Biomedical Science - Cell Biology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Cell
basic living units, smallest subdivision able to carry out life processes, contains organelles, specialised from specific physiological roles
specialised cells
in embryonic development, cell differentiation from stem cells leads to different cells adapted to specific functions eg. RBC
organelles
carry out cell functions
cell/plasma membrane
separates inside/outside of cell
cytoskeleton
microtubules/filaments/centrosome for support/movement
cystoplasm
jelly like fluid containing organelles (not nucleus)
Nucleus
contains DNA arranged in chromosomes, contains nucleolus where ribosomes are synthesised for protein synthesis, membrane bound by nuclear envelope which has small pores
mitochondria/ion
they metabolise/break down glucose in the presence of O2 to produce ATP for energy: respiration Glucose + Oxygen -> CO2 + water + ATP, contain small amount of DNA
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
side of protein synthesis
Smooth ER
side of lipid synthesis
Golgi body
proteins are sorted and transported/processed and packaged to other parts of cell/exported to outside of cell

Lysosomes
break down old organelles
phospholipid bilayer
keeps molecules at opt conc inside and out, is made of bilayer of phospholipid molecules, lipids face inwards hydrophobic, phosphate faces outwards hydrophilic
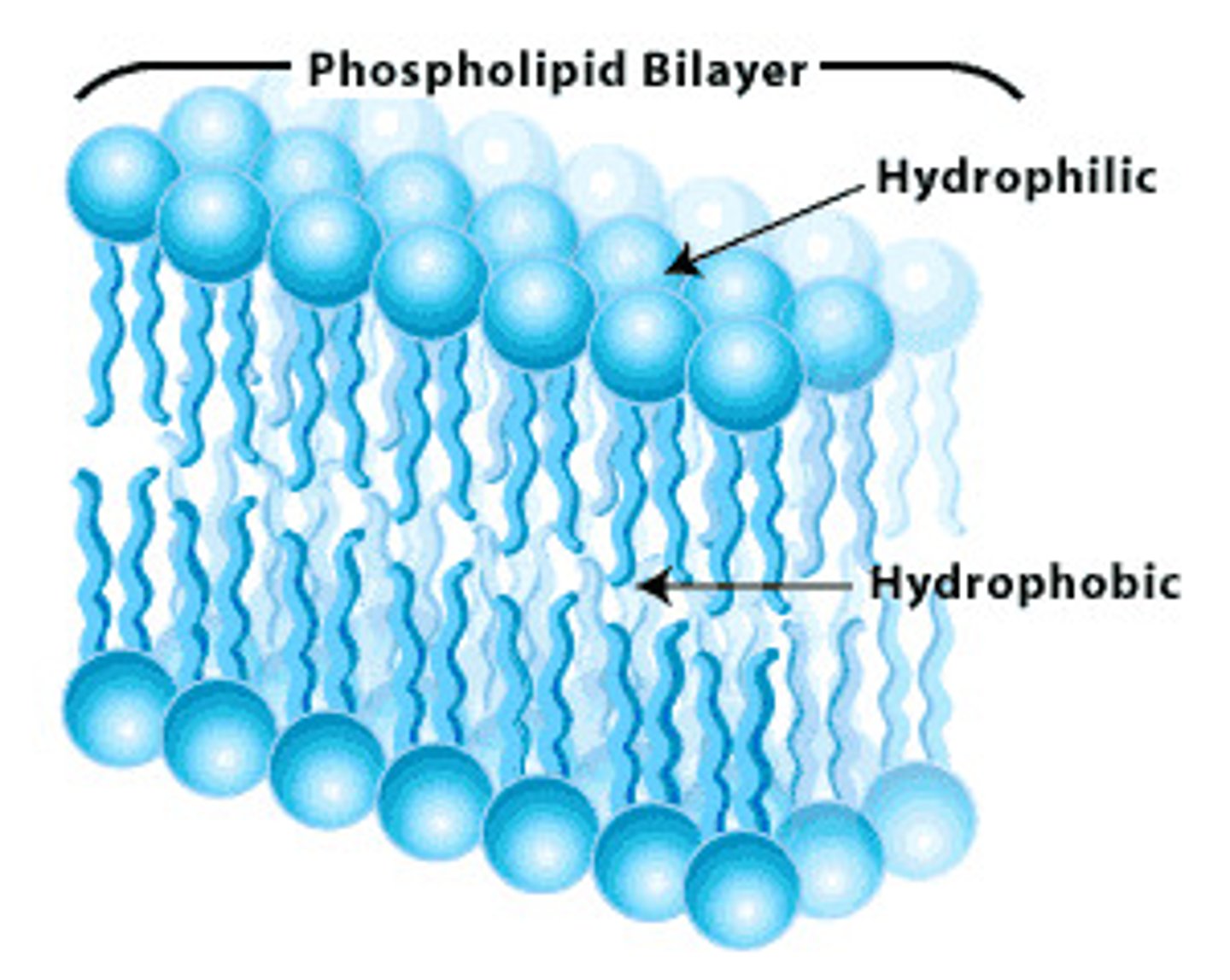
cell membranes are permeable to
gases eg O2 or molecules made of lipid eg. hormones like oestrogen (cross rapidly), small molecules eg water/ethanol (cross slowly)
cell membranes are impermeable to
large molecules such as glucose and amino acids they need membrane proteins to help them pass in/out, & ions (charged molecules) eg calcium and potassium which are repelled by lipids, need membrane proteins to come in/out of cell
water diffuses directly across phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes by
osmosis
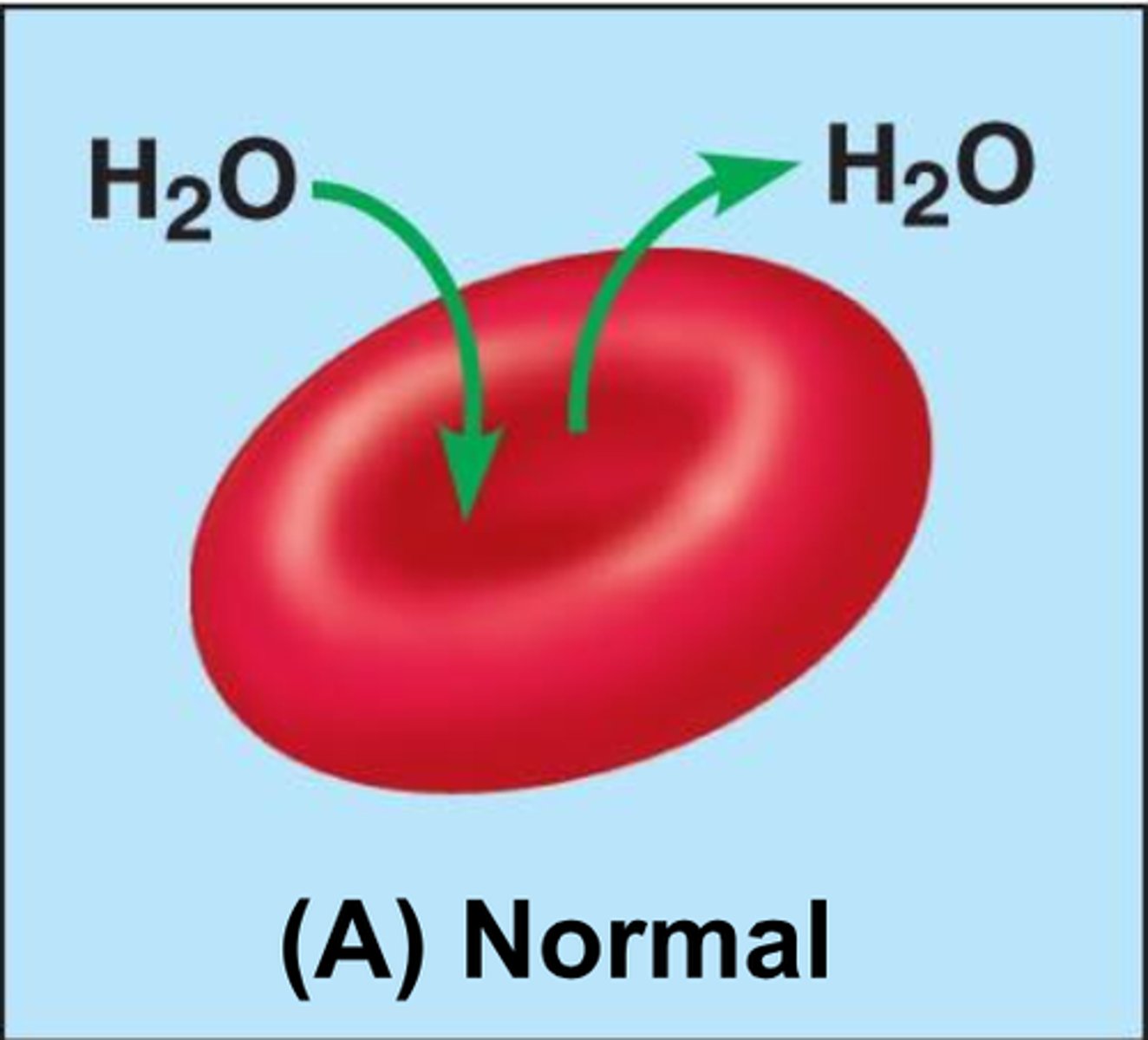
Isotonic
ion concentrations equal inside and outside the cell, no net movement
hypotonic
osmosis from high to low water conc, water moves into cell
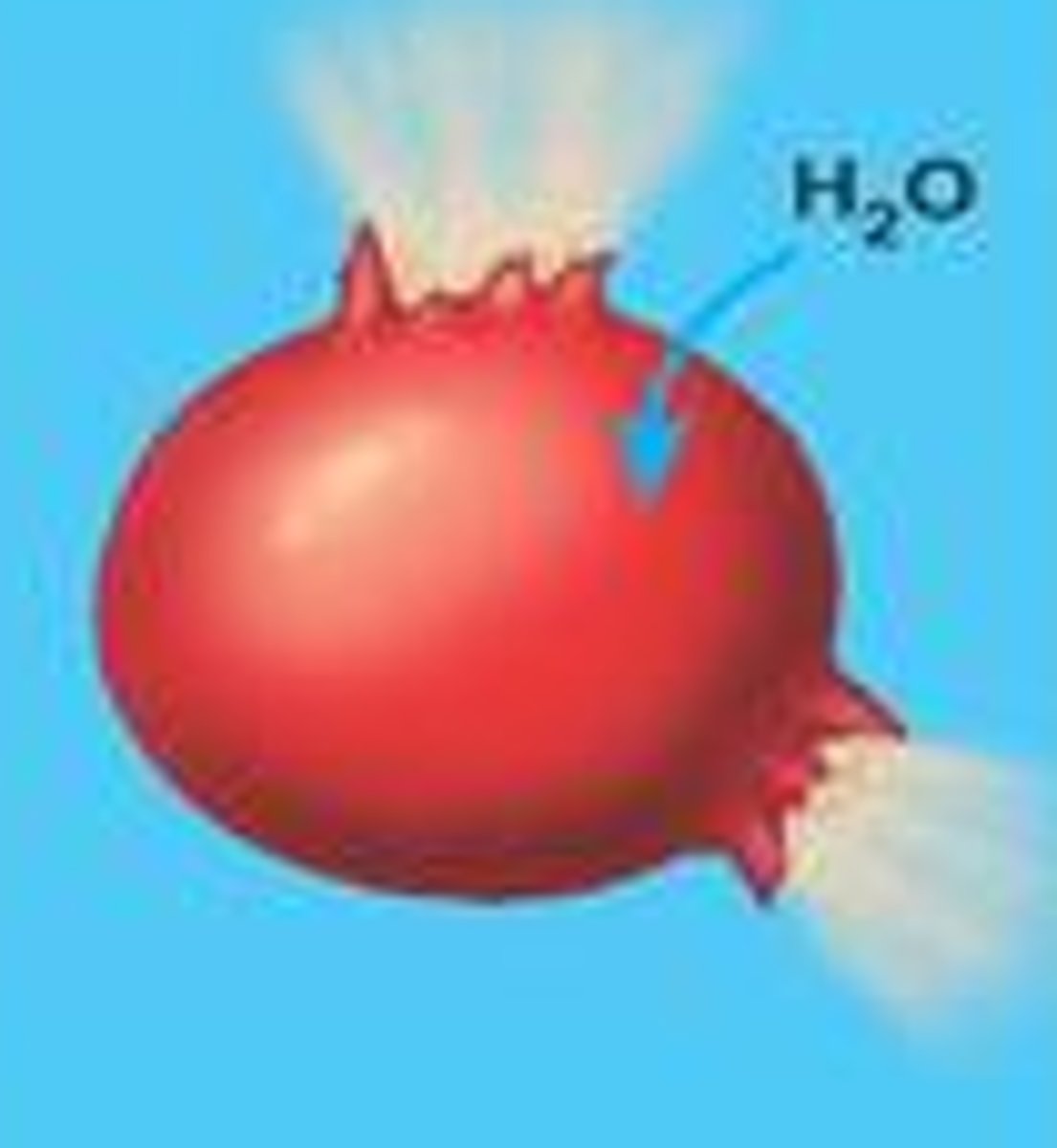

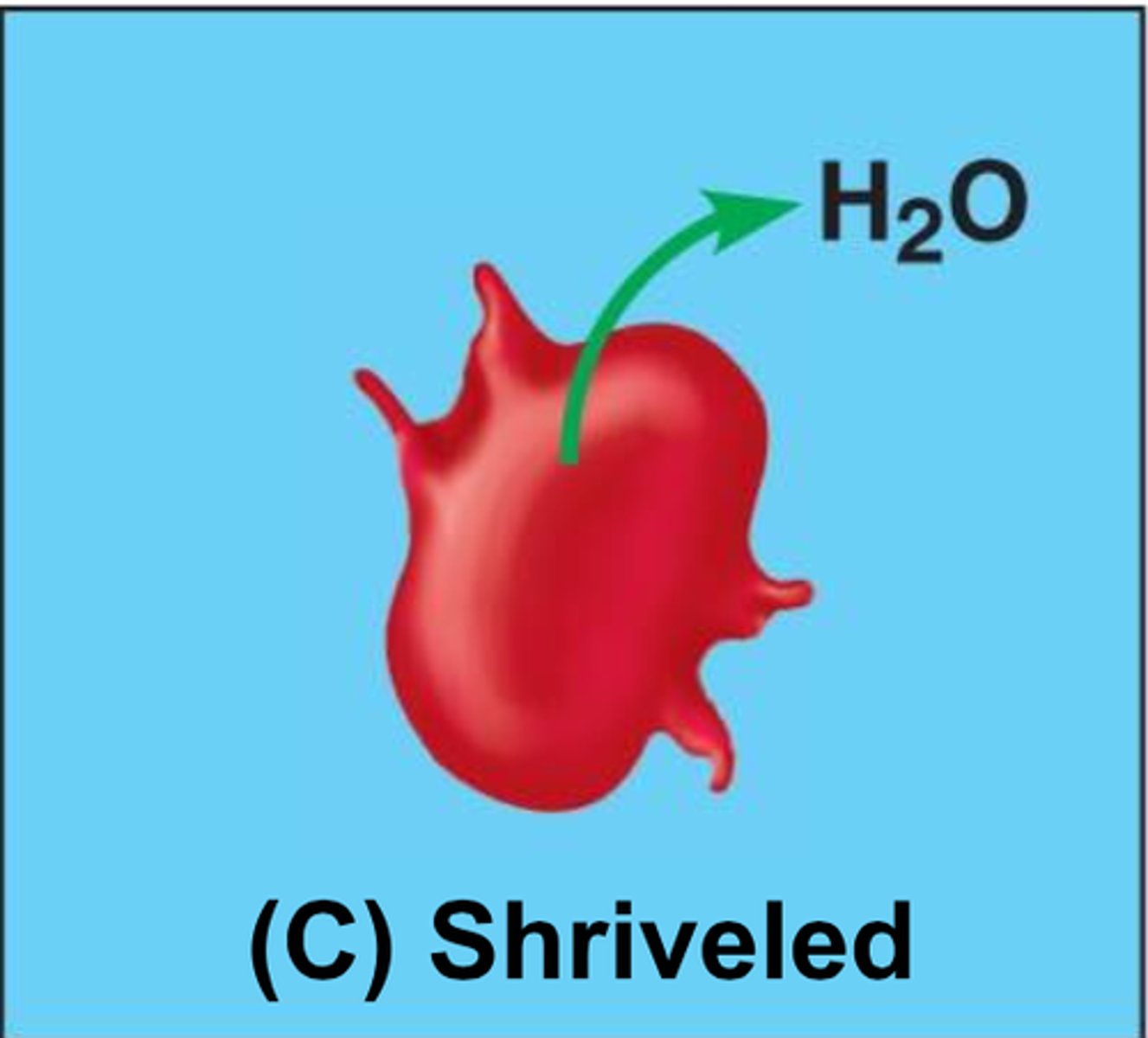
hypertonic
water leaves the cell
active transport
requires energy to move material through cell membrane LOW to HIGH against conc grad
Ions
atom/molecule with +/- charge, come from substances in diet called electrolytes