HP 353: EXAM 2 study guide
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
What are examples of primary care?
Immunizations, colds, physicals, ear infections
What are examples of secondary care?
OB/GYN, ENT, Surgery, Cancer treatment
What are examples of tertiary care?
organ transplant
congenital malformations
Which level of care is the most costly?
Tertiary care
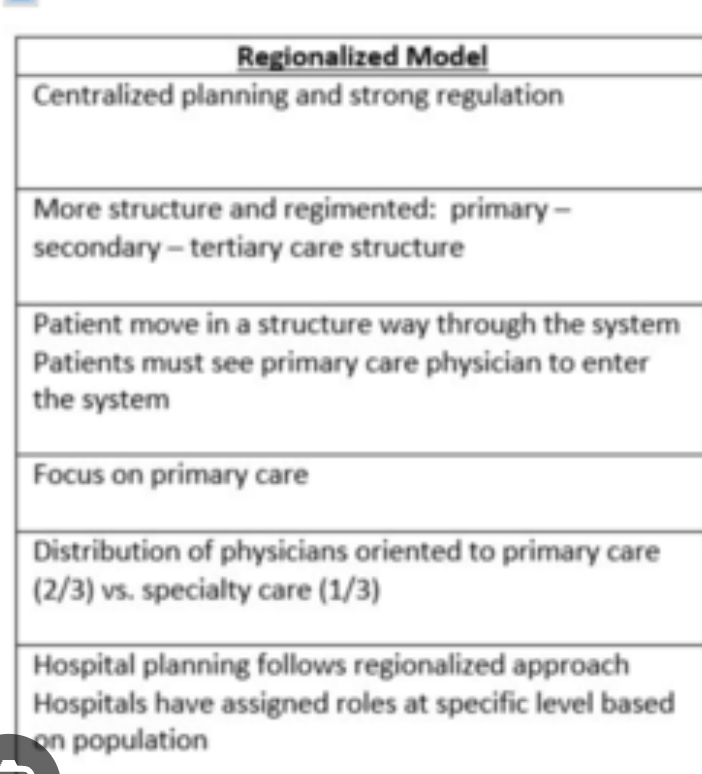
What are the features of the regionalized model?
structured hierarchy
primary care base
geographic coordination
general practitioners (GPs) at the primary level
What are the features of the dispersed model?
fluid access
emphasis on tertiary care
specialists provide primary care
less coordination
Why has the dispersed model grown in the U.S.?
Biomedical model, financial incentives (Medicare, Medicaid, blue shield), hospital expansion (Hill-Burton Act), physician autonomy
Arguments for the dispersed model?
pluralism
provider availability
patient choice
Arguments against dispersed model?
lacks coordination
higher costs
generalists provide comparable outcomes at lower costs
Why is the low supply of generalists a problem?
Generalists offer cost-effective care and meet common health needs; shortage leads to overuse of specialists
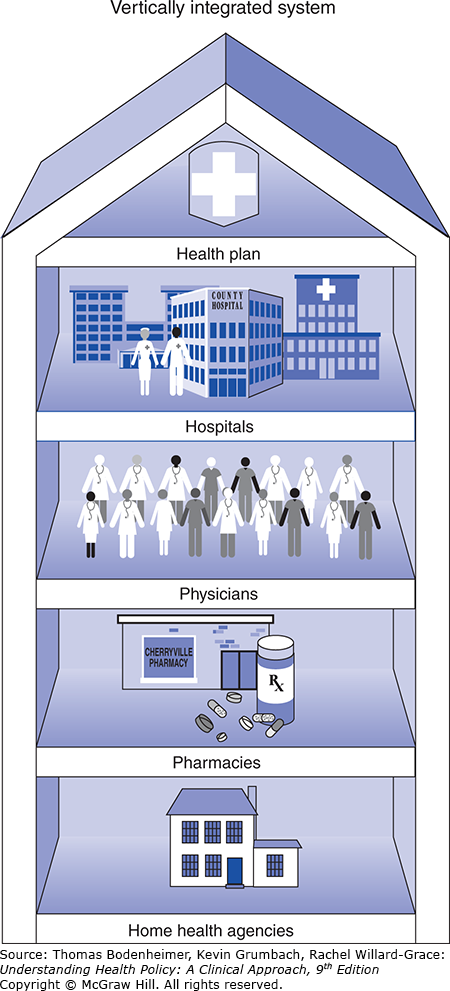
What is vertical integration?
Kaiser model:
all levels of care under one organization
capitated payment
population-based care
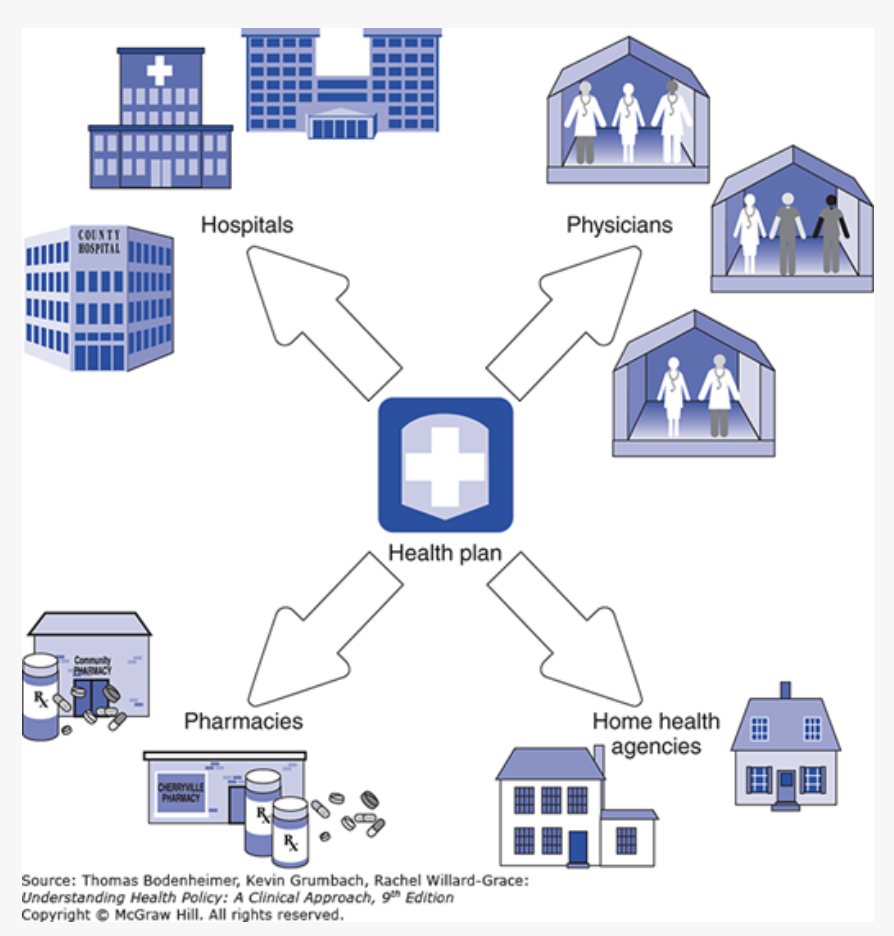
What is virtual integration?
IPAs (independent practice associations) and IMGs (integrated medical groups)
insurers contract with independent physicians
flexible
lower capital costs

Benefits of vertical integration?
Unified care, population health focus
Benefits of virtual integration?
flexibility
lower costs
market responsiveness
Disadvantages of virtual integration?
Less control, fragmented care, inconsistent coordination
Why is the HMO Act of 1973 important?
funded expansion of prepaid practices and independent practice associations (IPAs)
required employers to offer HMO plans
Differences between old and new primary care models?
Old: solo practice, fee-for-service
New: team-based, coordinated, EMR use, bundled payments
What is the role of hospitalists?
(Physicians who) care for hospitalized patients and return them to their regular physicians at discharge.
What are key features of patient-centered medical homes?
First contact is PCP
person-focused
comprehensive
coordinate care when patients need specialists
usually targets patients with chronic illnesses that are HIGH need
Practices must QUALIFY and meet standards to get certified
Accountable care organizations
Networks of physicians/other providers that are held accountable for the cost and quality of the continuum of care delivered to a group of Medicare patients.

Medical neighborhoods
Integrated services coordinated by PCPs, including specialists, pharmacies, hospice, etc.
Contributes to population health.
What percent of GDP was spent on healthcare in 2021?
17.9%
Why didn't health expenditures increase much in recent years?
weak economy
high-out-of-pocket costs
ACA cost controls
What does the health costs and outcomes model examine?
The relationship between cost and population health outcomes
What is the formula for cost
Cost = Price x Utilization/Quantity
What is painless cost control?
saving money by being more efficient with the money spent
saving money without lowering health outcomes
reducing WASTE, improving efficiency without harming outcomes
What is painful cost control?
Reducing beneficial services or access
What are regulatory strategies?
Government tax regulation (ex: Medicare A).
Weak because increasing taxes is political and inadequate tax support can lead to budget deficits
What are competitive strategies?
Market-based insurance competition. Weak because the U.S. hasn't been successful in controlling costs or quantity of care. Results in rising insurance plan premiums.
What are price controls?
Limit provider payments, may lead to increased quantity
What are quantity controls?
Limiting services via payment models, cost sharing, utilization management
What are mixed controls?
Combine price and quantity strategies.
What should cost containment policies focus on?
Capacity
budgets
capitation
provider mix
regionalizing high-tech services

Why is US healthcare quality lacking?
Poor access, practice variation
What are the 4 defects needing change?
overuse
underuse of effective care
misuse/errors in medical care
inefficiency/waste
Overuse
higher volumes
such as more office visits, hospitalizations, tests, procedures
more costly specialists, tests, procedures, and prescriptions than are appropriate
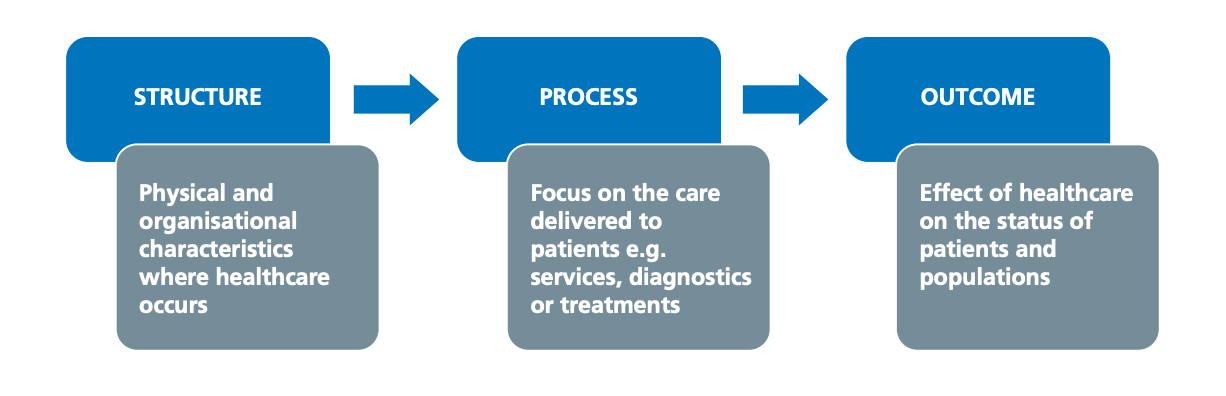
What are the 3 components of the Donabedian model?
structure
process
outcomes
Structure resource inputs include...
...facilities, equipment, staffing levels, staff qualifications, delivery systems
Process (actual delivery of services) includes...
...interpersonal aspects of care and technical aspects of care (ex: diagnosis, waiting time, service costs)
What is HEDIS?
healthcare effectiveness data and information set
set of performance indicators used to evaluate the quality of U.S. health plans
Examples of HEDIS indicators?
Immunizations, mammograms, prenatal exams, flu shots, BMI assessments
Wha are key proposals to improve healthcare quality?
licensure accreditation
peer reviews clinical practice guidelines
measuring practice patterns
continuous quality improvement
EMR
AI
pay for performance
What is Pay for Performance (P4P )?
Medicare initiative to reward quality across care settings (encourage improved quality of care).
What are the 4 principles of medical ethics?
Autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, justice

What is the four-box model?
medical indications
patient preferences
quality of life
contextual features
Medical indications
The goals of medicines what is felt to be clinically important and efficacious taking into account he medical history, accurate diagnosis, accurate prognosis and all treatment options
Patient preferences
Examination of the patient's ability to participate in decision-making must be considered. The patients personal history, religious and personal values, communicated preferences, advance directives, and self-assessed quality of life are relevant
Quality of life
3rd party assessment
Contextual features
External issues to consider such as economic constraints, family preferences, burdens on caregivers, other psychosocial parameters, and legal issues.
Why should we try and stay above the double line?
Focus in clinical facts and patient values before external factors.
What is rationing by medical effectiveness?
Prioritizing treatments with greatest benefit per cost
What is distributive justice?
Fair allocation of resources based on need, merits effort, etc
What does the patient self determination act require?
facilities must ask about advance directives (legal document that outlines your medical treatment preferences for future scenarios when you cannot speak for yourself)
and educate patients
What is competence?
Assumed in adults unless proven otherwise in a court of law
What is DMC (decision making capacity)?
Criterion applied clinically to assess a patient's ability to make authentic, self-determining decisions (task specific).
What is an advance directive?
A legal document that allows an individual to state one's wishes for future medical decisions under certain qualifying conditions
What are the 2 most used types of advance directives?
Living will
Durable power of attorney for healthcare
Living will
Written request to forego life-sustaining treatments in the event of a terminal condition when the patient lacks decision making capacity
Durable power of attorney for health care
Allows an individual to name a proxy or surrogate decision-maker who can speak for them should they become unable to participate in medical decision-making
Informal advance directives
Statements a person has made regarding certain health care situations and treatments, or a physician documentation of a discussion of the patient's wishes regarding future healthcare
Surrogate decision makers
One who has the moral and legal authority to make decisions for an individual who cannot make decisions for oneself.
The proxy can be assigned through an advance directive or informally in certain circumstances.
Substitute judgment
(What patient would want) Making decisions the patient would have, based on one's values and preferences.
Best interest standard
(What benefits patient most)
In the absence of knowledge of what decision the patient would have made, making a decision that is felt to be in the patient's best interest.
Assent
informal agreement from some unable to fully consent, but who can provide a preference related to medical care
Informed consent
Patient understands risks/benefits and agrees to treatment
Can patients refuse treatment?
yes, adults who posses DMC (decision making capacity) have the right to refuse medical treatment, even life-sustaining treatment.
surrogates can refuse based on values or best interest
Withholding vs withdrawing treatment
Legally and ethically equal, but emotionally different for those involved
What are the 4 main components of the ACA reform?
individual mandate
employer mandate
Medicaid expansion
insurance market regulations
T/F: all Americans are required to have health insurance under the ACA
True, but Trump revoked this in 2018
Primary feature of national health insurance plan?
How is the plan financed? Government, employer, or individual?
Secondary features of national health insurance plans
benefit package (which services are covered)
patient cost-sharing
effect of existing programs
cost containment
delivery system reform (coverage expansions and eligibility criteria)
What is "pay or play" requirements for employers
Employers with 50+ employees must offer health insurance coverage or pay a penalty ($2000 per employee excluding the first 30 employees)
How do we get insurance?
through work (employer-based)
Medicare
Medicaid
health exchange marketplace (if we don't qualify for any of the above).
What are small business tax credits?
Employers with <25 employees with an avg yearly wage <50K can purchase employee health insurance w a tax credit up to 35% of the employers contribution. Helps small employers afford coverage.
How is the ACA funded?
taxing people without coverage
increase Medicare tax on wages and unearned income
excise taxes on insurers that provide costly health plans
fees on pharma, insurers, and devices
What are health insurance exchanges?
Online marketplaces for individuals to compare and purchase insurance plans.
What efforts help contain costs?
Payment reform
prevention incentives
ACOs
Medical homes
FDA approving more generic drugs
Monitoring waste
What are the characteristics of long-term care?
Supports individuals with chronic illness, disability, or aging-related needs, includes medical and non-medical care over extended periods.
Who qualifies for long term care (LTC) services?
Individuals with chronic conditions, disabilities, or limitations in activities of daily living (ADLs) or instrumental ADLs (IADLs).
What is hospital (acute) care?
Short-term, intensive medical management for acute or exacerbated conditions.
What is rehabilitation facility?
provides complex medical management and intensive rehab, patients must tolerate and benefit from 3+ hours of therapy/day.
What is a skilled nursing facility (SNF)?
Offers skilled nursing and rehab, Medicare covers up to 100 days for skilled care, includes skilled and custodial levels.
What is a nursing home (custodial only)?
Provides unskilled, maintenance care (bathing, dressing), not covered by Medicare
What is hospice care?
For terminally ill patients (<6 months of life expectancy), includes intermittent skilled care, meds, counseling. Gaps: no 24 hour care
What is home health care?
Short-term skilled care at home. Patient must be homebound and show potential for improvement, Medicare pays lump sum for 60 days.
What did the Omnibus Budget ReconciliationAct (OBRA) of 1987 do?
Set federal standards for nursing homes, required ethics compliance programs, and improved oversight and accountability.
Does Medicare pay for long term custodial care?
No, only short term skilled care.
What does Medicaid cover?
Nursing home care, but not 24-hour custodial home care.
Private long term care insurance
people who most need it cannot afford it or are rejected due to chronic disease
polices have high deductibles
may not cover the services a person needs
What are strategies to improve long term care?
Develop social insurance, shift to community based care, train and support family members as caregivers, expand comprehensive acute and LTC organizations modeled on On Lok.
Social insurance
Publicly funded system where people contribute while healthy to cover future long term care needs (making small payments when you are well and earning money against sickness, unemployment, and retirement).
What is the On Lok program?
A community based capitated care model for frail elders (now PACE) that blends Medicare and Medicaid to reduce hospitalizations
Who does On Lok serve?
Adults 55+ eligible for nursing home care, average 7 chronic conditions, 4+ ADL dependencies, high cognitive impairment.
How does On Lok reduce hospitalizations?
Provides year-round, comprehensive care with fewer acute hospital days