L2_DEVELOPMENT OF MAINTENANCE PROGRAM
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Process Oriented Approach
Task Oriented Approach
Maintenance Programs currently use in commercial aviation were developed by the industry using 2 basic approaches:
Hard Time
On Condition
Condition Monitoring
Process Oriented Approach to maintenance uses 3 primary maintenance processes to accomplish the scheduled maintenance actions.
Hard Time and On-Condition Processes
are used for components or systems that, respectively, have definite limits or detectable wear out periods.
Condition Monitoring Process
is used to monitor systems and components that cannot utilize either the HT or OC processes.
CM items
are operated failure, and failure rates are tracked to aid in failure prediction or failure prevention failures.
These are the “operate to failure” items.
task oriented approach to maintenance
uses predetermined maintenance task to avoid in-service failures.
Equipment redundancies
are sometimes used to allow in service failures to occur without adversely affecting safety and operations.
reliability program
is usually employed (similar to, but more elaborate than, the CM process) from those components or systems whose failure rates are not predictable and for those that have no scheduled maintenance task.
logical
Airlines and manufacturers experience in developing scheduled maintenance programs for new aircraft has shown that more efficient programs can be developed through the use of _____ decision processes.
B747
With the development of the ____ airplane in 1968, the Boeing Company initiated the more sophisticated, modern method of generating maintenance program development.
Maintenance Steering Group Approach
MSG Approach
maintenance program development
The Boeing Company started the modern approach to _____ in 1968 with the Boeing 747 airplane, then the largest commercial airplane.
jumbo jets
It was the start of a new era in aviation, the era of the _____, and the company felt that this new era should begin with a more sophisticated approach to maintenance program development.
They organized teams of representatives from the Boeing Company's design and maintenance program groups along with representatives from the suppliers and the airlines who were interested in buying the airplane.
industry working groups
IWG
structures
mechanical systems
engine and auxiliary power plant (APU)
electrical and avionics systems
flight controls and hydraulics
Zonal
MSG I
Representatives from the Boeing Company's design and maintenance program groups, FAA, suppliers and airlines who were interested in buying the airplane formed 6 IWGs:
Each group addressed their specific systems in the same manner to develop an adequate initial maintenance program.
functions, failure modes, failure effects, and failure causes
MSG I
Equipped with information on system operation, maintenance significant items (MSIs) and their related _____, _____, _____, and _____, the group analyzed each item using a logical decision process to determine the appropriate maintenance requirements.
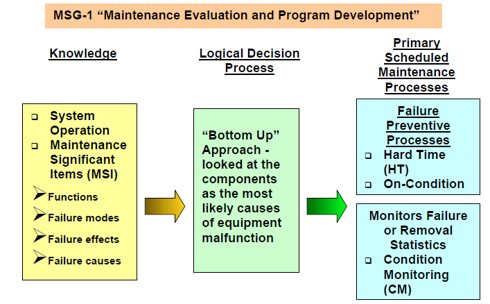
Maintenance Evaluation and Program Development
This results the Handbook MSG-1 “_____”.
"bottom up" approach
looked at the components as the most likely causes of equipment malfunction.
MSG I
The purpose of the analysis was to determine which of three primary scheduled maintenance processes – hard time (HT), on-condition (OC), and condition monitoring (CM) – would be required to repair the item and return it to service.
MSG 2
this MSG approach to maintenance program development was triumphant on the B747.
1970
In _____, ATA (Air Transport Association of America) Committee revised MSG-1’s philosophy slightly with new generalized process so as to apply universally to other aircraft types and variants.
Logic diagram
was refined to assure maximum safety and reliability at lowest possible cost using process-oriented approach to maintenance.
Airline/Manufacturer Maintenance Program Planning Document
It was renamed MSG-2 “_____” and applied to the development of maintenance programs for the Lockheed L-1011 and McDonnell-Douglas DC-10 airplanes.
systems and components
structures
engines
MSG-2 process was slightly different for the 3 maintenance areas studied:
maintenance
functions and failure
tasks
applicability
Here are the MSG-2 process steps:
Identify the _____ or structure items requiring analysis.
Identify the _____ and _____ modes associated with the item and the effect of a failure.
Identify those _____ which may have potential effectiveness.
Assess the _____ of those tasks and select those deemed necessary.
For structures only, evaluate initial sampling thresholds.
Decision diagrams
are the basis of an evaluation process applied to each system and its significant items using technical data provided by the manufacturer for determining the content of the scheduled maintenance programs for systems.
Process-oriented maintenance programs
are developed for aviation using decision logic procedures developed by the Air transport Association of America (ATA).
MSG-2 process
is a bottom-up approach whereby each unit (system, component, or appliance) on the aircraft is analyzed and assigned to one of the primary maintenance processes, HT, OC, or CM.
hard time
means the removal of an item at a predetermined interval, usually specified in either so many flight hours or so many flight cycles.
calendar time
In some cases the hard time interval may be in _____.
On-condition
means that the item will be checked at specified intervals (in hours, cycles, or calendar time) to determine its remaining serviceability.
Condition monitoring
involves the monitoring of failure rates, removal rates, etc. to facilitate maintenance planning. Let us look at each process in more detail.
hard time (HT) process
is used for components or systems that have definite life limits.
hard time
means the removal of an item at a predetermined interval (usage), usually specified in either certain number of flight hours or certain number of flight cycles.
hard time interval
In some cases the ____ may be in calendar time (age).
scheduled maintenance
To get maximum time out of the component and the component would never fail in service ideally, the components would be replaced at the last _____ period prior to the accumulation of time to failure.
hard time
Structural inspection, landing gear overhaul, and replacement of life limited engine parts are all controlled by _____.
hard time
Very often, mechanical linkages and actuators, hydraulic pumps and motors, electric motors and generators that are safety-related will also be identified as _____.
on-condition (OC) process
is used for components or systems that have detectable wear out periods.
On-condition
means that the item will be inspected and tested at specified intervals (in hours, cycles, or calendar time) to determine its remaining serviceability to the next OC check period.
On-condition
must be restricted to components, equipment, or systems on which a determination of continued airworthiness may be made by measurements, tests that exclude simple operational checks, or other means without doing a tear-down inspection.
OC
For ____ checks such as tyre tread and brake linings; measurement of wear, end or side play, backlash of linkages, control rods and pulleys; scheduled borescope inspections of engines, engine oil analysis, and in-flight engine performance analysis (ECM – engine condition monitoring), measure degradation and determine, from established norms, how much life or serviceability remains.
condition monitoring (CM) process
is applied to monitor systems and components that cannot employ failure preventive processes, i.e. either the HT or OC processes.
CM items
do not have definite lifetime or noticeable wear-out periods that make failures unpredictable.
failure rates
Since CM items must have no direct, adverse effect on safety when fail, they are operated to failure and _____ are tracked to aid in failure prediction or failure prevention efforts.
CM
In aviation, _____ is frequently applied to components where failure has no serious effect on safety or airworthiness, due to redundancy for examples the navigation and communication electronic components, and to items not affecting airworthiness at all, such as coffee makers, lavatories passenger entertainment systems,etc.
hard time (HT) process
is used for components or systems that have definite life limits where removals are planned at predetermined intervals before failures.
on-condition (OC)
If the check performed provides enough information regarding the condition and failure resistance of the item to give reasonable assurance of its continued airworthiness during the next check period, the item is categorized as _____.
condition monitored (CM) item
If the check constitutes merely a maintenance task servicing, adjustment, or a go/no-go determination and is not making a meaningful disclosure of actual condition, the item is, in fact, operating as a _____.
Condition monitoring
does not really monitor the "physical condition" of a component.
Condition monitoring
It essentially monitors the failure or removal statistics of the unit.
on condition process
Component's actual condition is monitored with the _____ process.
condition monitoring
involves the monitoring of failure rates, removal rates, etc. to facilitate maintenance planning.
Hard Time
controlled by the definite lifetime.
On-Condition
monitor condition and measure to determine serviceability remaining.
USA Navy
In 1978, United Airlines, commissioned by the _____, developed a methodology for designing maintenance programs based on tested and proven airline practices.
Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)
addressed the shortcomings of MSG-2 and revolutionizes the logic structure for selecting scheduled maintenance tasks.
RCM
is called a "Task Oriented Approach".
Maintenance Review Board (MRB)
New design rules for use of damage tolerance enhancement of manufacturer/operator partnership through _____ process, and in considering the increasing complexity of aircraft equipment,
fuel
ATA took lead to integrate MSG-2 and RCM into the new MSG-3 to further reduce maintenance cost to offset rising _____ prices.
MSG 3
is also a task-oriented approach to maintenance that was developed by ATA that uses predetermined maintenance tasks to avoid in-service failures.
Equipment redundancies
are sometimes used to allow in-service failures to occur without adversely affecting safety and operation.
MSG 3
In such cases, it may be determined that no scheduled maintenance action for certain systems or components unless aircrew reports malfunction in primary unit and that backup unit has taken over the function to support the flight mission.
reliability program
is usually employed (similar to, but more elaborate than, the CM process of MSG-2) for those components or systems whose failure rates are not predictable and for those that have no scheduled maintenance tasks.
MSG-3 process
is a “top down” approach or “consequence of failure” approach whereby failure analysis is conducted at the highest manageable level of aircraft systems instead of at the component level as in MSG-2.
MSG 3
it looks at how does the failure of items affect the operation and it does not matter whether a system, subsystem, or component fails or deteriorates.
airframe systems task
Structural item tasks
Zonal task
3 categories of scheduled maintenance tasks developed to prevent failures and to maintain the inherent level of reliability of the system are:
Task-oriented maintenance programs
are created for aviation using decision logic procedures developed by the Air "transport Association of America.
MSG 3
is a modification of and an improvement on the MSG-2 approach.
Lubrication
an act of replenishing oil, grease, or other substances that maintains the inherent design capabilities by reducing friction and/or conducting away heat.
Servicing
an act of attending to basic needs of components and/or systems for the purpose of maintaining the inherent design capabilities.
Inspection
an examination of an item and comparison against a specific standard.
Functional check
a quantitative check to determine if each function of an item performs within specified limits.
Functional check
this check may require use of additional equipment.
Operational check
a task to determine if an item is fulfilling its intended purpose.
Operational check
is a failure-finding task and does not require quantitative tolerances or any equipment other than the item itself.
Visual check
an observation to determine if an item is fulfilling its intended purpose.
Visual check
is a failure-finding task and does not require quantitative tolerances.
Restoration
that work necessary to return the item to a specific standard.
Restoration
may vary from cleaning the unit or replacing a single part up to and including a complete overhaul.
Discard
the removal from service of any item at a specified life limit.
Environmental Deterioration
Accidental damage
Fatigue damage
Airplanes are subjected to 3 sources of structural deterioration
Environmental Deterioration
the physical deterioration of an item's strength or resistance to failure as a result of chemical interaction with its climate or environment.
Accidental damage
the physical deterioration of an item caused by contact or impact with an object or influence that is not a part of the airplane, or damage as a result of human error that occurred during manufacture, operation of the vehicle, or performance of maintenance.
Fatigue damage
the initiation of a crack or cracks due to cyclic loading and subsequent propagation of such cracks.
General visual inspection
Detailed inspection
Special detailed inspection
The MSG-3 process defines 3 types of structural inspection techniques:
General visual inspection
a visual examination that will detect obvious, unsatisfactory conditions or discrepancies.
General visual inspection
this type of inspection may require removal of fillets or opening or removal of access doors or panels.
Work stands and ladders may be required to facilitate access to some components.
Detailed inspection
an intensive visual inspection of a specified detail, assembly, or installation.
Detailed inspection
is a search for evidence of irregularity using adequate lighting and, where necessary, inspection aids, such as mirrors, hand lenses, etc.
Surface cleaning and detailed access procedures may also be required.
Special detailed inspection
an intensive examination of a specific location. It is similar to the detailed inspection but with the addition of special techniques.
Special detailed inspection
this examination may require such techniques as nondestructive inspections (NDIs): dye penetrant, high-powered magnification, magnetic particle, eddy current, etc.
zonal maintenance program
ensures that all systems, wiring, mechanical controls, components, and the installation contained within the specified zone on the aircraft receive adequate surveillance to determine the security of installation and general condition.
General visual inspection
Detailed visual inspection