LAB 2 test
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
1
New cards
Foraminifera
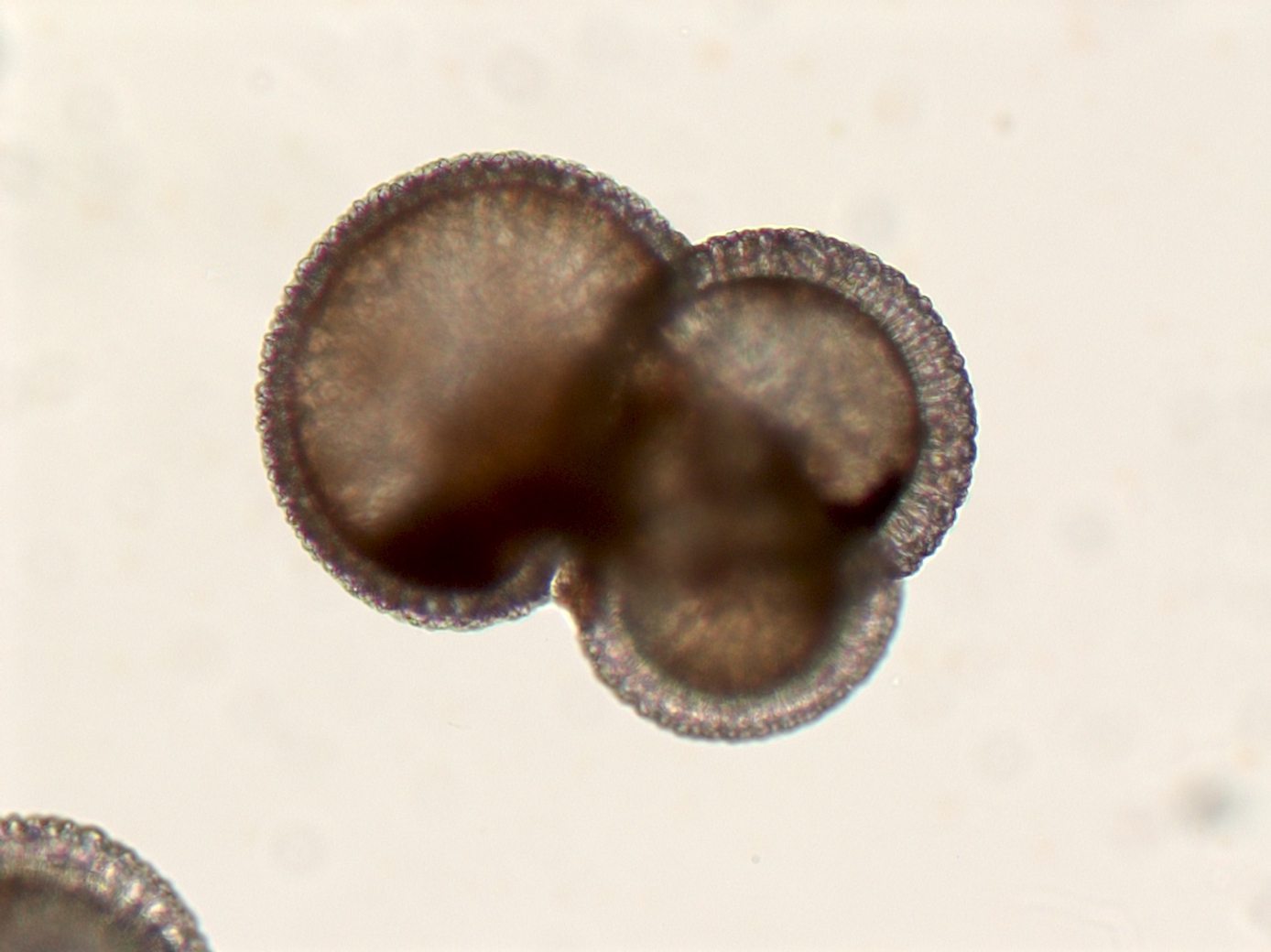
2
New cards
radiolara
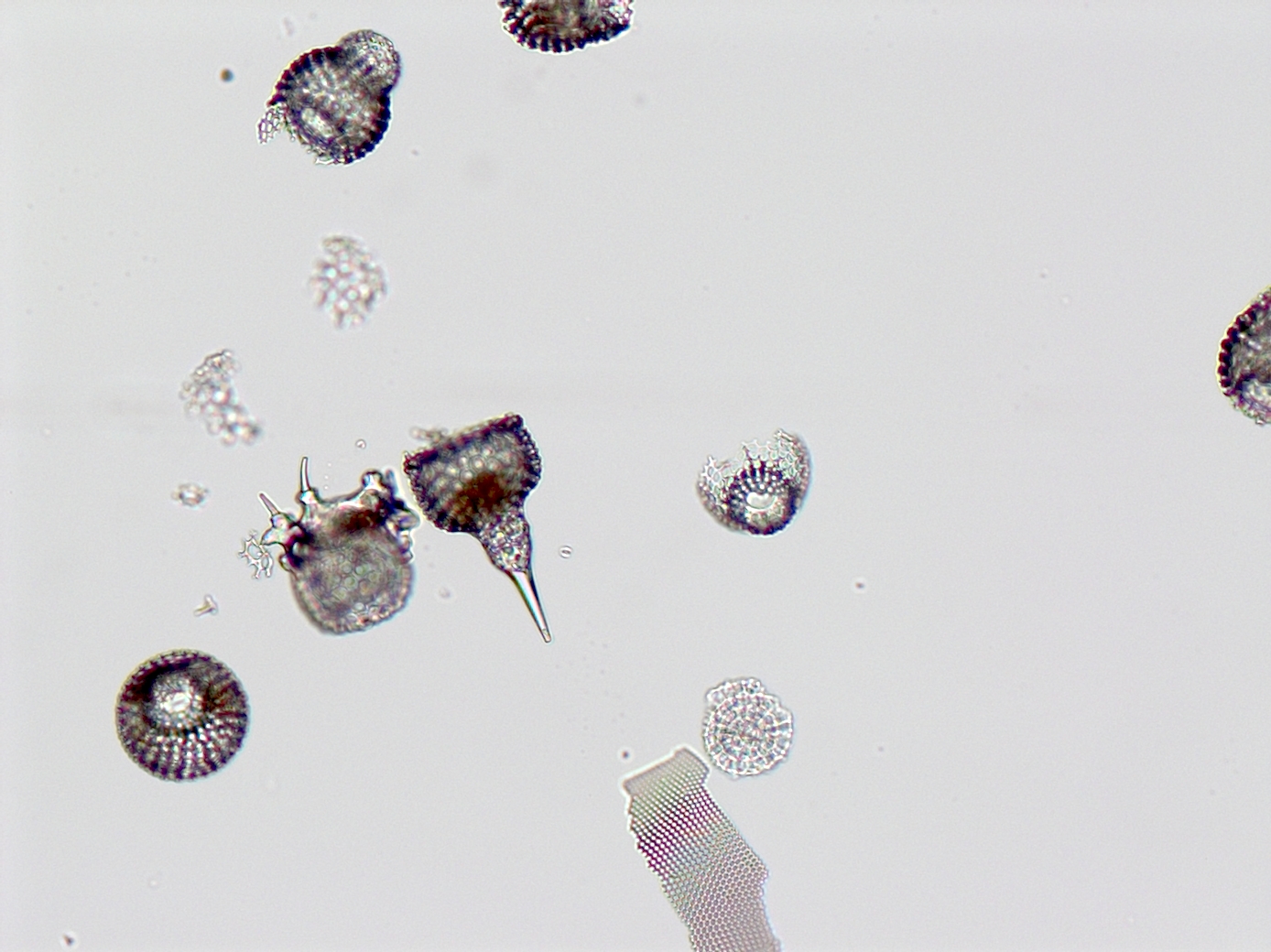
3
New cards
plasmodium
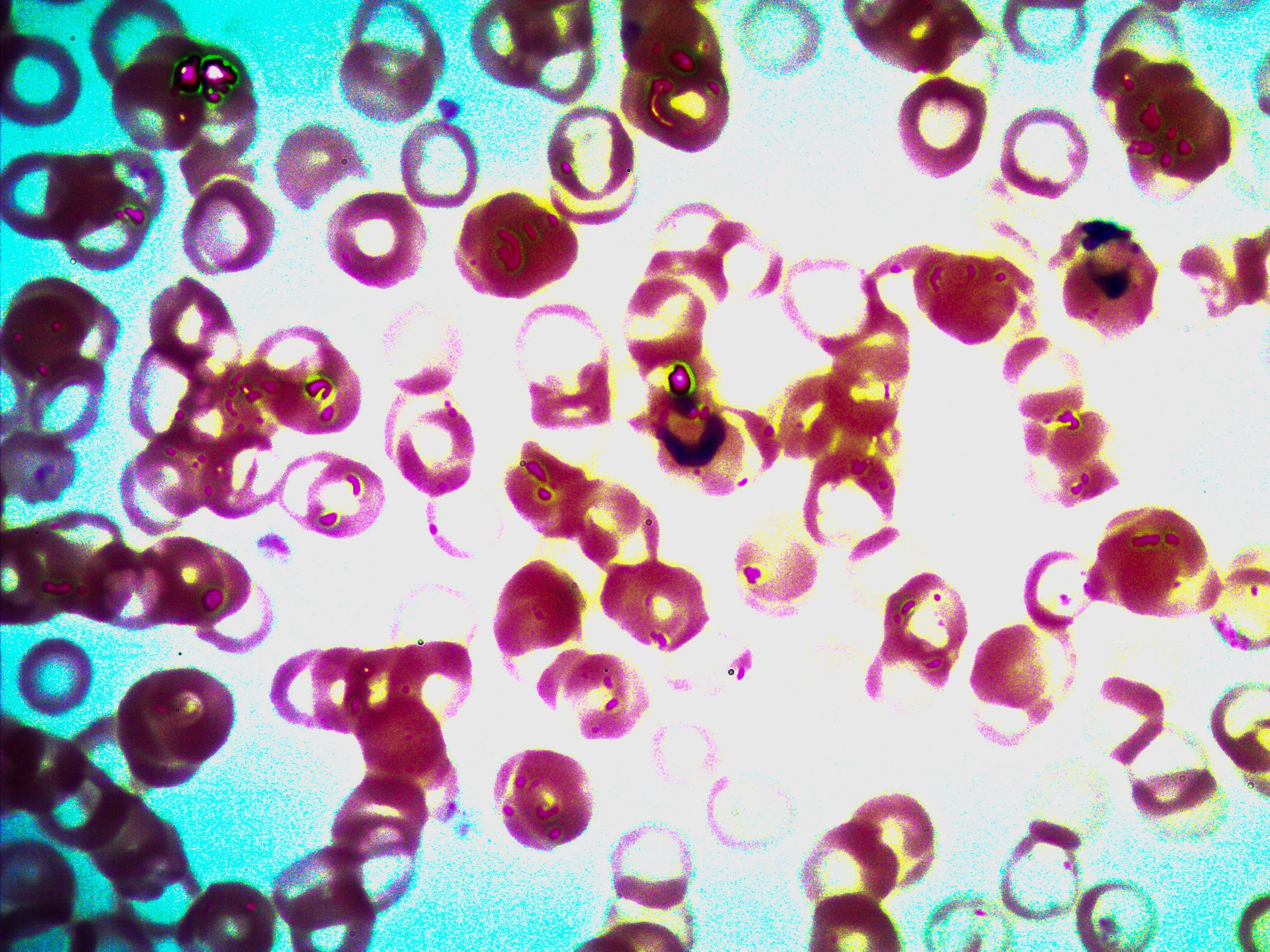
4
New cards
malaria cycle
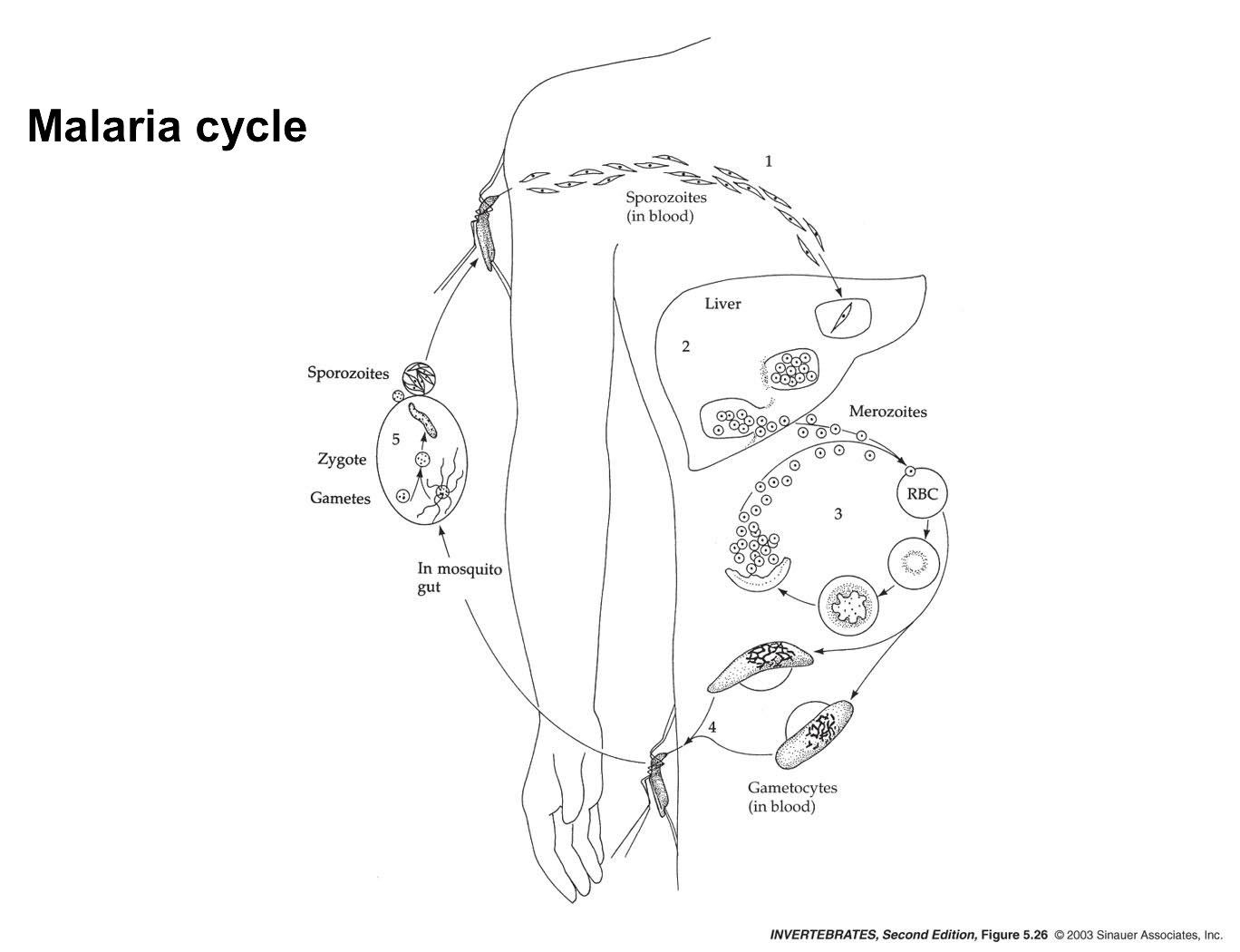
5
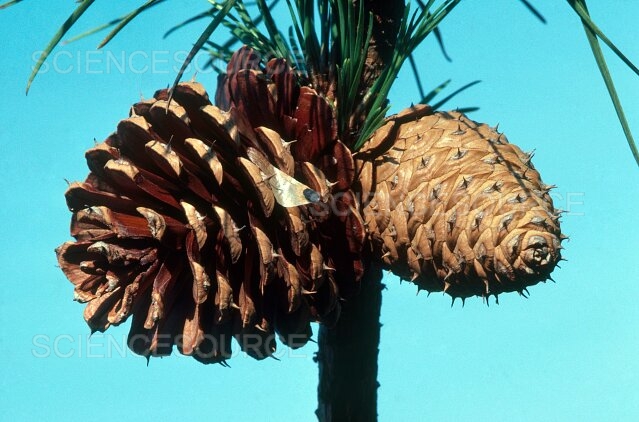
New cards
female pinecone

6
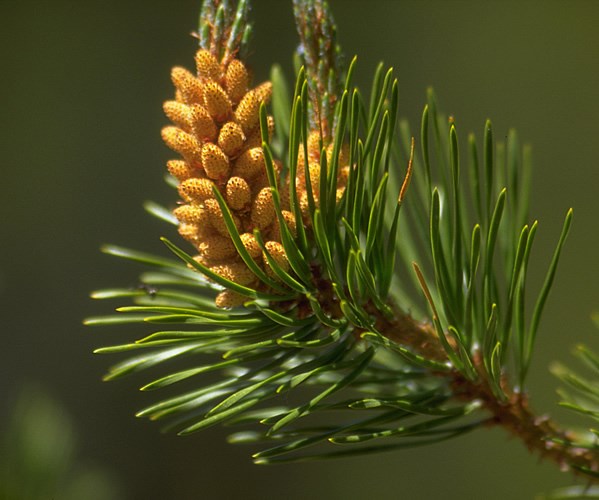
New cards
male pinecone

7
New cards
monocot vs dicot
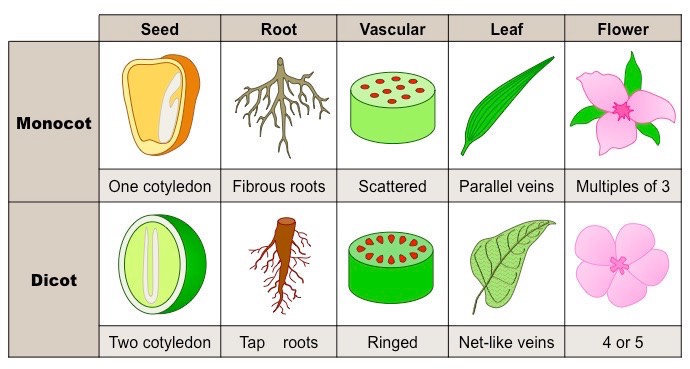
8
New cards
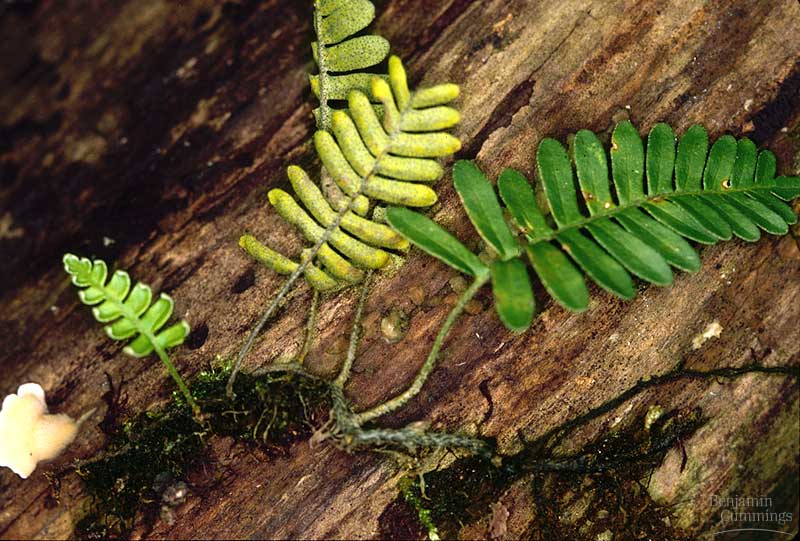
fern

9
New cards
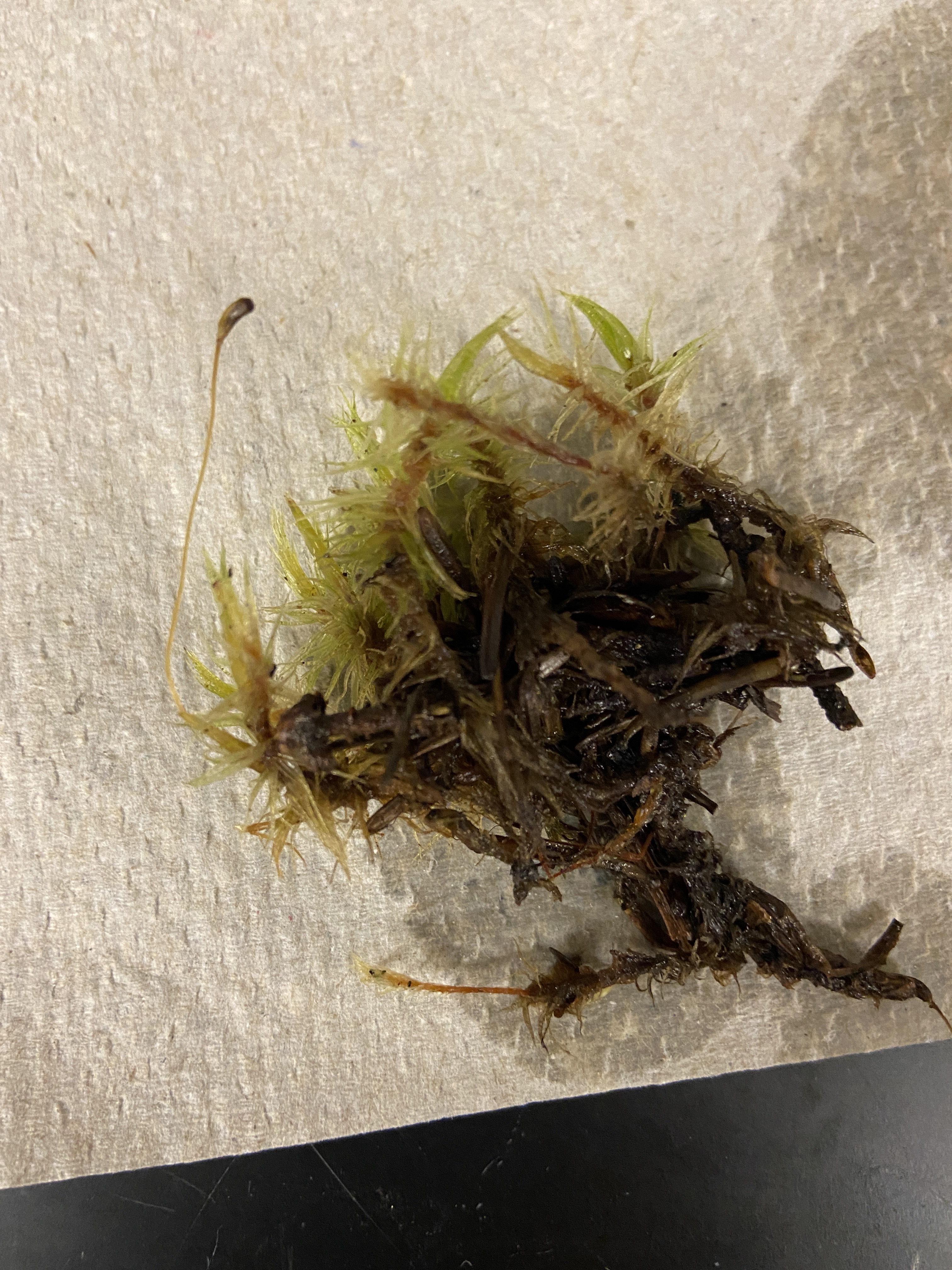
moss

10
New cards
bryophyta
11
New cards
trypanosome
12
New cards
rotatoria
13
New cards

coccus
spherical
14
New cards
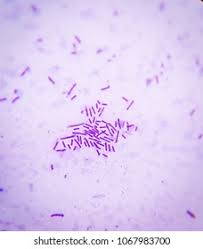
bacillus
rod shaped
15
New cards
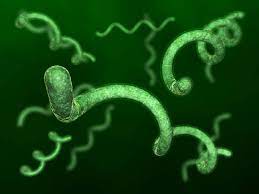
spirillus or spirochete
spiral
16
New cards
cynobacteria
17
New cards
bacteria
18
New cards
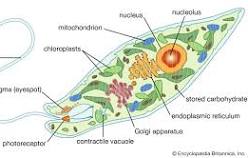
euglena
19
New cards
diatoms

20
New cards
brown algae

21
New cards
red algae

22
New cards
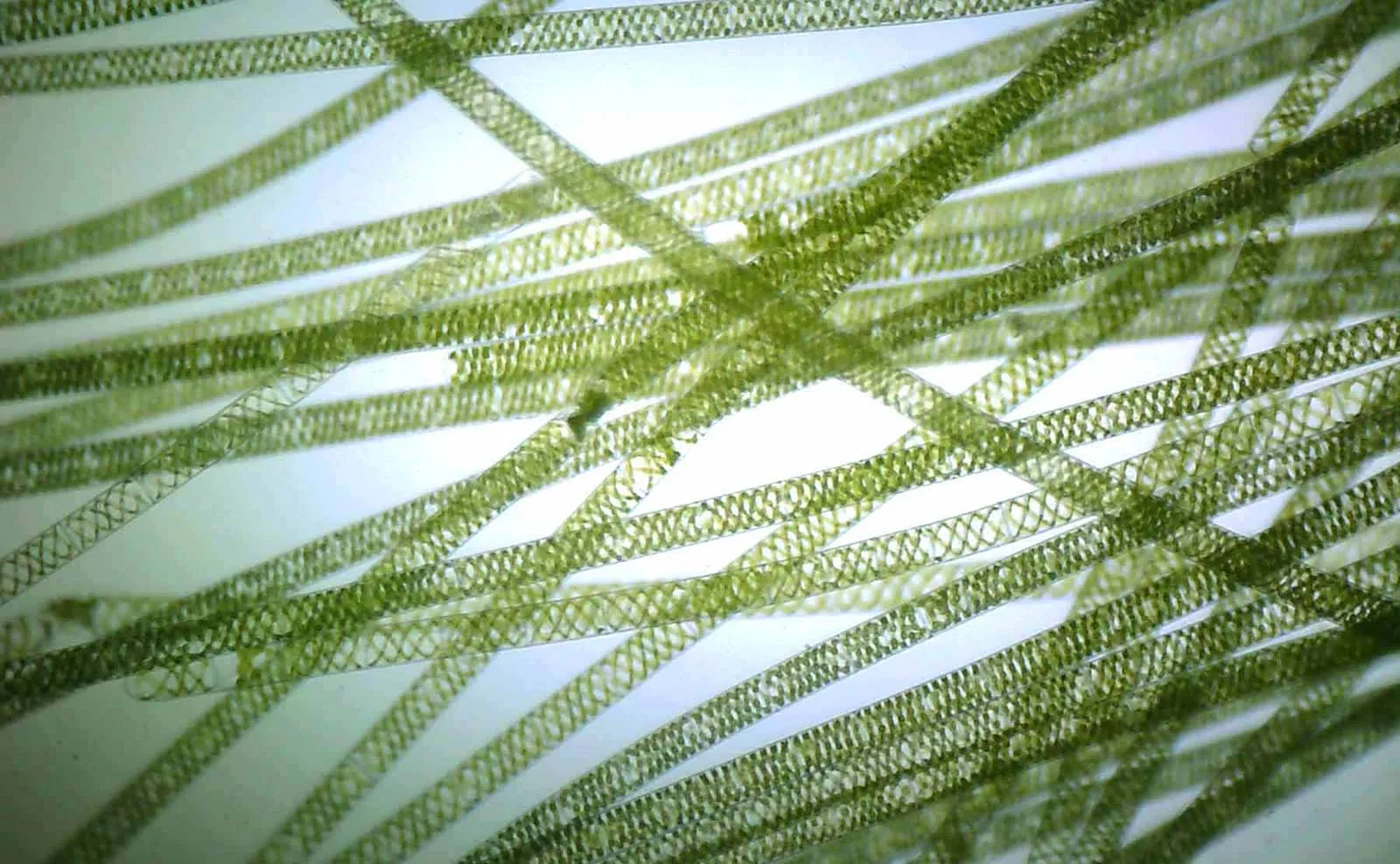
Chlorophytes - Spirogyra

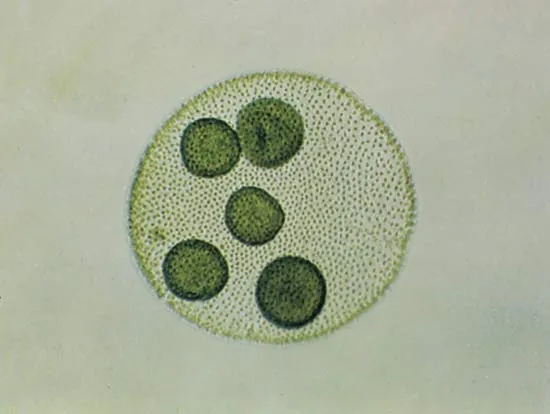
23
New cards
Chlorophytes - Volvox
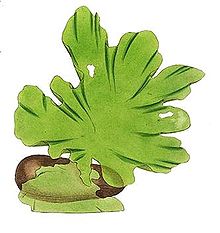
24
New cards
Chlorophytes - Ulva
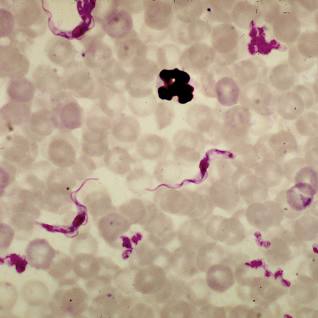
25
New cards
Trypanosoma
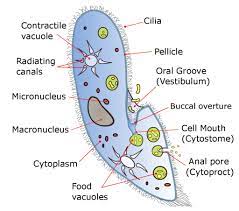
26
New cards
Ciliates - Paramecium
27
New cards
Ciliates - Vorticella
28
New cards
Foraminifera
29
New cards
Radiolaria

30
New cards
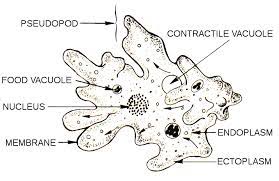
Amoeba
31
New cards
protists
range from the microscopic, single-celled
(a) *Acanthocystis turfacea*
(b) ciliate *Tetrahymena thermophila*, both visualized here using light microscopy, to the enormous, multicellular
(c) kelps (Chromalveolata) that extend for hundreds of feet in underwater “forests.”
(a) *Acanthocystis turfacea*
(b) ciliate *Tetrahymena thermophila*, both visualized here using light microscopy, to the enormous, multicellular
(c) kelps (Chromalveolata) that extend for hundreds of feet in underwater “forests.”
32
New cards
protist
\-Classified into the Domain Eukarya & the Kingdom Protista
\-Complexity and diversity of protists makes them difficult to classify
-Cannot be classified as plants, animals, or fungi
\-Complexity and diversity of protists makes them difficult to classify
-Cannot be classified as plants, animals, or fungi
33
New cards
Morphology
\-Most are unicellular, not all!
\-Many with amazingly high level of structural and functional complexity
\-Many with amazingly high level of structural and functional complexity
34
New cards
protist
most are free living
35
New cards
protists
some are parasitic
36
New cards
protist
asexual reproduction common and sexual may occur when conditions deteriorate
37
New cards
Photoautotrophic forms
* Produce oxygen
* Function as producers in both freshwater and saltwater ecosystems
* Major component of plankton
* Function as producers in both freshwater and saltwater ecosystems
* Major component of plankton
38
New cards
algae
refers to many phyla of protists that carry out photosynthesis
39
New cards
green algae: chlamydomonas
actively moving flagellate
40
New cards
ulva
multicellular green algae
41
New cards
volvox
a colony is a loose association of independent cells
42
New cards
red algae
\-multicellular
\-about 5,00 species
\-mostly live in warmer sea water
\-about 5,00 species
\-mostly live in warmer sea water
43
New cards
brown algae
\-about 1,500 species
\-most live in colder ocean waters along rocky coasts
\-no unicellular or colonial brown forms
\-most live in colder ocean waters along rocky coasts
\-no unicellular or colonial brown forms
44
New cards
diatoms
the most numerous unicellular algae in the oceans
45
New cards
amoeboids
protists that move and ingest their food with pseudopods
46
New cards
phagolysomes
amoeboids use this to digest food
47
New cards
streptophytes
the green plants or charophytes
48
New cards
embryophytes
the land plants
49
New cards
bryophytes
seedless plants that are nonvascular
50
New cards
liverworts, hornworts, and mosses
examples of bryophytes
51
New cards
club mosses, quillworts, and spike mosses
examples of lycophytes
52
New cards
whisk ferns, horsetails, and ferns
pterphytes
53
New cards
lycophytes and pterophytes
other types of seedless plants but are vascular
54
New cards
gymnosperms and angiosperms
examples of spermatophytes
55
New cards
spermatophytes
seed plants
56
New cards
haplontic
refers to the life cycle in which there is a dominant haploid stage
57
New cards
diplontic
refers to a life cycle in which diploid is a dominant stage (humans are diplontic)
58
New cards
gametophyte
haploid
59
New cards
sporophyte
diploid
60
New cards
streprophytes
land plants and closely related to green algae are part of a new monophyletic group
61
New cards
charales
the closest living relative of land plants
62
New cards
hepaticophyta
asexual reproduction involved production of gemmae that can develop int gametophyte
63
New cards
Sori
appear as small bumps on the underside of a fern frond
64
New cards
homosporous
most ferns are
65
New cards
vascular tissue
xylem and phloem
66
New cards
xylem
transports water and minerals from roots upward to the shoot system
67
New cards
phloem
carries organic nutrients upward or downward within plant
68
New cards
rhizome
ferns have an underground stem anchored by roots
69
New cards
gametophytes
photosynthetic autotrophs
70
New cards
sporophyte
siploid
71
New cards
gametophyte
haploid
72
New cards
pterophyta
fern
73
New cards
lycophyta
club moss
74
New cards
mycelium
composed of threadlike filaments also called hyphae
75
New cards
spores
formed in hyphae or in sporangia
76
New cards
fungi
haploid but reproduce sexually and asexually
77
New cards
zygomycota
black bread mold
78
New cards
ascomycota
truffles, morels, and yeast
79
New cards
basidiomycota
mushrooms
80
New cards
deuteromycota
parasites such as athletes foot and ringworm
81
New cards
penicillium
first antibiotic included in deuteromycota
82
New cards
mutualism
both members benefit from the association
83
New cards
lichen
fungus and alga
84
New cards
crustose, foliose, and fructicose
3 forms of lichen
85
New cards
crustose
thin crust that tightly attaches to trees or rocks
86
New cards
foliose
thicker than crustose but have a flattened body
87
New cards
fructicose
branched erect body forms
88
New cards
gymnosperms
\-have roots, stems and leaves
\-have xylem and phloem vascular tissue
\-produce seeds in cone
\-have xylem and phloem vascular tissue
\-produce seeds in cone
89
New cards
ginko, pine, mormon tea, conifer
examples of gymnosperms
90
New cards
angiosperms
flower structure
91
New cards
carpel
fermale reproductive structure in flowers
92
New cards
stamen
male reproductive structure in flower
93
New cards
sepals
enclose flower before opening
94
New cards
the seed
ovule inside the ovary becomes
95
New cards
angiosperms
flowering plants
96
New cards
dormacy
helps survive harsh periods before germinating
97
New cards
seed
\-embryo protected by integument
\-an extra layer of sporophyte tissue
\-hardens into seed coat
\-an extra layer of sporophyte tissue
\-hardens into seed coat
98
New cards
male gametophytes
\-within pollen grains
\-dispersed by wind or pollinator
\-no need for water
\-dispersed by wind or pollinator
\-no need for water
99
New cards
female gametophytes
\-develop within an ovule
\-enclosed within diploid sporophyte tissue in angiosperms
\-enclosed within diploid sporophyte tissue in angiosperms
100
New cards
coniferophyta
cycadophyta
gnetophyta
ginkophyta
cycadophyta
gnetophyta
ginkophyta
examples of gymnosperms