Coasts final
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Fetch
the distance wind blows
Wave break ratio
the wave length cant be more then 7x the height as this is when the wave breaks (1:7)
Swash
water washed up the beach when a wave breaks -can deposit sediment.
Backwash
When water runs back into the ocean - can remove sediment with it
Constructive Waves
Adds sediment to the beach - high swash and low backwash. Longer wavelength, low height and wave frequency, and elliptical orbit.
Destructive Waves
Take sediment from the steep beach - high backwash and low swash. Shorter wavelength, higher height, more frequent wave frequency, and circular orbit.
Sediment Cell
A section of coastline which is relatively contained and flows of sediment act in dynamic equilibrium
disruption within the cell therefore has minimal impact on neighbouring areas
however human impact may upset the DE in the long term
What are tides
The regular rising and falling movements of the sea caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun
Spring Tides
Occur when the sun, moon and earth are in one straight line
so the gravitational pull is the greatest causing large tidal range
the high tide is the highest and low tide is the lowest
Neap Tides
When the Sun and moon are perpendicular from each other
so their forces partially cancel each other out as they pull in different directions
So there’s a smaller tidal range then spring tides
What is biological weathering - give examples
the breakdown of rock by living organisms (eg. plant roots, animals, microorganisms) which can physically or chemically alter the rock
What is chemical weathering - give examples
alteration of the rocks chemical structure - oxidation, carbonation, solution, acid rain
Examples of mass movement
Soil creep, mudflow, landslide, rockfall, landslip/slump, runoff, solifluction
Mass Movement definition and give examples
When gravity causes the downhill movement of material
Examples of things which influence the power of marine erosion
power of waves
how sandy a beach is (rock is more resistant)
geology - types of rocks and permeability
hard/soft engineering strategies

What are revetments
Concrete or wooden walls placed at angles along the beach to take in wave energy
What is Rock armour/rip-rap
Large boulders dumped in front of a cliff or sea wall to take the full force of the waves. Gabions are rocks in metal cages
What is cliff fixing
Driving iron bars into the cliff face to stabilise it and absorb some wave power - sometimes they use metal mesh netting
What do offshore barriers encourage
waves to break offshore to reduce their impact on the base of cliffs
Hard Enginering definition and examples
Man made structures use to control disruption of natural processes - groynes, sea walls, rip rap, revetments, offshore barrier.
Soft Engineering definition and examples
Natural methods to reduce erosion and stabilise coastlines - Beach nourishment, dune stabilisation, marsh creation
what does it mean if managed retreat is being undertaken - give examples
allowing the sea to flood/erode low value or low lying land in a controlled way, rather than defending the land
eg allowing flooding of low value land which creates salt marshes - which reduce wave energy thus reducing flood risk to nearby housing
How much of Britains coastline is the Environment Agency responsible for
DELETE
How do headlands and bays form
due to varying resistances of rocks
How are caves formed
Continuous erosion (eg. hydraulic action and abrasion) of a headland can create a cave
how are arches formed
As a cave continues to erode through to the other side of the headland an arch is formed
how is a stack formed
(A cave forms, then an arch)
Over time, the top of the arch can collapse due to erosion and gravity, leaving a column of rock
how is a stump formed
(A cave forms, then an arch, then a stack)
then further erosion at the base of a stack can cause it to collapse, leaving a stump
What is a wave-cut platform and how does it form
A wide gently-sloping surface found at the foot of a cliff
how does a wave cut platform form
As a wave cut notch increases in size the cliff becomes unstable and collapses leading to the retreat of the cliff face, the backwash carries away the eroded material, leaving a wave-cut platform
what is a wave-cut notch
a dent in the cliff usually at the level of high tide caused by erosion
How does a wave cut notch form
the sea attacks the base of a cliff (between the high and low water mark) using erosional processes such as abrasion and hydraulic action
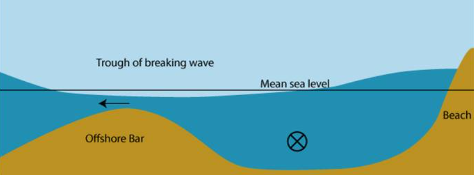
How do offshore bars form
strong backwash of destructive waves carries sediment into the sea
the sediment accumulates in shallow water where reduced wave energy stops further transport
causing a bar to develop parallel to the coast UNDERWATER
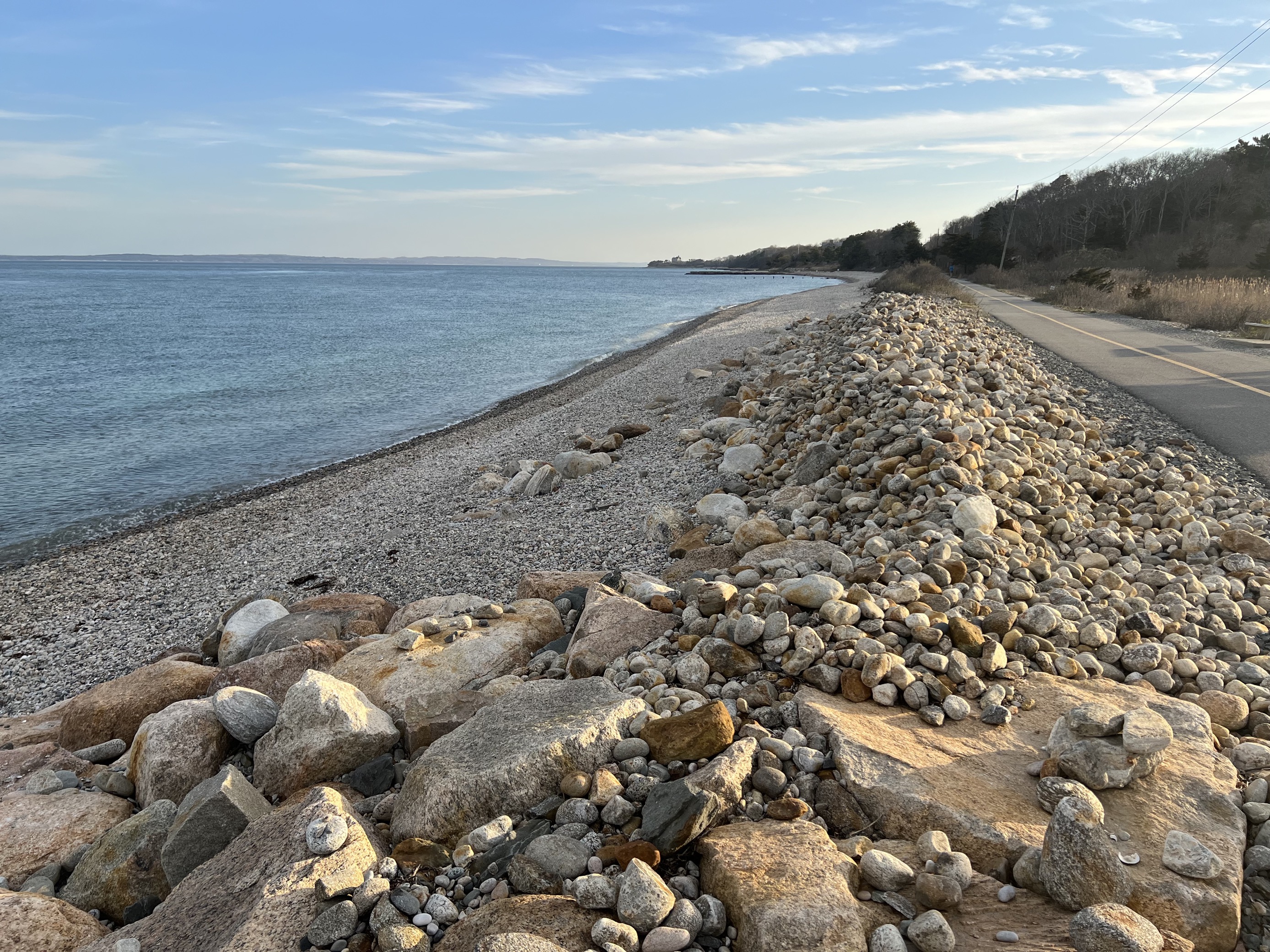

What are berms
Ridges of sediment that form on the upper part of a beach
how are berms created
by constructive waves
swash carries sediment up the beach and as the wave energy dissipates material is deposited at the high tide mark
over time, repeated deposition during multiple high tides builds up a berm
they can increase in summer when constructive waves are more frequent
How do spits form
Longshore drift caused by prevailing winds (45) transports sediment (in a zigzag motion) along the coast
it is then deposited where the coastline changes direction
As deposition continues the spit extends out into open water
It may curve due to changes in wind direction
salt marshes can form in the sheltered area behind (eg. Spurn point, Holderness coast)
How does a barrier bar form
when a spit extends across a bay joining two headlands ABOVE WATER
Often occurs in shallow, sheltered areas, with lower wave energy
A lagoon or salt marsh may form behind it
How are sand dunes formed
Mounds or ridges of sand formed by on shore wind
the accumulation sand is then stabilized by vegetation roots or driftwood to form an embryo dune
what conditions do sand dunes require to form
Dry loose sand
Wind
A flat area
what processes create sand dunes
Saltation
Depositon
Vegetation fixing (marram grass)
what is Isostatic Change
the local change in land level (eg. due to tectonic activity or post glacial rebound) which can lead to relative sea level changes
Explain post glacial rebound - example of isostatic change
During glacial periods the weight of ice caused the land to sink
when the ice melts the land slowly rises again making the relative sea level appear to fall
Eustatic Change
A global change in sea level caused by a change in the volume of water in the oceans
usually due to ice melting or thermal expansion
What are Fjords and how do they form
A steep deep glacially-carved valley that have been filled with seawater
how do fjords form
A glacier carves out a valley through erosion
The glacier then retreats and rising sea levels flood the valley creating a narrow, deep waterway (eg Norway fjords)
what is a Ria
a drowned V shaped river valley with the higher land (the peaks) exposed
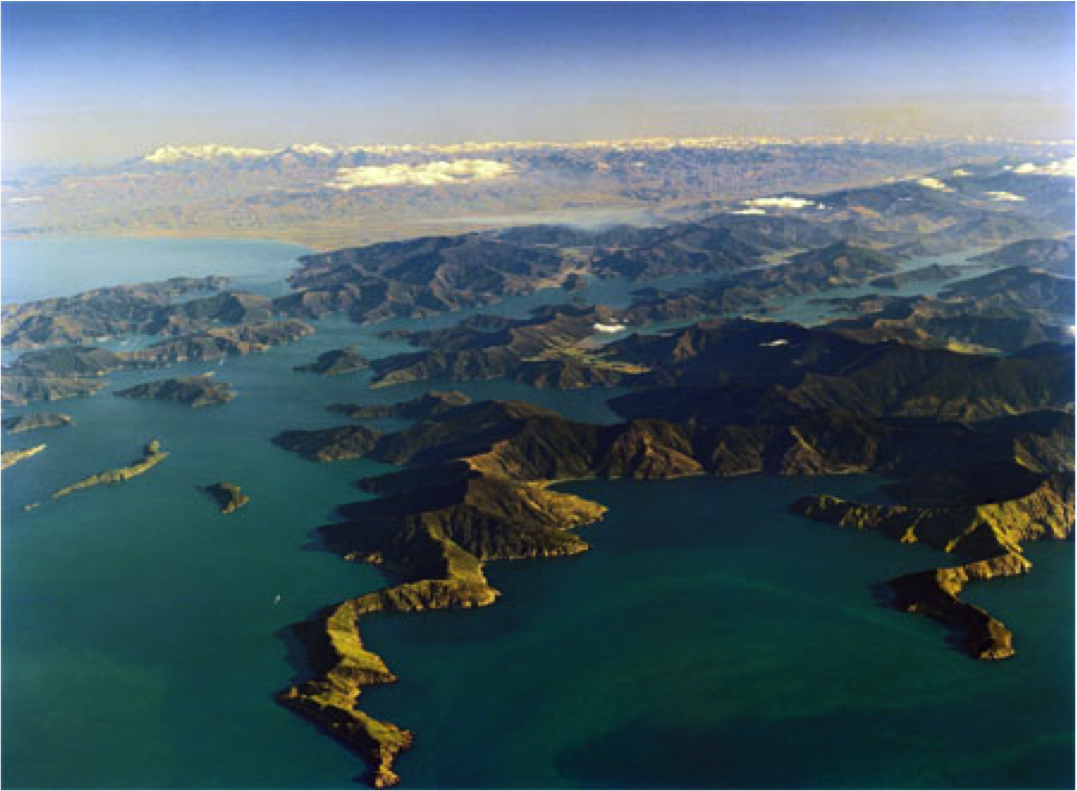

How do rias form
Rising sea levels (eustatic change) flood a river valley - usually happens after an ice age or due to global warming
As the sea levels rise the sea submerges the the lower part of the river valley while the higher land remains exposed (Rias)
An example of a ria is the Dartmouth ria in the UK.
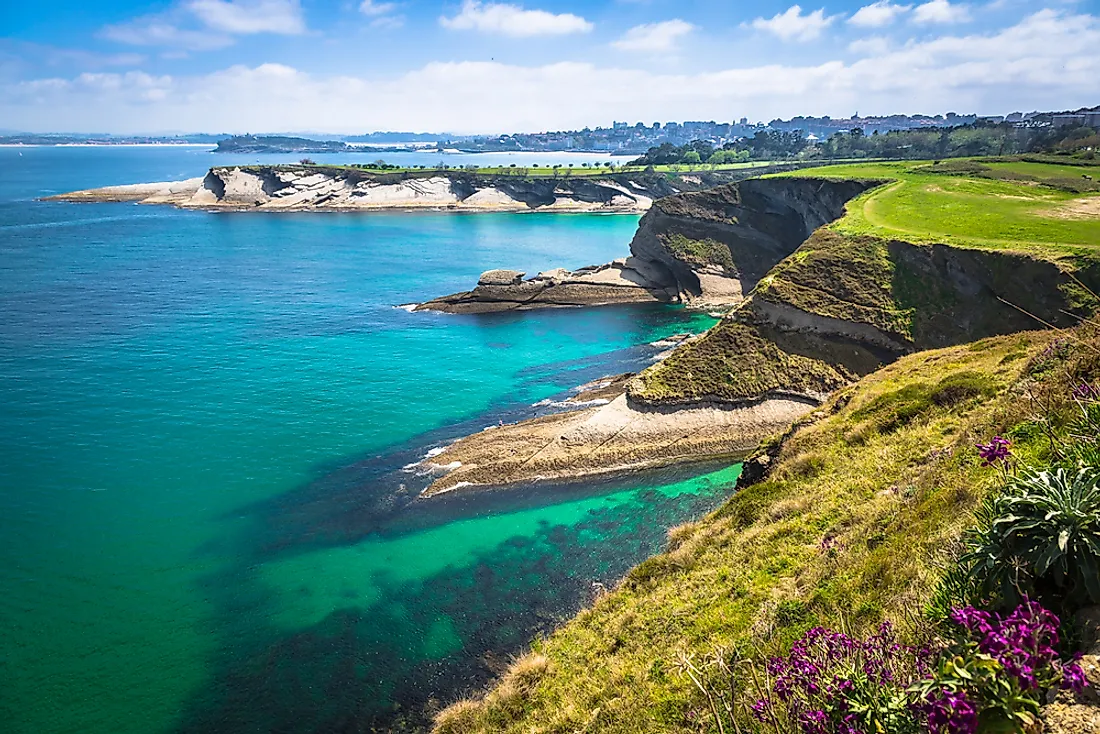

What is a raised beach
An emergent landform of a former wave-cut platforms and beaches that are now located above the current sea level
how is a raised beach formed
as land rises due to isostatic rebound or sea level falls former wave cut platforms emerge
Dalmatian Coasts
Occur on a concordant coastline
Rising sea levels (eustatic change) cause parallel ridges and valleys to flood and become partially submerged
often leaving tops of ridges exposed
eg Dalmation coasts of Croatia
Examples of mechanical weathering
Freeze thaw
Thermal expansion and contraction
Wetting and drying
Hydraulic action
The sheer power of water hitting against a cliff causing rock to break away
air becomes trapped in the cracks of the cliff and causes the rock to break apart
Corrasian
Sediment is thrown against the cliff face by waves which wears down the cliff face by causing material to break away
(acts like sand paper scraping and eroding the cliff)
Attrition
Sediment wearing down the surface of the shoreline
through constant friction as it moves against the coast
(as it moves along it smooths and erodes the sediment/rock)
Corrosion
Chemicals in sea water react with some rocks (eg chalk and limestone) as the water is slightly acidic due to dissolved CO2
example factors which effect erosion
wave intensity
beach size (eg a larger beach has more sediment to erode and dissipate energy)
Suspension
Very small particles carried in the water without touching the sea bed and stay suspended in the water column
Saltation
Smaller pebbles bounced or skipped along the sea bed in hopping/leaping motion
the waters strong enough to lift medium size sediment up but not enough to keep it suspended
Traction
stones and boulders are rolled/slid/dragged along the seabed due to the force of water (usually from waves/currents) - their weight means they stay in contact with the sea bed
Solution
Soluble minerals dissolved in water and transported in the dissolved state
primarily effects limestone and chalk containing calcium carbonate which is soluble in weak acids present in sea water
Wave quarrying
When waves break against unconsolidated materials eg sand, they can scoop out loose material
The wave’s strong upward force can dislodge rocks from the shore and drag them back as the wave retreats
Cavitation
When waves break they put pressure on the vapour bubbles in rocks
this creates an extra force causing the bubble to implode, becoming liquid
this energy can cause the rock to blast apart
Longshore drift
Prevailing winds cause waves to approach the shore at a 45 angle, swash carries sediment up the coast at this angle and backwash carries it back at a 90 angle (zig zag motion), over time sediment is deposited laterally along the shore causing the coast to get longer
How is a drift-aligned beach formed
Longshore drift causes sediment to move laterally along the beach
Swash-aligned beach
Sediment moves up and down the beach with little lateral (left/right) transfer
Swash and backwash occurs with little influence from longshore drift so waves approach head on rather then at an angle so sediment moves up/down the beach rather then along it
Often found in sheltered areas (eg bays) where energy is lower
What is a shoreline management plan (SMP)
Docs outlining the plan of intervention for a sediment cell
what are the 4 choices of shoreline management plans
hold the line
no active intervention
managed retreat/realignment
advance the line
What is hold the line
Maintaining the current position of the coastline, usually using existing defences
cheap but requires constant maintenance
What is advance the line
Extending the coastline out to sea, using new defences (eg beach nourishment)
protects natural habitats but can be expensive
What is no active intervention
Letting nature take its course - allowing the sea to erode cliffs, flood low-lying land, existing defences to collapse
cost-free but homes and farmland on land can be lost
What is Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM)
The management of different pressures and conflicts at the coast
aiming to balance environmental protection with socioeconomic needs
what is a barrier island
A long narrow island running parallel to the mainland coast
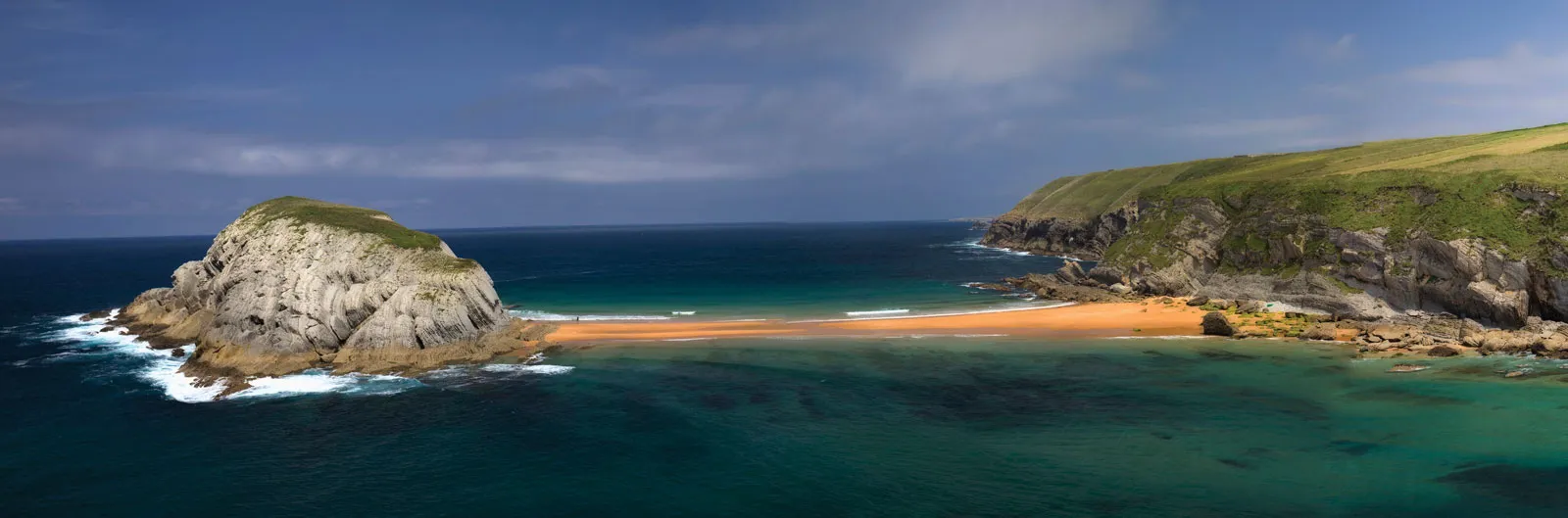

Tombolo
A bar which connects an island to the mainland
Long shore drift causes a spit to grow out from the mainland and meet the island
Positive feedback
Where a flow/transfer leads to increase/amplifying of the original event
Negative feedback
Where a flow/transfer leads to decrease/decline/nullifying of the original event
How do rip currents form
breaking waves are funnelled back to sea through a narrow concentrated channel
creating a strong offshore flow
can transport sediment and disrupt coastal processes
they can be very dangerous for swimmers
What occurs at a low energy coast
More deposition than erosion
Waves aren’t very powerful
Depositional land forms (eg beaches and spits) often form
eg Lincolnshire
What occurs at a high energy coast
More erosion than deposition
Powerful waves
Erosional landforms (eg headlands, cliffs and wave-cut platforms) often form
eg Cornwall
What have the recent sea level changes been like globally (in the last 10,000 years)
There’s been global sea level rise following the end of the last glacial period
Beach zones order
Land to sea
Backshore, foreshore, nearshore, offshore
Predicted changes in sea level rise
By 2100 sea levels will have risen by 30-100 cm
how do steep cliffs form
strong resistant rock requires high energy waves to be eroded - because they erode less quickly they remain strong
any high energy waves removes debris quickly preventing a gentle slope from forming
how do gentle cliffs form
weaker rock and low energy environment means they’re more susceptible to erosion
less erosive waves allow debris to build up and act as a buffer against further erosion contributing to gentler/gradual slope
how does negative feedback effect cliff retreat
erosion causes the cliff to retreat so the fallen debris reduces further erosion by providing protection at the base
whats a halophyte
a salt tolerant plant (commonly found in mudflats and estuaries)
how do waves form
wind moves across the water surface causing frictional drag
this leads to the circular orbital motion of water
the sea bed is shallower towards the coastline so the water particles become elliptical
leading to the horizontal movement of waves
the waves height increases but wavelength and velocity decreases so water backs up behind the waves until the wave breaks
3 factors affecting wave energy
strength of wind
duration of wind
size of fetch (distance wind blows)
which waves dominate in summer
constructive - due to lighter winds and longer fetch)
this may increase with climate change
what is cost benefit analysis used for
to compare the projected cost of management plans to its expected benefits
what does s DEFRA 1:1 analysis
the expected benefits must outweigh costs for the project to go ahead
What are the goals of sustainable coastal management
creating long term sustainability which manages resources for long term productivity and creates jobs
educates communities
monitor environmental changes
what is soil creep
the slow movement of soil on a slope due to the force of gravity
it’s slow as soil particles repeatedly expand and contract in wet/dry periods
what is solifluction
occurs mainly in periglacial environments when the top layers thaw during summer and flow over still frozen layers
how do mudflows occur
increased water content in soil leads to reduced friction
gravity causes the soil to surge down a slope with tremendous force
is a serious threat to life as it can be very fast flowing
what is rockfall
the abrupt movement of masses of geological material which becomes detached from steep slopes/cliffs
often due to weathering processes eg freeze thaw weathering
what is a landslide
the mass movement of material rapidly down a slope due to reduced friction caused by heavy rainfall
how do landslips/slumps occur
heavy rainfall saturates land adding weight and reducing friction of particles
gravity acts on it causing it to move down in a rotational manner along a curved surface
creating a terraced appearance
what is runoff
when heavy rainfall washes material from the surface of a cliff over the edge and down onto the shore
how do salt marshes form
Mud and silt is deposited along a sheltered coastline to form a mudflat
Pioneer plants colonise the mudflat so more sediment is trapped
how do estuarine mudflats form
NO