ENTREP REVIEW 2nd QUARTER
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Includes the financial projections of the new venture.
It must provide a summary of projected sales.
Must anticipate the amount and timing of expected cash inflows and outflows.
Provide a summary of the assests the business will own.
FINANCIAL PLAN
It shows the sales forecast of a hypothetical shoe retailer named Pinoy Corporation.
preparing financial projections
also known as a pro forma income statement or forecasted income statement
Its like a "money plan" for your business. A way to predict how much money your business will make and spend in the future.
PROJECTED INCOME STATEMENT
Under PROJECTED INCOME STATEMENT:
1.Revenue (Sales) Projections
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
3. Gross Profit
4. Net Income Before Taxes
5. Taxes
6. Net Income (or Net Profit)
The estimate of how much money the business expects to earn from its products or services.
Revenue (Sales) Projections
These are the direct costs of producing the goods or services sold by the business.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
This is the difference between revenue and COGS.
Gross Profit
The profit before any taxes are deducted.
Net Income Before Taxes
Estimates the amount of taxes the business will need to pay based on its income.
Taxes
The final profit after all expenses, including taxes, have been deducted.
Net Income (or Net Profit)
Why Projected Income Statements Important?
Financial Planning: They help businesses plan for the future by predicting profitability and identifying potential financial challenges.
Budgeting: They provide a benchmark to compare actual performance against.
Decision Making: They inform key decisions, such as whether to invest in new projects, hire more staff, or cut costs.
Attracting Investors: They are often used to demonstrate the business’s potential profitability to investors or lenders.
Financial estimates that predict the inflow and outflow of cash in a business over a specific period.
CASH FLOW projections
key components in CASH FLOW projections
Cash Inflows
Cash Outflows
Net Cash Flow
Beginning and Ending Cash Balances
Includes all expected income, such as sales revenue, loans, investments.
Cash Inflows
Covers all expected expenses, such as operating costs, salaries, rent, loan payment.
Cash Outflows
Difference between cash inflows and outflows.
A positive net cash flow means more cash is coming in than going out, while a negative net cash flow means the business may need additional funding to cover expenses.
Net Cash Flow
Beginning cash balance is the amount of cash on hand at the start of the period.
Beginning and Ending Cash Balances
why is cash flow projections relevant?
lanning and Budgeting: Helps businesses plan for future expenses and investments.
Liquidity Management: Ensures there’s enough cash to meet short-term obligations.
Risk Management: Identifies potential shortfalls or cash crunches in advance.
Decision Making: Aids in making informed decisions about financing, expansion, or cost-cutting measures.
Under Projected Balance Sheet
Assets.
Liabilities.
Owners’ equity/Shareholders’ equity.
Refer to everything that the business owns that can be used to create value.
Assets.
These represent everything that the business owes to banks and other creditors.
Liabilities.
Representing the excess of all assets over all liabilities.
this is also known as the net worth of the business.
Owners’ equity/Shareholders’ equity.
The volume of sales at which the business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss.
Breakeven
indicates how many units of the product the business must sell to cover both variable and fixed costs and expenses.
The breakeven sales
BREAKEVEN ANALYSIS
Determining which of the costs are variable and, which are fixed.
Fixed costs: salaries, rent, utilities, sales expense, insurance and depreciation.
Variable costs, typically include direct labor and materials, are captured in cost of goods sold.
Behave differently even when they are faced by the same situation. That is because they perceive situations in different ways.
Individuals
Understanding how Customers make decisions
(a) recognizing a need or want.
(b) seeking or retrieving information.
(c) evaluating choices.
(d) making a purchase.
(e) assessing the product or service experience
When an individual recognizes a need or want, the buying process begins. This need or want can be triggered by internal or external stimuli.
Recognizing a need or want
Consumers evaluate their options differently:
Some make conscious, rational decisions, while others respond emotionally to the marketing stimuli.
When evaluating product
options, individuals betray
their beliefs and attitudes
Evaluating choices
Something one accepts as true or real; a firmly held opinion or conviction.
It serves the purpose of guiding action, and not necessarily of indicating truth.
BELIEF
A settled way of thinking or feeling about someone or something, typically one that is reflected in a person’s behavior.
ATTITUDE
Evaluation Stage where a consumer becomes clearer about his/her preference from among the items in his/her choice set.
Making a purchase
If the performance of the product falls short of his her expectations, he is disappointed (nadismaya); if it meets his/her expectations, he/she is satisfied (nakotento); if it exceeds his/her expectations, he/she will be delighted (nasiyahan).
Assessing the Product service or experience
Product claims must truthfully represent the product's ability to satisfy the consumer's needs.
Truth in Advertising
Assesing the product or service experience
A. For dissatisfied customers
-Might choose to return the product and ask for a replacement.
B. For satisfied and delighted customers
-There is a greater chance for them to purchase the product or avail the service again.
How customers react to dissatisfaction:
The Exit Option - deciding not to buy the product.
The Voice Option - warning others not to buy the product, or seeking redress from the company that sold the product.
the total lifetime value (or estimated lifetime revenues less expenses) a company can generate from all of its customers.
Customer equity
Types of customer equity & HOW TO IMPROVE
Value Equity
Brand Equity
Relationship Equity
The customer's objective assessment of the utility of a product or service based on his perception of what he is giving up for what he is receiving.
Improve: The business must find ways to address issues related to price, quality, and convenience.
Value Equity
The customer's subjective and intangible assessment of the brand, above and beyond its objectively perceived value.
Improve: The business must find ways to increase brand awareness, to improve the customer's attitude toward the brand.
Brand Equity
The customer's tendency to stick with the brand, above and beyond his objective and subjective assessments of the same.
Improve: The business can introduce loyalty programs, community-relations programs, knowledge-building programs, among others.
Relationship equity
Under Customer equity
CUSTOMER LOYALTY
Frequency Programs
Personalize Customer Relationships
Add Structural Ties with the Customer
Customers are now more demanding and harder to please, because they have more options to choose from.
CUSTOMER LOYALTY
Designed to reward customers who buy often and in substantial amounts.
Frequency Programs
Some loyal clients, for example, will go back to the same barber shop or parlor.
Personalize Customer Relationships
Examples include multiyear newspaper or magazine subscriptions that are offered at a large discount.
Add Structural Ties with the Customer
A"category of products that are all made by a particular company," all having a particular name.
Also defined as a "unique design, sign, symbol, words, or a combination of these.
Brand
To build Brand equity.
It must choose brand elements that
will serve to identify and differentiate
the brand.It must engage in marketing programs
aimed at building the brand.
These include brand names, logos, symbols, mascots, jingles, and slogans.
Brand elements
Choosing brand elements
Memorable
Meaningful
Likeable
Humorous
Short brand names are easy to recall.
Memorable
Must be credible and must also communicate the distinction of the brand.
Meaningful
Must be visually and verbally appealing to customers.
Likeable
Recognizable theme in the brand building efforts of Filipino companies, particularly micro- and small-scale enterprises, is humor.
Humorous
Allows consumers to be more actively involved with the brand by creating opportunities for the company to interact with existing or potential customers beyond the commercial transaction.
Experiential marketing
For small and medium enterprises, advertising is quite an expensive way of making their products and services known.
These include buzz marketing and social media marketing.
Emerging Practices
A viral marketing technique, focused on maximizing the word-of-mouth potential of a particular campaign or product.
BUZZ MARKETING
Maintaining a presence in social media platforms. To interact with customers, receive feedback, address their issues.
Social media marketing
A component of management that deals with planning, implementing and monitoring of the process of producing goods and services.
Operation Management
plans the structure of production by identifying the output to the produced.
Operation manager
Supervises the process of combining materials with other inputs according to the technology utilized to produce the identifies product.
Assesses the performance of production in terms of effectiveness,
The operations manager
OPERATIONS REALTED ACTIVITIES
Warehousing
Maintenance
Inventory management
Quality control
the company can buy materials in bulk and secure the stability of the next production round.
Warehousing
An important operations activity since it ensures the continuous productivity of the firm's capital equipment.
Maintenance
Crucial in narrowing the gap between the proximate future demand and the next production round.
Inventory management
Mechanisms are instituted to assure customers of the firm that its products are consistent and reliable.
Quality control
Evaluating the Performance of a Business
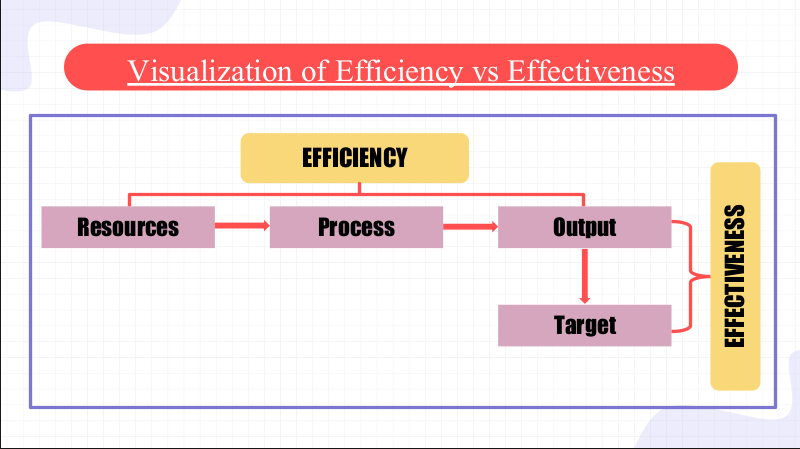
Performance Effectiveness
Performance Efficiency
indicates how the output of the firm was able to achieve the objectives set by the business enterprise.
Performance Effectiveness
How Performance effectiveness can be assessed
Quality
Speed
Dependability
Flexibility.
The product has fulfilled the minimum requirements set by the market and regulatory bodies.
Quality
The punctual delivery of the product to its customers.
Speed
The adaptability of the operations of the company to changing market environments.
Flexibility
Denotes how the output of the firm was realized through the use of resources.
Performance efficiency
Framework for Analyzing the Operations of an Enterprise
System Approach
Value Chain Approach
Under Systems Approach:
Input
Process
Output
Resource Inputs
Materials
Manpower
Machinery
Method
Money
Are semi processed goods that will be subjected to further transformation in the production process.
Materials
Human resource input used in the production process, including not only labor or muscular power but intellectual, creative abilities.
Manpower
Denotes the process of combining raw materials and jow these are going to be transformed using the other factor inputs of production.
Method
A financial resources used to purchase all the resources needed by the firm for its operations.
Money
2 major resource input categories
Intermediate Inputs
Factor Inputs
Semi processed materials that need further transformation to produce a finish product.
Intermediate Inputs
These are transforming inputs that will process the intermediate inputs into finished products.
Factor Inputs
Process
Physical Transformation
Locational Transformation
Information Transformation
Exchange Transformation
Extractive Transformation
Processing of raw materials convert them into significantly altered new products.
Physical Transformation
Arises when product changes its location through various means of transportation and communication.
Locational Transformation
Happens when knowledge andspecialized skills of providers are transmitted to their customers.
Information Transformation
Takes place when a commodity is transmitted from the supplier to its buyer.
Exchange Transformation
It happens when a natural resources is taken out from its habitat.
Extractive Transformation
Where it Outputs
Outputs from physical transformation
Outputs from locational transformation
Outputs from locational transformation
Outputs from information transformation
Outputs from exchange transformation
Outputs from extractive transformation
Seeks to understand the firms that operate within an industry—from input suppliers to end market buyers.
Value Chain Approach
Measures of cost
Measures of productivity
Measures of cost
Average productivity of labor
Average productivity of capital
Average Cost
Marginal productivity of labor
Marginal productivity of capital
Marginal Cost
Value of total production per unit of labor input.
Average productivity of labor
Value of total production per unit of capital unit.
Average productivity of capital
Total cost of production per unit of output.
Average Cost
Additional output per additional unit of labor input
Marginal productivity of labor
Additional output per additional unit of capital input.
Marginal productivity of capital
production per additional unit of production.
Marginal Cost