Lymph Node
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Introduction:
Shape
Location
What occurs to it during infection
Shape: Round, oval or bean shaped
Location: Along the course of blood vessels
During an infection: It enlarges making it easily palpated
What is the 4 functions of the lymph nodes?
Produces lymphocytes and antibodies
Filter the lymph
Serve as a defense mechanism to prevent spread of malignant cells
Represent potential haemopoetic organs (produce blood cells)
What is lymph?
Clear/yellowish fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system and contains:
Water
Proteins
Lymphocytes (WBC)
Fats
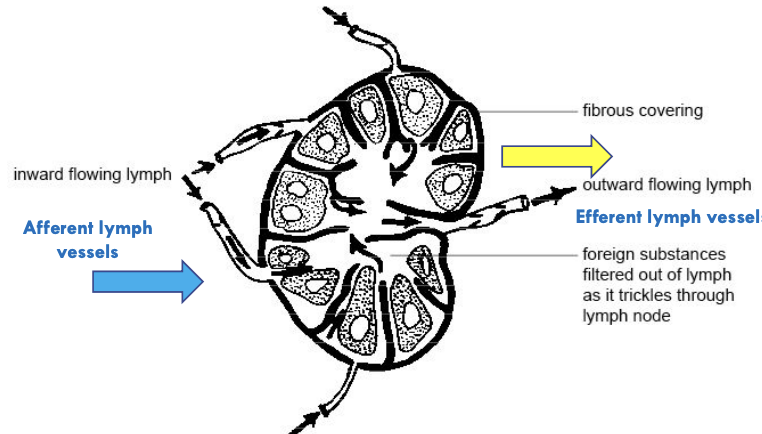
Describe the flow of lymph through a lymph node
Afferent lymph vessel:
Lymph enters the lymph node through the afferent lymph vessels
Where it carries antigens, pathogens and etc
Inward flowing lymph:
Once inside, lymph flows through network of sinuses (subcapsular, trabecular and medullary sinuses)
This allows immune cells to screen for harmful substances
Filtering process:
Lymph passes through the cortex (where B cell are) and paracortex (where T cells are)
Foreign substances are processed by immune cells
Efferent lymph vessel:
Cleansed lymph exits the lymph node through efferent lymphatic vessel
Where it is led to larger lymphatic trunks and eventually return lymph to bloodstream
What does the lymph node contain?
Capsule #ff7000
Afferent lymph node
Subcapsular sinus #ffcc2a
Hilus #00c2ef
Efferent lymph vessels
Trabeculae
Petritrabecular sinuses
Cortex #ae00ff
Medulla #ff00ac
Medullary cords
Medullary sinuses
Structure of Lymph Node: Capsule
What is it made of
Function
Made of: Dense irregular CT such as
Collagenous fibers
Elastic fibers
Fibroblast
Smooth muscle fiber (sometimes)
Function: Provides structure and protection
Structure of Lymph Node: Afferent Lymph Vessels
Function
Lined by
Surrounded by
Contain valves?
Function: Carry lymph to the lymph node
Lined by: Epithelium
Surrounded by: Thin layer of CT
Contain: Valves
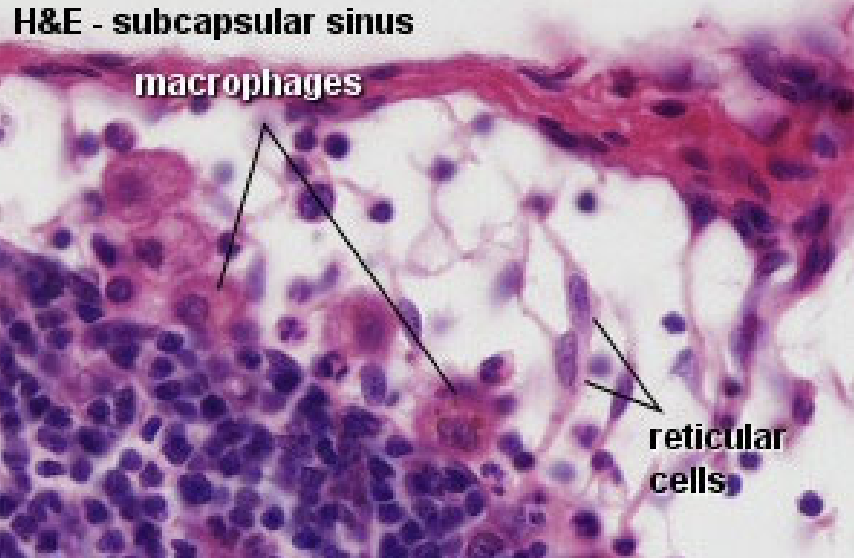
Structure of Lymph Node: Subcapsular sinus
What
Location
Function
What extends across the sinus?
What: Lymphatic sinus
Location: Below the capsule
Function: Represents the site of termination of the afferent lymph vessels
What extends across the sinus: Loose network of cells and fibers
Structures of Lymph Node: Hilus
What
Contains
What: Slight indentation on one side of node
Contains: Blood vessels, nerves and efferent lymph vessels
Structure of Lymph Node: Efferent Lymph Vessels
What
Function
Distribution compared to afferent lymph vessels
Diameter compared to afferent lymph vessels
As they leave the node, what does it pierce
Do they have valves?
What: Open-ended thin walled tubes within lymph node
Function: Carry lymph out from the lymph node
Distribution compared to afferent lymph vessels: Fewer in number
Diameter compared to afferent lymph vessels: Larger
As they leave the node, what does it pierce: Hilus
Do they have valves: Yes
Structure of Lymph Nodes: Trabeculae
What
Location
Function
Contain
What: Projections of CT which extend from the capsule
Location: Straight in the cortex and branched in the medulla
Function: Separate the cortex into incomplete compartments
Contain: Blood vessels
Structure of Lymph Nodes: Peritrabecular Sinuses
AKA
Identified as
Location
AKA: Trabecular sinuses
Identified as: Areas of diffuse lymphatic tissue
Location: Next to trabeculae
Structure of Lymph Node: Cortex
What
Contain
Types
What: Outer zone of the lymph zone
Contain: Lymphatic nodules that are either
Active (posses a corona and a germinal center)
Inactive
Structure of Lymph Node: Medulla
What
Are there lymphatic nodules present?
What: Inner zone
Are there lymphatic nodules present: No
Structure of Lymph Node: Medullary Cords
What
What: Strands of dense lymphatic tissue
Location: Which extend from lymphatic nodules of the cortex into the medulla
Structure of Lymph Nodes: Medullary Cords
What
What: Areas of loose lymphatic tissue in the medulla which lie between the medullary cords and trabecular