Organic Chemistry I - Functional Groups
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Super fun flashcards to help memorize all the functional groups for OChem!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
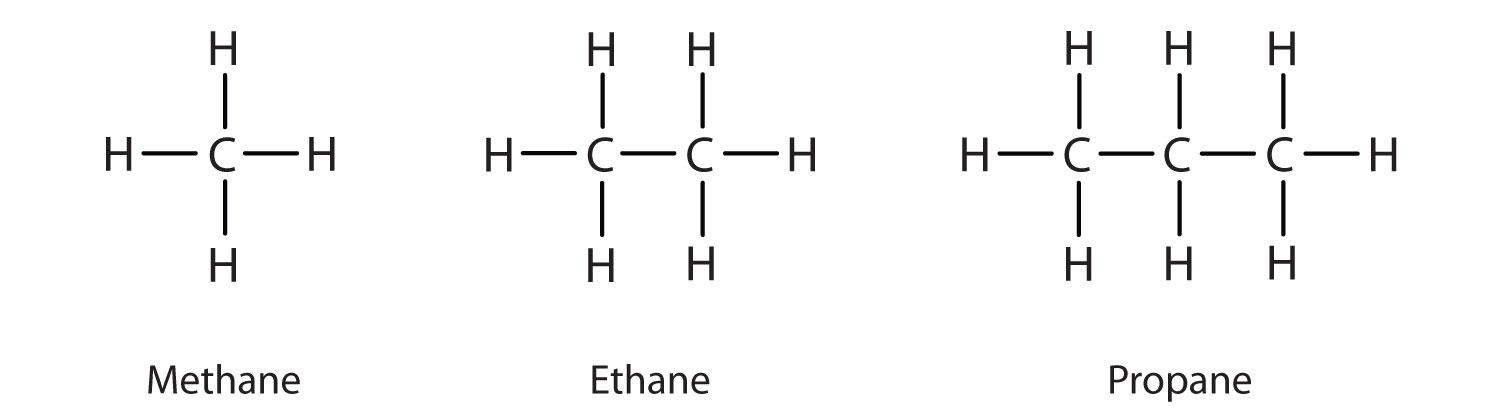
Hydrocarbons
molecules that contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms
alkanes (and cycloalkanes)
contain only single bonds between carbon atoms
-are not considered functional groups by most organic chemists because they are very limited in their reactivity
-instead, they are looked upon as the backbone onto which other functional groups are attached
alkenes
consists of a double bond between carbon atoms
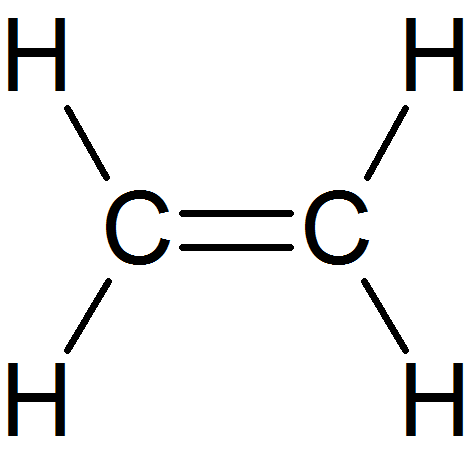
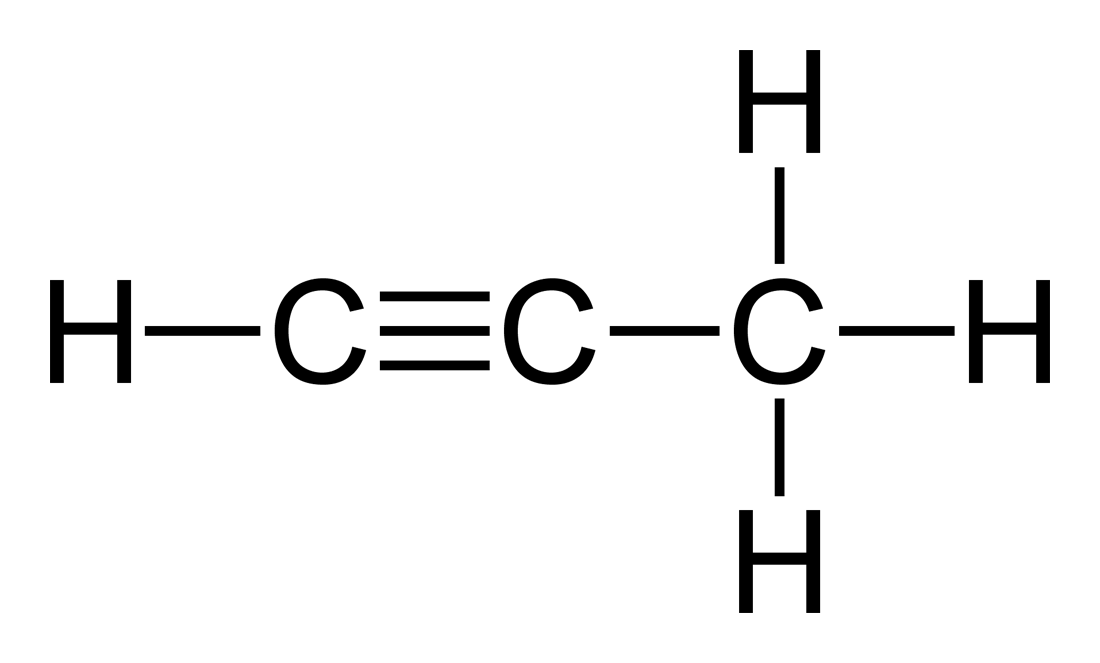
alkynes
consists of a triple bond between carbon atoms
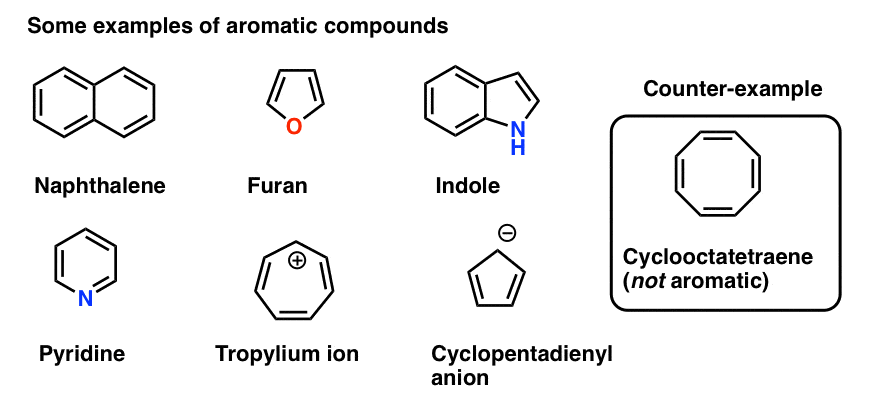
aromatic or aryl groups
the most common of these is a phenyl ring structure
-usually a benzene ring with an R group attached
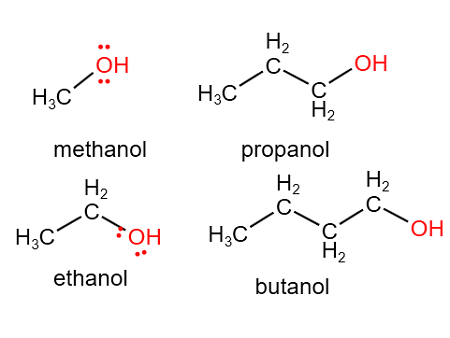
alcohol
R-OH
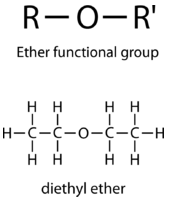
ether
R-O-R
thiol
R-SH

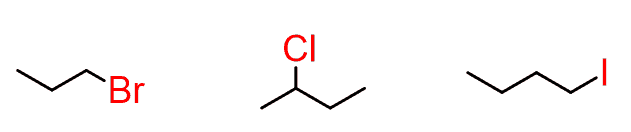
alkyl halide (note C must be sp³)
R-X
(X = Cl, Br, or I)
primary (1°) amine
R-NH₂
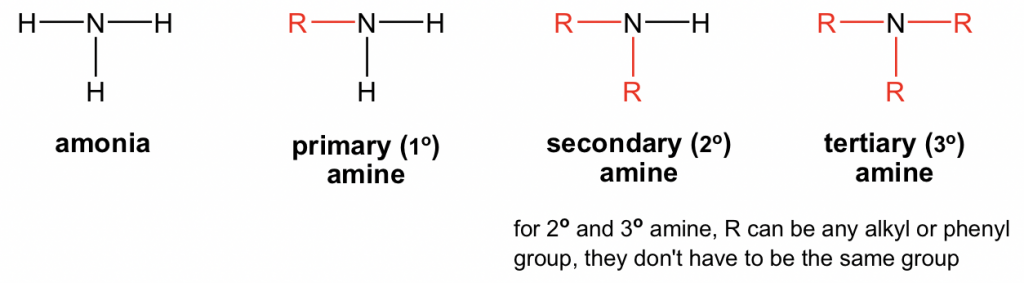
secondary (2°) amine
R₂-NH
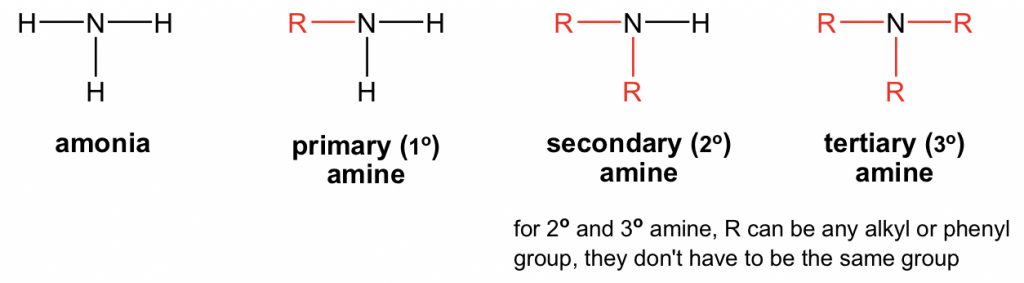
tertiary (3°) amine
R₃-N
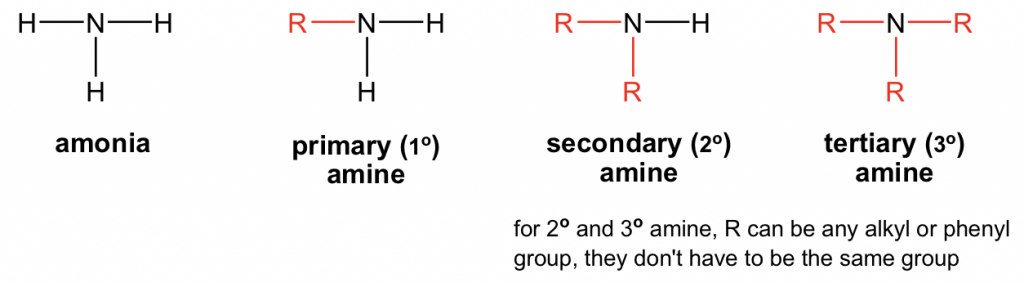
aldehyde
double bonded oxygen attached to an R group and a hydrogen
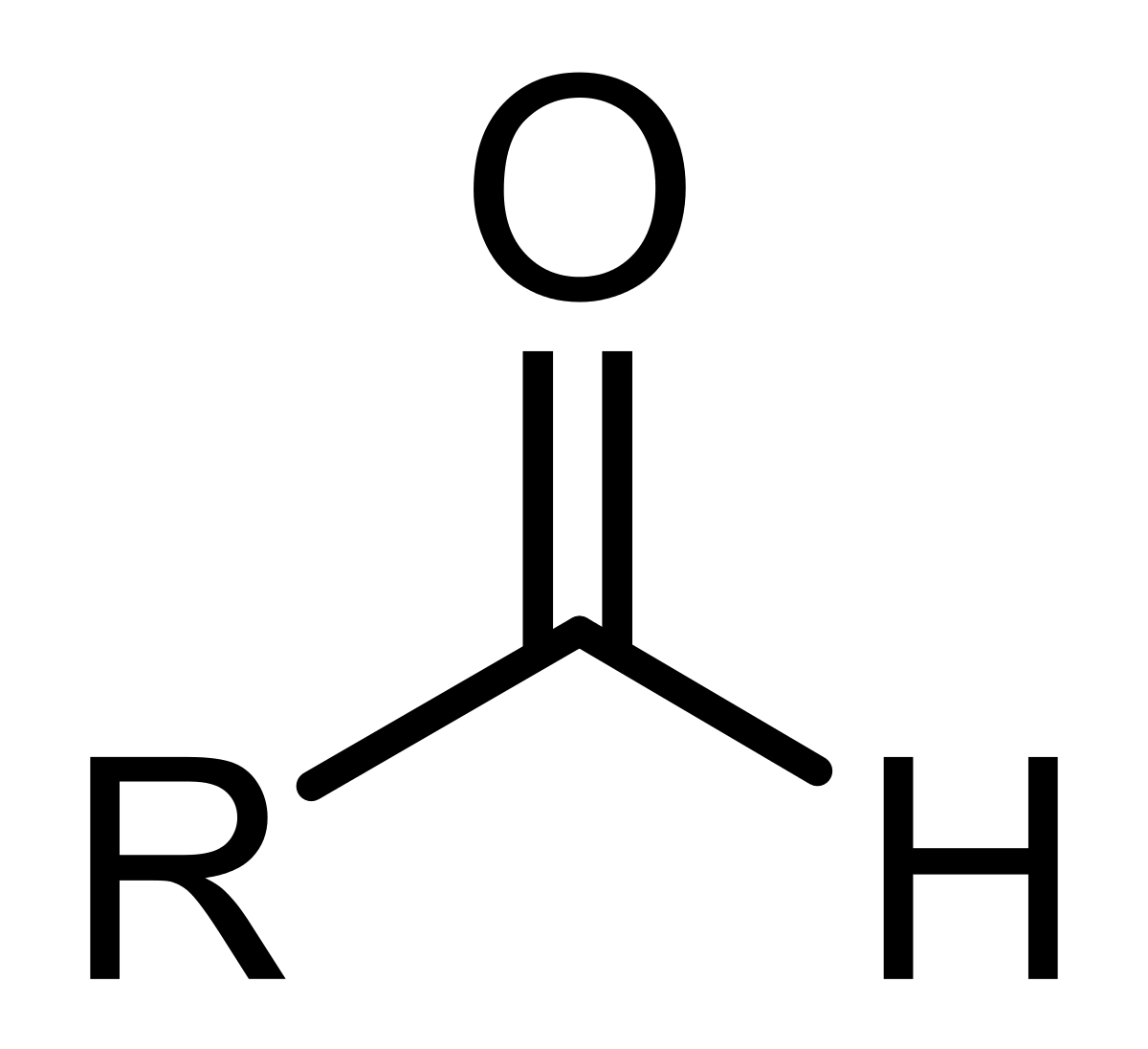
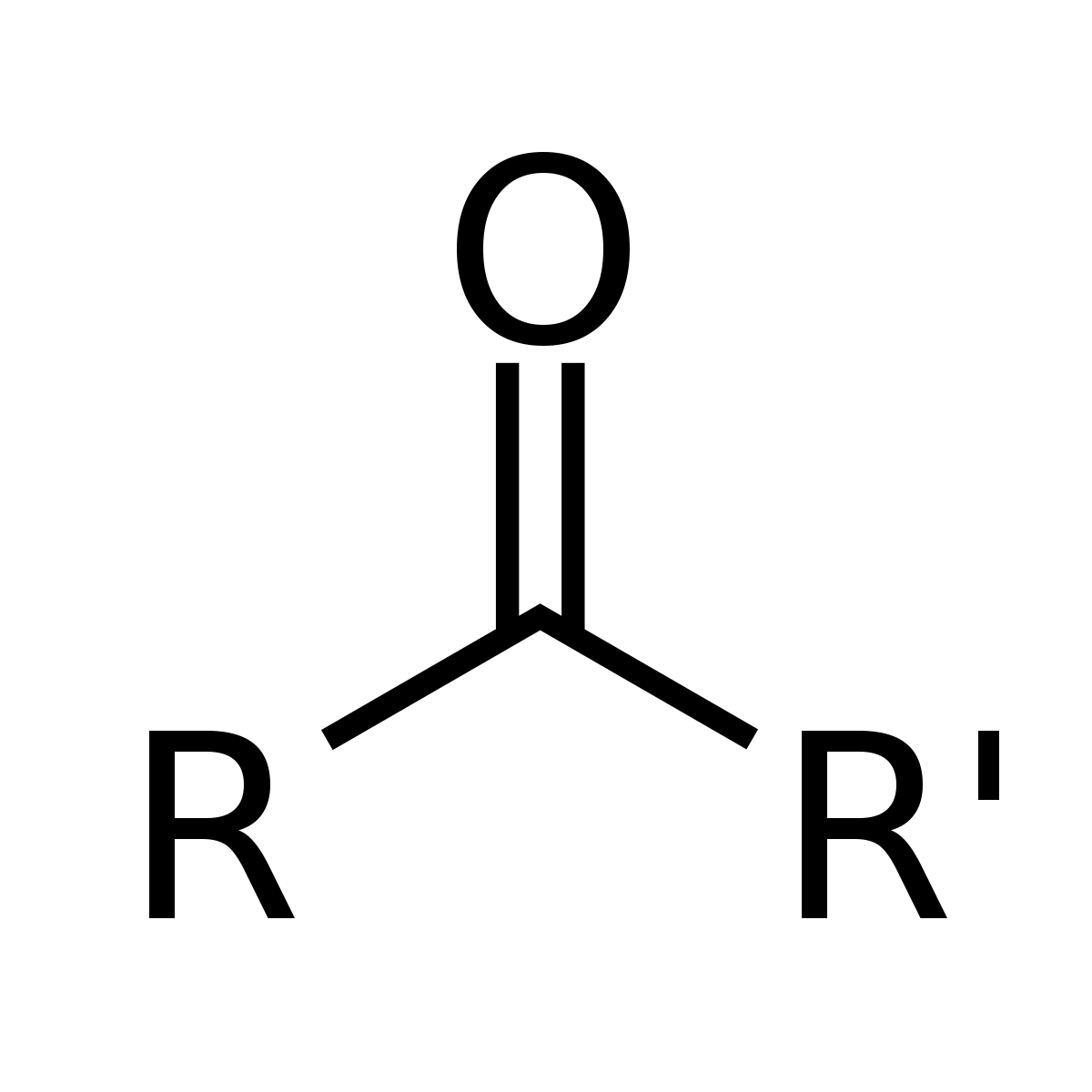
ketone
double bonded oxygen attached to two separate R groups
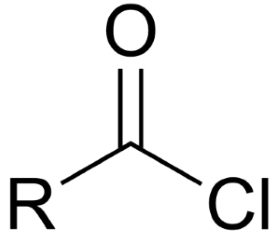
acid chloride
double bonded oxygen attached to an R group and a Cl
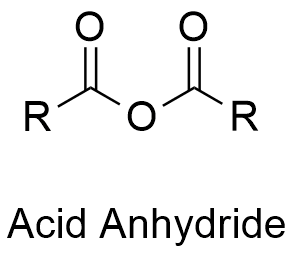
anhydride
(from left to right)
R group attached to a double-bonded oxygen, connected to a single oxygen, connected to another double-bonded oxygen, attached to an R group
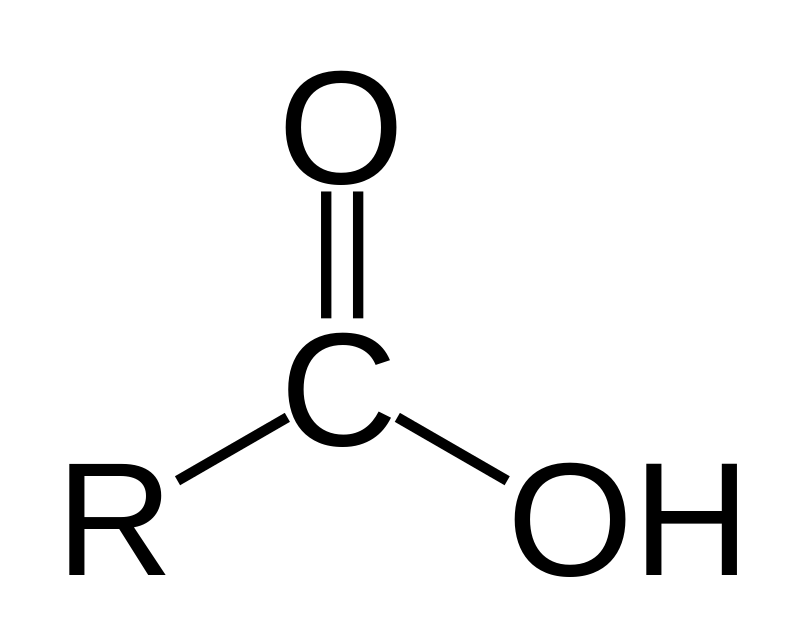
carboxylic acids
R group attached to a double-bonded oxygen attached to an OH
esters
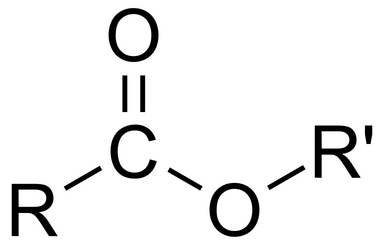
R group attached to a double-bonded oxygen attached to another oxygen attached to an R group
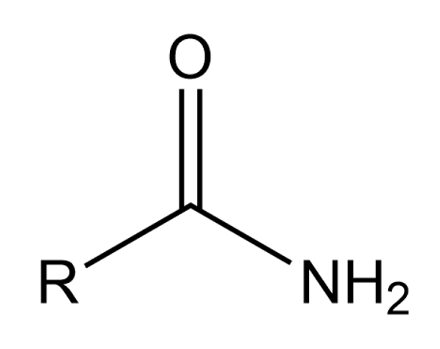
primary (1°) amides
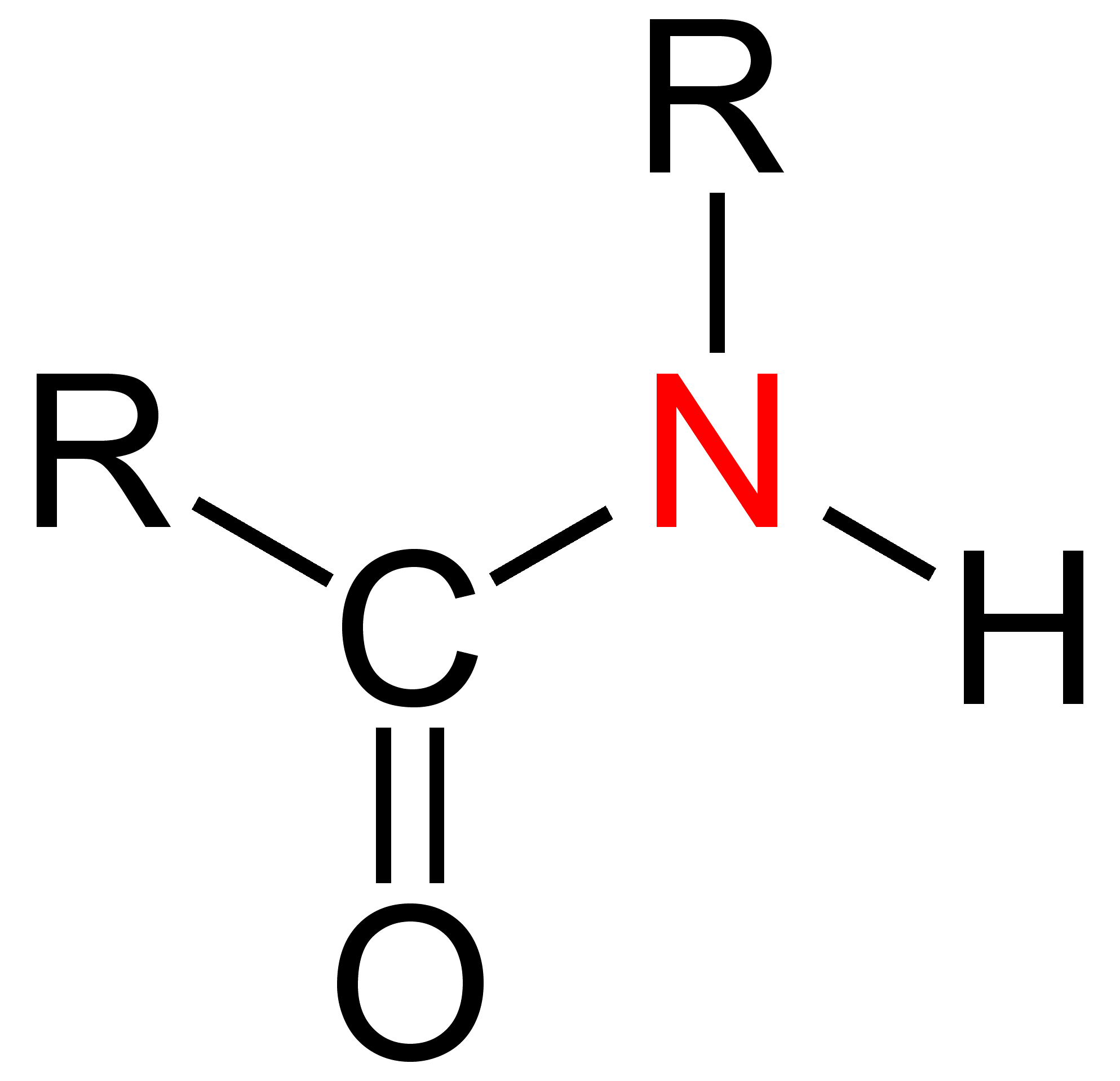
secondary (2°) amides
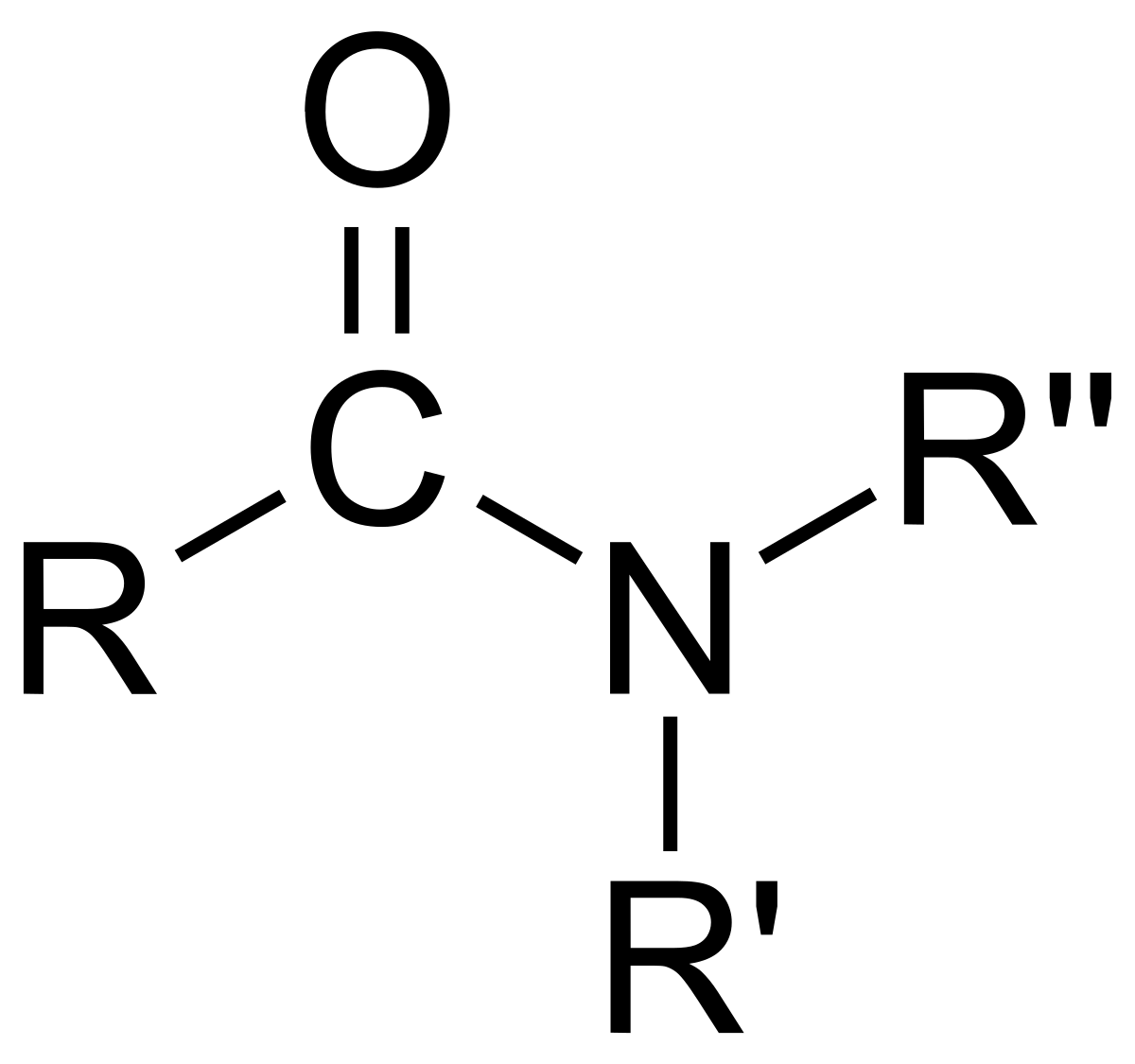
tertiary (3°) amides
nitriles
contain a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen atoms
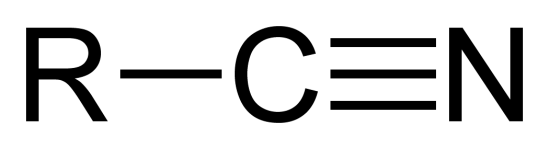
primary (1°) carbon atom
attached to one other carbon atom
secondary (2°) carbon atom
attached to two other carbon atoms
tertiary (3°) carbon atom
attached to three other carbon atoms
quaternary (4°) carbon atom
attached to four other carbon atoms
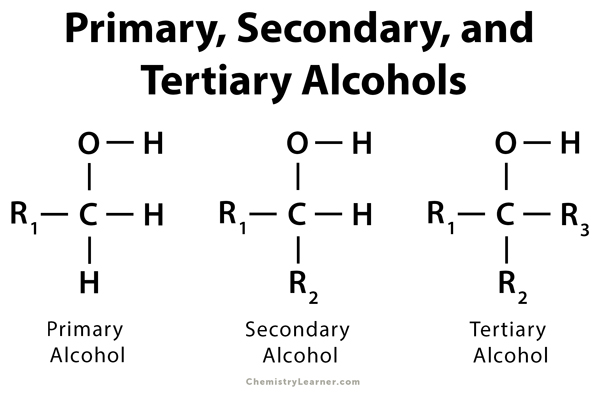
primary (1°) alcohol
a carbon atom with an alcohol and one R group attached
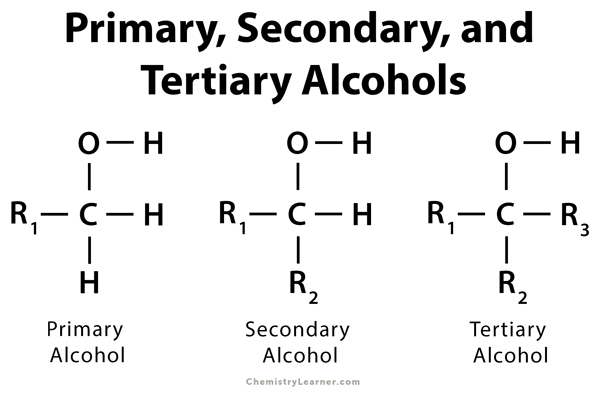
secondary (2°) alcohol
a carbon atom with an alcohol and two R groups attached
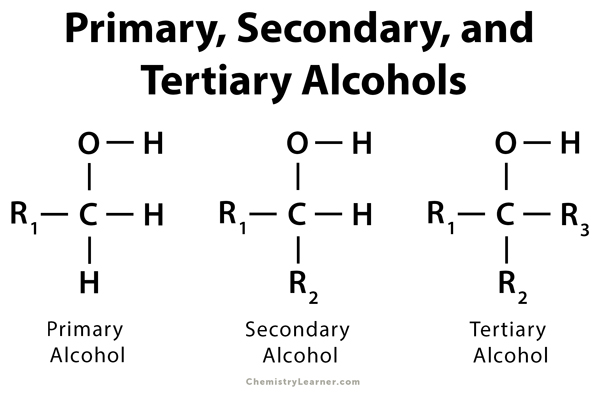
tertiary (3°) alcohol
a carbon atom with an alcohol and three R groups attached
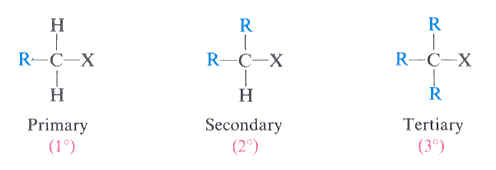
primary (1°) alkyl halides
a carbon atom attached to an X and one R group
(X = Cl, Br, or I)
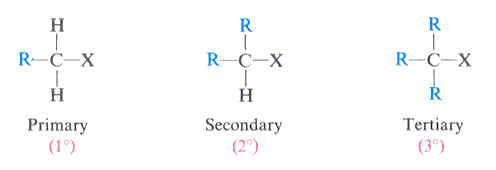
secondary (2°) alkyl halides
a carbon atom attached to an X and two R groups
(X = Cl, Br, or I)
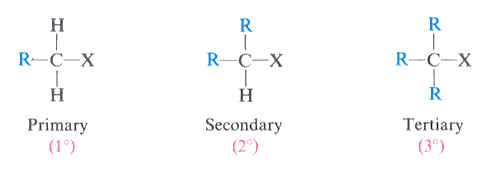
tertiary (3°) alkyl halides
a carbon atom attached to an X and three R groups
(X = Cl, Br, or I)