1.5 - nucleic acids - garlick
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
codes for the sequence of amino acids in the primary structure of a protein, which in turn determines the final 3D structure and function of a protein.
contains the genetic code and can be passed on to make new cells and passed on to the next generation.
DNA is a polymer - and two polymer chains join together to create a double helix
DNA nucleotide
monomer that makes up DNA is called nucleotide.
made up of deoxyribose (pentose sugar), a nitrogenous base and one phosphate group.
nitrogenous group can either be guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine.
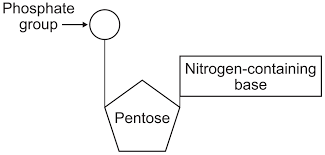
Have to mention the pentose sugar and nitrogenous base that is relevant to DNA
polynucleotides
polymer of nucleotides is called a polynucleotide
created via condensation reactions between the deoxyribose sugar and the phosphate group (of another nucelotide), creating a phosphodiester bond, water is removed - makes sugar phosphate back bone very strong from the phosphodiester bond its a strong covalent bond.
DNA polymer occurs in pairs joined by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs. this creates the double helix.
hydrogen bonds can only from between complementary base pairs
cytosine and guanine (CG)
adenine and thymine (AT)
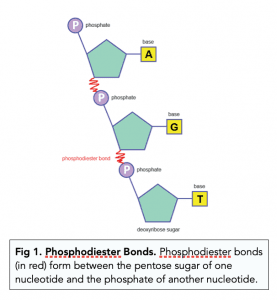
RNA
another nucleic acid that is single stranded
RNA is a polymer of a nucleotide formed of ribose, nitrogenous base and phosphate group
pentose sugar is = RIBOSE, not deoxyribose
nitrogenous bases = adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil
doesn’t have thymine - pairs up like AU CG
RNA is much shorter polynucleotide than DNA polynucleotide - this is because mRNA is only a copy of one gene whereas DNA is all of the genes. tRNA are relatively short also
all of the polymers are single stranded for RNA
rRNA
the function of RNA is to transfer the genetic code from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes. Some RNA (rRNA) is also combined with proteins to make ribosomes
DNA replication
before cells divide (by mitosis or meiosis) all the DNA (genome) must replicate to provide a copy for the new cell
this process of DNA replication is semi conservative replication
(in the daughter DNA one strand is from the paternal DNA and one strand is newly synthesised strand to create new molecule)
semi conservative replication
step 1 - Enzyme DNA helicase breaks hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs between the two strands within a double helix - this causes the DNA double helix to unwind and the strands separate.
step 2 - both of these strands will act as a template
free floating nucleotides within the nucleus will align opposite their complementary base pairs (are attracted to) on the template strands of the parental DNA
step 3 - Enzyme DNA polymerase will join adjacent nucleotides together which then form hydrogen bonds between the bases by a condensation reaction
(DNA polymerase catalyses the joining together of adjacent nucleotides)
step 4 - One strand of rental (original) DNA and one newly syntheisised strand are now two sets of daughter DNA
each new DNA molecule contains one strand from the original DNA molecule nd one new strand
evidence for semi conservative replication
Watson and crick discovered the structure of DNA in 1953 (double helix) helped by Rosalind franklins research on X-ray diffraction
Meselson and Stahl conducted an experiment which proved DNA replication must be semi conservative.
type of bond between complementary base pairs
hydrogen
type of bond between adjacent nucleotides in DNA strand
phosphodiester bonds
describe how a phosphodiester bond is formed between two nucleotides within a DNA molecule
condensation reaction between phosphate and deoxyribose catalysed by DNA polymerase
how does separation of strands occur in semi conservative replication
DNA helicase breaks hydrogen bonds between base pairs (AT/GC) (complementary bases)
describe the role of DNA polymerase in the semi conservative replication of DNA
DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides and catalyses condensation reactions which catalyses the formation of phosphodeister bonds between the adjacent nucleotides
role of single stranded DNA fragments in semi conservative replication
1.) they are the template which determines order of nucleotides/bases
role of DNA nucleotides in semiconservative replication
forms complementary pairs (AT) (CG)/ forms complementary DNA strand
give two features of DNA and explain how each one is important in the semi conservative replication of DNA
DNA is double stranded which gets separated by DNA helicase in replication to both be used as a template
weak hydrogen bonds between bases allow two strands to be separated/ unzip
Describe the role of two names enzymes in the process of semi conservative replication
DNA helicase unwinds the DNA strands to form two strands that can act as a template - causes the breaking of hydrogen bonds
DNA polymerase joins the DNA nucleotides
forming phosphodeister bonds
use figure 1 and figure 2 and ur knowledge of enzyme action to explain why the arrows point in opposite directions
Figure 1 shows = DNA has antiparallel strands/ shape of nucleotides is different/ aligned differently
enzymes have active sites with specific shape
only substrates with complementary shape can bind with active site of enzyme/ active site of DNA polymerase
wot.
DNA structure
double helix structure
strands are polynucleotides
made up of lots of nucleotides joined together in a long chain
DNA molecules are long and coiled up very tightly so that a lot of genetic information can fit into a small space in the cell nucleus.
complementary base pairing
two DNA polynucleotide strands join together by hydrogen bonds between the bases
each base only join with one particular partner
AT CG
two hydrogen bonds form between AT, 3 form between CG
polynucleotide are antiparallel - opposite directions which twits to form a DNA double helix
Action of DNA polymerase
Each end of DNA strand is slightly different in its structure
one end called the 3’ (three prime end) and one end is called the 5’ (five prime) end
During DNA replication, the active sit of the DNA polymerase is only complementary to the 3’ end of the newly forming DNA strand - so the enzyme can only add nucleotides to the new strand at the 3’ end
this means that the new strand is made in a 5’ to 3’ direction and that DNA polymerase moved down the template strand 3’ to 5’ (antiparallel strands)
antiparallel strands means that the DNA polymerase working on one of the template strands moves in the opposite direction to the DNA polymerase working on the other template strand.