Atomic Structures Vocabulary (unit 1)
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Atomic Structure & Electromagnetic Radiation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
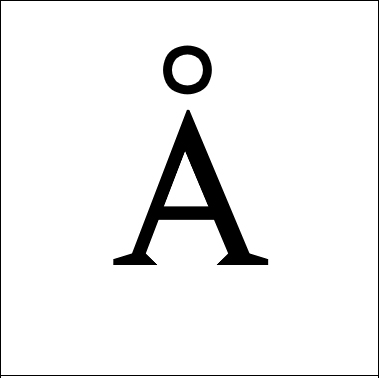
Angstrom Å
subatomic unit of distance equal to 10-10 meters, used to measure wavelength
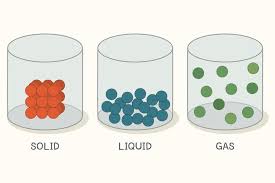
Matter
has form or shape and occupies space
Mass
quantity of matter contained in object
units: kilogram or grams
Weight
force that object exerts under influence of gravity
Substance
a material with a definite and constant composition

Element
a simple substance which cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by ordinary means
Compound
a complex substance made of two or more elements that are chemically united in definite proportions
Molecule
when 2 or more atoms chemically unite
smallest unit of chemical compound
Atom
smallest particle of an element that still possesses chemical properties of that element
Atomic #
Z-number - determined by the number of protons in an atom which is unique to each element
Proton
positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom - determines the atomic number
Neutron
subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom - has no charge & is considered neutral
Nucleon
Nuclear particle - includes protons and neutrals
Atomic Mass (A)
total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons) in an atom
amount of matter in an object - generally considered the same as weight for rad. purpose
Electron
negatively charged subatomic particle that orbits the nucleus and has essentially no weight
Covalent Bond
occurs when two atoms share their unpaired electrons - the most common form of Bonding (forms a weak bond)
Ionic Bond
atoms with opposite charges are attracted - this force pulls them together to form a strong bond
Ionization
the process of adding or removing an electron from an atom
Periodic Table
a table of elements listed in order of their atomic or Z number, with elements in the same columns having similar chemical properties
Radiation
energy that is emitted and transferred through space
Isotope
atoms of an element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
makes atom unstable which results in radioactivity
atom gains or loses neutrons
Radionuclide
any atom which is radioactive (unstable)
Radioisotope
any atom which is radioactive because it has too few or too many neutrons
Radioactive Decay
the loss of any mass or energy from the nucleus of an atom
AMU
atomic mass units - mass of particles of an atom
Electron Binding Energy
the amount of energy needed to remove the electron from the atom
Frequency
the number of waves passing a particular point in a given time
Photon
a small bundle of energy - amount of energy depends on the frequency
Valence
the number and configuration of the electrons in the outer shell
Octet Rule
the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom never exceeds 8 electrons
K Shell
the orbital shell closest to the nucleus
Dual Nature of X-rays
X-rays travel in waves but behave as a particle when interacting with matter
Speed of light
186,000 miles/sec in a vacuum OR 3×108 meters/sec in a vacuum
Wavelength of X-rays
0.1 to 0.5 Å
Energy
the ability to do work
Kinetic Energy
energy of motion
Potential Energy
energy of position (stored energy until converted)
Chemical Energy
energy resulting from a chemical reaction
Electrical Energy
energy that is emitted and transferred thru matter
Thermal Energy
energy resulting from movement of atoms of molecules
Nuclear Energy
energy resulting from the nucleus of an atom
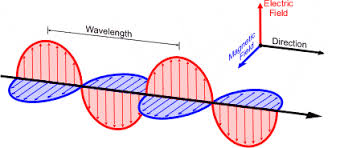
Electromagnetic Energy
energy that is emitted and transferred thru matter
radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray, gamma rays