6.2 Stars and the Universe
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Explain the lifecycle of a star
A star begins its life in a nebula, a vast cloud of gas and dust, where gravity pulls particles together to form a protostar, which heats up as it becomes denser.
Once the temperature and pressure are high enough, nuclear fusion starts, converting hydrogen into helium, and the star enters the main sequence stage, where it remains stable for millions to billions of years.
As the hydrogen supply depletes, the core contracts while the outer layers expand and cool, turning the star into a red giant if it is of low to medium mass, or a red supergiant if it is massive.
Eventually, a low-mass star sheds its outer layers, leaving behind a white dwarf, whereas a massive star undergoes a supernova, an enormous explosion that can either form a neutron star or, if the core is extremely dense, collapse into a black hole.
Explain how redshift supports big bang
Redshift refers to the observed increase in wavelength of light from distant galaxies, indicating they are moving away from us. This phenomenon supports the Big Bang theory by demonstrating that the universe is expanding, as initially proposed by Edwin Hubble, suggesting that all matter was once concentrated in a singular point.
Which type of force keeps the planets in orbit around the Sun?
Planets orbit the sun due to strong gravitational attraction
Explain why it is summer in the northern hemisphere when it is winter in the southern hemisphere
Due to the Earth’s 23.5° tilt, when the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, it receives more direct sunlight and experiences warmer temperatures, while the southern hemisphere is tilted away, receiving less sunlight and cooler temperatures.
One light year equals?
9.5 × 10^15 m
How to find the value of one light year?
3×10^8 x (60 sec) x (60min) x (24h) x (365 days) = 9.5 × 10^15m
Where are asteroids found in?
The asteroid belt, located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
What are the 8 planets in the solar system? (My very excellent mother just served us nuggets)
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune.
Which planets are small & rocky?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars.
Which planets are large & gaseous ?
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune.
How does the Earth’s tilt (23.5°) affect the length of day and night?
Due to the earth’s tilt, when one hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, it experiences longer days as it is facing the sun for longer hours whereas the opposite hemisphere experiences shorter days, resulting in a variation in day length throughout the year. Causing seasons to occur.
How long does it take the moon to complete one full orbit around the Earth?
27.3 days
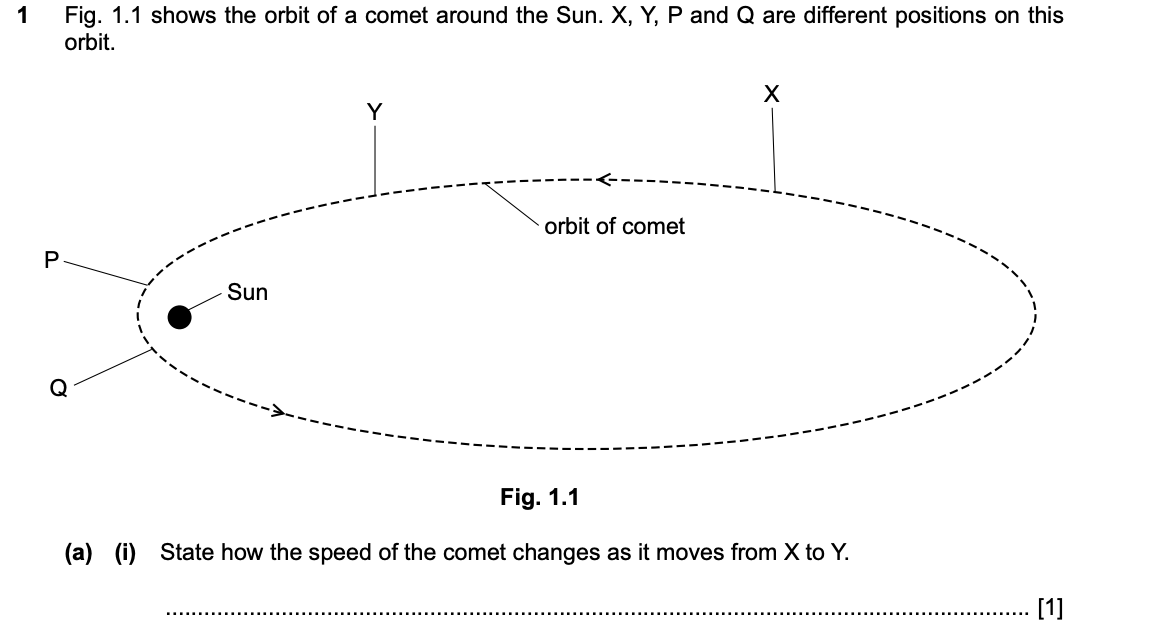
State how the speed of the comet changes as it moves from X to Y.
As the comet moves from X to Y, the speed increases when it moves closer to the sun.
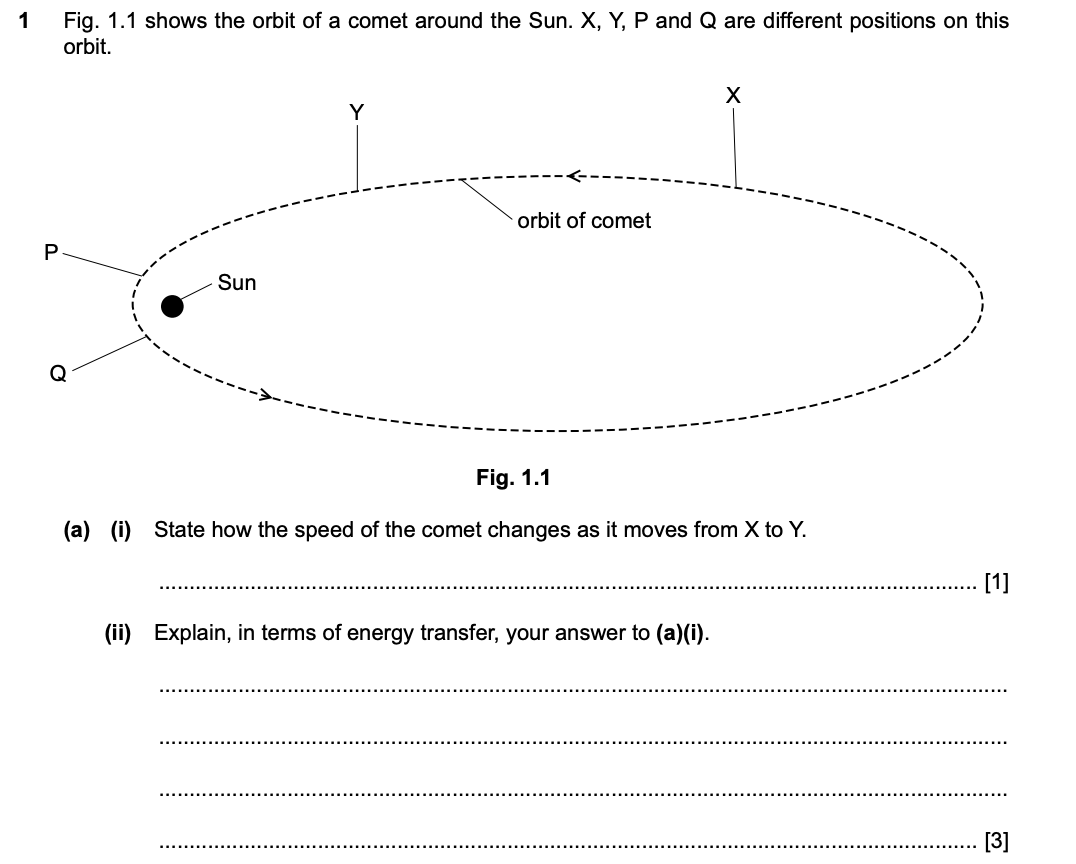
(a)(ii) Explain, in terms of energy transfer, your answer to (a)(i).
As the comet moves closer to the sun, the gravitational potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increases as the distance form the Sun is smaller.
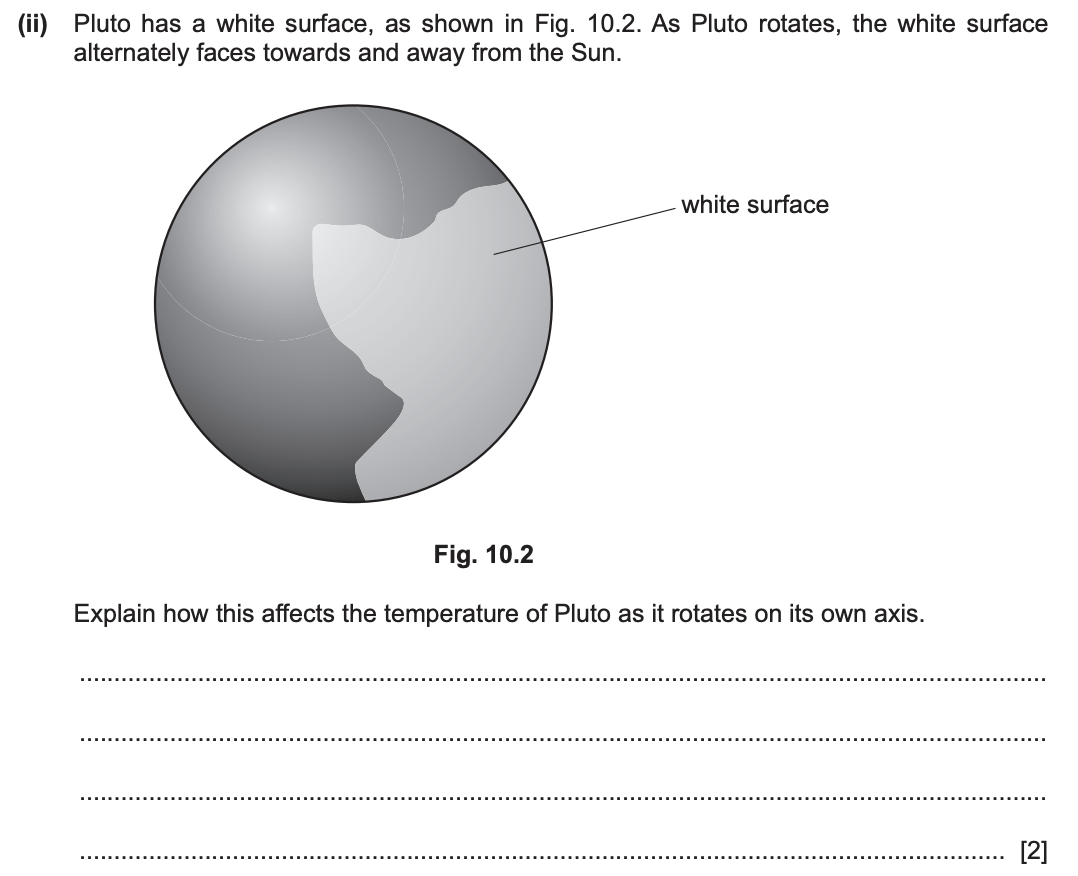
Explain how this affects the temperature of Pluto as it rotates on its own axis.
As Pluto rotates on its own axis, when the white surface is facing the Sun, the temperature of Pluto rises at a slower rate as white colour absorbs and emit heat slower. The black surface increases temperature more as it absorbs and release heat very quickly when facing the sun.
What are objects that orbit the planets called?
moons
Explain why the Moon is visible from the Earth
The light from the Sun is reflected from the Moon’s surface.
Describe what is meant by redshift on light.
The change in wavelength
State what can be deduced from the redshift of light from glowing hydrogen in a distant galaxy
It indicates that the galaxy is moving away from us.
What is the hubble constant?
2.2 × 10^-18 per second
What’s the formula for hubble’s law?
H0 = V /d
How can we find the speed of which galaxy is moving away from Earth?
Can be found in the change in wavelength due to redshift
How can we find distance of a galaxy from Earth?
The brightness of a supernova from the galaxy
Describe how a black hole can be formed from a more massive star.
Hydrogen converts into helium. And forms a red supergiant then explodes into a supernova. The core of the red supergiant will form a blackhole.
What is meant by a light-year?
Distance travelled by light in one year.