Coastal Weathering and Erosion
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Salt Weathering
Seawater gets into cracks in rocks, seawater evaporates, forming salt crystals in cracks.
Chemical Weathering
Breakdown of rock by altering its chemical composition.
Biological Weathering
Living organisms break down rocks eg. plant roots growing into cracks in rocks and pushing them apart
Mass Movement
Shifting of rocks and material down a slope.
Slides mass movement
When loose material shifts downhill along a straight line
Slumps mass movement
When saturated soil and weak rock slump down a curved surface, often after heavy rain.
Rockfalls mass movement
Material breaks up and falls down a slope.
what causes mass movement
Weathering (especially freeze-thaw and biological weathering)
Saturation by water (from rainfall)
gravity
what are the three types of erosion that affect coats
- hydraulic power : Waves compress air in rock cracks, causing erosion.
- abrasion : Eroded particles scrape against rocks, removing pieces.
- attrition : eroded particles in the water collide collide and break into smaller fragments.
Sub-aerial Processes
Weathering and mass movement occurring above water.
Cliff Retreat
Rapid erosion causing coastal cliffs to move back.
What is the Lubricant Effect and how it affects mass movement
Water makes material heavier and facilitates movement enabling more mass movement
what causes coats to rapidly retreat
mass movement
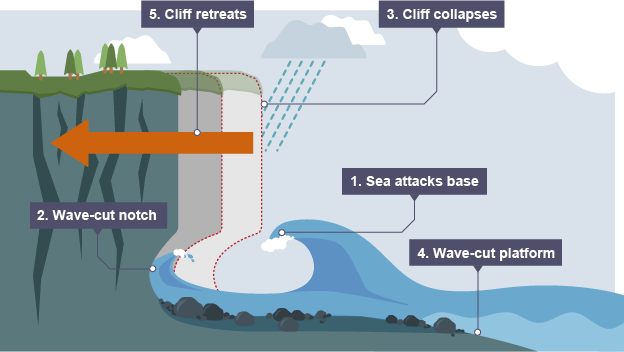
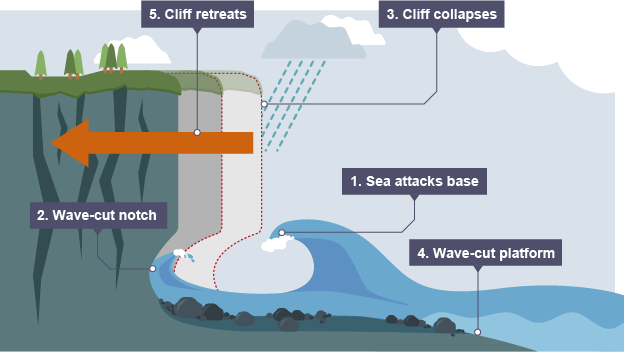
explain the formation of a wave cut platform
1) water attacks the base of the cliff caused by erosion by hydraulic action
2) this forms a wave cut notch and it enlarges as erosion continues
3) the rock above the notch becomes unstable and collapses
4) the collapsed material is washed away and and a new wave cut notch starts to form
5) repeated collapsing results in the cliff retreating
6) a wave cut platform is the platform left behind as the cliff retreats
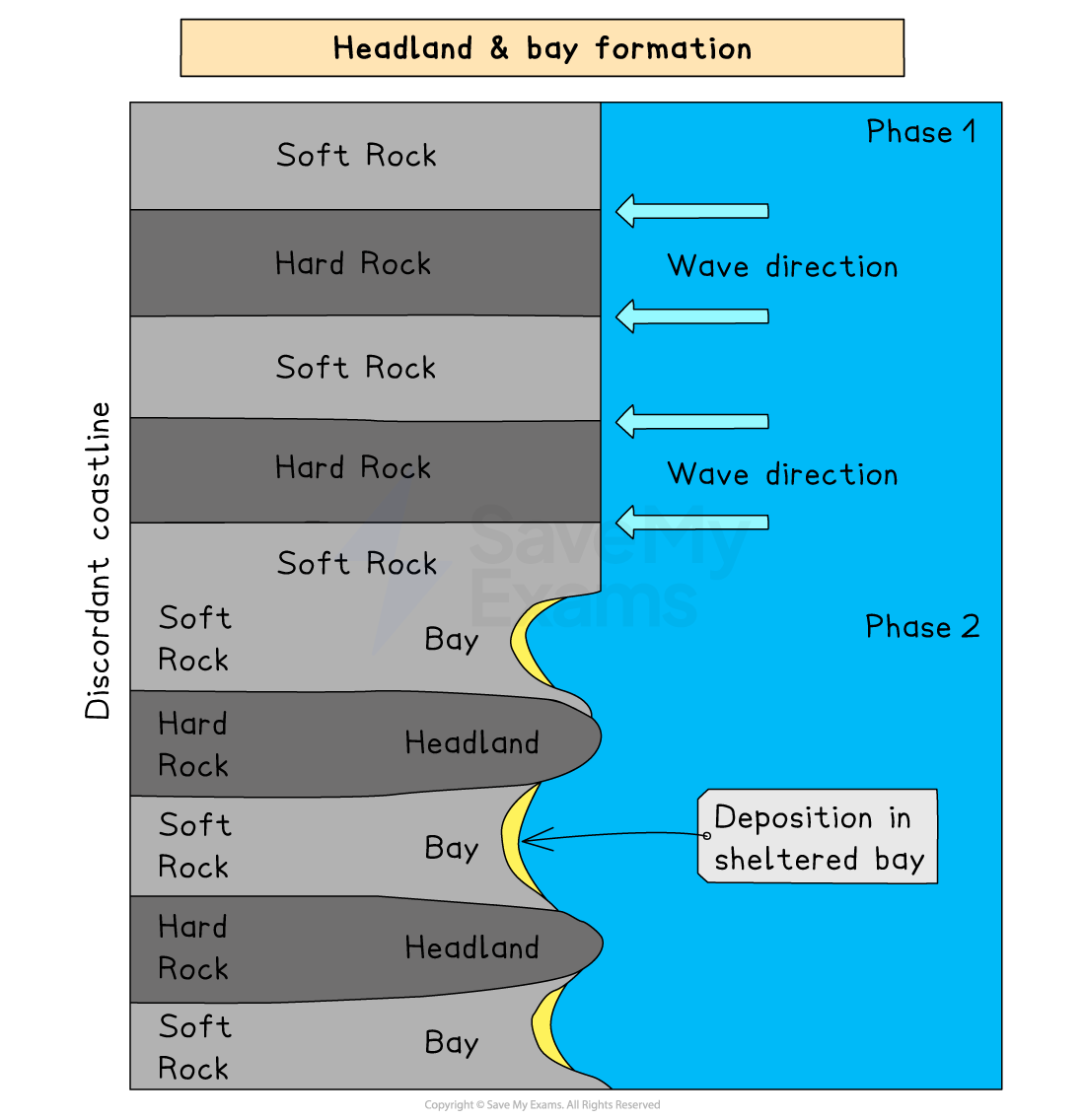
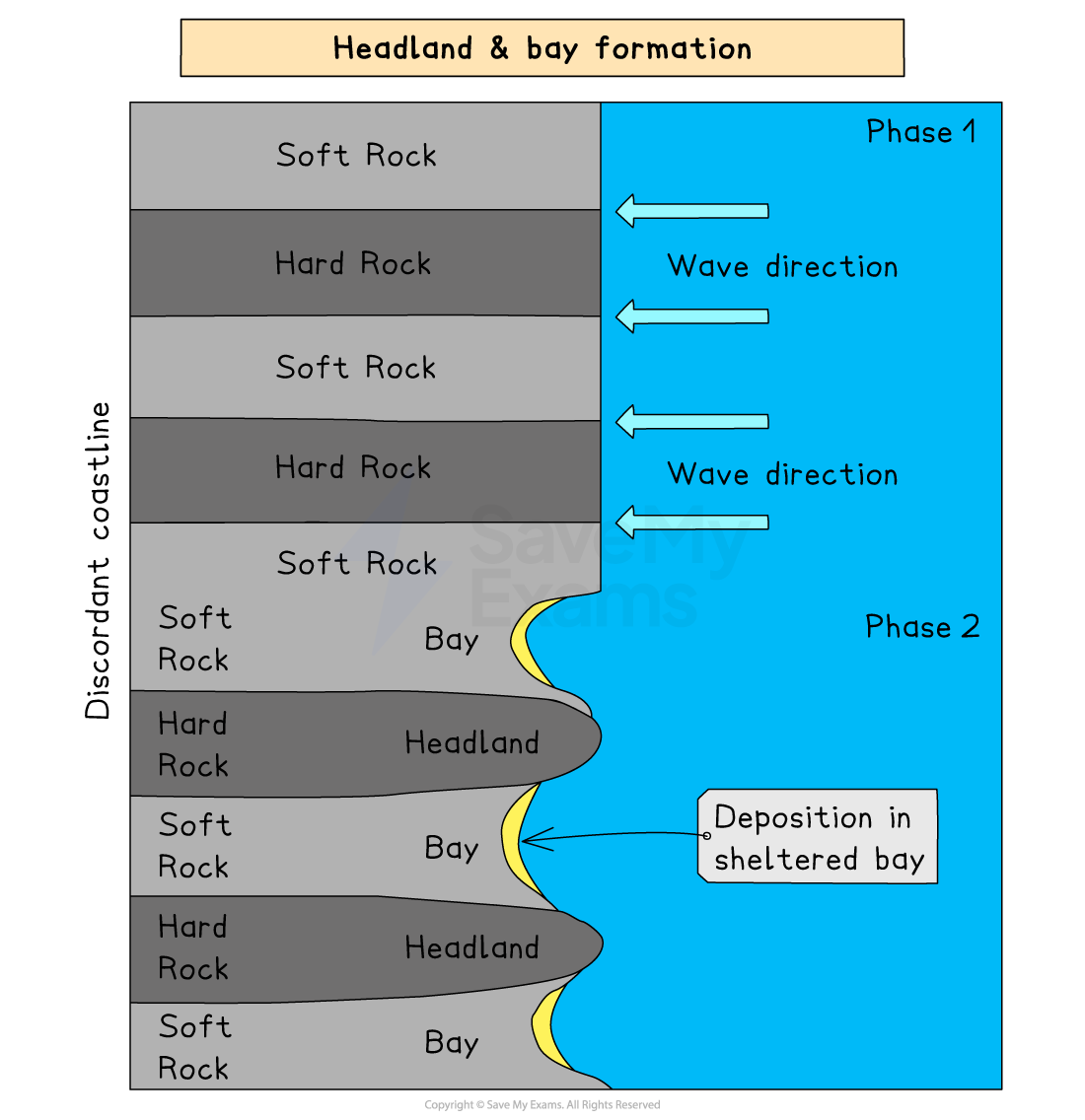
formation of a bay and headland
the less resistant rock on the discordant coastline is eroded quickly by hydraulic action and abrasion and this forms a bay with a gentle slope
Harder rocks resist erosion and remain as headlands jutting out to sea
how are headlands eroded to form caves, arches and stacks
1) waves crash into the headlands where there is weakness such as a crack and the cracks enlarge
2) the repeated erosion and enlargement of the cracks causes a cave to form
3) continued erosion deepens the cave until it breaks through the headland forming an arch
4)erosion continues to wear away the rock supporting the arch until it eventually collapses
5) this forms a stack, an isolated rock that's separate from the headland
Concordant Coastline
Coastline with parallel rock bands to shore.
Discordant Coastline
Coastline with alternating rock bands at right angles.
Hard Rock
More resistant rock, erodes slowly over time.
Soft Rock
Less resistant rock, erodes quickly compared to hard rock.
how do joints and faults affect erosion rates
they increase erosion rates
why are erosional landforms like bays and headlands more common on discordant coastlines
because the bands of rock are being eroded at different rates
Destructive Waves
High, steep waves that erode coastlines effectively, they have a stronger backwash, so more material is removed from the beach
Backwash
Water movement returning to the sea after a wave.
Swash
Water movement advancing up the beach from a wave.
how do hotter temperatures affect salt weathering and therefore coastal erosion
the hotter temperatures increase the rate of salt weathering as more water evaporates
Storm Impact on coastal erosion
Increased erosion due to high energy waves caused by strong winds of the storm
intense rainfall causes cliffs to become more saturated increasing mass movement
how does the UK climate affect coastal erosion
The UK's climate is considered to be temperate maritime, (1) meaning summers are warm and wet and winters are mild and wet. (1) The prevailing winds bring frequent rainfall to the country, leading to increased erosion, weathering and mass movement along the coast. (1)
Storm frequency is high, which brings heavy rainfall and strong winds that increase the destructive power of the waves. (1)
During the winter the UK frequently sees temperatures dip below freezing at night and then rise above 0°C by day. (1) This repeated freezing and thawing, results in weathering of cliff faces and headlands adding to erosion and cliff collapse. (1)
hard rock cliffs are more _______ and soft rock cliffs are more sloping
hard rock cliffs are more VERTICAL and soft rock cliffs are more SLOPING