Heterotrophic Nutrition
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Define Nutrition
process of acquiring energy and materials needed for cell metabolism including repair of cells and maintenance and growth
Classes of organisms depending on how they obtain energy/carbon
chemoautotrophs co2 and synthesize energy through chemical reactions (nitrifying bact)
photoautotrophs; use photosynthesis
chemoheterotrophs; get carbon from organic substances and use chemical reactions to generate energy
photoheterotrophs; use light energy to synthesize organic matter from other organic material (purple non-sulfur bact)
3 ways in which heterotrophs obtain their food
parasitic - get nutrients from other living organisms
holozoic - complex food being broken down into smaller pieces to be absorbed
saprophytic - feeding on dead organic remains of other organisms
Main way of how food is processed in all heterotrophs
digestion - breaking down of food into small pieces to be absorbed
absorption - taking up of the products of digestion into body tissues
assimilation - using the absorbed nutrients for a particular purpose
General Description of Saprophytic Nutrition
secrete enzymes onto dead matter
soluble products of extracellular digestion are absorbed and assimilated
many of simple substances formed by breakdown of dead bodies are used by plants NOT the saprotroph
Explain Saprophytic Nutrition through Mucor and Rhizopus
fungi
hyphae penetrate the food and secrete hydrolyzing enzyme
extracellular digestion
carb and protease enzymes turn starch → glucose and protein → amino acids
branched nature - large sa for absorption
glucose - organism metabolic activities
amino acids - synthesize proteins for growth and repair
xs glucose is converted to glycogen and fat, amino acids in xs are stored as protein granules in the cytoplasm
Holozoic
free-living animals which have a specialized digestive tract - alimentary canal
Holozoic Nutrition Involves
Ingestion
Digestion
Absorption
Assimilation
Egestion
Ingestion
ingestive eaters - use a mouth to ingest food
filter feeders - small organisms and particles from the surrounding water
substrate feeders - eat the material they burrow through
fluid feeders - piece the body of a plant or animal and withdraw fluid
microphagous feeders - take in food in the form of relatively small particles
microphagous feeders - take in food in the form of relatively large particles.
Digestion
breakdown of large organic molecules into smaller soluble molecules
sac-like plans (gastrovascular cavities) - dual function of digesting and distributing digested products
tubular plan - food enters through one opening and waste leaving through another
mechanical or chemical digestion
intracellular digestion
cell englufs food
extracellular digestion
digestion occurs in the lumen of digestive system
Absorption
uptake of soluble molecules from the gut
directly into cells
uptake into the bloodstream
Assimilation
absorbed molecules are used to provide energy and materials to be incorporated into the body
Egestion
elimination of undigested waste material
In humans where does digestion and absorption occur
the alimentary canal /gut which is a coiled muscular tube extending from the mouth to the anus with several specialized compartments
Accessory Digestive Organs
connected to the main system by a series of ducts
produce compounds that contribute to digestion and release them into the gut
11 Main Parts of the Gut and their main functions
Buccal Cavity: ingestion, masticiation and digestion of starch starts
Pharynx; swallowing
Oesophagus; connects the pharynx to the stomach
Stomach; food storage and digestion of Proteins
Duodenum; digestion and absorption
Liver; production of bile to emulsify fats
Pancreas; digestion of proteins, fats carbs
Ileum; completes digestion and absorption
Colon; absorption of water
Rectum; storage and formation of faeces
Anus; egestion
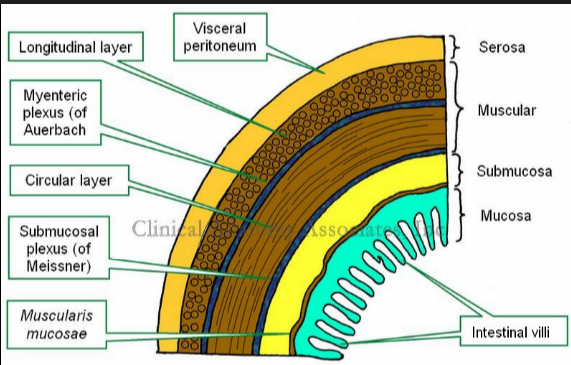
Generalize Structure of the Human Gut
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
serosa
Mucosa
→ mucosa is the major absorbing/secreting layer
Glandular Epithelium
secretes mucus to lubricate food
digestive enzymes
brush border of microvilli - increase SA
prevents digestion of the gut wall by its own enzymes
Lamina Propria
connective tissue containing blood and lymph vessels (carry absorbed nutrients away)
glands
Muscularis Mucosa
smooth muscle - produces folds of mucosa and submucosa to increase SA
Submucosa
its a layer of connective tissue containing nerves, lymph, blood vessels, collagen and elastin fibres
carries digestion and absorbed food away from ileum
nerves r sensory and regulatory
in duodenum Brunner’s glands
secretion of mucus
Meissner’s Plexus
nerve tissue which controls secretion from glands in the gut wall
Muscularis Externa
inner circular smooth muscle
constricts the gut when they contract
Sphincters
thickening of the circular muscle, control the movement of food from one part of the alimentary canal to the other
gastroesophageal - oesophagus/stomach
pyloric - stomach/duodenum
anal - anus
Longitudinal Muscle
shorten the gut
the interaction between these two layers causes the persitaltic movements which also mix the food
Auerbach’s Plexus
nerve tissue which controls peristalsis
sympathetic stops digestion and parasympathetic resumes digestion
Serosa
outermost layer coat of the gut wall
lines abdominal cavity and forms mesenteries
peritoneum
covers serosa - helps to reduce friction as peritoneum cells are moist
mesenteries
double layers of peritoneum which contains nerves, blood vessels and lymph vessels that pass to and from the gut
attach stomach and intestines to the body wall
Buccal Cavity
chamber inside the mouth where mechanical digestion takes place
tongue mixes and moistens the food with saliva
Saliva
contains salivary amylase or ptyalin
lysozyme → kill bacteria
mucus → lubricate food making it easier to swallow
mineral ions such as chloride ions which activate the salivary amylase
saliva is secreted via the salivary glands
Swallowing of Food
bolus forms and is then pushed toward the pharynx by the tongue
here a reflex is triggered where the larynx closes, soft palate moves up and the epiglottis covers the entrance of the trachea
Teeth
located on the fixed upper jaw and the moveable lower jaw
function is to masticate food - mechanical digestion, increases surface area for enzymes
deciduous vs permanent teeth
Types of Teeth + Dental Formula
up to 32 permanent teeth in humans
8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 12 molars

Incisors
located at the front of the buccal cavity
flat and sharp edges
cutting and biting food
Canines
pointed teeth
highly developed in carnivores
piercing, killing and tearing flesh
Premolars
posses one or two roots
2 cusps
crushing, grinding and in humans tearing food
Molars
more then 1 root
upper molars have 3 roots
lower molars have 2 roots
they have 4/5 cusps
crush and grind food
The Oesophagus
made of stratified squamous epithelium (abrasion) - also contains mucus glands
entry of food stretches muscles in the muscularis externa triggering peristalsis
contraction/shortening of circular and longitudinal muscles respectively causes the bolus to advance
passes through cardiac sphincter into the stomach
Function of cardiac sphincter
prevent backflow of gastric juices
causes heartburn if doesnt prevent backflow
Stomach
muscular bag which can hold up to 5L of food
has 3 layers of smooth muscle instead of 2
mechanical digestion - churning which produces chyme
dotted with gastric pits which lead to tubular gastric glands lined with gastric juice secreting cells
contains endocrine cells which secrete GASTRIN
2 types of specialized cells in the gastric glands
parietal cells (oxyntic cells) - SECRETE HCL
Chief Cells (zymogen cells) - Secrete inactive enzymes pepsinogen and prorennin
Function of hcl secreted by parietal cells
kills many bacteria
alters 3’ structure of proteins - increasing surface area
acidic pH for enzymes to work
converts pepsinogen/prorennin into their active forms
hydrolysis of sucrose into fructose
loosens fibrous and cellular components of tissue - increases surface area
Function of Pepsin
hydrolyses proteins into smaller polypeptides
pepsin by POSITIVE FEEDBACK activates other pepsinogen molecules
Function of Rennin
rennin coagulates casein (protein in milk) into insoluble calcium salts making it easier to digest
What can be absorbed directly through the stomach
alcohol, caffeine, aspirin
Significance of sphincters
prevent uncontrolled exit of food
regulation of pyloric sphincter ensures the duodenum only works on small amounts of food at a time.
Small intestine
carbs and protein digestion continues, and digestion of fats and absorption starts here
first part is the duodenum - pancreatic and bile ducts
leads to jejunum and ileum
folded mucosa and submucosa
goblet cells secrete mucus - lubricate food
What does the mucosa possess in the small intestine
villi with many blood and lymph vessels
able to contract/relax which brings them closer to the food
many microvilli which increase surface area
base of epithelium folds inwards to form the crypts of Lieberkühn
Purpose of Crypts of Lieberkühn
epithelial cells r produce to replace those being shed from villi
secrete intestinal juice - slightly alkaline - increases volume of fluid
paneth cells - secrete lysozyme
Duodenum secretes alkaline fluid - what is its function
neutralize acid of stomach
provides and optimum pH for enzymes of small intestine
Digestion of Fats
bile is produced in the liver from cholesterol and stored in the gallbladder
enters via bile ducts
contains bile salts which EMULSIFY large fat globules into smaller ones
pH of 7.6 - 8.6
increase the surface area for lipase to work
MECHANICAL DIGESTION - CHEMICAL DIGESTION INVOLVES HYDROLYSIS
Digestion of Proteins and Carbs
through the pancreas
secretes lipases, amylases and proteases such as trypsin, chymotrypsin and carboxypeptidases
enter through pancreatic duct - joins w bile duct
enzymes (proteases esp) are released as zymogens
trypsinogen → trypsin by enterokinase
trypsin activates more trypsinogen molecules and chymotrypsin
pancreas also produces a secretion rich in bicarbonate ions (alkaline)
small intestine also has enzymes immobilized on the microvilli
hydrolysis of disaccharides, dipeptides and tripeptides producing monosaccharides and amino acid
Saliva - source, enzyme, action, site of action and pH
salivary glands in buccal cavity
salivary amylase
starch → maltose
buccal cavity
6.7-7.5
Gastric Juice - source, enzyme, action, site of action and pH
gastric glands in the stomach
rennin ; (prorennin) casein → insoluble salt of casein
pepsin (pepsinogen) proteins → large peptides
stomach
ph 2
Enzymes bound to microvilli - source, enzyme, action, site of action and pH
microvilli
amylase - starch → maltose
maltase - maltose → glucose
lactase - lactose → glucose + galactose
sucrase - sucrose → glucose + fructose
aminopeptidase - proteins → large polypeptides
dipeptidase - dipeptides → amino acids
enterokinase - trypsinogen → trypsin
nuclease - nucleic acid → nucleotides
site of action - duodenum
ph - 8.5
Pancreatic Juice - source, enzyme, action, site of action and pH
pancreatic glands in the pancreas
pancreatic amylase; starch → maltose
trypsin (trypsinogen); large peptides/proteins + small peptides and chymotrypsinogen → chymotrypsin
chymotrypsin (chymotrypsinogen); large peptides/proteins → small peptides
carboxypeptidase; small peptides → amino acids (attacks c-terminus)
lipase; lipids → glycerol + fatty acid
nuclease; nucleic acids → nucleotides
Endopeptidases + exopeptidases
endo; hydrolysis of peptide bond in the interior of the polypeptide chain (trypsin, pepsin, chymotrypsin)
exo; hydrolysis of single amino acids from the end of polypeptide chain (aminopeptidase, carboxypeptidase)
Absorption/Assimilation
takes place in the villi of ileum (dense blood supply + microvilli (high sa))
monosaccharides, amino acids, depeptides are absorbed via active transport or diffusion depending on conc gradient
capillaries join to form hepatic portal vein, delivering the products of digestion to liver
fatty acids and glycerol - diffuse into columnar epithelial cells → lipids → chylomicrons → lacteal by exocytosis (lymph vessel)
chylomicrons → near heart where enter blood circulatory system, enzyme in blood lipids → fatty acids and glycerol and they r taken up by cells
inorganic salts, vitamins + water r also taken up
some bile is reabsorbed and return to liver
What is the point of chylomicrons
so they dont clump up together in the water of the lymph/blood
chylomicrons are coated with protein - lipoproteins
Large Intestine
No digestion takes place here
only absorption of water
mucus lubricates faeces
metabolic waste/inorganic substances r excreted here
symbiotic bacteria exist here which synthesize amino acids and vitamin K which is absorbed into the blood stream
Appendix
posses no function in humans
if material gets trapped here - appendicitis
Faeces
dead bacteria
cellulose
other plant fibres
mucus
cholesterol
bile pigments and water
dead epithelial cells
stored for 36 hours in colon before being passed to rectum then anus
Anal Sphincters
1 smooth muscle - involuntary
1 straited muscle - voluntary
Control of Digestive System
nervous/hormonal control
Mention Stimuli which control digestion through the NERVOUS SYSTEM
sight/smell/thought of food
Taste
Stretching of Stomach
Acidic Chyme in Duodenum
Sight Smell and Thought of Food
conditioned response
produces saliva
Food in contact with tastebuds - reflex and response
Unconditioned reflex
sends nerve impulse to the brain which stimulates the salivary glands to release saliva
stimulates liver to release bile
stimulates stomach to release gastric juices
stimulates pancreas to release enzymes
Stretching of stomach by food
stretch receptors in the stomach send a nerve impulse to meissner’s plexus
this stimulates release of gastric juice
nerve impulse travels to colon without going through CNS
this stimulates stronger peristaltic conditions from stomach to large intestine - expulsion of faeces
presence of acidic chyme in duodenum
sends nerve impulses to brain
inhibits secretion of gastric juices
slows release of chyme into duodenum
→ this is because the role of the stomach at this point is done, and we dont want to overload the duodenum.
Stimuli which control digestion through HORMONAL CONTROL
stretching of stomach by food
presence of chyme rich in partially digested fats and proteins in duodenum
presence of partially acidic chyme in duodenum
Stretching of Stomach By food - site of production, hormone, target, response
produced in the lower mucosa of stomach
gastrin
stomach
stimulates secretion of gastric juices in upper stomach mucosa
increases movements (peristaltic movements) of the stomach
Presence of chyme with partially digested fats and proteins in duodenum - site of production, hormone, target, response
duodenal mucosa
CCK cholecystokinin
stomach → inhibits stomach emptying
pancreas → release of pancreatic juice and digestive enzymes
gallbladder → contraction, stimulating release of bile
Presence of Acidic Chyme - site of production, hormone, target,response
duodenal mucosa
secretin
stomach - inhibits secretion of gastric juices
pancreas - increases production of hydrogen carbonate in pancreatic juice
liver - more hco3- in bile, making it more alkaline
Fate of Absorbed Glucose
stored in the liver or muscle as glycogen
stored in adipose tissue beneath the skin
used in respiration or other functions
Fate of Absorbed Amino Acids
deaminated via the ornithine cycle in the liver
synthesis of enzymes, hormones and proteins needed for growth and repair
Fate of Absorbed Fats
stored in adipose tissue beneath the skin, around the heart/kidneys or around the mesenteries
incorporated into cell membranes as phospholipids
Dental formula of sheep
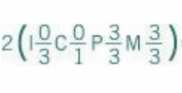
Adaptations of Herbivore Dentition (6)
No upper incisors or canines - instead there is a horny pad with which the lower incisors and canines bite when chopping grass
diastema (gap between front and cheek teeth) allows to manipulate grass keeping the fresh grass separate from that being chewed
Teeth have a broad grinding surface area (W and M shape which fit into each other)
open roots - teeth are constantly growing and therefore have to be worn down by the constant chewing
loose jaw - back,forward and side movement → w shaped ridges coming into close contact into grooves of m shaped - grind grass
large masseter muscle (grinding), small temporal muscle (biting)
Ruminant
animal which has a stomach with several chambers to maximize the benefits of their endosymbiotic microorganisms
Chambers of a ruminant stomach
Rumen
Reticulum
Omasum
Abomasum
Rumen
microorganisms which breakdown cellulose by fermentation produce carboxylic acids, co2 and methane
provide source of protein for animal
carboxylic acids - respiration in animal
microorganisms get a source of energy and an ideal temperature
Reticulum
microorganisms here too
food is turned into pellets
this is regurgitates and rechewed - CHEWEING THE CUD
this is then swallowed again and undergoes fermentation
- being properly chewed provides a large surface area for digestive enzymes
Omasum
absorption of water - concentrating partially digested food (cud)
Abomasum
HCL and proteases are secreted here
microorganisms killed by the acid and digested by proteases
in small intestine regular digestion by the usual mammalian digestive enzymes + absorption takes place
Hind-gut fermenters
which have a single chambered stomach and microbial fermentation chambers in the caecum
What makes hind-gut fermenters digestive system inefficient
since caecum empties into the large intestine absorption of nutrients produced by the microorganism is ineffective
so they must re-ingest their faeces
caecal material passes through the body once again and nutrients r absorbed producing a diff type of faeces which is discarded
Adaptations in carnivorous mammals
large carnassial teeth which allow for scraping of flesh off of bones
large temporal muscle used for biting, small masseter muscle used for grinding
incisors which meet and grip to rip flesh off of bones
large canines to grip and kill prey quickly
Why is herbivores digestive system longer?
because plant material is more complex to digest - requires specialized stomachs and microorganisms
protein is easier to digest and more nutrient dense so carnivores can go longer w out eating