ANAPHY - 1M (Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology)
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Anatomy
investigates the body’s structure and the relationship between the body part and its function
Developmental anatomy
studies the structural changes that occur between conception and adulthood
Embryology
subspecialty of developmental anatomy that, considers changes from conception to the end of the eighth week of development
Cytology
examines structural features of cells
Histology
examines tissues, which are composed of cells and the materials surrounding them
Histology
also known as Microscopic Anatomy
Gross anatomy
study of structures that can be examined without the aid of a microscope
Systemic Anatomy
Regional Anatomy
2 Ways to Study Anatomy:
Systemic anatomy
studied system by system, i.e., cardiovascular, nervous, skeletal, etc.
Systemic anatomy
“by organ systems”
Regional anatomy
studied area by area, within each region such as head, abdomen, or arm
Regional anatomy
“by areas”
Anatomical Anomalies
physical characteristics that differ from the normal pattern
Anatomical Anomalies
can vary in severity from relatively harmless to lifethreatening
Anatomical Anomalies
use x-rays to see inside the body back in 1895
Physiology
scientific investigation of the processes or functions of living things
Physiology
often examines systems rather than regions because a particular function can involve portions of a system in more than one region
Cellular physiology
examines processes occurring in cells
Systemic physiology
deals with organ system function
Neurophysiology
focuses on the nervous system
Cardiovascular physiology
deals with heart and blood vessels
Pathology
deals with all aspects of disease, with an emphasis on the cause and development of abnormal conditions, as well as the structural and functional changes resulting from disease
Exercise physiology
focuses on the changes in function and structure caused by exercise
Chemical
Cell
Tissue
Organ
Organ System
Organism
Six Levels of Organization
Chemical
involves interactions between atoms that combine to form molecules, such as water, sugar, fats, and proteins
Cell
molecules combine to form organelles, small structures that make up cells
Tissue
composed of a group of similar cells and the materials surrounding them which determine the function of the tissue
Organ
composed of two or more tissue types that perform one or more functions. examples are heart, stomach, and lungs
Organ system
group of organs that perform a common function and are viewed as a unit
Organism
any living thing considered as a whole; it is a complex organ of organ systems, all mutually dependent on one another
Integumentary System
Skeletal System
Muscular System
Respiratory System
Lymphatic System
Digestive System
Nervous System
Endocrine System
Cardiovascular System
Urinary System
Female Reproductive System
Male Reproductive System
12 Major Organ System
Integumentary System
• provides protection
• regulates temperature
• prevents water loss
• helps produce vitamin D
• consists of skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands
Skeletal System
• provides protection and support
• produces blood cells
• regulates temperature
• stores minerals and fat
• consists of bones, associated cartilages, ligaments, and joints
Muscular System
• produces body movements
• maintains posture
• regulates temperature
• produces body heat
• consists of muscles attached to the skeleton by tendons
Respiratory System
• exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood and air and regulates blood pH
• consists of the lungs and respiratory passages
Lymphatic System
• removes foreign substances from the blood and lymph
• combats disease
• maintains tissue fluid balance
• absorbs fat from the digestive
Digestive System
• performs chemical and mechanical digestion, absorption of nutrients, and elimination of waste
• consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and other accessory organs
Nervous System
• major regulatory system that detects sensations and controls movements, physiological processes, and intellectual functions
• consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors
Endocrine System
• major regulatory system that influences metabolism, growth, reproduction, and many other functions
• consists of glands, such as the pituitary, that secretes hormones
Cardiovascular System
• transports nutrients, waste products, gases, and hormones throughout the body
• plays a role in immune response and regulation of body temperature
Urinary System
• removes waste products from the blood and regulates blood pH, ion balance, and water balance
• consists of the kidneys, urinary bladder, and ducts that carry urine
Female Reproductive System
• products oocytes
• site of fertilization and fetal development
• produces hormones that influence sexual functions and behaviors
Male Reproductive System
• produces and transfers sperm cells to female and produces hormones that influence sexual functions and behavior
• consists of the testes, accessory structures, ducts, and penis
Organization
Metabolism
Responsiveness
Growth
Development
Reproduction
Characteristics of Life:
Organization
refers to the interrelationships among the parts of an organism and how those parts interact to perform specific functions
Metabolism
refers to all the chemical reactions taking place in an organism
Responsiveness
an organism’s ability to sense changes in its external or internal environment and how it adjusts to those changes
Growth
an increase in the number of cells, which produces an overall enlargement of all or part of an organism
Development
includes the changes an organism undergoes through time from fertilization to death
Differentiation
change in cell structure and function from generalized to specialized
Morphogenesis
change in the shape of tissues, organs, and the entire organism
Reproduction
formation of new cells or new organisms
Homeostasis
refers to the existence and maintenance of a relatively constant environment within the body
Negative Feedback
the response to the original stimulus results in deviation from the set point, therefore becoming smaller
maintaining room temperature
regulation of body temperature
Negative Feedback Example:
Positive Feedback
mechanism that occurs when a response to the original stimulus results in the deviation from the set point, therefore becoming even greater
blood clotting
childbirth
Positive Feedback Example:
Negative Feedback
the response stops the effector
Positive Feedback
the response keeps the reaction going
Anatomical Position
refers to a person standing erect with the face directed forward, the upper limbs hanging to the sides, and the palms of the hands facing forward
Supine
lying face upward
Prone
lying face downward
Right-Upper Quadrant
Left-Upper Quadrant
Right-Lower Quadrant
Left-Lower Quadrant
4 Quadrants of the Body:
Epigastric
Right and Left Hypochondriac
Umbilical
Right and Left Lumbar
Hypogastric
Right and Left Iliac
9 Regions of the Body:
Sagittal plane
runs vertically through the body, separating it into right and left portions
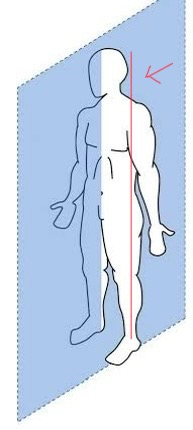
Median plane
sagittal plane that passes through the midline of the body, dividing it into left and right halves
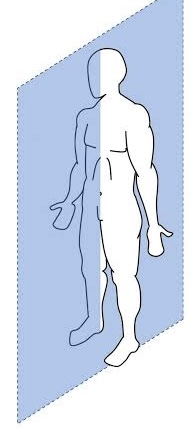
Transverse plane
runs parallel to the ground, dividing the body into superior and inferior portions
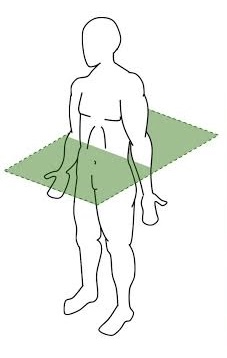
Frontal plane
runs vertically from right to left and divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
Longitudinal section
a cut through the long axis of the organ
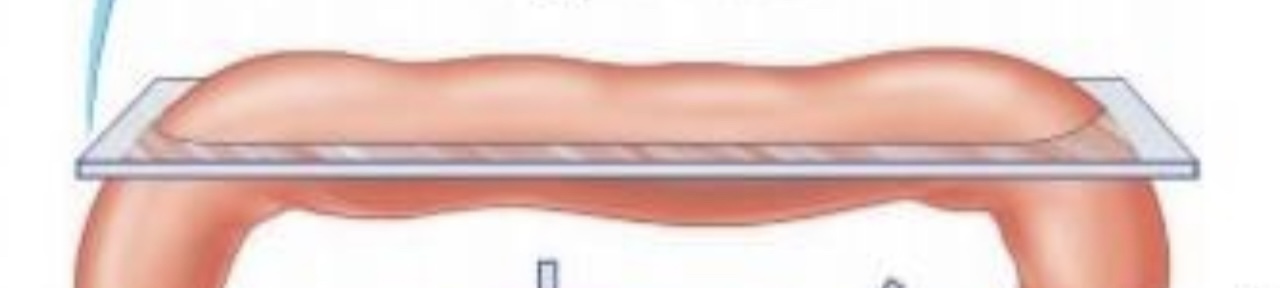
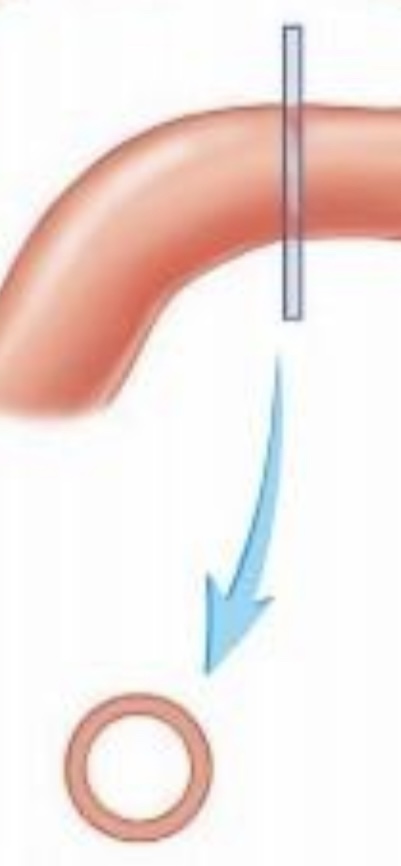
Transverse section
a cut at right angles to the long axis
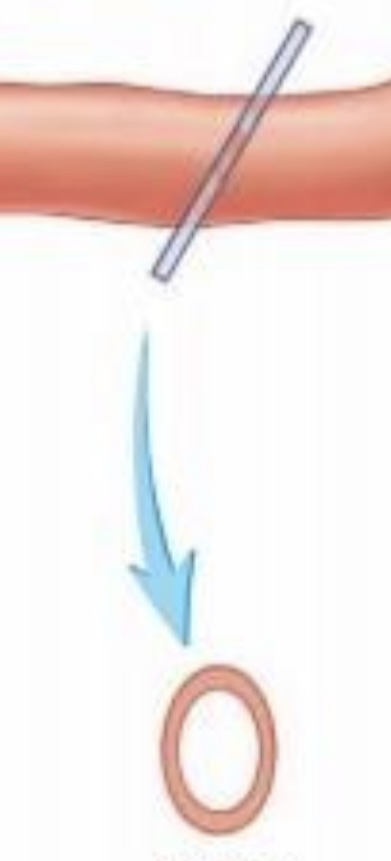
Oblique section
a cut made across the long axis at other than a right angle
Thoracic cavity
Abdominal cavity
Pelvic cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity
Body Cavities:
Thoracic cavity
o surrounded by the rib cage while the muscular diaphragm separates it from the abdominal cavity
o contains the heart, the thymus, the trachea, the esophagus, and other structures such as blood vessels and nerves
Mediastinum
median partition of the right and left thoracic cavity
Abdominal cavity
o enclosed by the abdominal muscles
o contains the stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, pancreas, and the kidneys
Pelvic cavity
o encased by the pelvic bones
o houses the urinary bladder and the internal reproductive system
Abdominopelvic cavity
o refers to the abdominal and pelvic cavities that are not physically separated
Directional terms
anatomical terminologies that describe the parts of the body relative to each other
Supine
lying face upward
Prone
lying face downward
Right
toward the right side of the body
Left
toward the left side of the body
Superior
a structure above another
Interior
a structure below another
Cephalic
closer to the head than another structure (usually synonymous with superior)
Caudal
closer to the tail than another structure (usually synonymous with inferior)
Anterior
the front of the body
Posterior
the back of the body
Ventral
toward the belly (synonymous with anterior)
Dorsal
toward the back (synonymous with posterior)
Proximal
closer to the point of attachment to the body than another structure
Distal
farther from the point of attachment to the body than another structure
Lateral
away from the midline of the body
Medial
toward the midline of the body
Superficial
toward or on the surface
Deep
away from the surface, internal
Serous Membranes
line the trunk cavities and cover the organs within them
Visceral serous membrane
covers the organ
Parietal serous membrane
represents an outer wall
Cavity
space between the visceral and parietal that is normally filled with a thin, lubricating film of serous fluid produced by the membranes