Bipolar Disorders
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Types of Bipolar Disorders (6)
1. Bipolar 1 disorder
2. Bipolar 2 disorder
3. Cyclothymic disorder
4. Substance/medication-induced bipolar and related disorder
5. Bipolar and related disorder due to another medical condition
6. Other
Bipolar disorders Specifiers
1. With anxious distress
2. With mixed features
(at least 3 criteria for the opposite pole mood episode have been met)
3. With mood-congruent or mood-incongruent psychotic features
4. With melancholic features
5. With atypical features
6. With rapid cycling
(4 ore more mood episodes in 1 year)
7. With catatonia
8. With peripartum onset
With seasonal pattern
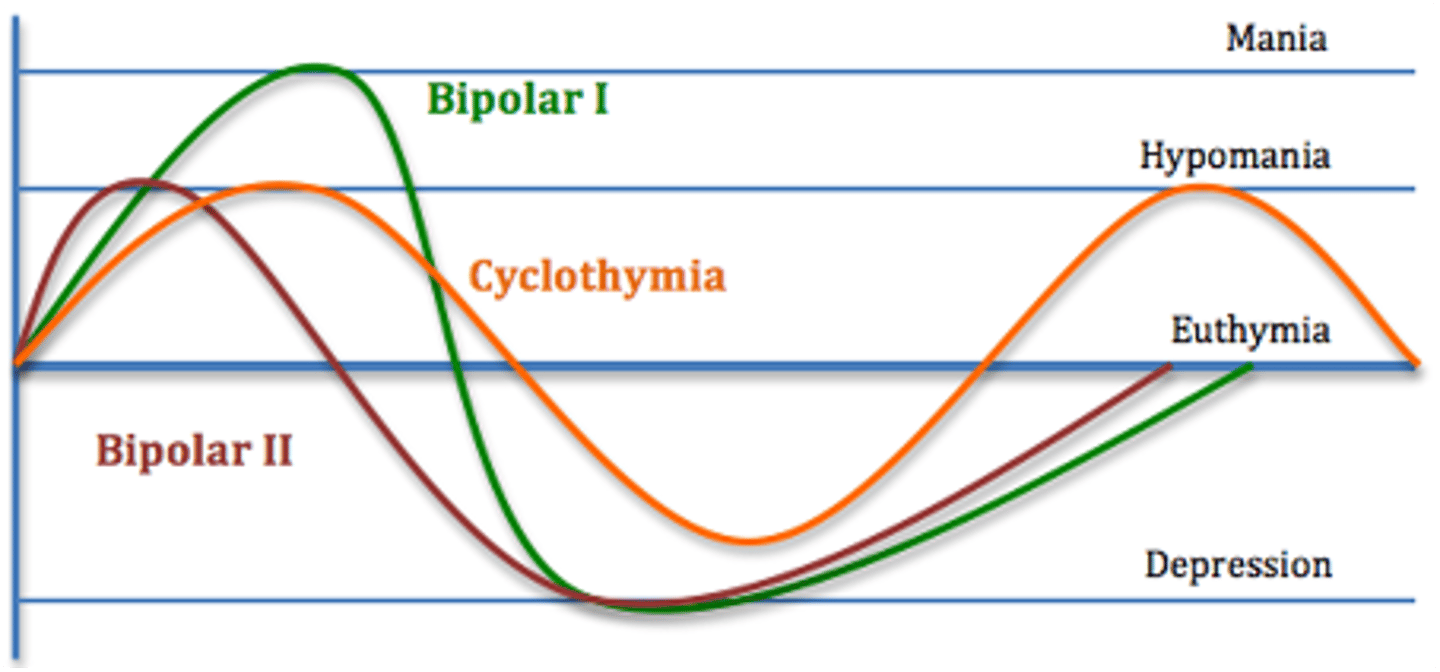
Graph of Bipolar disorders
1. Bipolar 1 --> hits depression and mania
2. Bipolar 2--> hits depression and hypomania
3. Cyclothymia--> hit hypomania
Bipolar disorder (definition)
- Bridge between schizophrenia and depression disorder in terms of sx, family hx, and genetics
Time is takes to for proper bipolar disorder dx?
- Average length of time from start of symptoms to proper diagnosis 6 years
Manic episode criteria (2)
A.
.A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and abnormally and persistently increased goal-directed activity or energy, lasting at least 1 week and present most of the day, nearly every day (or any duration if hospitalization)
B
During the period of mood disturbance and increased energy or activity, 3 or more of the following symptoms (4 if the mood is only irritable) are present to a significant degree and represent a noticeable change in behavior.
Symptoms of Criteria B for manic disorder (7)
Must have 3 or more of the following (4 if mood is only irritable)
DIG FAST
1. Distractibility and easy frustration
2. Indiscretion (excessive pleasurable activities)
3. Grandiosity
4. Flight of ideas
5. Activity increased
6. Sleep deficit
7. Talkativeness
Diagnostic features of Manic episode (6)
1. During manic episodes, individuals have poor insight (do not perceive that they are ill or need of treatment, and resist efforts to be treated)
2. May change dress, makeup, or appearance to be more sexually suggestive or flamboyant
3. Gambling and antisocial behaviors may accompany manic episode
4. Some become hostile and physically threatening to others, and when delusional, physically assaultive, or suicidal
5. Episodes often result in involuntary hospitalization, difficulties with the law, and serious financial difficulties
6. Mood may shift very rapidly to anger or depression.
Bipolar 1 criteria (6)
A. 3 ore more symptoms of mania (4 if mood is only irritable), of DIGFAST sx
B. 7 or more consecutive days and present nearly most of the day every day
C. Hospitalization to prevent harm to self or others
D. Psychotic features-ideas of reference
E. Include depressive episode
F. Mania may have been preceded by and may be followed by hypomania and MDD episodes
Bipolar 1 consequences (3)
1. High rates of serious and/or untreated medical conditions, most commonly metabolic syndrome and migraine headaches
2. Impairment in occupational function in euthymic state, resulting in lower SES despite equivalent levels of education.
3. Cognitive impairments often persist through the lifespan, even euthymic periods
Bipolar 1 comorbidities (3)
1. 75% have anxiety disorder
2. Higher risk for ADHD, ODD, IED, conduct disorder, substance use disorders
3. Alcohol use disorder or a disruptive/impulse control disorder
Psychotic features definition
-Delusion or hallucinations are present at any time in the episode
Mood congruent definition
-During manic episodes the content of all delusion and hallucinations is consistent with typical mania themes or grandiosity, invulnerability.. ect but may also include themes of suspiciousness and paranoia
Mood incongruent definition
-Content of the delusions and hallucinations are inconsistent with the episode polarity themes
Depressive episode (sx of bipolar disorder) definition
SIGECAPS basically
-Episode of either depressed or sad mood
-Anhedonia
-Change in eating or sleeping patterns,
-Feelings of guilt and worthlessness
-Lack of concentration
-Suicidal ideation or behavior
Mixed episode (sx of bipolar disorder) definition
-Symptoms consistent with both mania and depression last at least 1 week
Hypomania (sx of bipolar disorder) definition
-Episodes of at least 4 days of elevated, expansive, or irritable mood accompanied by same symptoms of mania (DIGFAST)
Prevalence of bipolar disorder
- Equal prevalence in gender and races
- Influenced by genetic and familial factors
Age of onset of bipolar disorder
- Onset of bipolar disorder 18-20 years
- Onset of manic symptoms in mid to late life should prompt consideration of medical conditions or substance/withdrawal
Children and onset of bipolar disorder
-Children usually has a more severe, chronic, and refractory course of illness
How does bipolar disorder affect children (6)
1. Neurodevelopmental delays (language, social, motor)
2. Greater vulnerability to stress and disruptions
3. Higher degree of associated psychotic symptoms
4. Poor/ineffective response to lithium
5. Increased alcohol disorders
6. 90% of children with BP disorder have comorbid ADHD
Reasons why bipolar disorder is difficult to manage (4)
1. 10% suicide rate (15x greater than general population)
2. Often presents with other psychiatric co-morbidities
3. Personality traits: ↑extraversion, neuroticism, openness
4. No simple treatment algorithm
Bipolar 2 criteria (5)
A. 3 or more symptoms of mania DIG FAST (4 if mood is only irritable)
B. 4 or more consecutive days and present nearly most of the day every day, of DIGFAST sx
C. Not severe enough to cause marked impairment in social or occupational functioning or to necessitate hospitalization
D. No Psychotic features
E. Must include depressive episode(s)
Bipolar 2 Characteristics (6)
1. Increased self-esteem
2. Thoughts are more organized
3. Thinking is quick and creative
4. Speech is loud and fast
5. Psychosocial functioning is good
6. Risk taking is mild to moderate
Bipolar 2 prevalence (Gender, onset age)
-Age of onset: 20 years
- More common in women
*RFs: genetic, familial
Bipolar 2 comorbidities
- 60% have 3 or more comorbid mental disorders
- 40% have eating disorder
Consequences and prognosis of Bipolar 2 disorder
- Economic burden: 4x greater than Bipolar I
- Better prognosis: married, higher ed. Level, fewer years ill.
Comparison of bipolar 1 and 2
- Bipolar 1 --> Manic episode and depressive episode
last more than 7 days
severe impairment
possible hospitalization and psychosis
- Bipolarr 2 --> hypomanic episode and depressive episode
lasts more than 4 days
Minore to no impairment
no hospitalization or psychosis
Cyclothymic Disorder Criteria (4)
A. For at least 2 years (1 yr. for children and adolescents) there have been numerous periods with hypomanic symptoms that do not meet criteria for hypomanic episode and numerous periods with depressive symptoms that do not meet criteria for a major depressive episode.
B. During the above 2-year period, the hypomanic and depressive periods have been persistent for at least half the time and the individual has not been without symptoms for more than 2 months at a time
C. Criteria for major depressive, manic, or hypomanic episode have never been met
D.Symptoms cause marked impairment in social or occupational functioning
Prevalence of cyclothymic Disorder (gender and onset)
-Equal prevalence in gender
-Begins in adolescence or early adult life
*RF --> familial
Comorbidities of cyclothymic disorder (3)
1. Substance abuse disorder
2. Sleep disorders
3. Children w/ADHD
Cyclothymic disorder is at risk of Developing what?
- 15-50% risk of developing bipolar I or bipolar II
Character traits of cyclothymic disorder (5)
1. Extroverted
2. Creative
3. Sociable
4. At times cheerful exuberance turns into irritability and extreme sensitivity to rejection or loss
5. Often impulsive
Treatment goals of bipolar disorders (4)
1.Full symptomatic remission
2.Return of psychosocial functioning
3.Prevention of relapse
4.Rapidly control agitation, aggression and impulsivity
Things to look at in bipolar disorder tx (3)
1. Assess for presence of alcohol or substance abuse or other factors that may contribute to disease or complicate treatment
2. Evaluated safety: suicidal evaluation , consider hospitalization
3. Directly related to the phase of episode, phase of treatment
a) Pt hx
b) Team approach: meds, CBT, family issues, social/school functioning
First line tx for bipolar disorder
- Mood stabilizers +/- antipsychotic
-They decrease the severity of mood episode
Different mood stabilizer
1. Lithium (gold standard)
2. Lamotrigine
3. Valproic acid
4. carbamazepine
Lithium
- Indicated for tx acute mania
- Prevention of recurrent manic and depressive episodes
- May have specific anti-suicidal effect
Starting dose of lithium
300-600 mg
Maintenance dose of lithium
600-1800 (lower in elderly pt)
What to measure when prescribing lithium
- Serum level
-Measure serum level 5-7 days after initiation or dose increase
* Should be drawn 12 hours after last dose
Acute side effects of lithium (6)
1. Nausea
2. Fine tremor
3. Polyuria and polydipsia
4. Weight gain
5. Loose stools
6. Cognitive impairment
Potential for serious side effects of lithium (4)
1. Weight gain
2. Diabetes insipidus
3. Renal failure
4. Hypothyroidism
S/S of toxicity for lithium (8)
1. Nausea,
2. Profuse vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration
4. ECG changes
5. Ataxia
6. Confusion
7. Tremor
8. Seizures
At what serum level can toxicity occur with lithium
-Can occur >1.5mmol/L
- >2.5mmol/L = medical emergency
Contraindication of lithium
1. Significant renal or cardiac disease (sick sinus syndrome)
2. Sodium depletion/extreme dehydration
3. Concurrent diuretic use
*kidney metabolism AVOID if CrCl <30mL/min
Preworkup when prescribing lithium (8)
1. UA
2. CBC with diff
3. BUN and Creatinine
4. TSH
5. Calcium
6. UPT
7. EKG
8. Weight
T/F you should taper lithium for discontinuation
TRUE
What is Valproate used to treat
1. Acute mania
2. Maintenance of bipolar disorder
* monotherapy or adjunct
*helpful with aggression
ADRs of Valproate (9)
1. Vomitting and nausea
2. Alopecia
3. Liver toxicity
4. Pancreatitis, PCOS, Low platelets
5. Rash
6. Obesity
7. Hyper ammonemia
8. Teratogenicity, tremors, thrombocytopenia
9. Exhaustion, encephalopathy
Black box warning of valproate (4)
1. Pancreatitis
2. Liver toxicity
3. Teratogenicity
4. Mitochondrial disease
Contraindications of valproate (4)
1. Significant hepatic impairment
2. Mitochondrial disorders
3. Urea cycle disorders
4. Pregnancy
Toxicity dose and S/S of valproate (5)
- Toxicity > 125 mcg/mL
1. Neurological: Can range from mild sedation, partial consciousness to coma
2. Cardiovascular
3. Hypotension
4. Tachycardia Gastrointestinal
5. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
*In severe toxicity must remove drug by dialysis
Monitoring for valproate (5)
1. VPA levels
2. LFTs
3. CBC w/ differential
4. Ammonia
5. Amylase/lipase
* may also do skin checks, body weight and waist size monthly
Use of Carbamazepine (3)
1. Acute mania
2. Mixed episodes
3. Maintenance of bipolar disorder
Contraindications of carbamazepine (4)
1. Hypersensitivity to carbamazepine or TCA's
2. Bone marrow depression
3. With or within 14 days of MAO inhibitor use
4. Auto-induces its own metabolism for first 4-8 weeks between dose changes.
When to check serum levels on carbamazepine
- 4 days after initiation or dose change
*Draw levels 12 hours after last dose
Toxicity S/S of carbamazepine (3)
1. Neurological:
Nystagmus, blurred vision, dizziness, convulsions
2. Cardiovascular
Arrhythmia, Hypotension, Tachycardia
3. Gastrointestinal
Nausea/vomiting, diarrhea
* In severe toxicity, remove via gastric lavage
Significant ADRs of carbamazepine (6)
1. Agranulocytosis/aplastic anemia
2. N/VD
3. Hepatotoxicity
4. Hyponatremia
5. CNS effects: drowsiness, nystagmus, blurred vision, dizziness
*risk suicide
6. Rash
Black box warning of carbamazepine (4)
1. Steven Johnson Syndrome
2. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in ppl with HLA- B 1502 allele
3. Aplastic anemia
4. Agranulocytosis
Carbamazepine (CBZ) drug interactions (8)
1. Oral contraceptive metabolism significantly induced
2. Phenobarbital, primidone, phenytoin can all induce CBZ
3. CBZ induces lamotrigine by 2-fold
4. Valproate inhibits epoxide hydrolase and increases active CBZ metabolite levels
5. CYP inducer induces metabolism antibiotics
6. Carbapenem antibiotics can decrease VPA levels
7. Psychiatric drugs: Clozapine
8. Antivirals
Most important drug related effects of CBZ
-Agranulocytosis
CBZ lab monitoring (4)
1. CBZ Levels
2. LFTs (every 2 weeks for first 2 months, then every 3 months)
3. CBC w/ differential (every 2 weeks for first 2 months, then every 3 months)
4. Sodium (baseline then periodically)
Other ways to monitor CBZ (3)
1. Skin checks for rashes at visits
2. Ophthalmologic exams
3. Patient's stance on pregnancy (if applicable)
Oxacarbazepine
- Structural derivative of carbamazepine
- Not effective for bipolar depression
- Improved adverse effect profile compared to CBZ
Oxacarbazepine (what it interferes with and the drug adjustments)
-May interfere with contraceptives
-Drug adjustments:
○ Hepatic: Use with caution in impairment
○ Renal: Cr Cl<30 mL/min: initiate at 1⁄2 usual dose
What drugs are used to treat Bipolar Depression (6)
1. Seroquel
2. Olanzapine/fluoxetine
3. Latuda, Lithium
4. Lamotrigine
5. Lumateperone
6. Vraylar
Drug that are indicated for both bipolar mania and depression (2)
1. Cariprazine (Vraylar)
2. Quetiapine (Seroquel)
Treatment for acute bipolar depression
1. Consider lithium (if appropriate/no contraindications) if patient reports suicidality
2. Use atypical antipsychotics (AAP)
3. Psychotherapy
4. Avoid lamotrigine as initial therapy
What drug to avoid when treating bipolar Depression and why?
- Avoid antidepressants as first line tx
- Bc they can precipitate a switch to mania or hypomania and are not effective for bipolar depression as monotherapy
Lamotrigine indication
-Used for bipolar maintenance and bipolar depression
-Generally well tolerated and safe for pregnancy
Drug interactions of Lamotrigine (4)
1. VPA: inhibits glucuronidation metabolism of LTG
2. CBZ: induces metabolism of LTG
3. Estrogen- containing contraceptives: induce LTG metabolism by 2x
4. Atazanavir, lopinavir, ritonavir: Induce LTG metabolism
ADRs or Lamotrigine (6)
1. Nausea/vomiting
2. Headache/dizziness
3. Somnolence
4. Ataxia
5. Diplopia, blurred vision
6. Rashes
Monitoring for Lamotrigine (4)
1. LFTs
2. CBC w/ differential
3. Skin check: no way to differentiate benign rashes from serious ones. If rash develops patient should stop LTG immediately
4. Adherence: if patient misses 5 days of LTG must restart titration
Blackbox warning for Lamotrigine
1. Life-threatening serious rashes, including SJS and Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
- Risk increased in pediatric patients, coadministration with valproate, exceeding recommendations for LTG initial dose or recommended dose escalation
SGA side effects
1. Sedation
2. Weight gain
3. EPS (drug induced movement disorder)
What drugs to avoid in pregnancy while treating bipolar disorder
1. Avoid CBZ and VPA in pregnancy whenever possible (VPA has higher right of birth defect)
2. Avoid lithium use in the first trimester (can be used in 2nd and 3rd trimester)
T/F in pregnancy antipsychotics are preferred over mood stabilizers in acute mania
TRUE
T/F for the first 6 months of treatment pts are at high right for relapse
TRUE
First line Treatments for bipolar disorder
- Lithium and VPA
Maintenance goal for bipolar disorder (4)
1. To treat relapse and recurrence,
2. Decrease subthreshold symptoms
3. Decrease suicide symptoms
4. Decrease cycling
Purpose of psychological interventions (3)
1. Reduce distress
2. Improve patient functioning between episodes
3. Decrease likelihood and/or severity of future episodes