L8: Pons
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
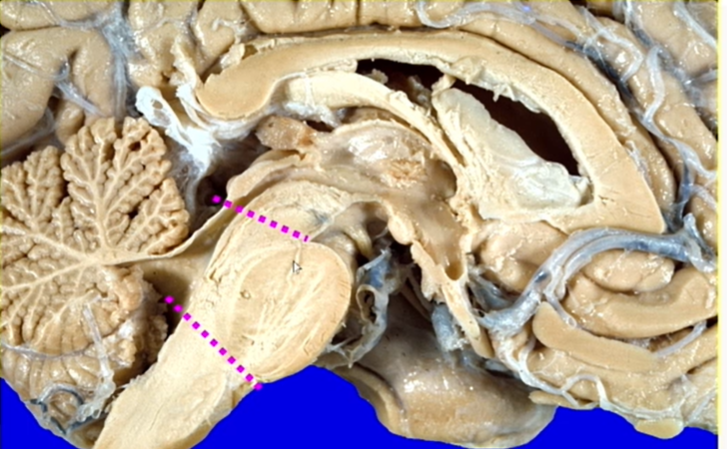
boundaries of pons
caudal
posterior pontine protuberance to the 4th ventricle
rostral
anterior pontine protuberance to point behind inf colliculus
what happens to the corticospinals/bulbars as we move up the pons
they spread out more
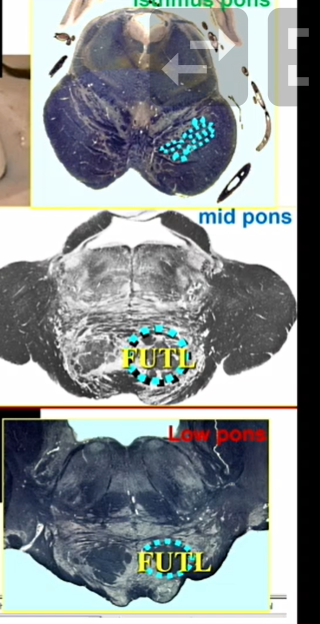
what happes to the sensory structures as we move up the pons
whale - low
boomerang - high
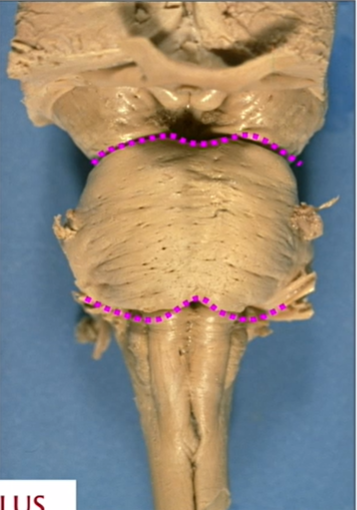
name and view
anterior and posterior pontine protuberance - borders of pons
ventral aspect
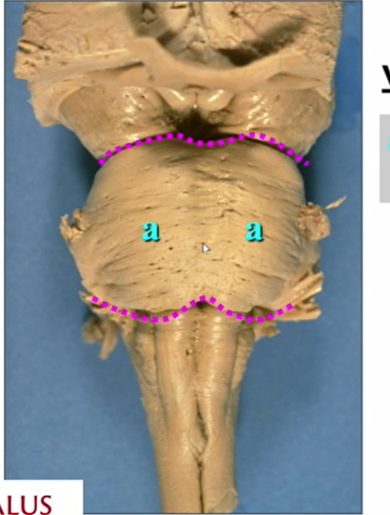
a
base (of pontine protuebrance)
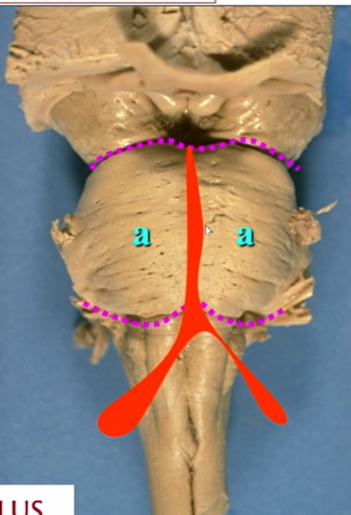
name red thing
basilar sulcus for basilar artery
vertebrals make of basilar
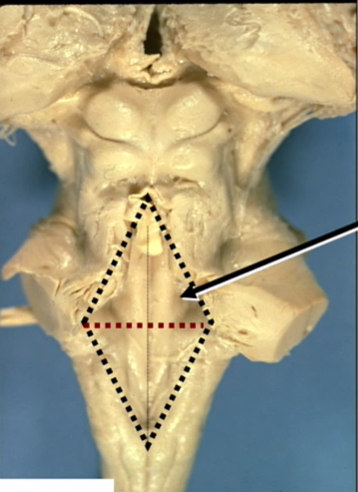
name arrow and what is in it
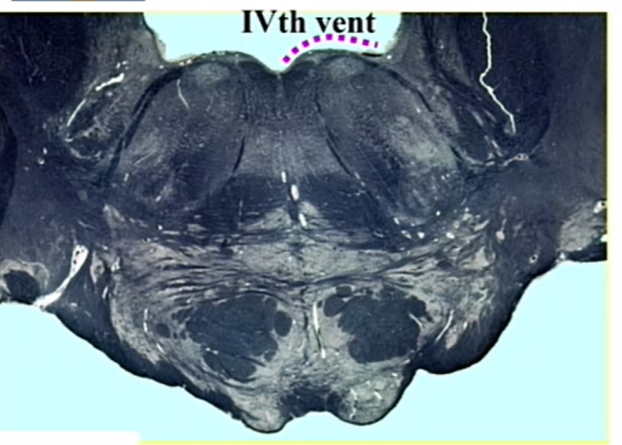
facial colliculus
nucleus of 7
root of 6
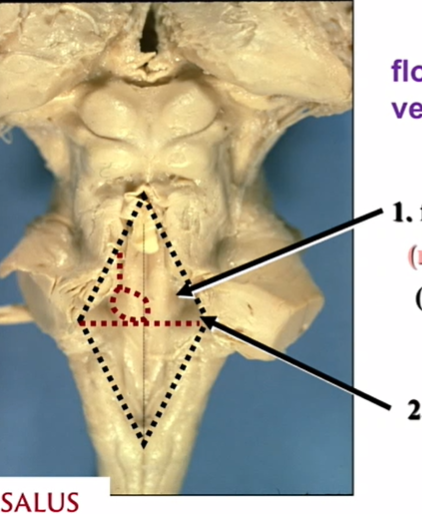
arrow 2 adn whats in it
lateral recess
has vestibular nuclei
its a depressed area
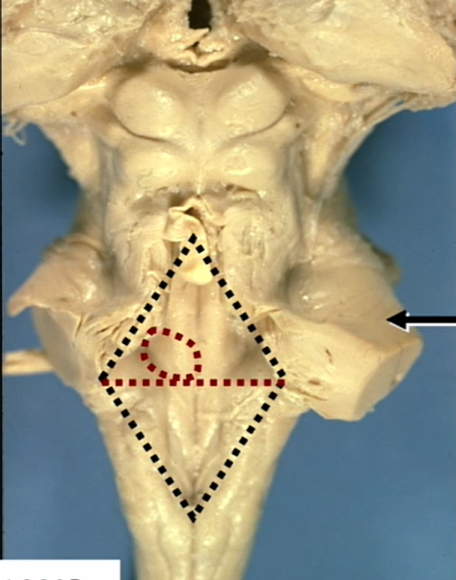
name arrow
middle cerebellar peduncle
what do peduncles communicate w
cerebellum
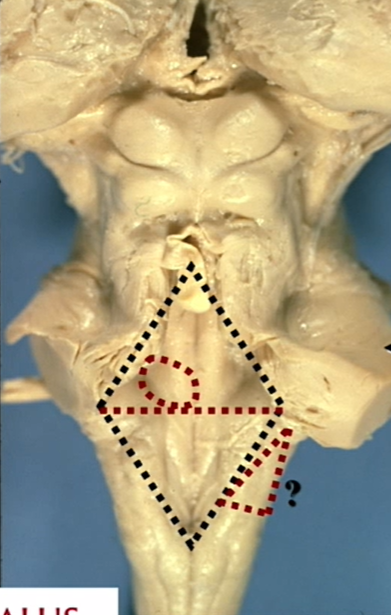
? structure
inferior cerebellar peduncle of medulla
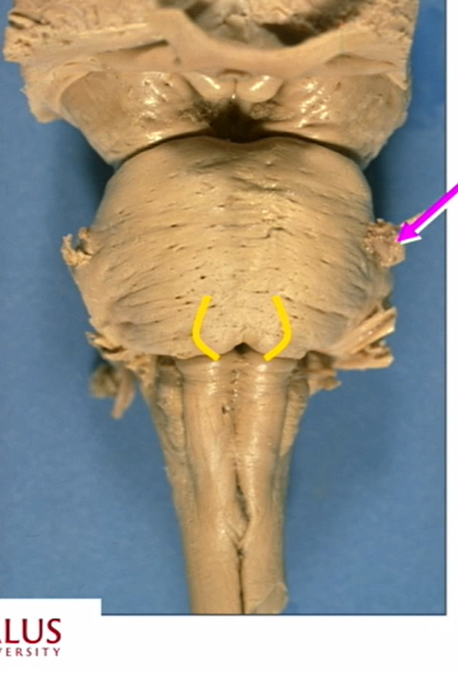
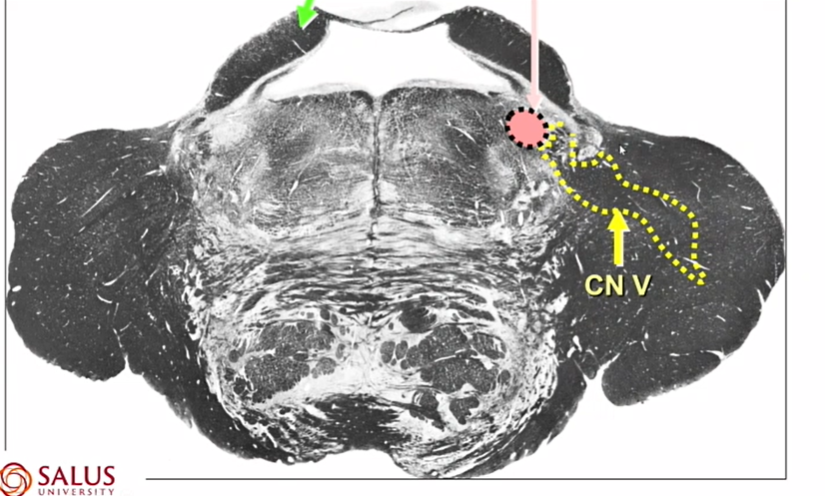
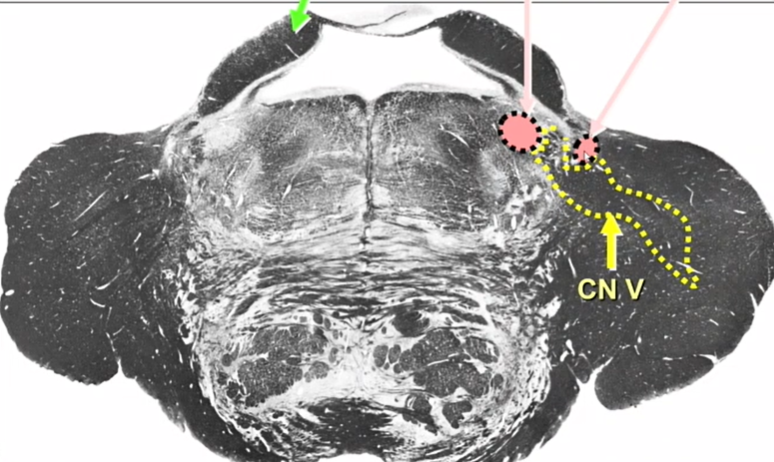
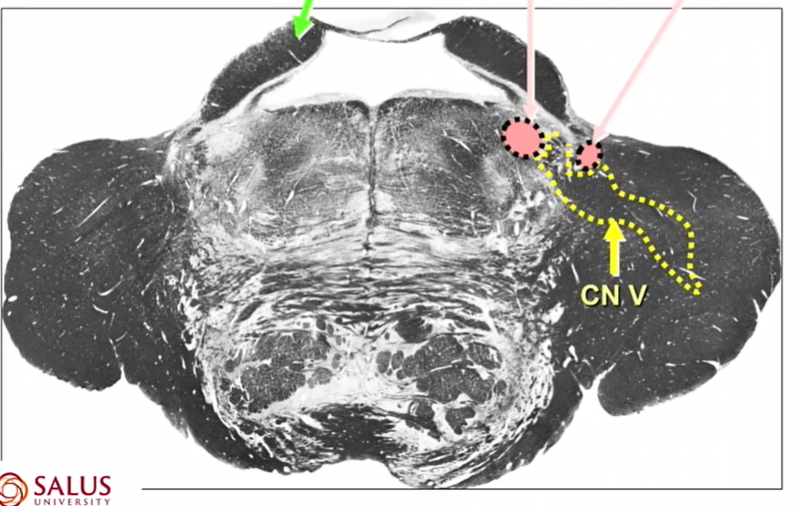
name pink arrow
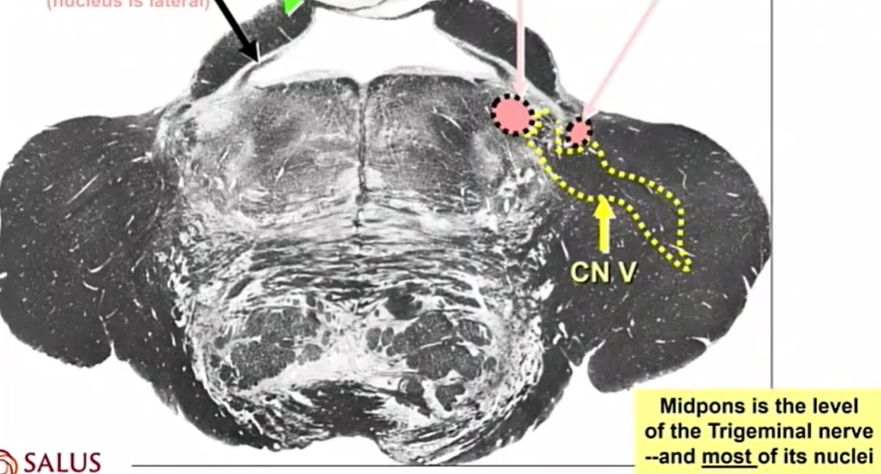
CN V
big bc it has 3 parts
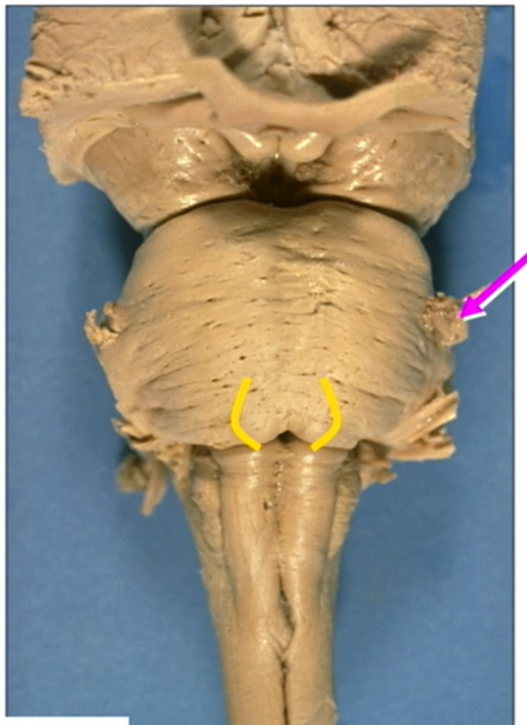
yellow lines
CN 6
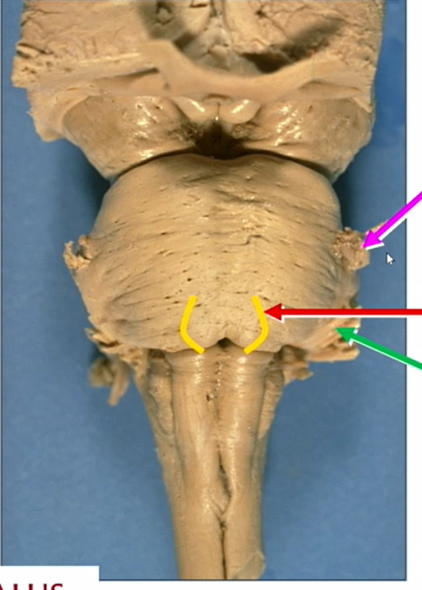
green arrow
CN VII
where are CN 6 and 7
low pons
where do we expect to see most CN coming off (ventral or dorsral)
ventral - they are trying to get towards the EOMs
EXCEPT 4 comes out the back (dorsal)
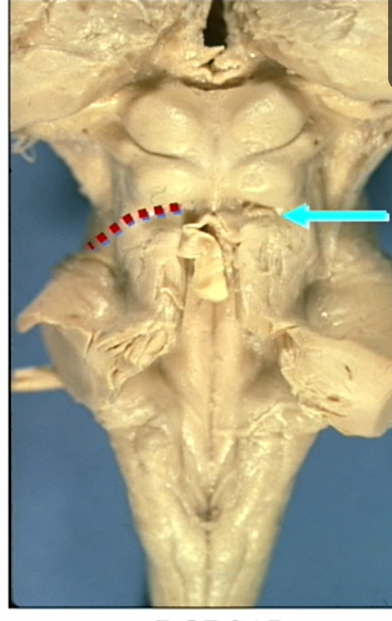
blue arrow
CN 4
isthmus pons level
low pons level CN
6 and 7
mid pons level CN
V
isthmus pons level CN
4
what view
low pons
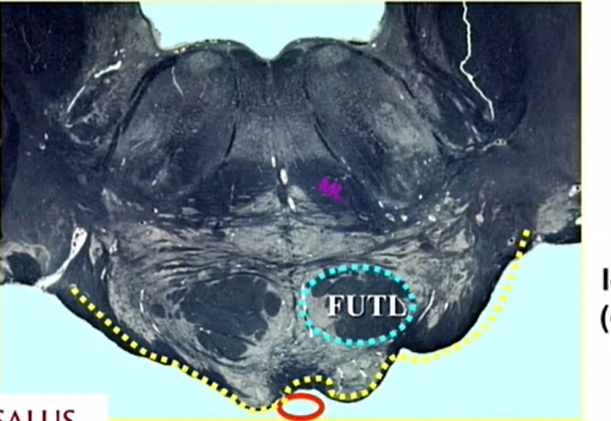
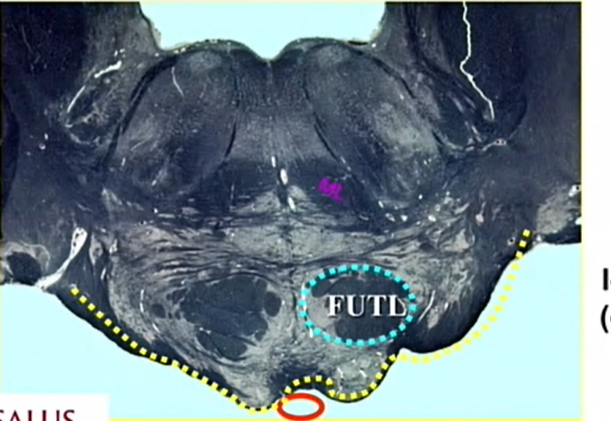
blue
longitudinal bundle
houses corticobulbars and spinals — pyramidal tract
low pons
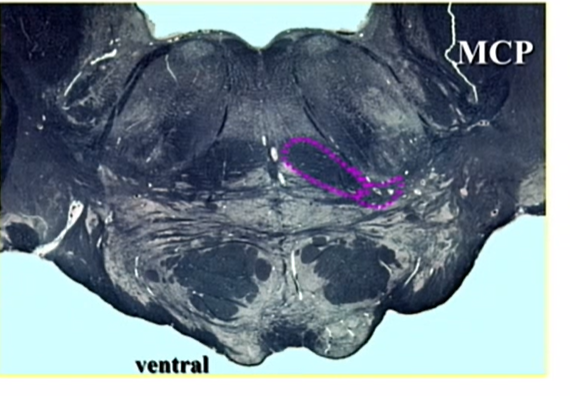
pink body
medial lemniscus - dorsal
low pons
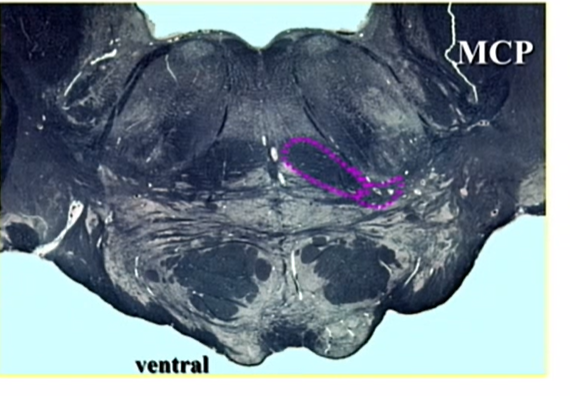
pink tail
ventral and lateral spinothalamics and spinotectal tracts
dorsal - sensory
low pons
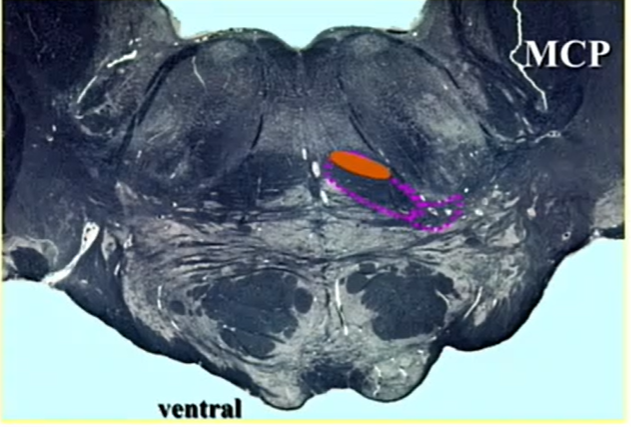
whale hat
ventral trigeminothalamic tract - new
low pons
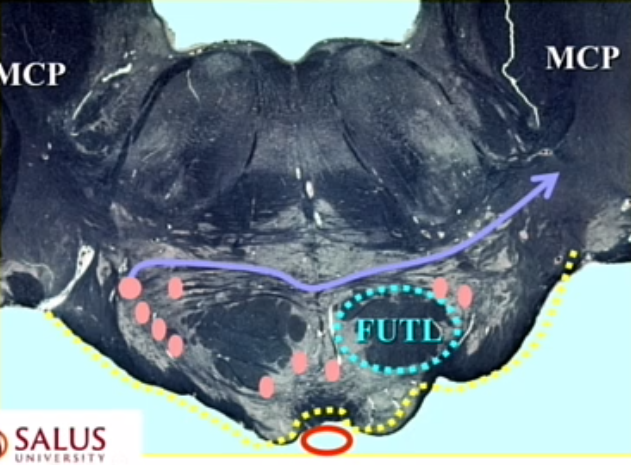
pink dots
pontine gray (nucleii)
so stains light
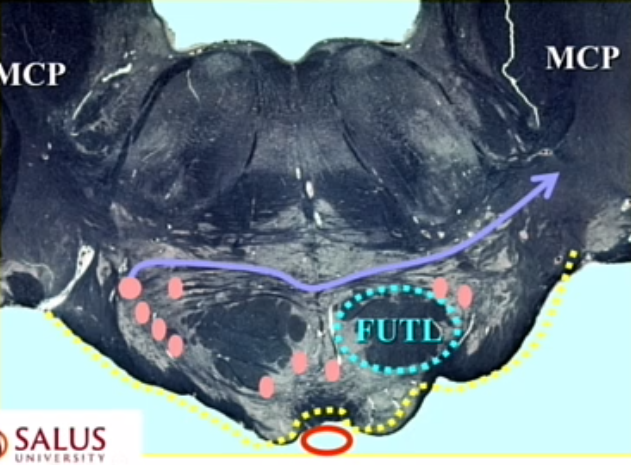
purple line
transverse fibers (pontocerebellars)
fxn of cerebellum
modulate and refine motor activity
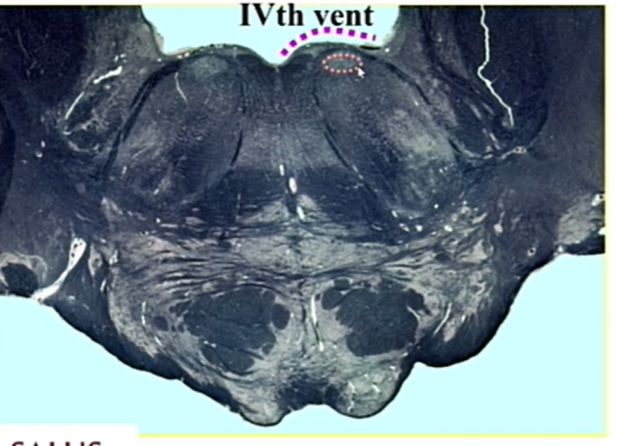
name
facial colliculus
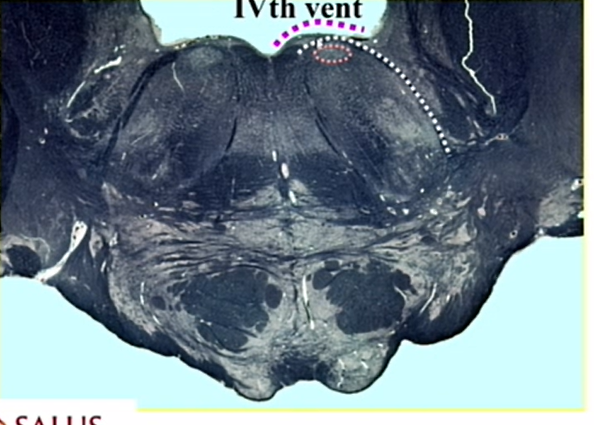
light pink
nucleus of 6
low pons
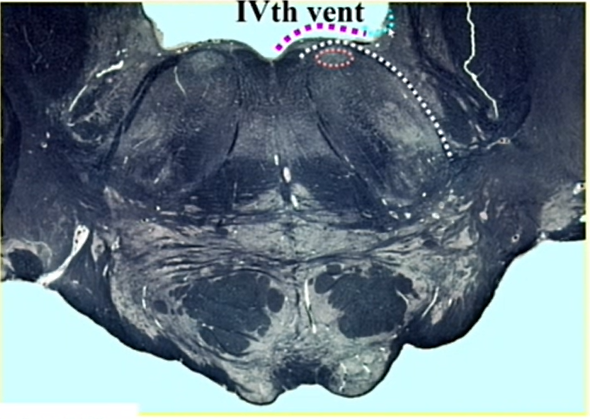
name white line
root of 7
low pons
teal
lateral recess
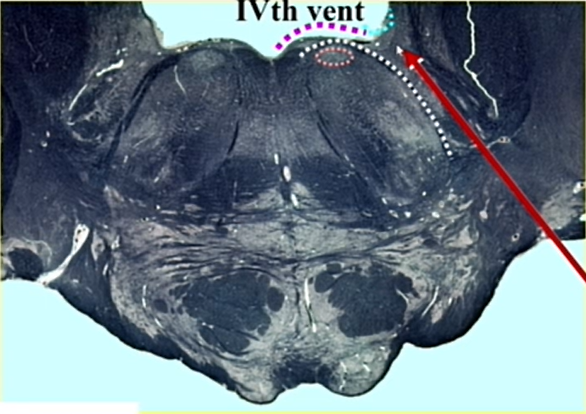
red arrow
vestibular nuclei
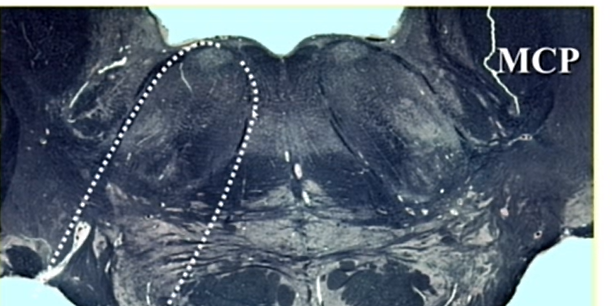
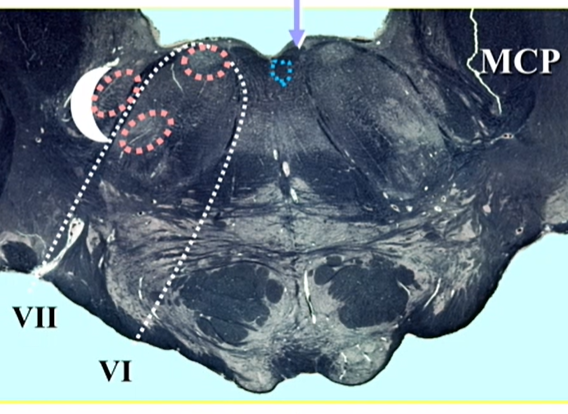
name these lines in low pons
travel parallel in low pons
7 - later = lateral
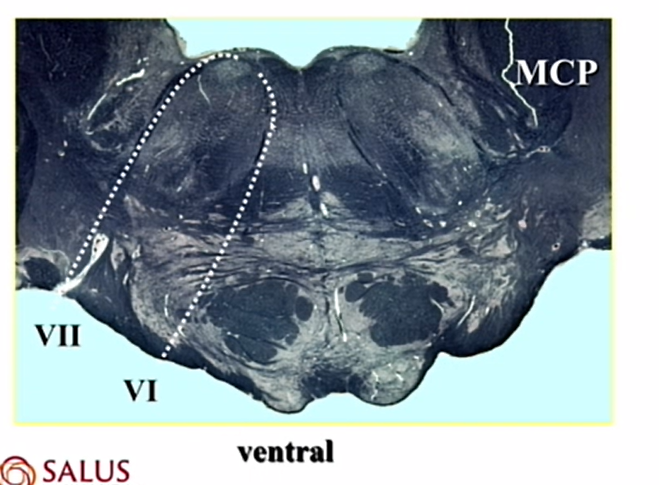
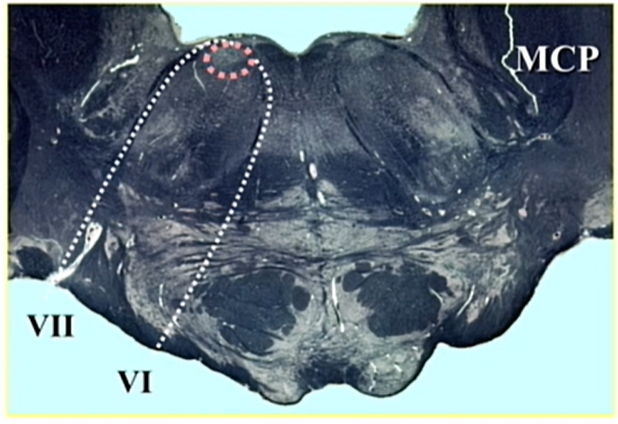
pink circle
CN 6 nucleus
LMN
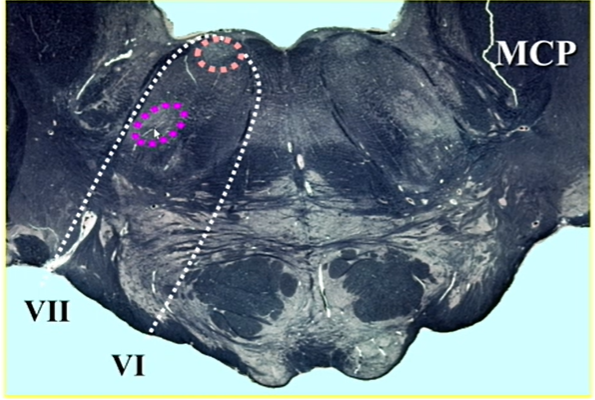
hot pink circle
CN 7 motor nucleus
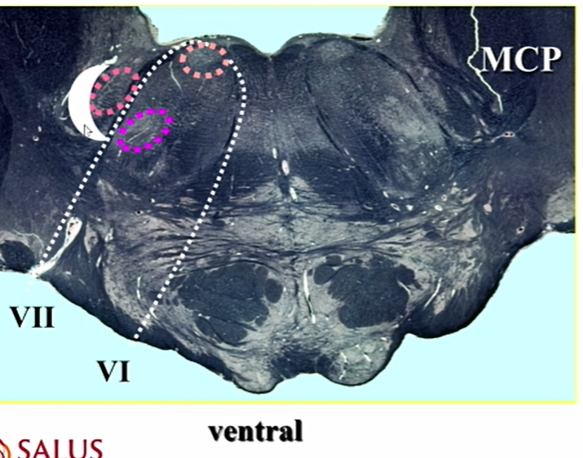
name moon and medium pink
spinal nucleus and tract of V
low pons
this is lower than it comes in so its dipping towards the spine
uncrossed general sensory info from head - esp pain
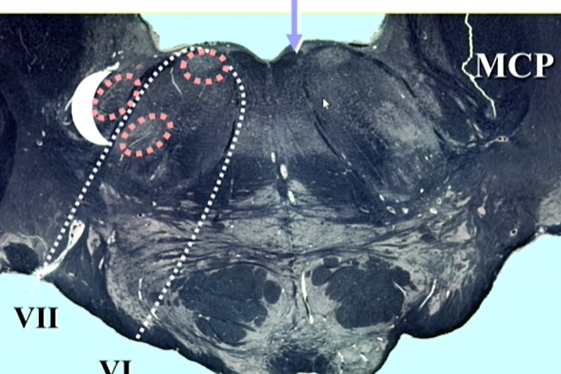
purple arrow
internal genu of VII (7)
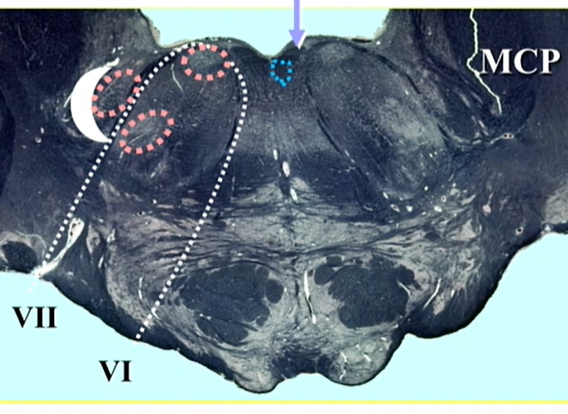
name blue
medial longitudinal fasciculus
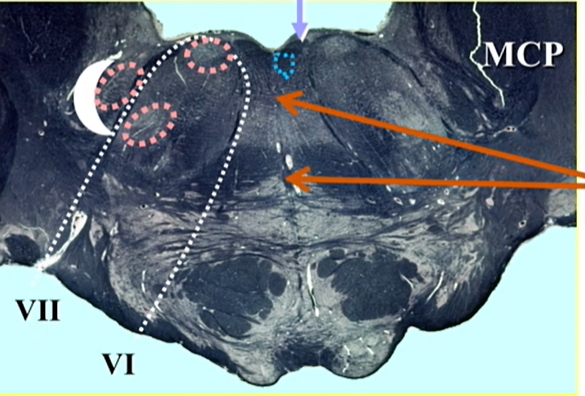
name orange arrows
nucleus raphe magnus —> serotonin
Pontine Paramedial Reticular Formation (PPRF)
low pons
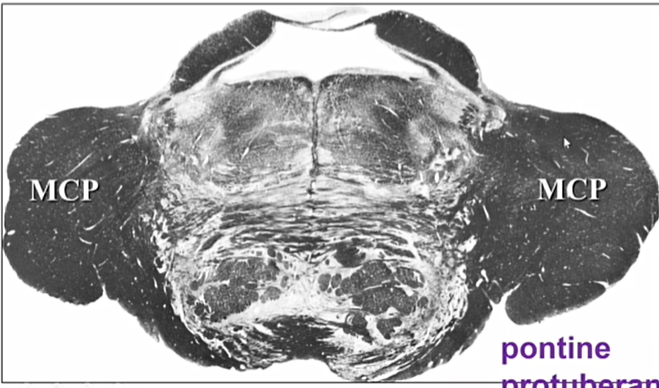
whats this a cut of
mid pons
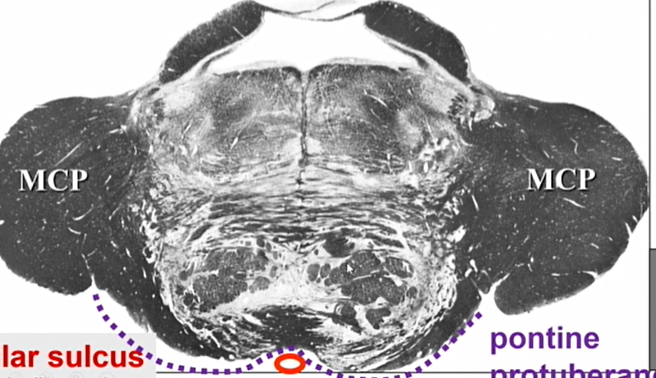
name purple and red
pontine protuberance - purple
basilar sulcus -
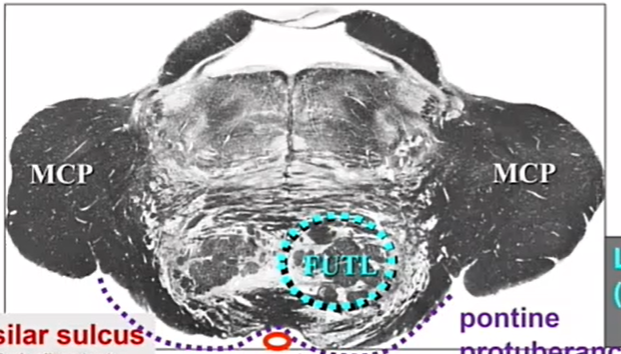
name blue
longitudinal bundle
corticobulbars adn spinals
mid pons
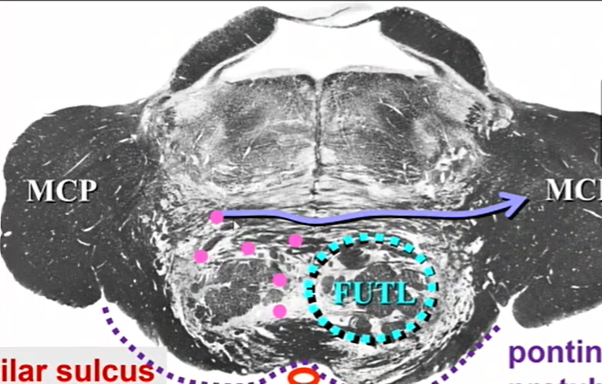
name pink and purple
pontine gray - pink
transverse fibers (pontocerebllars)- purple
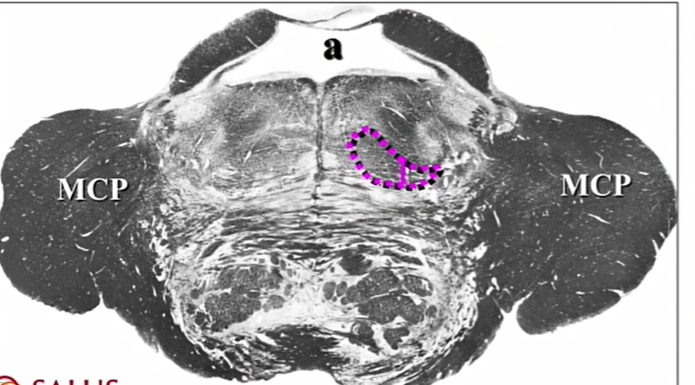
name
medial lemniscus
ventral and lateral spinothalamics, spinotectal
still kinda a whale w a tale
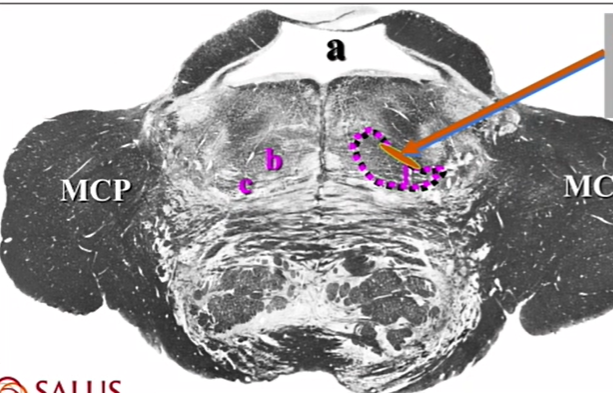
orange
ventral trigeminothalamic tract
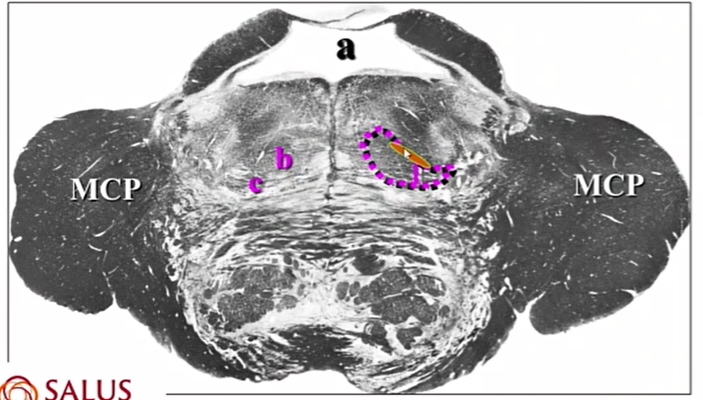
b and c
b - medial lemniscus
c - ventral and lateral spinothalamics, spinotectal
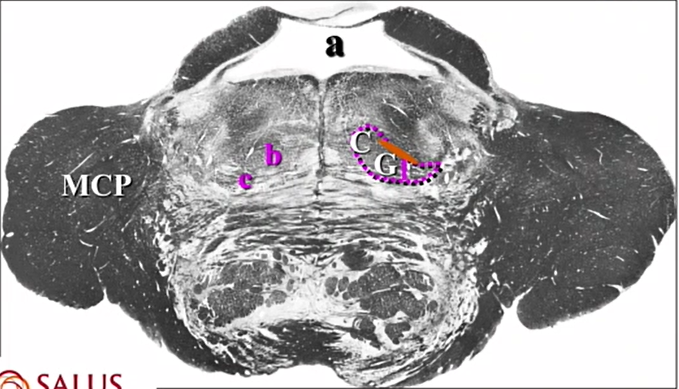
what does the C and G mean
cuneatus adn gracilis - its all medial lemnsicus here but those fibers are more in that area
rostral more medial and caudal more lateral
mid pons
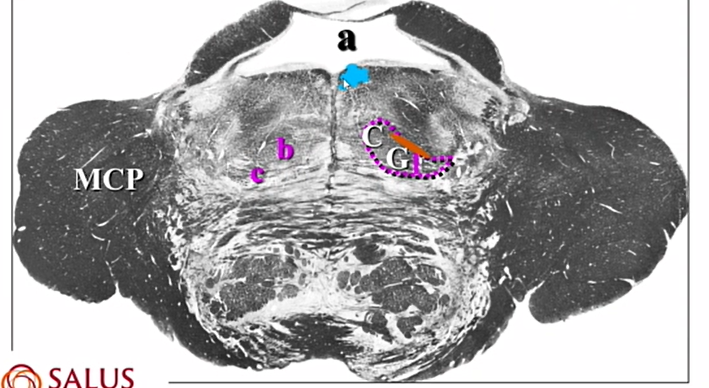
blue
MLF
where do we see CN 5 in mid pons
Middle cerebellar peduncle
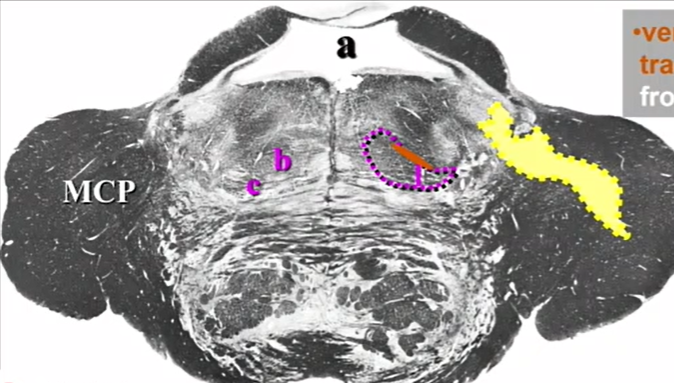
yellow
trigeminal nerve in MCP
pink circle
motor nucleus of 5
lateral pink circle
chief sensory nuc of 5
medial is more motor
green arrow
superior cerebellar peduncle
black arrow
mesencephalic root of 5
do we see nuc of CN 4 in isthmus pons
NO, just nerve itself
what cut of pons cuts thru superior cerebellar peduncle
isthmus pons
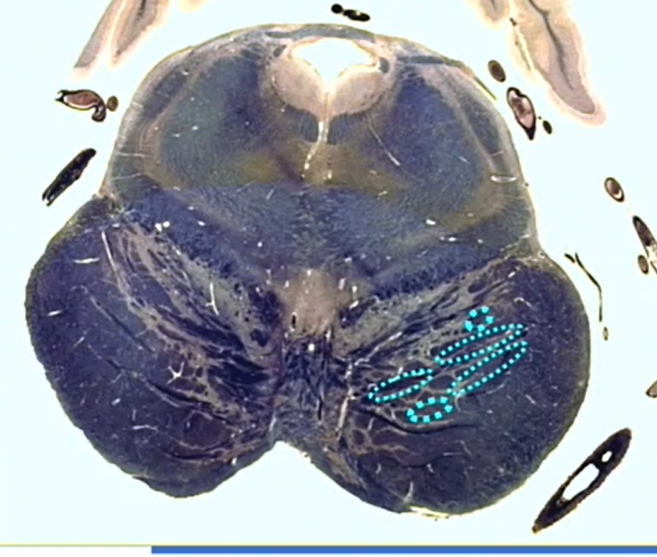
whats this a cross section of
isthmus pons
name
longitudinal bundles
corticospinals and bulbars
isthmus pons
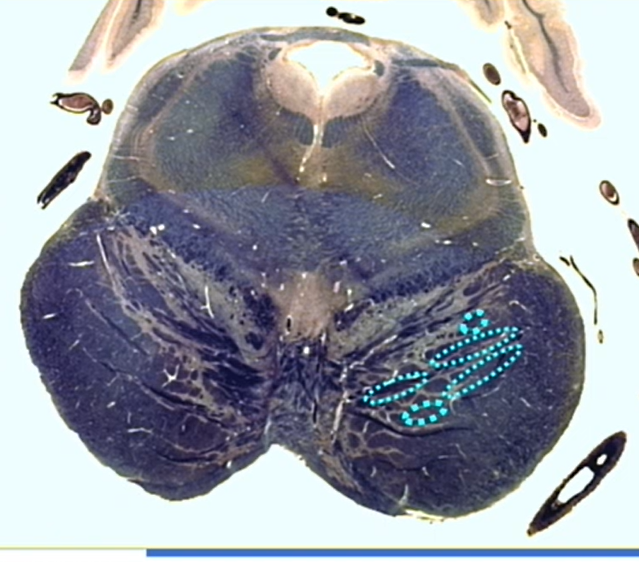
pink
pontile gray
transverse fibers not obvious
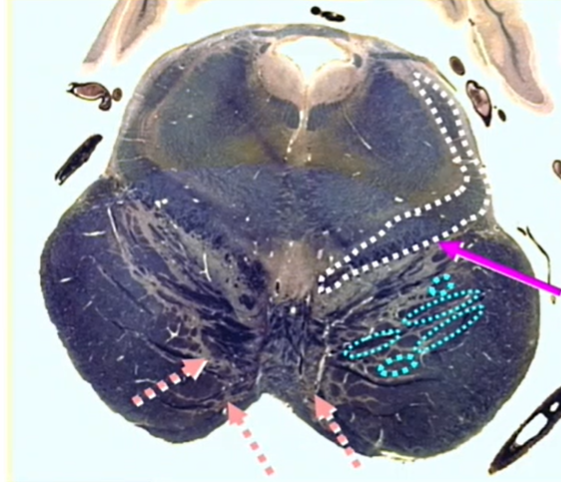
hot pink
medial lemniscus
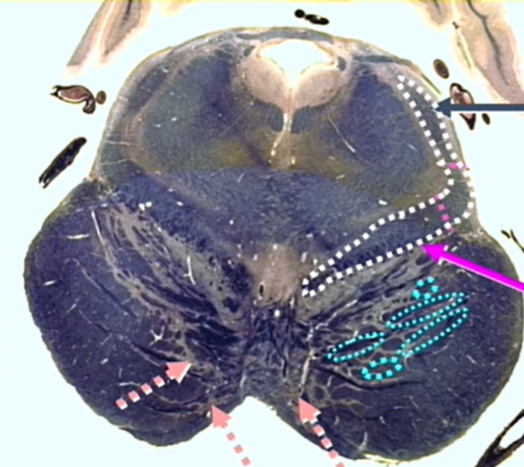
gray arrow
lateral lemniscus
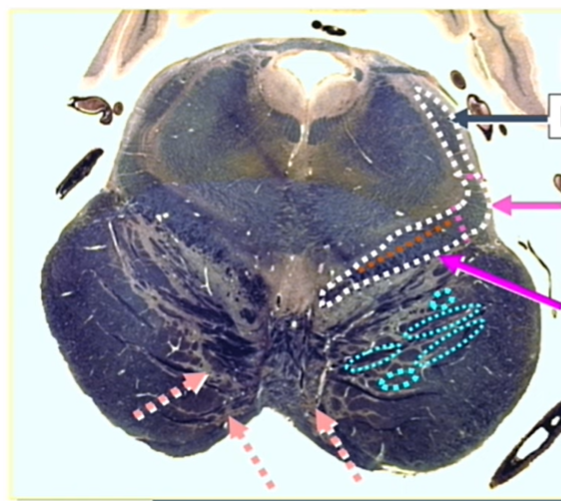
light pink
central and lateral spinothalamics and spinotectals
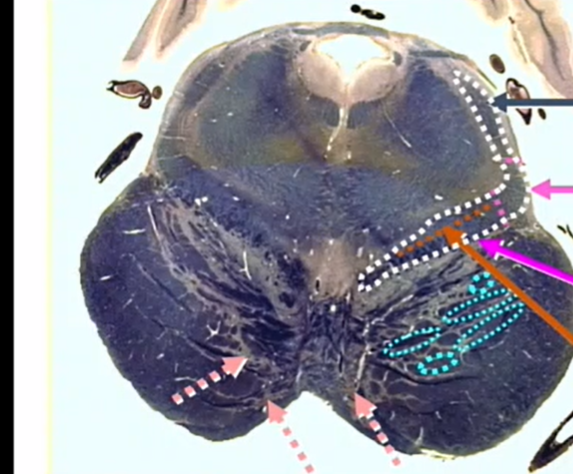
orange
ventral trigeminothalamic tract
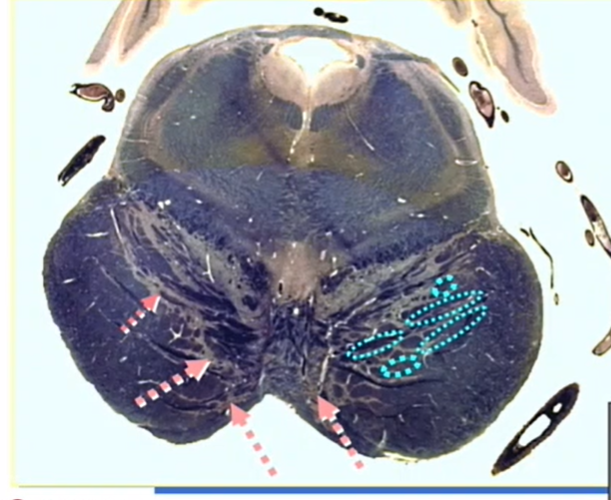
red area
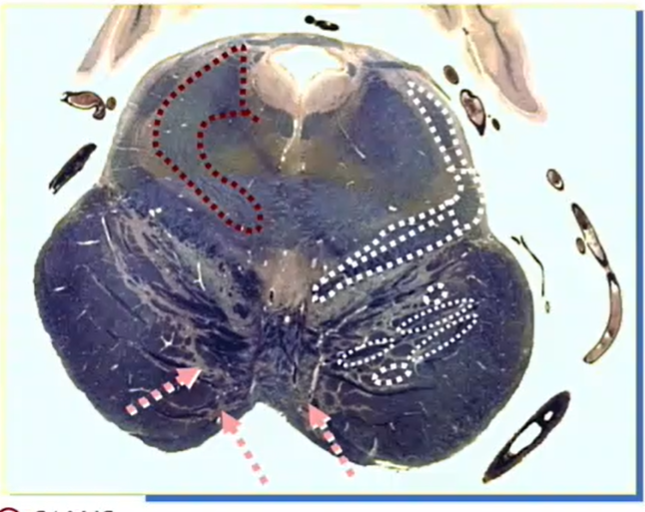
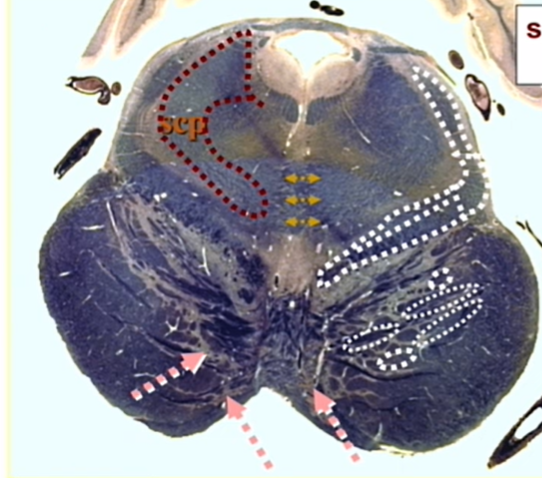
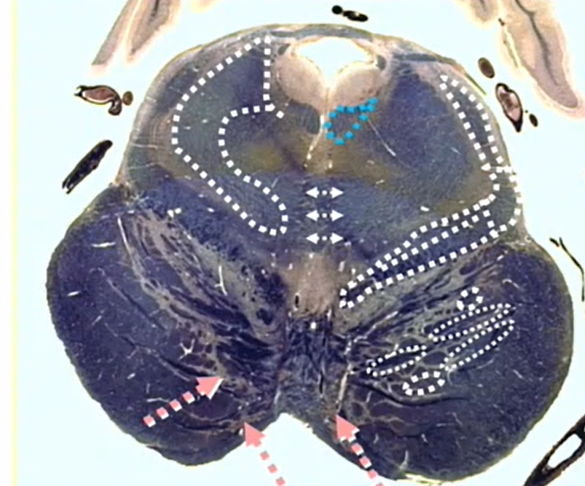
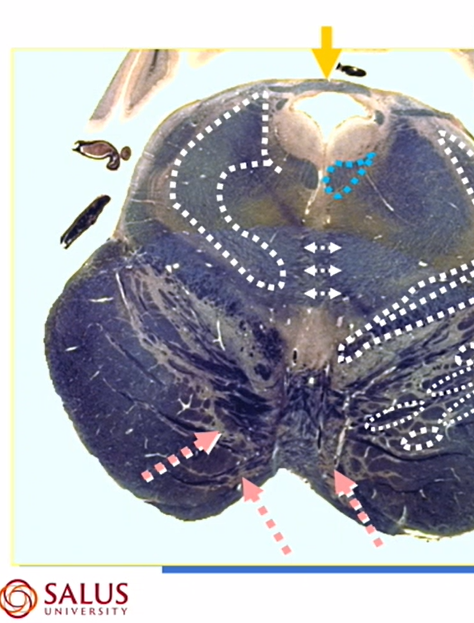
superior cerevellar peduncle
yellow
decussation of superior cerebellar peduncle
blue
MLF
orange arrow
decussation of CN 4
how does CN 4 exit the brainstem
dorsally
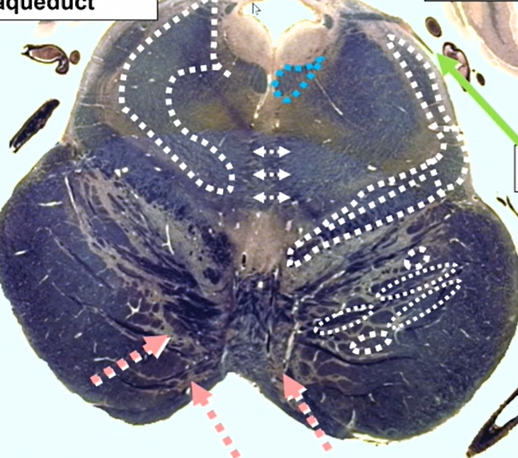
green arrow
CN 4
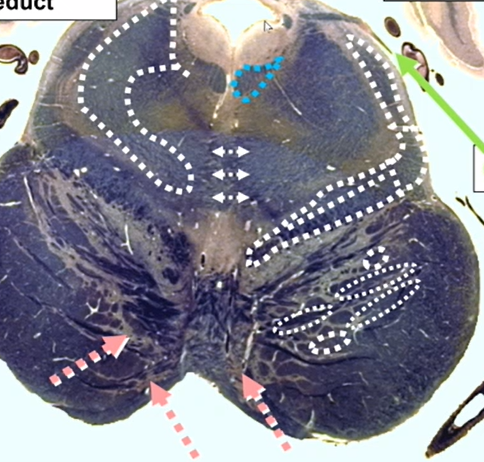
whats this openingn
4th ventricle
working up to cerebral aqueduct which is circular
which is more fragile 6 or 4
4 bc it takes the long way around
comes out the back way and goes around
where does CN 4 cross
anterior/ superior medullary velum
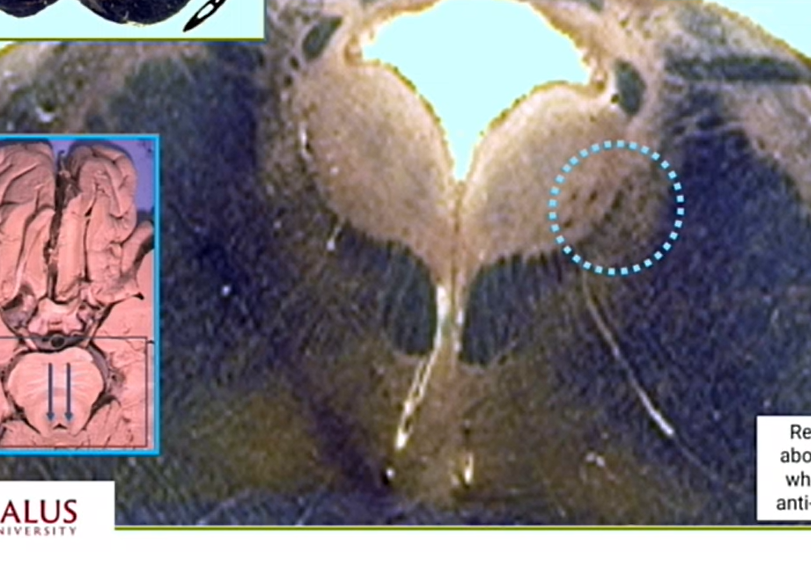
name
locus ceruleus
catecholamines - esp norepinephrine
what makes CN 4 unique
only CN to exit dorsally
only CN to totally cross
only CN to innervate EOM on dorsal aspect
small and delicate and prone to trauma
whats the patterns for a right CN 4 palsy
R hyper deviation
worse in left gaze
worse on R head tilt