09. Personality - Trait Theories
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Wilhelm Wundt
Used trait dimensions instead of categorical types of personality, people were placed along the dimensions rather than being placed into one category
Two dimensions of personality
Mood Stability
Strength of Emotions
Personality Traits
A dimension of personality used to categorise people according to the degree to which they manifest a particular characteristic
Four assumptions that underlie Trait Theory
Traits are relatively stable over time
Traits show stability across situations
Traits influence behaviour
Traits are continuous dimensions, people can be placed along this dimension
What are trait theorists
Interested in a typical group behaviour and making comparisons among people.
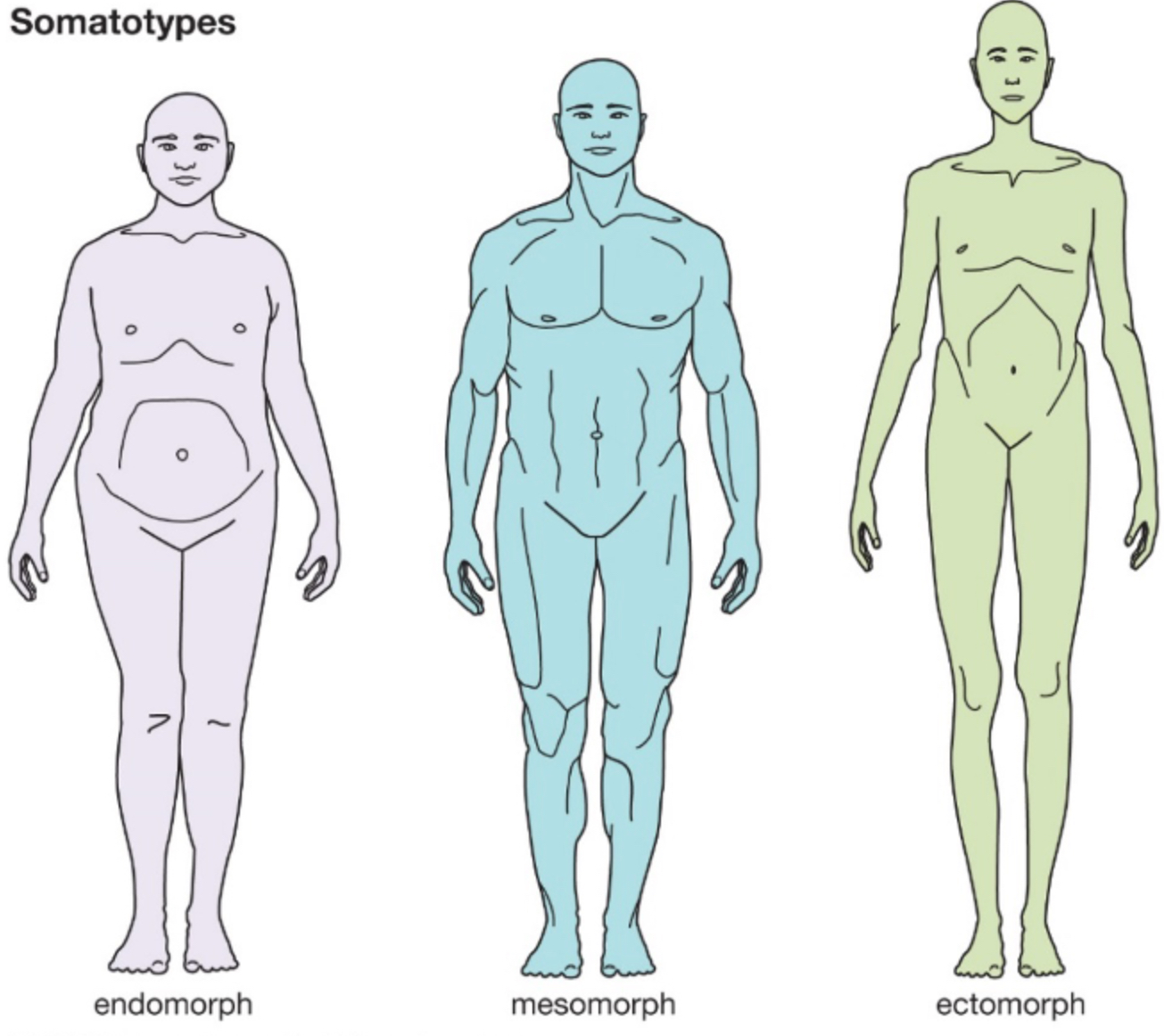
Sheldon’s Theory of Somatotypes
Described personality according to somatotypes which were based on physique and temperament.
Predicted that each body type was associated with a particular temperament
The three basic types of physique (Sheldon, 1970)
Endomorph: Rounded body tending towards fatness
Mesomorph: Large, bony with well-defined muscles
Ectomorph: Light-boned with a slight musculature
The Lexical Hypothesis
The personality traits and differences that are most important to people, become a part of their language more frequently.
For example, there are more synonyms for honest than pedantic, as we view honesty as an important personality trait
Allport and Odbent (1936)
Counted words used to describe personality, identified synonyms and produced a comprehensive list. They identified 18,000 words describing 4,500 personality traits
Allport suggested that the […] approach allows the identification of common personality traits. Why?
[nomothetic]
WHY: saw common traits as ways of classifying groups of people
Allport suggested that the […] approach allows the identification of the personal disposition of the individual. Why?
[idiographic]
WHY: represents the unique characteristics of each person, found this to be a useful approach towards developing a real understanding of personality
Allport’s three types of personality traits (1961)
Cardinal Traits: single traits that dominate an individual’s personality and heavily influence behaviour
Central Traits: 5-10 traits that best describe an individual’s personality
Secondary traits: an individual’s preferences, not a core component but become apparent in certain situations
Cattell’s Three Types of Traits (1965)
Ability traits: how well you deal with a situation and reach your goal in that situation
Temperament traits: individual differences in the styles people adopt when pursuing goals
Dynamic traits: motivate and energise behaviour
The three types of dynamic traits (Cattell)
Attitudes: the desire to act in a specific way
Sentiments: complex attitudes that include our opinions/interests that determine how we feel about people or situations
Ergs: innate motivators and drives
Common Vs Unique Traits
Common Traits: traits shared by many people
Unique traits: rare traits and specialised interests that motivate us
Surface Vs Source Traits
Surface traits: collections of trait descriptors that cluster together in many individuals and situations
Source traits: underlying traits identified by factor analysis
Eysenck’s Supertraits
Relatively stable, long-lasting characteristics of the individual
Eysenck’s three types of Supertraits that make up the structure of personality
Extraversion: socialbility
Neuroticism: emotional stability
Psychoticism: severe psychopathology
Supertrait: Extraversion
Extraversion - Introversion
Extroverts: sociable and impulsive, like excitement, orientated towards external reality
Introverts: quiet and introspective, prefer a well-ordered life, oriented towards inner reality
Supertrait: Neuroticism
A dimension that a person can be placed on.
Neurotics are emotionally unstable, displays an anxiety/fear level disproportionate to the reality
Supertrait: Psychoticism
Psychotics are insensitive to others, hostile, cruel and inhumane, a strong need to upset others
He et al., 2019
Explored the relationship between neuroticism and night eating.
Found that they were significantly and positively related.
Costa & McCrae’s Big Five Model (1992) - OCEAN
Five Supertraits make up the basic structure of personality
Openness to experience
Conscientiousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
Measured with the NEO-PI
The NEO-PI
Consists of 240 items that measure the Big Five Factors, and 30 specific traits/facets that define the factors
The Big Five Factors: Openness
The individual having an openness to new experiences, showing intellectual curiosity, divergent thinking, an active imagination and willingness to consider new ideas
The Big Five Factors: Conscientiousness
Degree of self-discipline and control, being determined, organised, and plan ahead
The Big Five Factors: Extraversion
The individual’s sociability, being sociable, energetic, optimistic, friendly and assertive
The Big Five Factors: Agreeableness
Characteristics of the individual that are relevant for social interaction, being trusting, helpful, soft-hearted and sympathetic
The Big Five Factors: Neuroticism
An individual’s emotional stability and personal adjustment, experiencing wide mood swings and having unstable emotions, or being calm, well-adjusted and not prone to extreme emotional states