2. Organizational Structure
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is Organizational Structure?
(restructuring)
Organizational structure is forward looking. It has to fit the goals and plans. It is firm-specific (there is no “ideal” org. structure).
Organizations can be restructured and they have to be. In order to adapt to environmental changes / company growth etc, at a certain time a different org. structure is needed.
Adaptation is costly and time-consuming; keeps people from doing their day-to-day jobs => eats up resources.
=> Think how to restructure, because you cannot do it frequently
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements (6)
Key elements are related!
Work specialization (division of labor → the bigger the company, the higher the level of specialization)
Departmentalization
Span of control
Chain of command
Centralization and decentralization
Formalization (degree of standartization of tasks and rules → the more people work together, the more structure is required → the bigger the company, the higher the level of formalization → the more formalized, the more bereaucratic.)
=> Toolbox - tools to build the structure that fits the goals, market, technology, products, environment etc.
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
How different units of organization are structured. Grouping jobs into functions and divisions.
Extreme cases:
functional org. structure
divisional org. structure
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
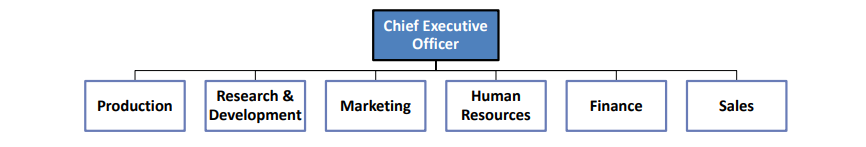
Functional Structure
An organizational structure composed of all the departments that an organization requires to produce its goods or services.
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
Functional Structure: Advantages (2+3)
Advantages:
Encourages learning from others doing similar jobs.
Easy for managers to monitor and evaluate workers
(people do similar work → managers can judge the quality
everything takes place in one unit → easy to keep track of what is going on in particular unit)
Specialization advantages → economies of scale
everything related takes place in one unit; no duplication of work
facilitates coordination and control (at least within the different functions)
centralizes decision-making
every decision with respect e.g. to R&D takes place in R&D department
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
Functional Structure: Disadvantages (2+2)
Disadvantages
Difficult for departments to communicate with others
very easy within the function, but between - difficult → conflicts
Preoccupation with own department and losing sight of organizational goals
Difficult to convince different functions to work together / collaborate.
competition between the functions for scarce resources / management attendance
If functions are quite big (in large companies), it is difficult to respond to changes in the environment
e.g. technology, customer needs → it might take too long to adapt
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
Functional Structure: When does it work best? (4)
in stable, not fast-moving environmets
environments with few competitors, products / services
routine technologies (if company wants to innovate - no go)
SMEs
e.g. Fraport AG
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
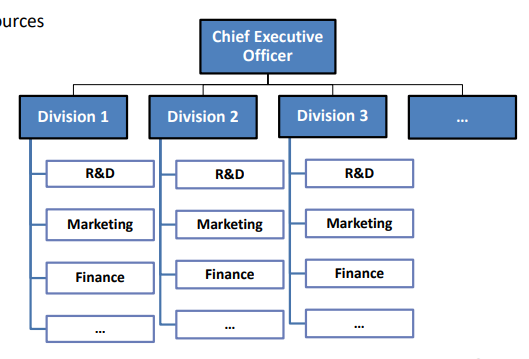
Divisional Structure
An organizational structure composed of separate business units within which are the functions that work together to produce a specific product for a specific customer.
Divisions can be products, technologies, markets, countries, types of customers etc. Each division has its own functions.
Divisional structure often is the result of organizational growth.
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
Divisional Structure: Advantages (2+1)
Advantages:
Quick response to important changes in external environment. (flexible)
Minimal problems of sharing resources across functional departments.
Easy to communicate → will never lose sight of the goals of particular division
Everything works weel as long as you stay within one division.
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
Divisional Structure: Disadvantages (4)
Disadvantages:
Can be dysfunctional competition among divisions.
compete for scarce resources, management attendance. communication / collaboration between different divisions is difficult
Can be very expensive.
large number of managers is required (one manager for each function within each division)
Can focus on short-term performance.
focus on divisional goals and might lose sight of organizational goals
Duplication
decresed communication between divisions leads to no learning effects and duplication of work
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
Divisional Structure: When does it work best? (4)
in complex, fast-moving environments (can adapt / react quickly)
for firms with a lot of different products / services; companies that address different markets
companies that invest in innovation / non-routine technologies
large companies
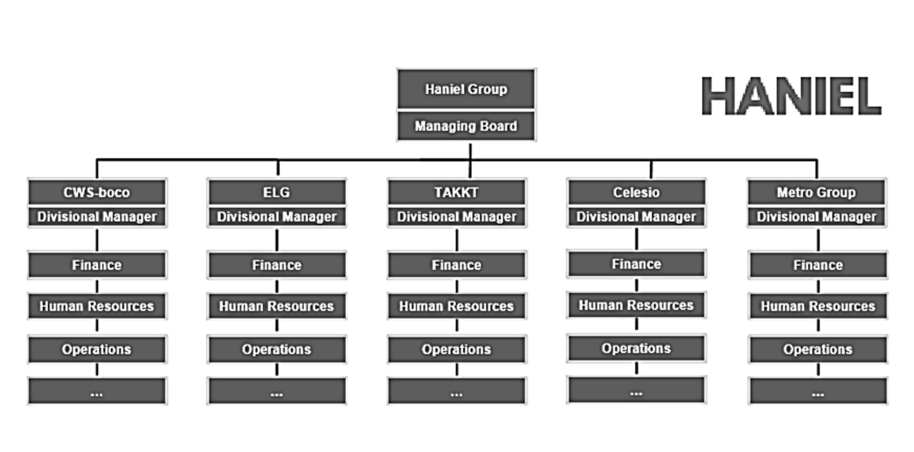
Types of Divisional Structures (3)
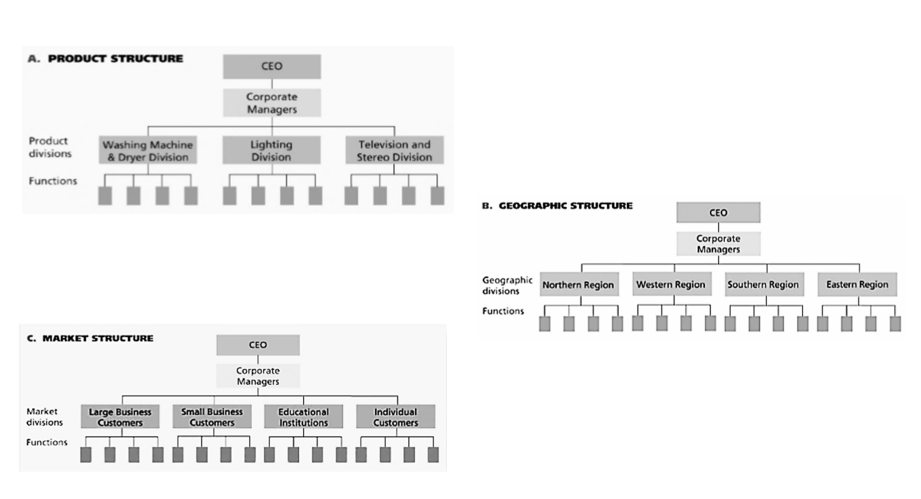
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
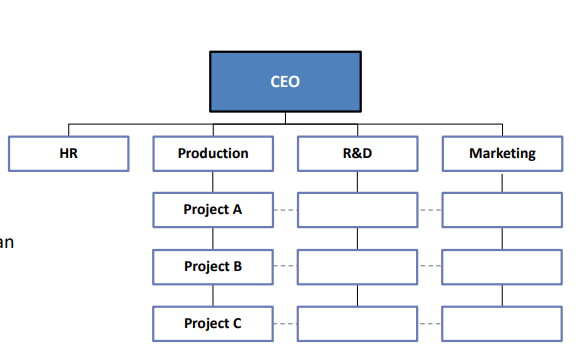
Matrix Structure
Matrix Structure: An organizational structure that simultaneously groups people and resources by function and product.
=> get the best of both worlds, but you will also get the worst of them
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Departmentalization
Matrix Structure: Advantages & Disadvantages (3+4)
Results in a complex network of superior-subordinate reporting relationships.
The structure is very flexible and can respond rapidly to the need for change.
Each employee has two bosses (functional manager and product / project manager) and possibly cannot satisfy both.
facilitates specialization / division of labor
people have broader range of responsibility → motivating, more autonomy
decisions can take longer. Communication process is very inflexible & time-consuming (you need decisions made by the functions AND the divisions)
requires high-level of interpersonal skills, otherwise conflicts
Requires high level of communication and coordination costs. But if it works, it is effective, because it is flexible. Many large organizations use it.
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Span of Control - Coordinating Functions and Divisions
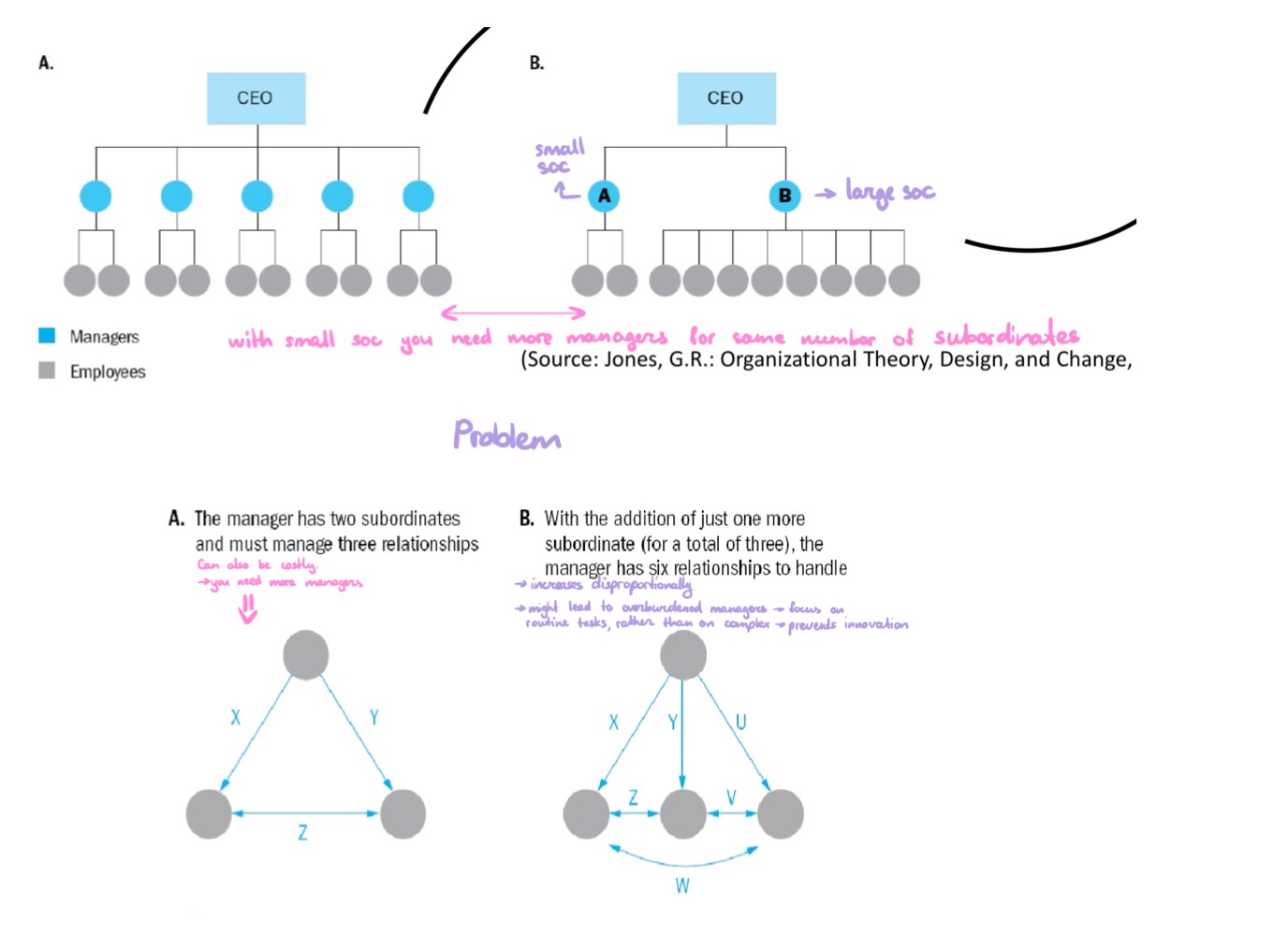
Span of Control refers to the number of workers a manager manages.
Dependent on the complexity and interrelatedness of the subordinates’ tasks
Small span of control: complex and dissimilar tasks
you need a lot of interaction between manager and people. Sometimes you do not even know how to best pursue the task → trial and error → work closely together (e.g. innovation)
Large span of control: routine and similar tasks
e.g. mass products to mass markets (subordinates do not need much guidance)
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Chain of Command
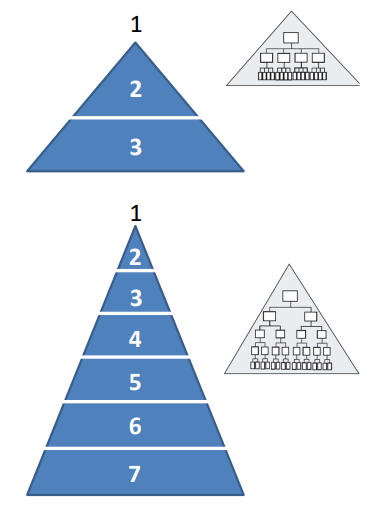
Chain of command - number of levelsof hierarchy
typically increase as the company grows
to reduce complexity, you have to change
Lvl. 1 is the CEO
1) CEO and 2 lvls of hierarchy
2) CEO and 6 lvls of hierarchy
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Chain of Command - Tall and Flat Organizations
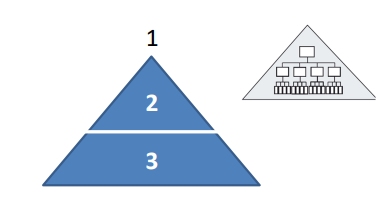
Flat structures + advantages (2)
Flat structures have fewer levels and wide spans of control. Structure results in quick communications but can lead to overworked managers.
(+) easy to reach the top management
(+) flexible, not very bureaucratic
When the company grows: if you do not want to increase the level of hierarchy, you need to increase the span of control
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Chain of Command - Tall and Flat Organizations
Tall structures + advantages & disadvantages (4+1)
Tall structures have many levels of authority and narrow spans of control.
As hierarchy levels increase, communication gets difficult creating delays in the time being taken to implement decisions.
Communications can also become garbled (distorted) as it is repeated through the firm. Some issues might even not reach the CEO.
More levels of hierarchy increases the number of managers → less responsibility of the workers reduces motivation.
Increased bureaucratic costs.
(+) specialization advantages
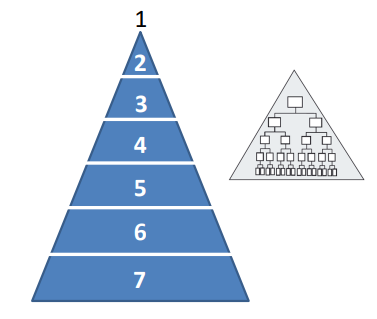
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Centralization and decentralization
Centralized vs. Decentralized Authority:
Decentralization puts more authority at lower levels and leads to flatter organizations. (smaller chain of command)
Works best in dynamic, highly competitive environment or for companies that work in totally different markets → can adapt to very specific environments
Stable environment (or products that are very resource-intensive) favors centralization of authority
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Centralization and decentralization - Decentralized
Advantages (2)
Another way to keep an organizational hierarchy flat.
Communication and motivation problems can be kept at a minimum. (within subunits)
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Centralization and decentralization - Decentralized
Disadvantages (2)
Disadvantage: too much decentralization of authority …
… divisions, functions or teams may start to pursue their own goals at the expense of the organization’s goals.
they might not even be aware of the organizational goals OR their subunit’s goalse diverge from organizational => Principal-Agent-Problem
… can cause lack of communication among functions or divisions; this prevents the synergies of cooperation and performance suffers.
duplication of work, people can’t learn from failures / success of others
information gets lost
if there is competition between the units, it gets ever worse
What is Organizational Structure?
Key Elements: Centralization and decentralization
Organizations need both:
Decentralization:
to be agile
react quickly
motivate people through delegation and autonomy
=> Different, to some extent independent, subsidiaries
Centralization:
to profit from synergies
allows learning
=> Everything has to be reported to HQ. Decisions that affect the overall goals of organization are made at HQ.