Redox and Standard Electrode Potetentials
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Meaning of oxidation
Loss of electrons
Gain of oxygen
Loss of hydrogen
Increase in oxidation number
Meaning of Reduction
Gain of electrons
Loss of oxygen
Gain of hydrogen
Decrease in oxidation number
Reduction half equation of iron(II)-dichromate(VI) reaction
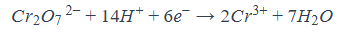
Oxidation half equation for iron(II)-dichromate(VI) reaction
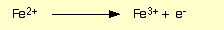
Overall equation for iron(II) - dichromate (VI) reaction

Colour change of the reduction process in the iron dichromate reaction
orange to green
Colour change of oxidation process in the iron dichromate reaction
Green to orange-rust
What happens and what are the observations for when OH- is added to dichromate ions
Orange to yellow
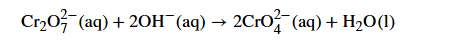
Reduction half equation for iron(II) - manganate (VII) reaction
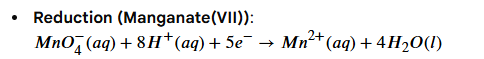
Oxidation half equation for iron (II) manganate (VII) reaction
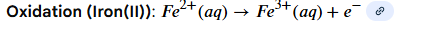
Overall equation for iron (II) manganate (VII) reaction and colour change
pink to colourless
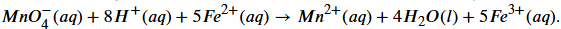
Equation for the reaction of Cu2+ and I-
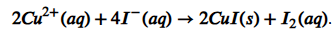
Equation of the reaction of S2O32- and I2
What indicator should be used for a titration of iodine against thiosulphate solution
starch blue/black to colourless
What is the salt bridge
a piece of filter paper soaked in KNO3 or NH4NO3
Function of salt bridge
completes the circuit and allows ions to transfer between the 2 half cells without any mixing of solutions
State structures present in a battery
Salt bridge
Potentiometer
Wire
2 beakers
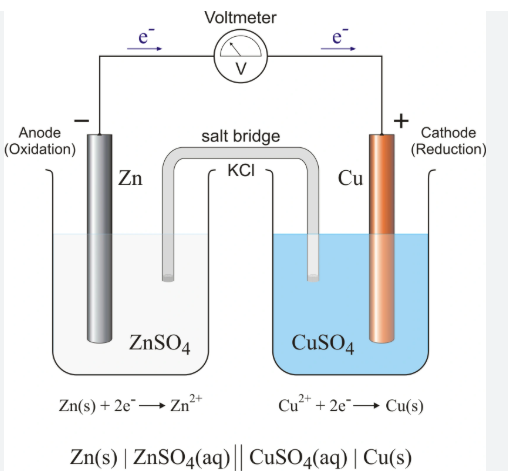
What happens on the left side of the cell
Oxidation
Electrons are being lost
Cell is negatively charged
What happens on the right side of the cell
Reduction
Electrons are being gained
Cell is positively charged
Draw a cell diagram
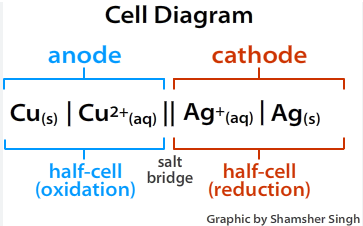
Define a standard electrode potential
The EMF of a half cell when connected to the standard hydrogen half cell.
Diagram of standard hydrogen electrode
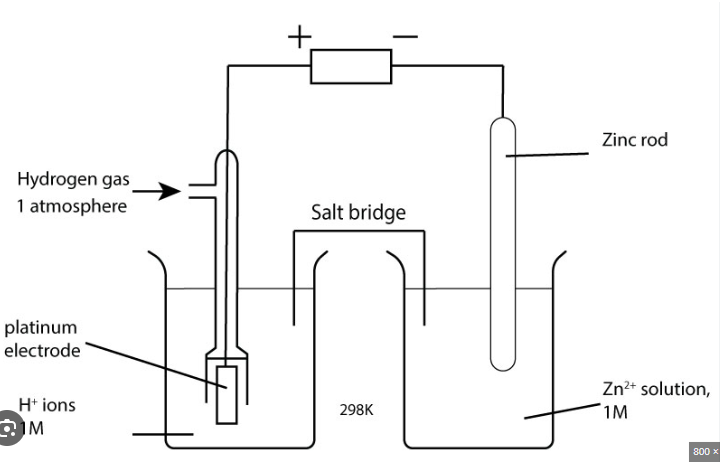
Conditions of standard hydrogen electrode
298K
1 atm hydrogen
1 mol dm-3
inert platinum electrode
Function of platinum electrode
Such low reactivity that it doesn’t interfere with the reaction
Completes the circuit because there is no metal in the half cell
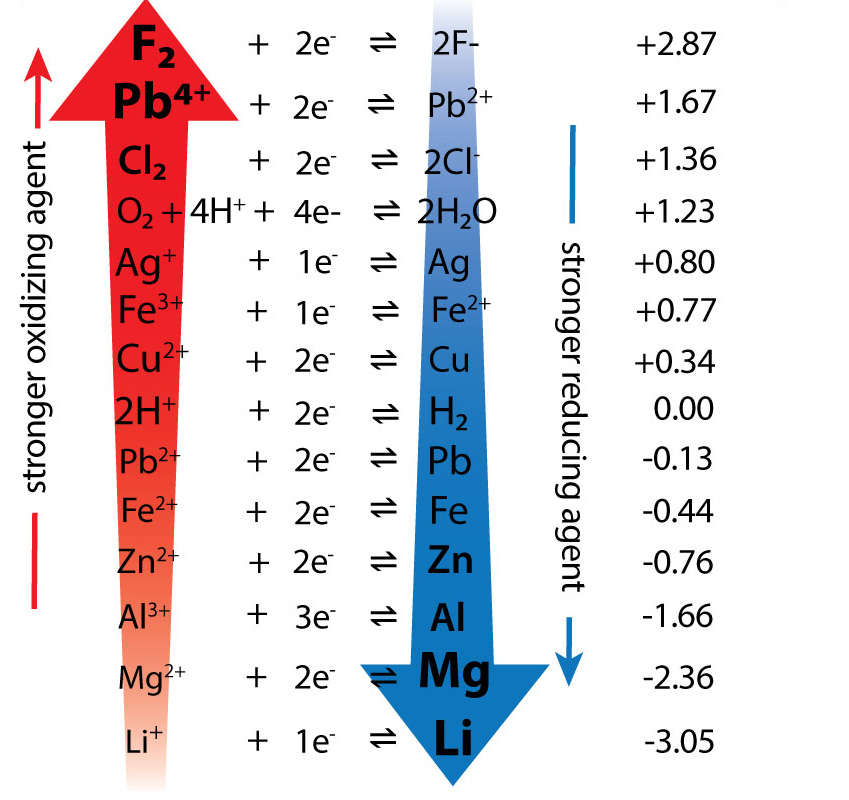
Predict whether the zinc half cell or the copper half cell will be reduced and which will be oxidised
Copper is on the RHS and is reduced
Copper has a more +ive E feta value
Copper is a stronger oxidising agent
Zinc is on the LHS and is oxidised
Zinc has a less +ive E feta value
Zinc is a stronger reducing agent
EMF = 0.34 - - 0.76 = 1.10V
Function of hydrogen fuel cell
uses electrochemical methods to get energy from hydrogen
How does a hydrogen fuel cell work
Hydrogen gas is fed into the anode
oxygen from the air is fed into the cathode
Catalyst in the hydrogen cell
platinum catalyst
Write the half-equations for the processes occurring at the electrodes in an hydrogen fuel cell and an equation for the overall reaction.
At the anode: H2 → 2 H+ +2 e-
At the cathode: O2 + 4 H+ + 4 e- → 2 H2O
Overall reaction: 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
State the disadvatages of a hydrogen fuel cell
expensive
Storage of hydrogen is problematic as it is expensive
very flammable and a gas
Lots of hydrogen is needed to produce enough energy
Cell does not last for long
A net energy loss as the energy produced by the cell is less than the energy required to produce the hydrogen for it
State the advantages of a hydrogen fuel cell
Clean technology
High efficiency
No combustion process required
simple to construct
No CO2 is produced