ENGG1700
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Concurrent
is done at the same time, existing
Coplanar
in the same plane
Colinear
lying in the same straight line
What is a roller and a hinge?
A roller has a force perpendicular to the surface and hinge has a vertical and horizontal force.
What are the equations of determinancy?
Determinate; stable; r + m = 2j
Indeterminate; stable; r + m > 2j
Unstable; r + m <2j
What are the four classifications of materials?
Metals, ceramics, polymer, composites
What are the components of metal?
Excellent heat and electrical conductors, deformable, strong, good machinability, e.g iron, copper
What are components of ceramics?
Electrical and thermal insulators, resistant to high temperature, hard, brittle, high BP, e.g cement, glass, oxides.
What are the components of polymers?
Primarily carbon and hydrogen, low densities, flexible, large molecule, e.g plastic and rubber
What are the components of composites?
To achieve a combination of properties or a combination of the best characteristics of each of the materials, e.g wood, fibreglass
What is a semi-conductor?
Properties that are intermediate between electrical conductors and insulators, e.g phones
What are biomaterials?
Non-toxic materials, used to replace infected things, e.g titanium
What is primary bonding?
Ionic, covalent, metallic. Usually stronger than secondary bonds.
What is secondary bonding?
Weaker than primary bonds, usually in polymers, very weak, induced dipoles and polar molecules.
Secondary bonding: What is hydrogen bonding?
H-F, H-O, H-N
What is a crystalline solid?
Atoms that are closely packed in a periodic 3D arrangement - crystalline solid is ordely packed and amphorhous is random packing
What is the coordination number?
The number of touching atoms
What is the atomic packing factor (APF)?
Volume of atoms in unit cell/total unit cell volume
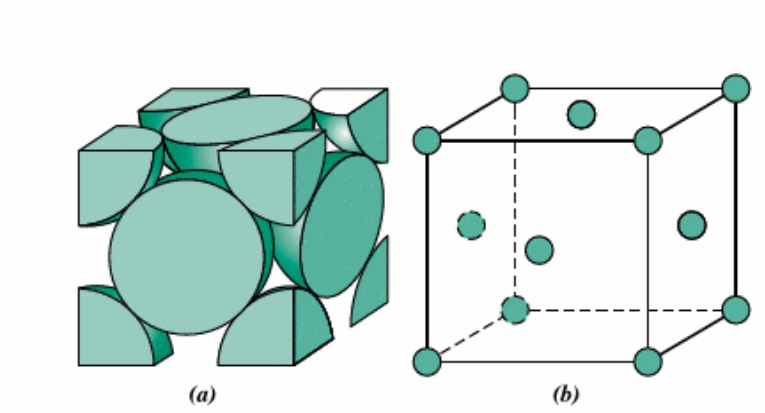
What is a face-centered cubic structure and its properties (coordination number etc)?
Unit cell with 8 atoms located at each corner and 6 in the center of cubed faces such as copper and aluminum. The coordination number is 12 and the APF is 0.74
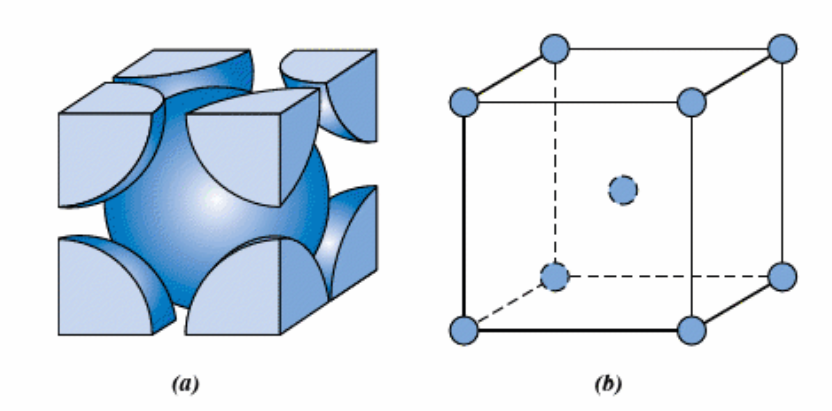
What is the body-centered cubic structure and its properties (coordination number etc)?
Atoms located at all eight corners and a single atom at the cubic center such as iron, tungsten. It has a lower coordination than FCC thus APF is lower
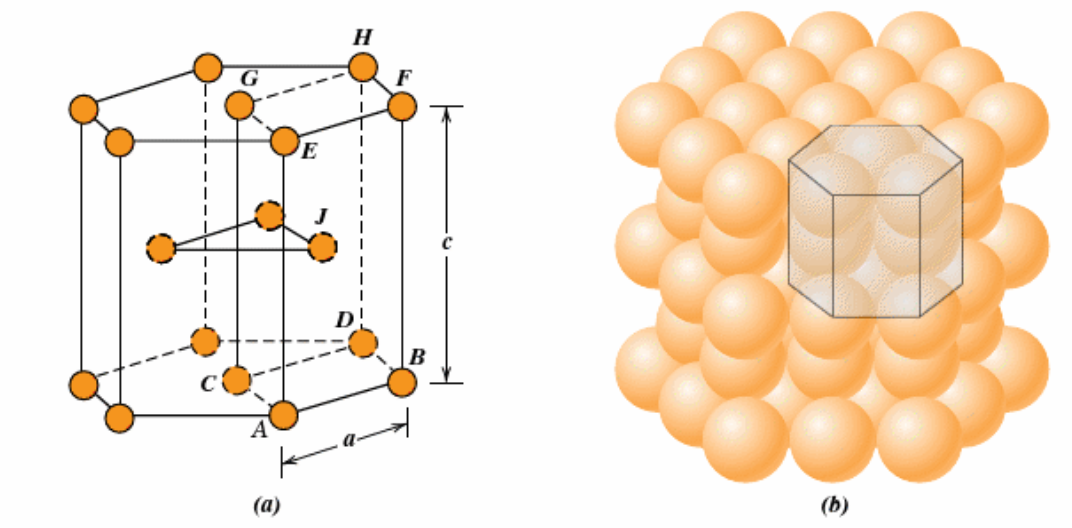
What is the hexagonal closed-packed structure and its properties (coordination number etc)
Top and bottom faces contain 6 atoms that form regular hexagons and single atom in center like titanium, zinc. Same APF and coordination number as FCC
Define elasticity
Allows a material to return to its original shape after being stretched.
What are the types of mechanical failure and explain them
Elastic deformation - returns to its original shape when unloaded. Plastic deformation - beyond yield strength, which causes permanent changes. Brittle failure - no significant plastic deformation
Define stress
The force acting on a unit area within a material, stress = F/Area
Define strain
The degree of deformation to the original size, strain = deltaL/original length
What is Hooke’s Law?
The force required to stretch or compress a material is directly proportional to the extension - F=kx
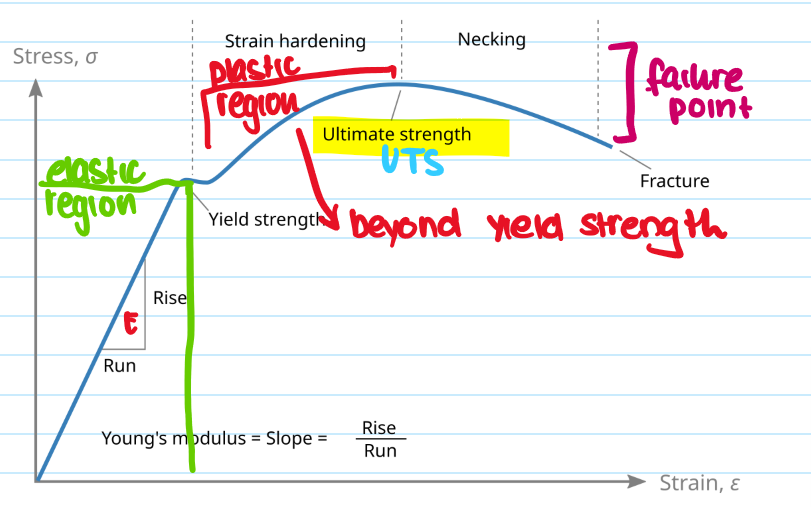
What is yield strength?
The stress at which a material begins to permanently deform - still in elastic region
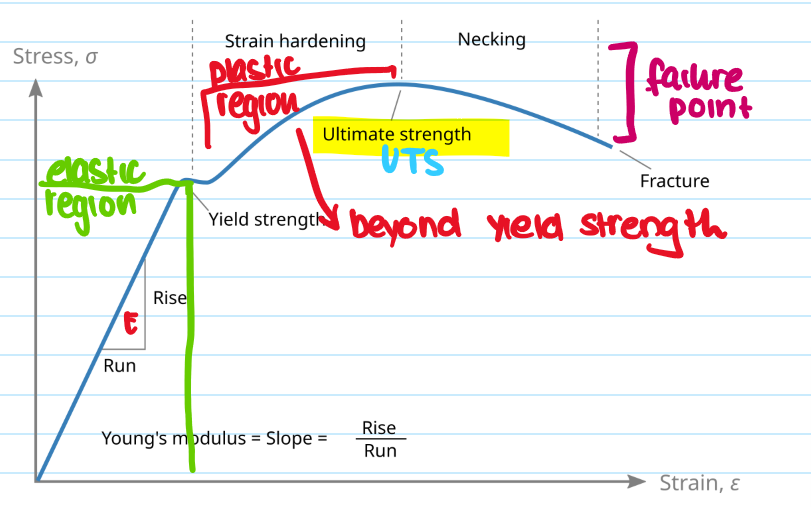
What is the ultimate tensile strength (UTS)?
The maximum stress a material can withstand before falling
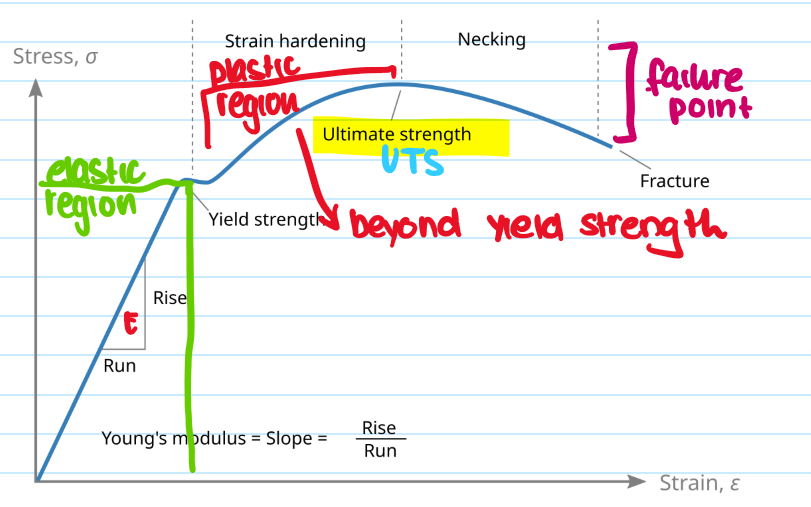
What is youngs modulus?
Measures materials stiffness in elastic region, E = stress/strain
Define ductility
Measures how much a material can stretch before deforming
What is percentage reduction in Area (%RA)?
Demonstrates the amount of thinning before failure, percentage decrease in cross-sectional area: Ao-Af/Ao x 100
What is percentage elongation (%EL)?
Indicates total extension before breaking, percentage increase in length at fracture: Lf-Lo/Lo x 100
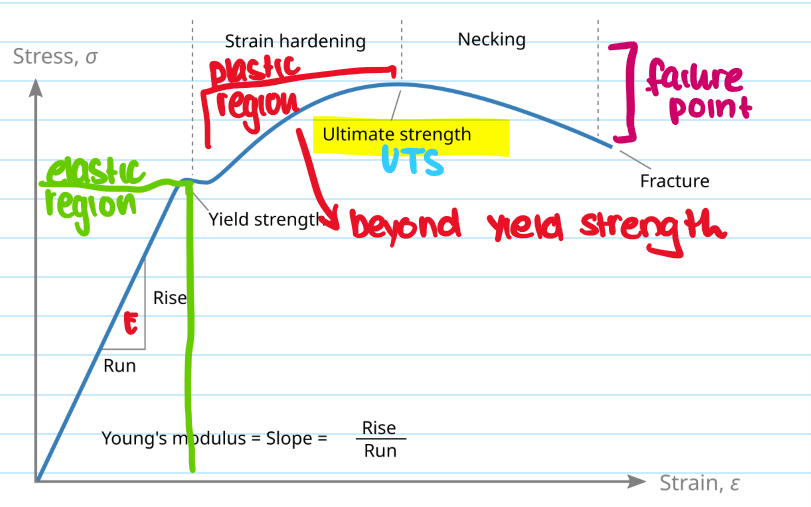
What is the necking region?
The localised reduction in cross-sectional area that occurs during plastic deformation under tensive stress - leads to a fracture
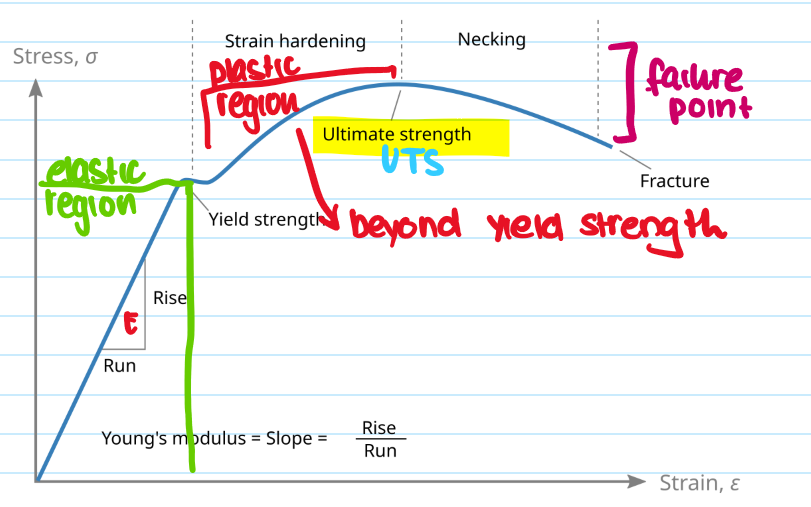
What is the failing point?
The end of a materials ability to sustain tensile stress - causes permenant deformation and packing
What is dislocation?
In crystalline solids, a dislocation is a type of linear defect within the lattice - irregularity where atomic planes are misaligned that allows metal to deform under stress without fractures.
What is edge dislocation? What happens to the burgers vector and direction of movement?
Occurs when an extra half-plane of atoms is inserted between normal atomic planes in a crystal structure. Burgers vector is perpendicular to the line and moved along a slip plane
What is screw dislocation? What happens to the burger’s vector and direction of movement?
Have extra atomic planes. Arranged in a helical pattern around a central axis, which allows atoms to shift position along a dislocation line. Burgers vector is parallel to line and moves in a tangential slip
Why is the dislocation motion important for plastic deformation?
It allows atoms to slide past each other without fractures; plastic deformation occurs when dislocations move freely through crystal structure.
Define strengthening mechanisms
Helps the strength of the materials by hindering dislocation motion
What are the two types of strengthening mechanisms?
Create more grain boundaries - finer grains
Introducing lattice strain through solid-solution alloying
What does the first strengthening mechanism do?
Impedes dicloation motion through smaller grain sizes, which leads to shorter paths and thus higher yield strength.
What is the hall petch equation?
sigmay = sigmao +ky(d)^1/2
What is alloying?
Used in metals, it strengthens metals by introducing lattice strain through substitutional or interstitial solutes.
What are substitutional or interstitial solutes?
Substitutional - replaces solvent atoms; interstitial - fills space and limits dislocation movement
What do solute atoms do?
Create local strain fields in a crystal lattice that interfere with dislocation movement - the field depends on the size of the solute atom.
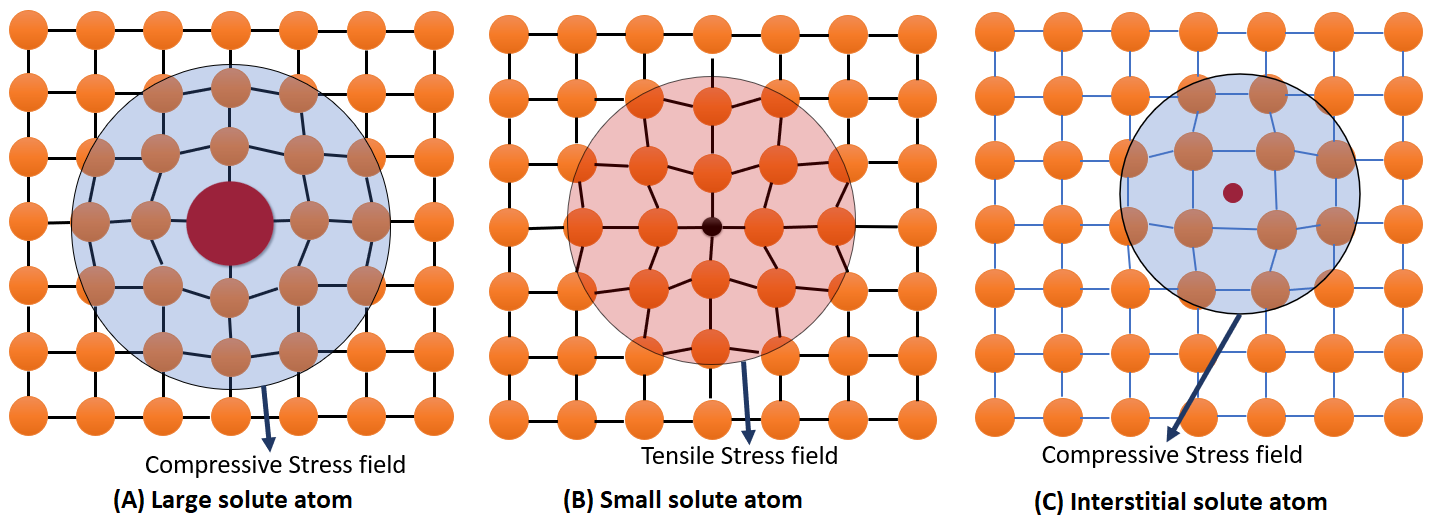
What are the different size of solute atoms and what happens to field?
Larger = compressive strain = substitutional
Smaller = tensile strain = substitutional
Very small = compressive strain = interstitial
What is a strain field?
Interacts with dislocations, making them harder to move thus strengthens the material
What is cold working?
A metal forming process where a material is deformed at room temperature, increasing dislocation density and thus strengthening the material.
What is cold work?
The percentage reduction in cross-sectional area of a metal during plastic deformation, which creates a small reduction in ductility.
What is the process of grain structure changes?
When the dislocations multiplu and organise themselves into cell walls
What are the steps for grain structure changes?
Initial formation of dislocations
Development of dense cell walls
Fragmentation into smaller cells
Thickening of cell walls
What is anisotropy and the different directions?
Formed from strength hardening, meaning its properties differ based on direction.
Along deformation = higher strength, low ductility
Perpendicular = opposite
What are the different arrangements of polymers?
Linear, branched, crosslinked, networks
What are the properties of linear and branched polymers?
Linear - flexible and soft, branched - more rigid than linear
What are the properties of crosslinked and network polymers?
Crosslinked - stiffer, less flexible, network - hardest, least flexible
What is a semicrystalline?
Both crystalline and amorphous or both ordered chains or not
What are the properties of a crystalline material?
High density, high strength, opaque
What are the properties of an amorphous material?
lower density, lower strength, transparent