity
d.Automaticity
a.Systole
Which of the föllowing rhythms would need immediate CPR and defibrillation?
a. Atrial fibrillation
b.Premature Ventricular Complexes
c.Ventricular Fibrillation
d.Accelerated junctional rhythm
c.Ventricular Fibrillation
A single beat that originates earlier from an ectopic focus from Atria, other than the SA node is called -----
a.Premature Atrial complex
b.premature Junctional complex
c.Premature sinus complex
d. premature ventricular
a.Premature Atrial complex
In a normal ECG tracing, the QRS complex represents the: ,
a.depolarization of the ventricles
b..repolarization of the ventricles
c.depolarization of the atria
d.repolarization of the atria
a.depolarization of the ventricles
The type of block in which the P waves have no relationship to the QRS complexes.
a.third degree heart block
b.first degree heart block
c.second degree heart block, type II
d. second degree heart block, type I
a.third degree heart block
During an exercise stress test, what will the patient be asked to do?
a.Decrease the level of exertion as the test progresses
b.Maintain same level of exertion throughout the test
c.Increase the level of exertion as the test progresses
d. The patient will not be asked to do anything during the test
c.Increase the level of exertion as the test progresses
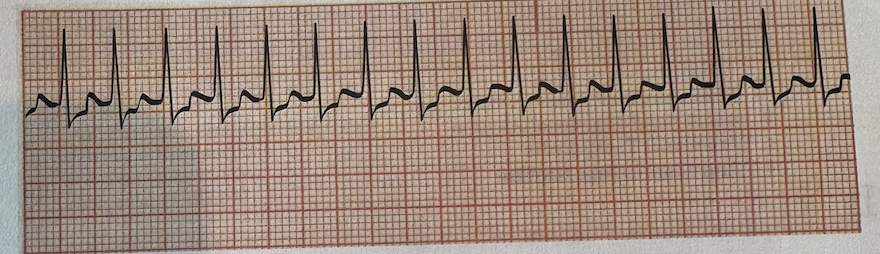
a.Premature Junctional Complex
b.Sinus Tachycardia
c.Supraventricular Tachycardia
d.Junctional Escape Rhythm
c.Supraventricular Tachycardia
8In pediatric population, which electrode is displaced to right chest?
a.V2
b.V3
c.V4
d.V5
b.V3
What is the heart rate?
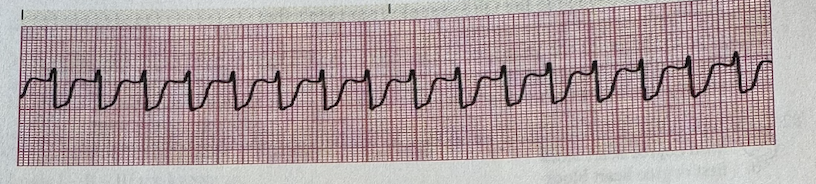
a.100 bpm
b.130 bpm
c.160 bpm
d.200 bpm
c.160 bpm
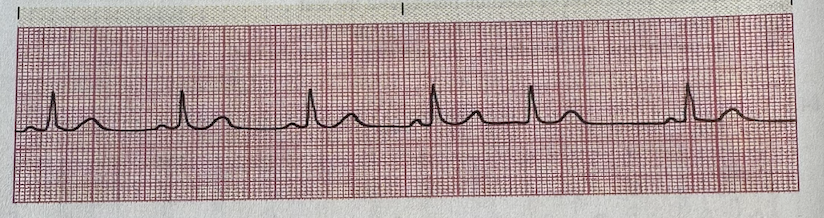
a.Premature Junctional Complex
b.Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
c.Junctional Tachycardia
d.Junctional Escape Rhythm
a.Premature Junctional Complex
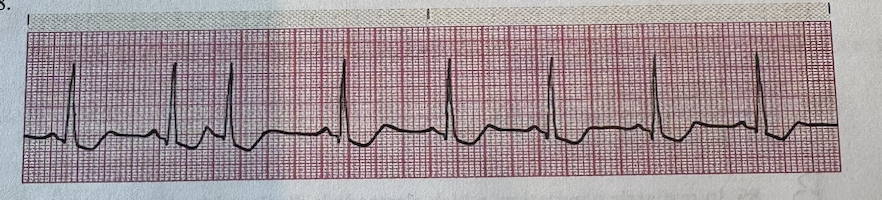
a.Atrial Fibrillation
b.Premature Atrial Complexes
c.Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
d. Sinus Bradycardia
b.Premature Atrial Complexes
A straight line connecting two waves is called
a.interval
b.Pause
c.Segment
dJunction
c.Segment
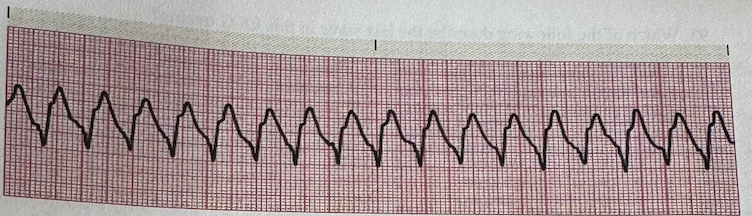
a.PVC Premature Ventricular Contraction
b.Ventricular Tachycardia
c.Idio-Ventricular Rhythm
d.Ventricular Fibrillation
b.Ventricular Tachycardia
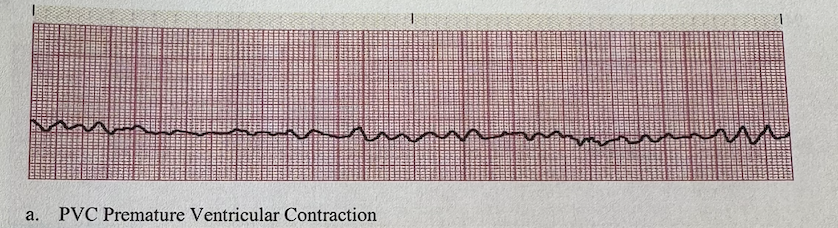
a.PVC Premature Ventricular Contraction
b.Ventricular Tachycardia
c.Idio-Ventricular Rhythm
d.Ventricular Fibrillation
d.Ventricular Fibrillation
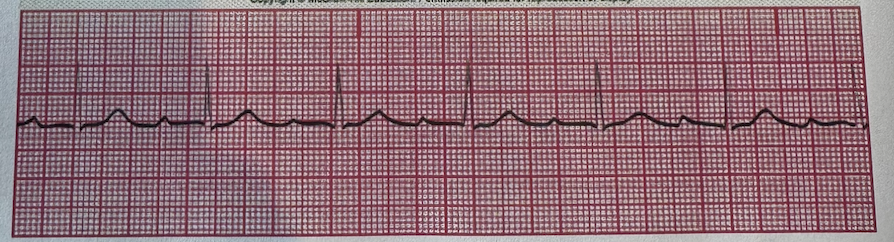
a.First Degree Heart Block
b.Second Degree, Type I Heart Block
c.Second Degree, Type II Heart Block
d.Third Degree (complete) Heart block
a.First Degree Heart Block
Which of the following describe the last wave in this EKG tracing?
a.Ventricular Fibrillation
b.Ventricular tachycardia
c.Premature Ventricular Complex
d.Premature Atrial Complex
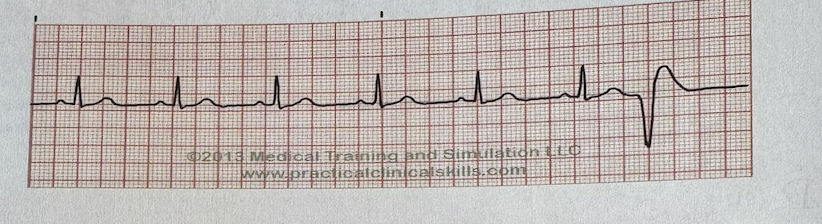
c.Premature Ventricular Complex
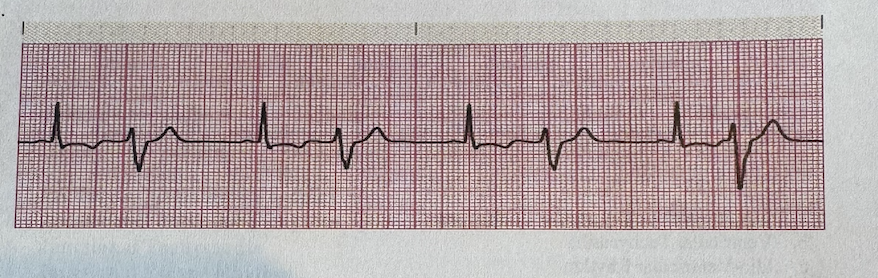
a.PVCs occurring as Run
b.PVCs occurring as Couplet
c.PVCs occurring as Bigeminy
d.PVCs occurring as Trigeminy
c.PVCs occurring as Bigeminy
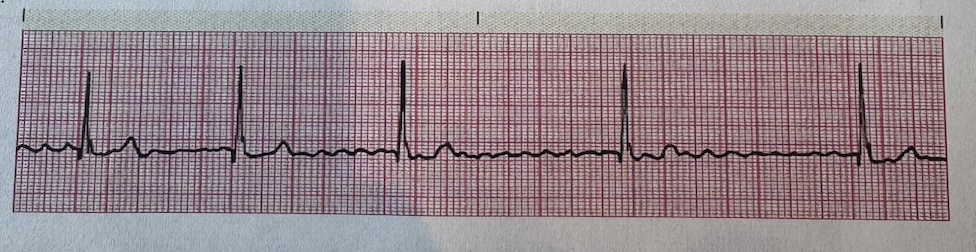
a.Atrial Fibrillation
b.Atrial Flutter
c.Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
d.Atrial Tachycardia
a.Atrial Fibrillation
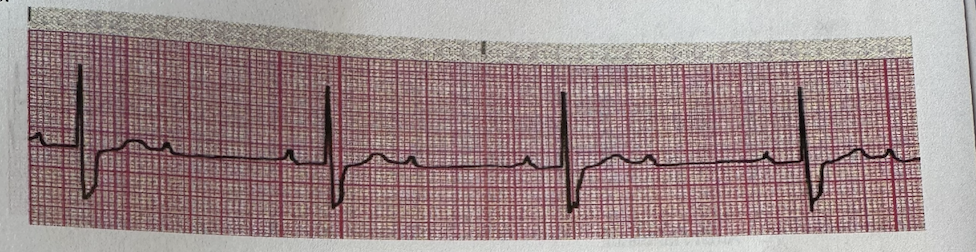
a.Ist Degree Heart Block
b.2 nd degree Heart block, type I
c.2 nd degree Heart block, type II (Mobitz II)
d.3 rd degree (complete) Heart block
c.2 nd degree Heart block, type II (Mobitz II)
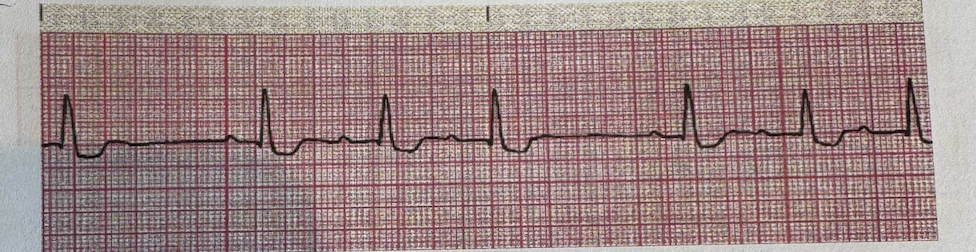
a.1st Degree Heart Block
b.2 nd degree Heart block, type I
c.2 nd degree Heart block, type II (Mobitz lI)
d.3 rd degree (complete) Heart block
b.2 nd degree Heart block, type I
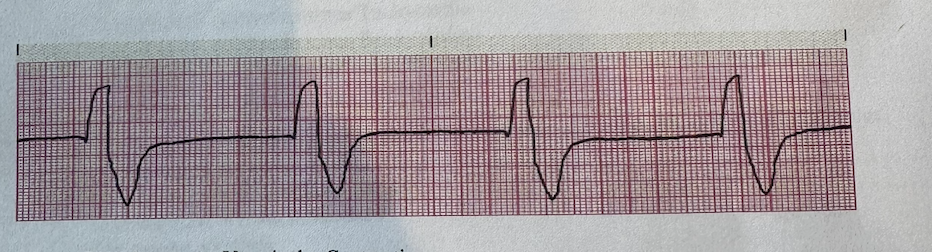
a.PVC Premature Ventricular Contraction
bVentricular Tachycardia
c.Idio Ventricular Rhythm
d. Ventricular Fibrillation
c.Idio Ventricular Rhythm
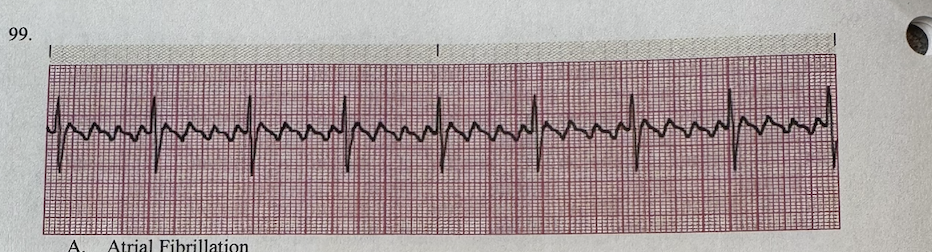
a.Atrial Fibrillation
b.Atrial Flutter
c.Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
d.Atrial Tachycardia
b.Atrial Flutter
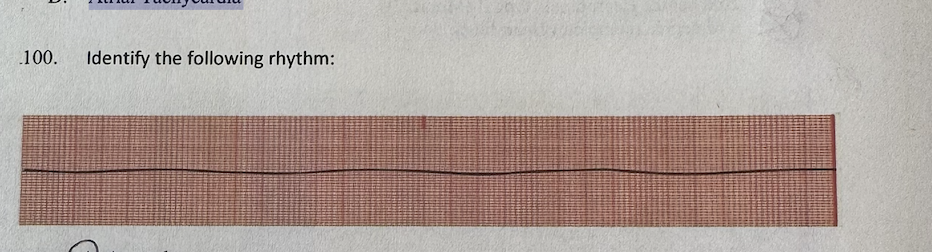
a.Asystole
b.Agonal
c.Ventricular fibrillation
d.Sinus bradycardia
a.Asystole