Week 1 - Development BV + Paediatric
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What are the 3 stages of embryology?
> Germinal period
> Embryonic period
> Foetal period
when does conception begin?
> when a sperm fertilises an egg to create a zygote
what is the name of the ball of cells when a zygote starts to divide?
- morula
> (the zygote divides into morula as it travels down the fallopian tube )
What does the morula separate into
- two distinct groups of cells
- outer cell mass + inner cell mass --> embryoblast which goes on to become a baby
How many cells does the embryo consist of around day 5 or 6 after fertilisation?
> ~100 cells and is known as a 'blastocyst'
> this goes on to implant into uterine wall around day 6-10
what period are the first 2 weeks referred to as ?
The Germinal period
What is the period from 2-8 weeks after fertilisation referred to as?
> embryonic period
> at this point foetus highly vulnerable to developmental errors
From what day of gestation is the first evidence of the eye being formed?
> 22 days of gestation in human embryo
What can happen at this early stage of development (22 days)?
> Abnormalities can lead to anopthalmos (no eye)
> & micropthalmos (an underdeveloped eye)
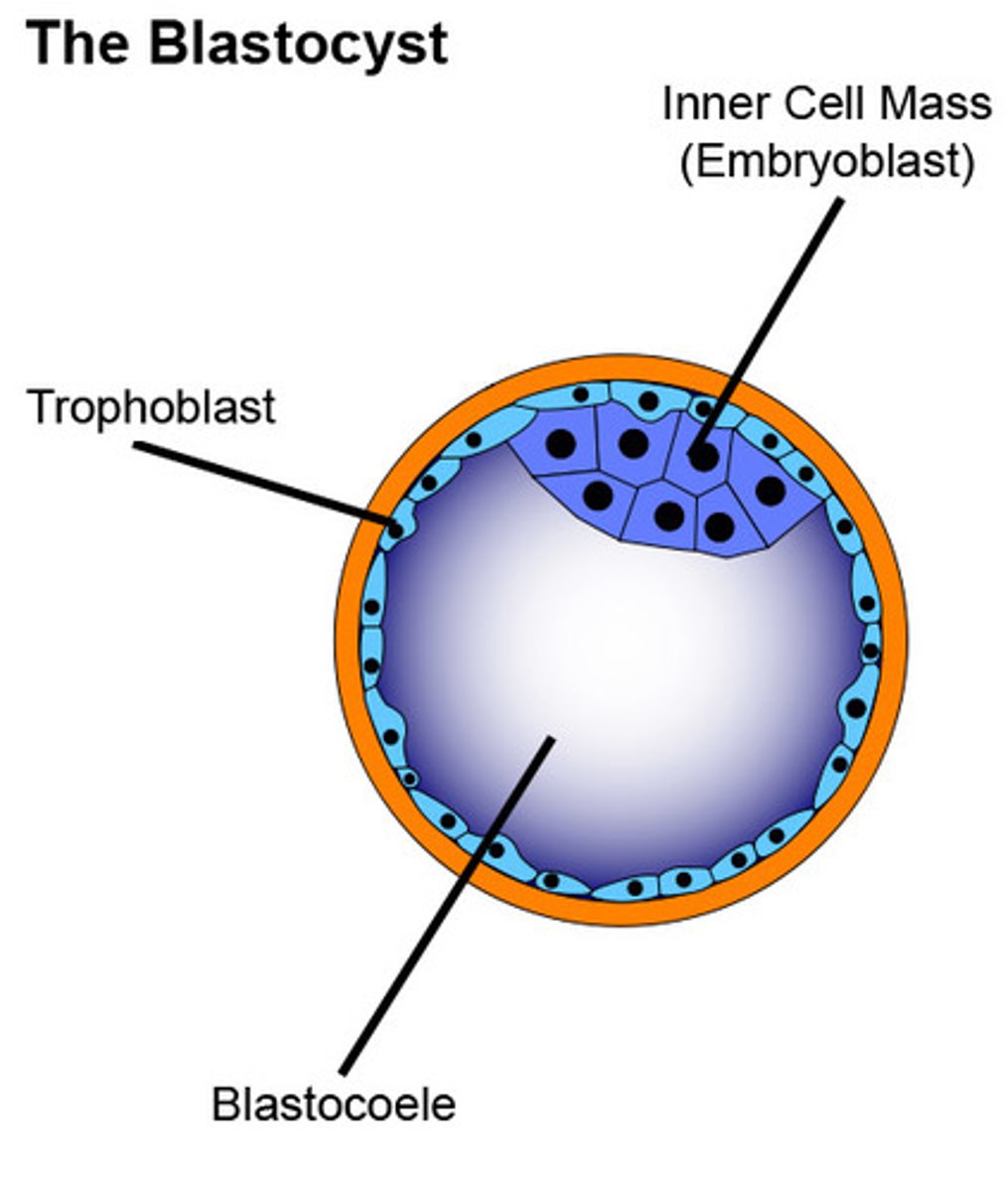
what is the structure of a blastocyst?
> outer cell mass (trophoblast) on the outside
> inner cell mass --> embryoblast (part that becomes baby)
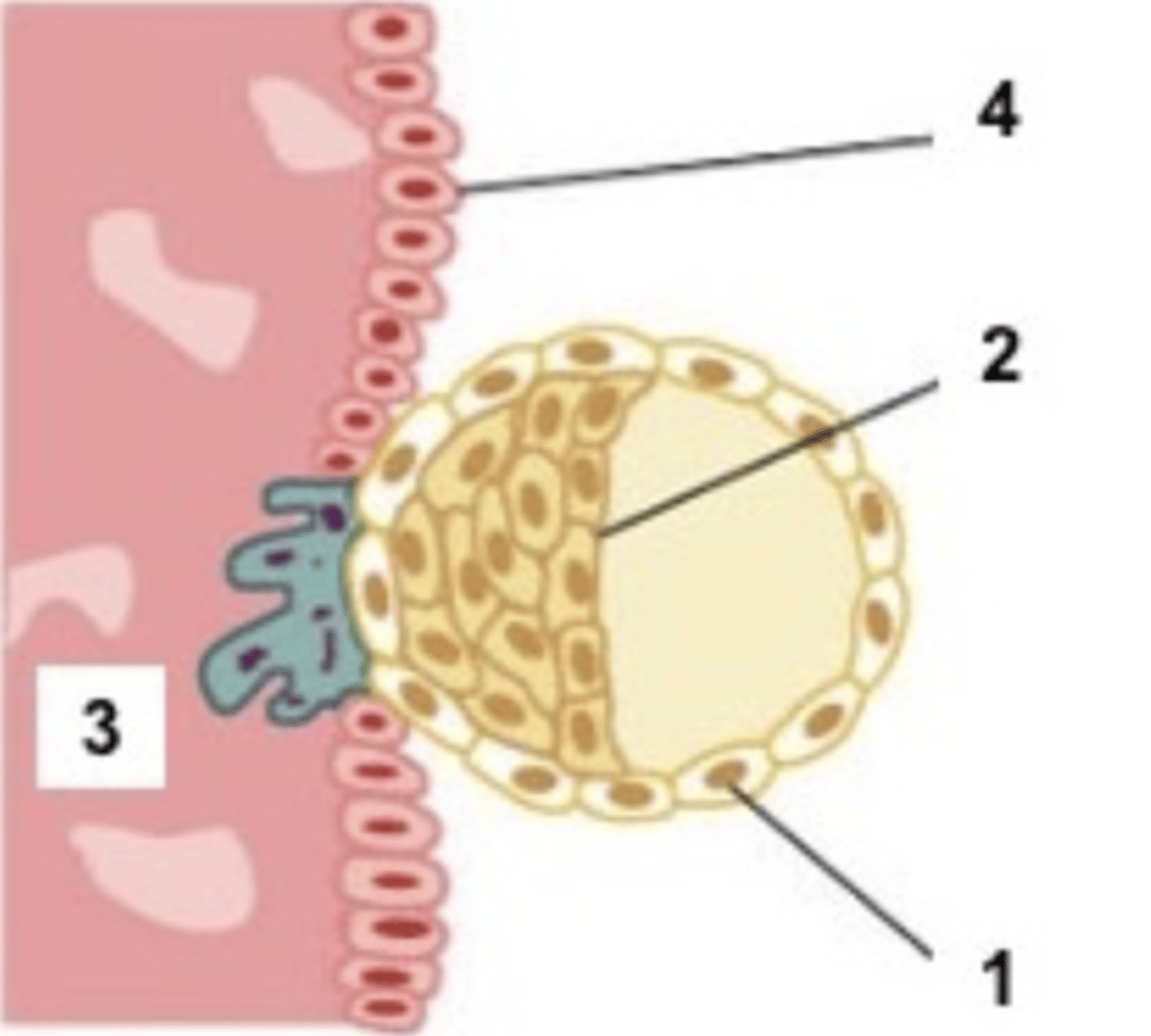
What happens at around day 14 to the embryoblast?
> embryoblast starts to differentiate into 2 distinct structures :
> epiblast + hypoblast
> 2 layered disc
Describe the gastrulation process
> cells from epiblast migrate downwards through opening/ridge known as primitive streak
> process of 'gastrulation' dislodges the hypoblast downwards + ends up with creation of 3 distinct layers
2 layers---> 3 layers
what is the structure of the primitive streak?
> Ridge at top
> cells from top layer go through ridge and fold in on themselves to create 3rd layer
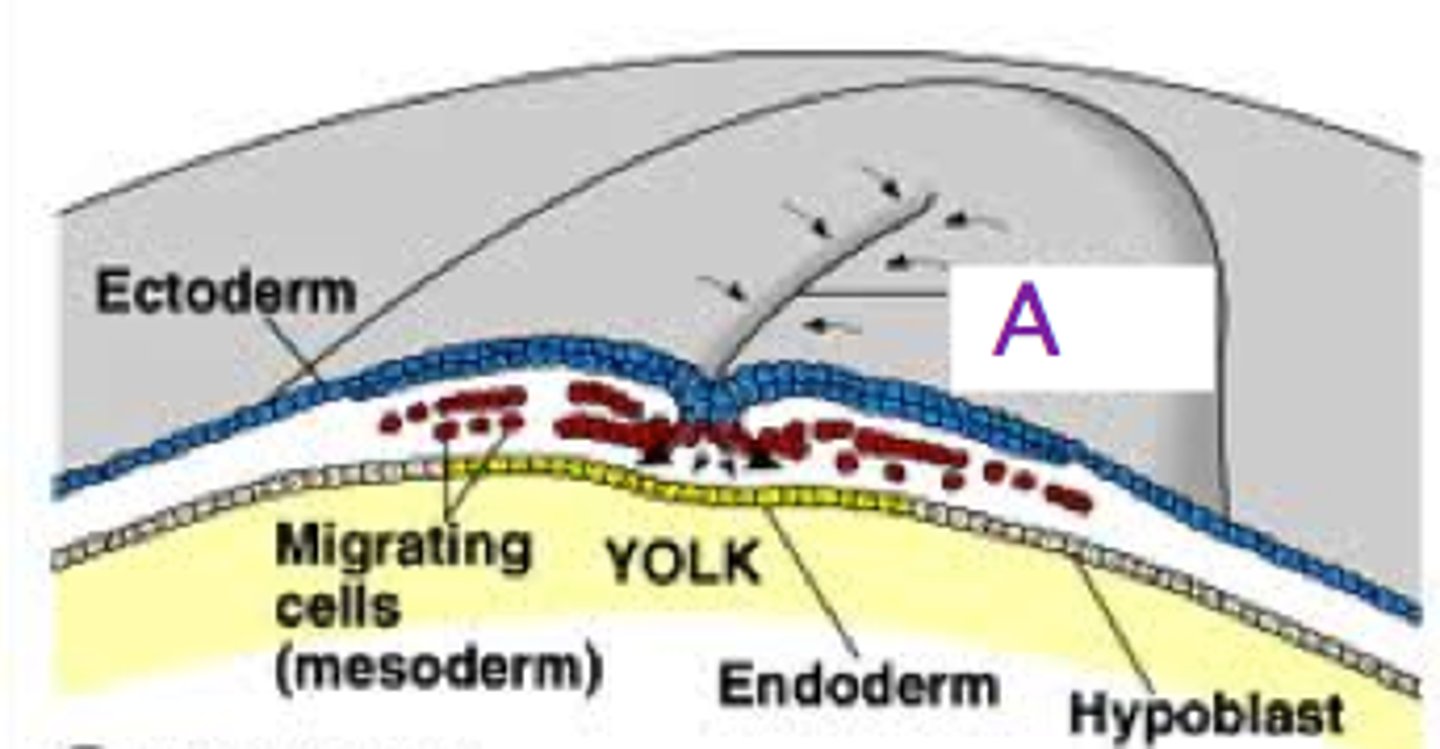
describe the 4 steps of gastrulation
> cells of inner cell mass begin to differentiate as amnion forms
> gastrula develops when cells begin to migrate inward, forming an indentation
> cells continue to push inward, forming ends-derm
> cells remaining on outer surface of gastrula are ectoderm
> mesoderm formed, as additional cells migrate inward between endoderm and ectoderm
what does the ectoderm become ?
> outer layer of skin
> hair
> lining of nose + mouth
> nervous system
> brain
> eyes
what does the endoderm become?
> digestive tract
> respiratory tract
> liver
> pancreas
What does the mesoderm become?
> Muscles + skeleton
> gonads
>kidneys
> heart
> blood vessels
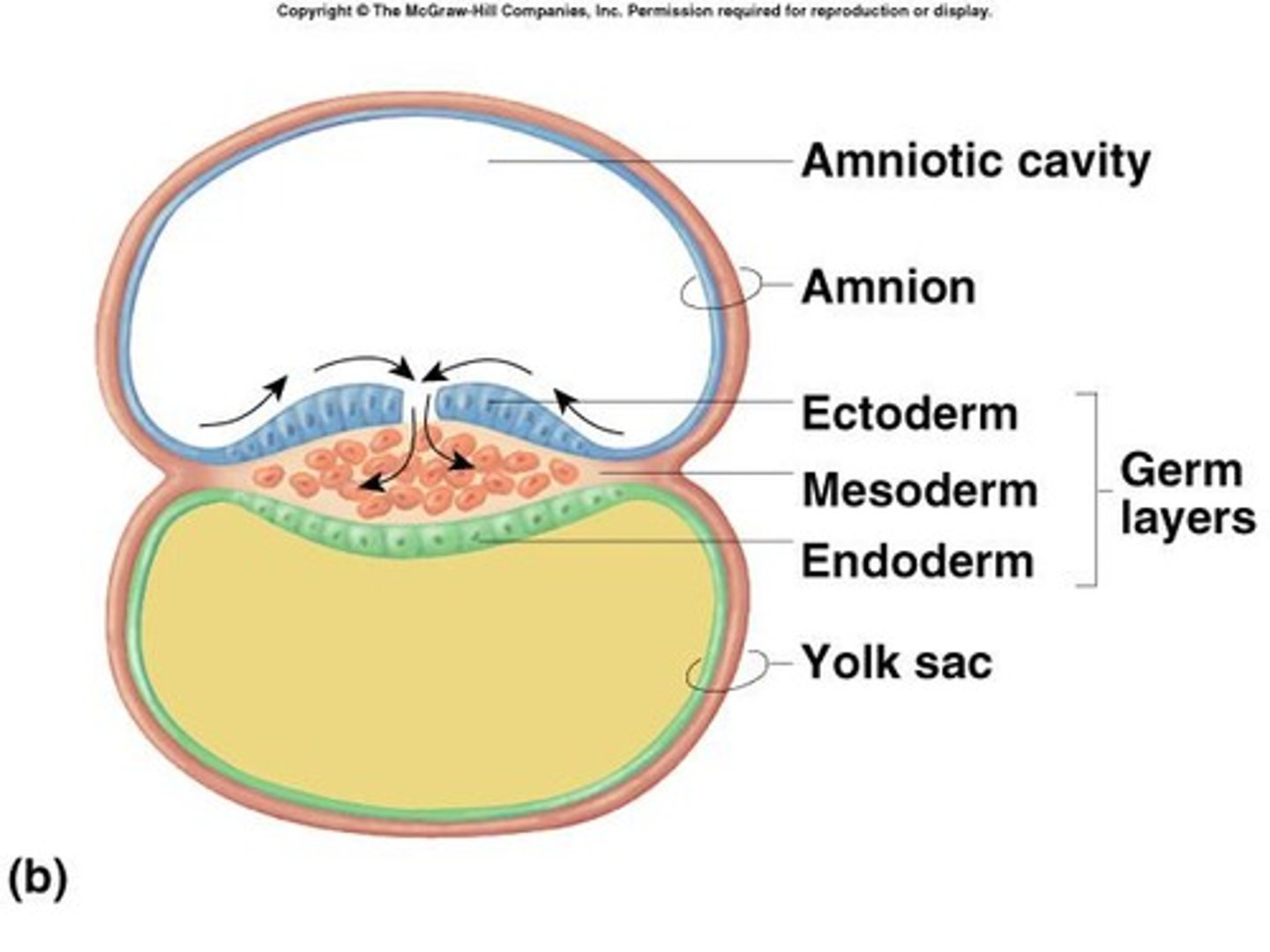
what happens at day 16
> Trilaminar germ disc with ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm forms
- entirety of baby formed from these 3 layers
Describe neural tube formation
> ectoderm begins to fold in on itself + when two edges meet they pinch off to form a tube with a separate layer above it
> neural tube destined to become brain + spinal cord
> initially tube has an opening at each end
what is the role of the notochord in neural tube formation?
> located in mesoderm and sets off process to form neural tube
> cells above notochord form wavy bumpy areas
> flat sheet of cells become m shape , tip of cells join and tube pinches off, cells at top rejoin together
describe the closure of the neural tube
> neural ectoderm rolling up to form a tube (will become brain)
> at anterior end of neural tube 2 small regions called 'eye fields'
> small bulges in eye fields begin to protrude + extend (whilst rest of tube seals)
--> called optic grooves
> rest of tube continues to develop into primitive brain
what can failure of the neural tube to close result in?
> conditions such as spina bifida (gap in spine)
> or anencephaly
what is the neural tube surrounded by?
> a layer of ectoderm, and as neural tube closes its encased by ectoderm
what happens to the optic grooves when they extend?
> they become optic vesicles
(beginning of eye)
- optic vesicles start to extend and grow
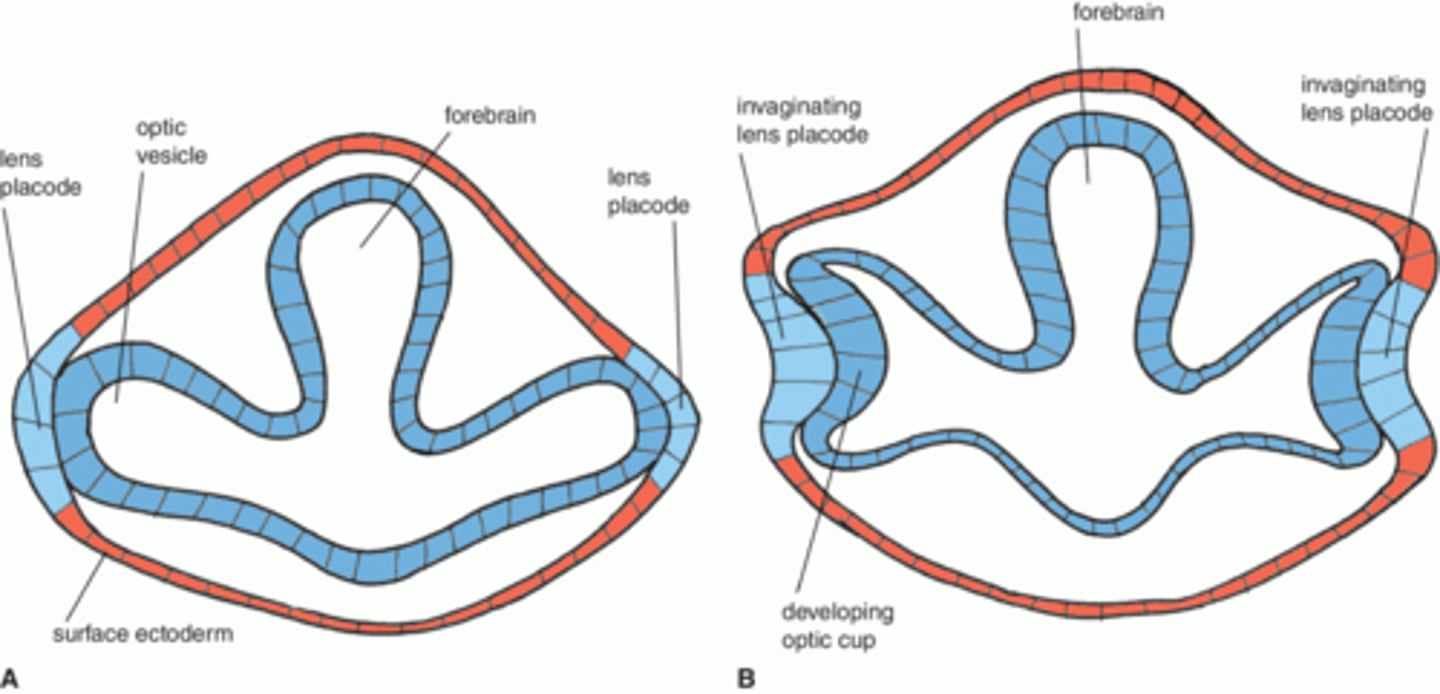
what happens around day 27/28?
- optic vesicles make contact with surface ectoderm surrounding them
- this triggers it to thicken and form lens placode
- this folding inward beigins formation of 2-layered optic cup
region at top --> primitive brain - extensions become our eyes
what happens to the lens placode after?
> starts to migrate inwards, eventually pinching off (creating double layer of cells) + sitting in mouth of optic cup
what does the hyaloid artery do?
> emerges beneath optic vesicle + a fissure (choroidal fissure) opens up to allow it to enter the eye
> this supplies the developing lens with nutrients
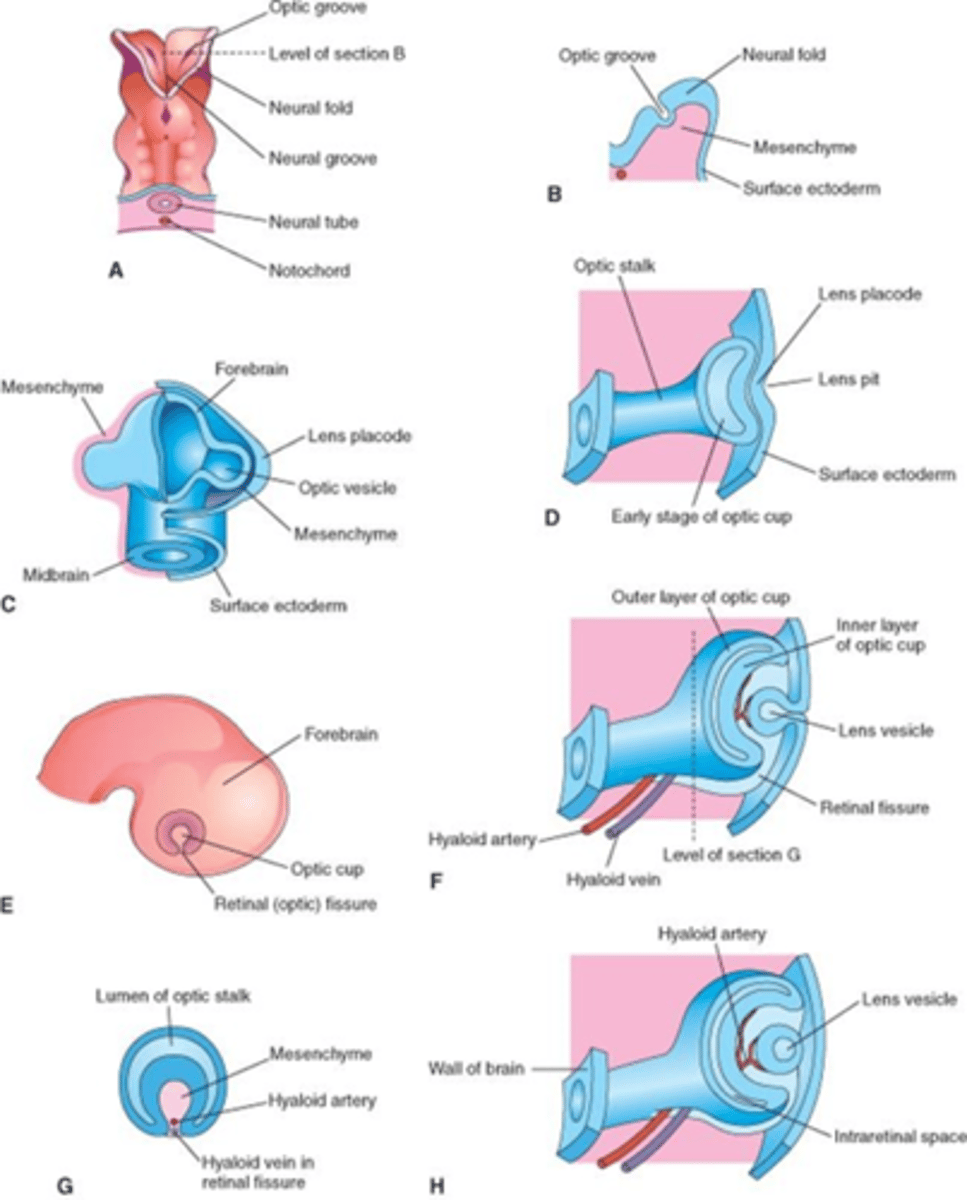
how are the neural retina and RPE formed ?
> from folding - invagination of optic cup
> resulting in 2 layers of tissue which are not physically attached
> this explains how its possible to get retinal detachment in some people
what occurs by week 6 of the eye forming?
- choroidal fissure begins to close, sealing hyaloid vessel + primitive vitreous into eye
- only place fissure doesn't completely close is at anterior end , where hole forms the pupil
What does failure of the choroidal fissure to close result in?
- abnormality called a coloboma
what does surface ectoderm (where lens placed originated) become?
> becomes cornea, conjunctiva and eyelids
> same ivagination process as formation of lens, without pinching off
what happens to retina + hyaloid artery?
> retina (now in several layers) will continue to develop and specialise
> hyaloid artery eventually degenerates and disappears leaving optically clear media
why are mesenchymal cells important?
> able to turn into anything
> help develop iris, sclera + cornea etc
> help develop extra ocular muscles , cranial nerves
how long do eyelids remain fused closed until?
> 28 weeks of pregnancy to protect developing cornea
formation of eye
> in 5th-7th weeks of gestation hollow lens starts to fill with fibres and by day 45 lens is solid
> small dense collections of tissue formed from mesoderm and neural crest cells (mesenchyme) appear between 26-29 days and become extra ocular muscles
> cranial nerves (3,4 and 6) grow from primitive brain into these tissues around days 31-33
> cornea forms from surface ectoderm + neural crest cells,+ 5 distinct layers visible by week 8
> sclera + choroid formed from mesenchyme start to condense into two layers surrounding primitive retina
what is the axial length, diameter of crystalline lens and optical power of cornea in a newborn eye?
> axial length ~16.5mm increasing to ~21mm by 3 years and 24mm in adulthood
> crystalline lens grows from ~6mm in diameter at birth to ~9.3mm by 16 years old
> At birth optical power of cornea 50D, which is greater than that of an adult
what are the stages of childhood?
- Prenatal (conception to birth)
- Neonatal (newborns) --> 0 to 8 weeks
- infancy : 8 weeks to 12 months
- Toddlers : 12 to 36 months
- preschool - 3 years starting to school
- key stage 1 -4/5 years to 7/8 years
- key stage 2 - 7/8 years onward
When is full term pregnancy considered and premature?
> 37-40 weeks, dated from mothers last period
> babies born before 37 weeks considered premature
> babies born very prematurely and/or with extremely low birth weight tend to be disadvantages in terms of IQ, motor performance, visual-motor integration and academic ability
statistics of premature babies
- 1/3 children born before 32 weeks have SEN
> prevalence of cerebral palsy as high as 15% in babies born between 24-27 weeks of pregnancy
> very premature babies at risk of retinopathy of prematurity and higher prevalence of strabismus (~10-30%), reduced VA (~40%) and reduced stereocauity (-36%)
What is the role of a health visitor
> baby assigned health visitor + red book which charts their development + vaccination history
> undergo no of assessments in first few weeks to screen them for developmental or congenital disorders
what is the supervision aimed to do ?
> supervision aimed to monitor growth, assessments in hearing + language, checking dentition, nutrition, offering help to parents
> goal to lower rates of child mortality, disability and morbidity, promote optimum growth + development to help children maximise their potential
what areas can we divide developmental milestones into ?
- physical
- cognitive
- social/emotional
The newborn (0-8 weeks)
> normal birth weight varies from ~2500g TO 4500g
> spend a lot of time sleeping
> start to recognise own parents - mothers voice
> like looking at faces
> responds to sounds
> demonstrate anticipatory behaviours (rooting)
- at this age minimal difference between typically developing baby and a baby with learning disability
what are early reflexes of newborns?
> primitive reflexes provide newborn with actions to aid their survival
- e.g sucking to find food)
> help brain to develop neural pathways for coordinated movement later in development
- eventually replaced with voluntary movement
what are the names of the early reflexes?
> palmar grasp reflex - marked repose from birth to 4 months + then diminishes
- poor/no response indicative of neurological abnormality (including cerebral palsy)
> stepping reflex : present from birth to 2-3 months
- preterm babies can demonstrate a dif pattern of walking
what are the physical milestones of an infant (2-3 months)
> start to support own head, raise head when lying on stomach
> open + close hands, bring hands to mouth
> swipe at dangling objects
what are the social milestones of an infant ,2-3months?
> use facial expressions
> cry when hungry/tired/wanting comfort
if no enjoyable eye contact noted by 8 weeks the baby should be referred for an assessment of vision
what are cognitive milestones for infants: 2-3 months
> focus on moving objects
> follow a person with their eyes
> turn towards a voice/sound
> enjoy looking at faces (25% of their time)
what are the physical milestones of a 3-6 month infant
> learns to roll , can grasp feet with hands
> can support own weight on legs (when held)
> grasp toys, shake toys
> start to sit up with support
cognitive milestones 3-6 months
> repeats sounds back to you and makes sounds like 'da', 'ba' or ga'
> recognise familiar faces
social/emotional milestones infant : 3-6 months
> laughs
> imitate facial expressions
physical milestones infant: 6-12 months
> start to sit unsupported
> get into crawling position - start to crawl/bum shuffle
> pull themselves up to stand , cruise around furniture
> bang two objects together , put objects into a container
cognitive milestones 6-12 months
> understand difference between animate and inanimate objects , enjoys games
> starts to make meaningful sounds like 'mama' or 'dada'
social/emotional 6-12 months
> may display separation anxiety
- avoidance of eye contact been linked to autism
physical milestones toddler: 1-3 years
> begin to walk independently , stand up from seated unaided
> climb stairs , push toys
cognitive milestone toddler : 1-3 years
> says single words (forming simple sentences by ~30 months)
> recognise parts of the body
> enjoy singing nursery rhymes
social/emotional milestones toddler: 1-3 years
> can start to evaluate opinions of others + modify their behaviour accordingly
physical milestones of 3-5 year olds
> often have a lot of energy
> can run, hop, kick and throw a ball
> safely manage stairs
> start to hold a pencil with a pincer grip
> dress themselves - do buttons and zips
> use scissors
cognitive milestones 3-5 years old
> able to follow instructions - asks "who, what, where" questions
> tells long stories, starts to understand o'clock
social/emotional milestones of 3-5 years
> starts to reflect on their own actions
> evaluate performance + react emotionally to success/failure, enjoys jokes
> often protective of younger siblings
> manages frustrations better
physical milestones key stage 1: 4-8 years old
> may develop skills in sports/music etc
> handwriting improving
> still lots of energy
cognitive milestones key stage : 4-8yrs
> sense of competitiveness
> very inquisitive
> fluent speech, reads simple stories
> solve puzzles
social emotional milestones key stage 1 : 4-8 yrs old
> friendships come and go
> may actively dislike opposite sex
> can understand other peoples thoughts + wishes - family important
what is Piagets theory of cognitive development ?
4 stages:
1) sensorimotor stage - 0-2 years
2) pre operational stage - 2 to 7 years
3) concrete operational stage - 7 to 11 years
4) formal operational stage - 12+ yrs
describe the sensorimotor stage
> child experiences world through their basic senses + motor responses
- how objects feel + what they can see/hear around them
> thought primarily based on action (e.g baby might accidentally knock a toy hanging from a mobile, then accidentally do it again, and eventually learns to purposefully make that particular action to make the toy move)
> object permanence develops - objects remain even when you cant see them
what is the pre operational stage ?
- language plays a key role --> child narrate own activities
- symbolic thinking develops - use of self imagery + symbols to represent objects (engage in imaginative)
decentration develops: child starts to consider multiple aspects at the same time , rather than one thing
theory of mind develops
concrete operational
> child can apply conservation - understand objects can change size or appearance but essentially remain the same
> can understand that one person can be a father , grandfather, and brother at the same time
> develop rational thinking
> can group objects
formal operational
> Child can now apply logical thinking and reasoning
> Able to think about hypothetical possibilities (generate hypotheses)
>Can understand ethics and moral reasoning
>Sophisticated thought processes
> can consider multiple perspectives
e.g can now devise long-term strategies to win at a board game by making predictions about possible future events