Chem exam 10-12/15
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Considering all the bonds in a molecule with trigonal bipyramidal geometry, what are the bond angles present?
A) 180° only
B) 120° only
C) 90° only
D) 90°, 120°, and 180°
E) 60° and 90° only
D) 90°, 120°, and 180°
What is the molecular shape of the thiocyanate anion, SCN–, as predicted by the VSEPR theory? (Carbon is the central atom.)
A) bent
B) linear
C) angular
D) trigonal
E) None of these choices are correct
Linear
What is the molecular shape of NOCl as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) bent
B) linear
C) trigonal planar
D) trigonal pyramidal
E) tetrahedra
Bent
What is the molecular shape of NH2Cl as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) T-shaped
B) trigonal planar
C) trigonal pyramidal
D) see-saw
E) tetrahedra
Trigonal pyramidal
What is the molecular shape of ClF2–as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) L-shaped
B) see-saw
C) T-shaped
D) linear
E) bent
linear
What is the molecular shape of XeO2F2 as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) square planar
B) octahedral
C) square pyramidal
D) see-saw
E) tetrahedral
see-saw
Predict the ideal bond angles around nitrogen in N2F2 using the molecular shape given by the VSEPR theory. (The two N atoms are the central atoms.)
A) 90°
B) between 120 and 180°
C) 180°
D) 109°
E) 120°
120
Predict the actual bond angle in SeCl2using the VSEPR theory
A) less than 90°
B) between 90° and 109°
C) between 109° and 120°
D) exactly 90°
E) more than 120
between 90 and 109
Which of the following molecules has a net dipole moment?
A) CO2
B) BeCl2
C) SF2
D) CCl4
E) KrF2
SF2
Which of the following has no net dipole moment?
A) H2Se
B) TeO3
C) CH3Cl
D) N2O
E) NF3
TeO3
What is the molecular shape of the thiocyanate anion, SCN–, as predicted by the VSEPR theory? (Carbon is the central atom.)
A) bent
B) linear
C) angular
D) trigonal
E) None of these choices are correct.
linear
What is the molecular shape of BCl3as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) bent
B) trigonal pyramidal
C) linear
D) tetrahedral
E) trigonal planar
trigonal planar
What is the molecular shape of NO2–as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) resonant
B) tetrahedral
C) trigonal planar
D) bent
E) linear
bent
What is the molecular symmetry around the carbons in CCl2CH2as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) trigonal pyramidal
B) linear
C) trigonal planar
D) tetrahedral
E) bent
trigonal planar
What is the molecular shape of ClO3F as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) octahedral
B) square planar
C) trigonal pyramidal
D) square pyramidal
E) tetrahedral
tetrahedral
What is the molecular shape of SiF62– as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) tetrahedral
B) octahedral
C) trigonal bipyramidal
D) hexagonal
E) see-saw
octahedral
What is the molecular shape of ClF4– as predicted by the VSEPR theory?
A) tetrahedral
B) square pyramidal
C) octahedral
D) square planar
E) see-saw
square planar
Use VSEPR theory to decide which one of the following molecules and ions will have a trigonal pyramidal geometry. (The central atom is always first in the formula.)
A) BF3
B) BrF3
C) CO32–
D) SO3
E) PCl3
PCl3
Predict the ideal bond angles in GeCl4using the molecular shape given by the VSEPR theory
A) 90°
B) 180°
C) 109°
D) < 90°
E) 120°
109
Predict the ideal bond angles in FNO using the molecular shape given by the VSEPR theory.
A) 120°
B) 109°
C) 180°
D) 90°
E) between 120 and 180
120
Predict the ideal bond angles around carbon in C2I2 using the molecular shape given by the VSEPR theory.
A) 120°
B) 180°
C) 90°
D) 109°
E) None of these choices are correct.
180
Which one of the following molecules has a zero dipole moment?
A) SO2
B) CO
C) Cl2O
D) HCl
E) CS2
CS2
According to valence bond theory, which orbitals on N and H overlap in the NH3 molecule?
A) sp3on N overlaps with sp on H
B) 2s on N overlaps with 1s on H
C) 2p on N overlaps with 1s on H
D) 2p on N overlaps with 2s on H
E) sp3on N overlaps with 1s on H
E) sp3on N overlaps with 1s on H
According to valence bond theory, Carbon uses ________ hybrid orbitals in ClCN.
A) sp3d
B) sp
C) sp2
D) sp3
E) sp3d2
sp3
Valence bond theory predicts that iodine will use ________ hybrid orbitals in ICl2-
A) sp3d2
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) None of these choices are correct.
sp3d
Valence bond theory predicts that bromine will use ________ hybrid orbitals in BrF5
A) sp3d
B) sp3d2
C) sp2
D) sp3
E) None of these choices are correct
sp3d2
according to valence bond theory, which of the following molecules involves sp2 hybridization of orbitals on the central atom? (central atom is bold)
A) C2H6
B) C2H4
C) CO2
D) C2H2
E) H2O1
C2H2
According to valence bond theory, the triple bond in ethyne (acetylene, C2H2) consists of
A) one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
B) no sigma bonds and three pi bonds.
C) two sigma bonds and one pi bond.
D) three sigma bonds and no pi bonds.
E)None of these choices are correct.
One sigma bond and two pi bonds
Valence bond theory predicts that iodine will use ________ hybrid orbitals in ICl2-.
A) sp3d2
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) None of these choices are correct
sp3d
Select the correct statement about ʌ-bonds in valence bond theory.
A) A pi bond between two carbon atoms restricts rotation about the C–C axis.
B) A carbon-carbon double bond consists of two pi bonds.
C) A pi bond is stronger than a sigma bond.
D) A pi bond can hold 4 electrons, two above and two below the ı-bond axis.
E) A pi bond is the same strength as a sigma bond
A pi bond between two carbon atoms restricts rotation about the C–C axis.
How many sigma and pi bonds, respectively, are in the molecule below?CH3CH2CHCHCH3?
A) 15, 0
B) 16, 1
C) 15, 1
D) 16, 0
E) 14, 1
14,1
Give the hybridization for the C in H2CCH2.
A) sp3
B) sp3d
C) sp2
D) sp3d2
E) sp
sp2
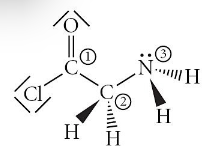
Consider the molecule below. Determine the hybridization at each of the 3 labeled atoms
A) 1=sp3, 2=sp3, 3=sp3
B) 1=sp3, 2=sp3, 3=sp2
C) 1=sp2, 2=sp3, 3=sp2
D) 1=sp, 2=sp2, 3=sp3
E) 1=sp2, 2=sp3, 3=sp3
1=sp2, 2=sp3, 3=sp3
Liquid ammonia (boiling point = –33.43°C) can be used as a refrigerant and heat transferfluid. How much energy is needed to heat 25.0 g of NH3(l) from –65.0°C to –12.0°C?
Specific heat capacity, NH3(l):4.7 J/(g·K)
Specific heat capacity, NH3(g):35.1 J/(g·K)
Heat of vaporization:23.3 kJ/mol
Molar mass,M:17.0 g/mol
57 kJ
Diethyl ether, used as a solvent for extraction of organic compounds from aqueous solutions, has a high vapor pressure which makes it a potential fire hazard in laboratories in which it is used. How much energy is released when 100.0 g is cooled from 53.0°C to 10.0°C?
Boiling point:34.4°C
Heat of vaporization:358 J/g
Specific heat capacity, (CH3)2O(l):2.37 J/(g·K)
Specific heat capacity, (CH3)2O(g):2.35 J/(g·K
340 kJ
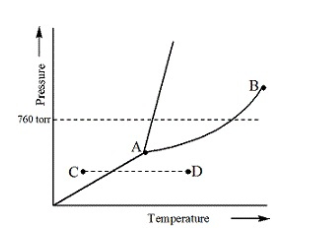
Examine the phase diagram for the substance Bogusium (Bo) and select the correct statement
Point B represents the critical temperature and pressure for Bo.
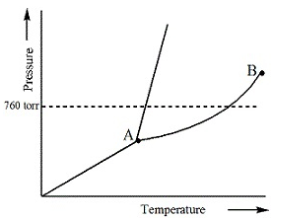
Examine the following phase diagram and identify the feature represented by point A.
Triple point
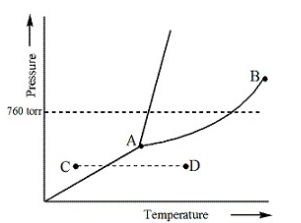
Consider the following phase diagram and identify the process occurring as one goes from point C to point D
increasing temperature with a phase change from solid to vapor
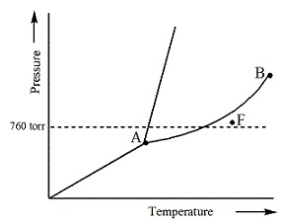
Examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase exists at point F.
vapor
Neon atoms are attracted to each other by
London dispersion forces
Ammonia's (NH3) unusually high melting point is the result of
hydrogen bonding
Octane (C8H18) is a component of fuel used in internal combustion engines. Thedominant intermolecular forces in octane are
London dispersion forces.
In hydrogen iodide (HI) ________ are the most important intermolecular forces
dipole-dipole forces
What types of forces exist between molecules of CO2
dispersion forces only
The strongest intermolecular interactions between ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) molecules arise from
hydrogen bonding
Which one of the following pure substances will have hydrogen bonds between molecules?
A) CH3CH2–OH
B) CH3–O–CH3
C) CH3CH2–F
D) (CH3)3N
E) HI
CH3CH2–OH
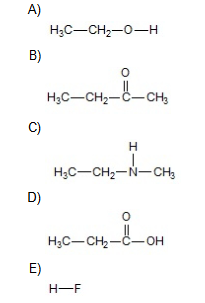
In which of the following compounds will the molecules not form hydrogen bonds with each other (in the pure substance)
B
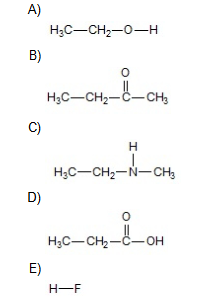
How many of the Question 14 compounds will form hydrogen bonds with water?
5
Which of the following pairs of molecules can form hydrogen bonds between them?
A)CH4and H2O
B) H2 and O2
C) CH3OH and NH3
D) HCl and HI
E) SO2 and CH2O
CH3OH and NH3
Which of the following should have the highest boiling point?
A) CI4
B) CCl4
C) CH4
D) CBr4
E) CF4
Cl4
Which of the following should have the lowest boiling point?
A) C10H22
B) C8H18
C) C5H12
D) C12H26
E) C6H14
C5H12
Select the pair of substances in which the one with the higher vapor pressure at a given temperature is listed first
A)H2O, H2S
B) CCl4, CBr4
C) Xe, Kr
D) C7H16, C5H12
E) CH3CH2OH, CH3–O–CH3
CCl4, CBr4
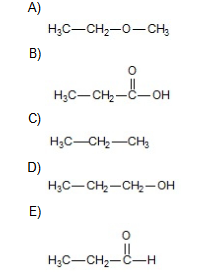
Which of the following should have the highest surface tension at a given temperature?
B
Which of the following terms refers to the resistance of a liquid to flow?
A) adhesion
B) viscosity
C) capillary action
D) surface tension
E) cohesion
viscosity
Which of the following factors contributes to a low viscosity for a liquid?
A) high boiling point
B) high molecular weight
C) hydrogen bonding
D) low temperature
E) spherical molecular shape
spherical molecular shape
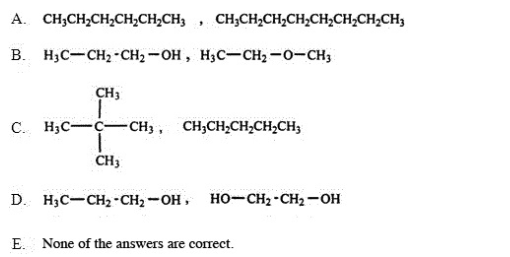
Which of the following pairs of substances is arranged so that the one with higher viscosity is listed first?
B
The energy of a hydrogen bond is greater than that of a typical covalent bond.
F
Only molecules that do not have dipole moments can experience dispersion forces.
F