The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Reflexes- Chapter 15
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
motor nervous system that controls glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
Visceral nervous system
Another name for the autonomic nervous system
- Viscera of thoracic and abdominal cavities
- Some structures of the body wall
What are the primary target organs of the autonomic nervous system?
Cutaneous blood vessels, sweat glands, piloerector muscles
What are the structures of the body wall the autonomic nervous system innervates?
involuntarily
The autonomic nervous system carries out actions ______________________
True
True or False: Visceral effectors do not depend on ANS to function
To adjust their activity to body's changing needs
What do visceral effectors depend on the ANS for?
Visceral Reflexes
unconscious, automatic, stereotyped responses to stimulation
- Receptors: nerve endings that detect stretch, tissue damage, blood chemicals, body temp, and other internal stimuli
- Afferent neurons: lead to CNS
- Integrating center: interneurons in CNS
- Efferent neurons: carry motor signals away from CNS
- Effectors: carry out response
What is the visceral reflex arc?
They have a slower response
What makes the effectors of the visceral reflex arc different than the effectors of the somatic reflex arc?
Baroreflex: 1. High blood pressure detected by arterial stretch receptors
2. Afferent neuron (glossopharyngeal nerve) carries signal to CNS
3. Efferent signals on vagus nerve of ANS travel to the heart
4. Heart then slows, reducing blood pressure
What is an example of a visceral reflex?
Sympathetic division and parasympathetic division
What are the two divisions of the ANS?
Sympathetic division
prepares body for physical activity: exercise, trauma, arousal, competition, anger, or fear
- Increase heart rate, blood pressure, airflow, blood glucose levels
- Decrease blood flow to skin and digestive tract
What two things does the sympathetic division do that happen at the same time?
"fight-or-flight"
The sympathetic division creates a ______________________ reaction
Parasympathetic division
calms body function reducing energy expenditure and assists in bodily maintenance
Digestive waste
What does the parasympathetic division help eliminate?
resting and digesting
The parasympathetic vision controls the ___________________________ state
Autonomic tone
normal background rate of activity; represents the balance of the 2 systems; balance shifts with body's changing needs
Parasympathetic tone
maintains smooth muscle tone in intestines, holds resting heart rate down to about 70 to 80 BPM
Heart rate would go to about 100 BPM (resting)
What would happen if you severed the parasympathetic tone?
Sympathetic tone
keeps most blood vessels partially constricted and maintains blood pressure
Would faint, blood goes to easily to all parts of the body
What would happen if you lost the sympathetic tone?
Sympathetic division, parasympathetic division
______________________________ excites the heart but inhibits the digestive and urinary function, while __________________________ has the opposite effect
2 neurons to get to target organ
What must signals travel across in autonomic pathways?
synapse, autonomic ganglion
In an autonomic pathway, the signal must cross a __________________ where these 2 neurons meet in an __________________________
Preganglionic neuron
first neuron with cell body in brainstem or spinal cord, part of autonomic pathway
postganglionic neuron
The preganglionic neuron synapses with a _____________________ whose axon extends the rest of the way to the target cell
Varicosities
What does the postganglionic neuron have that allows it to synapse with multiple cells?
Comparison of somatic and autonomic pathways
What is this?
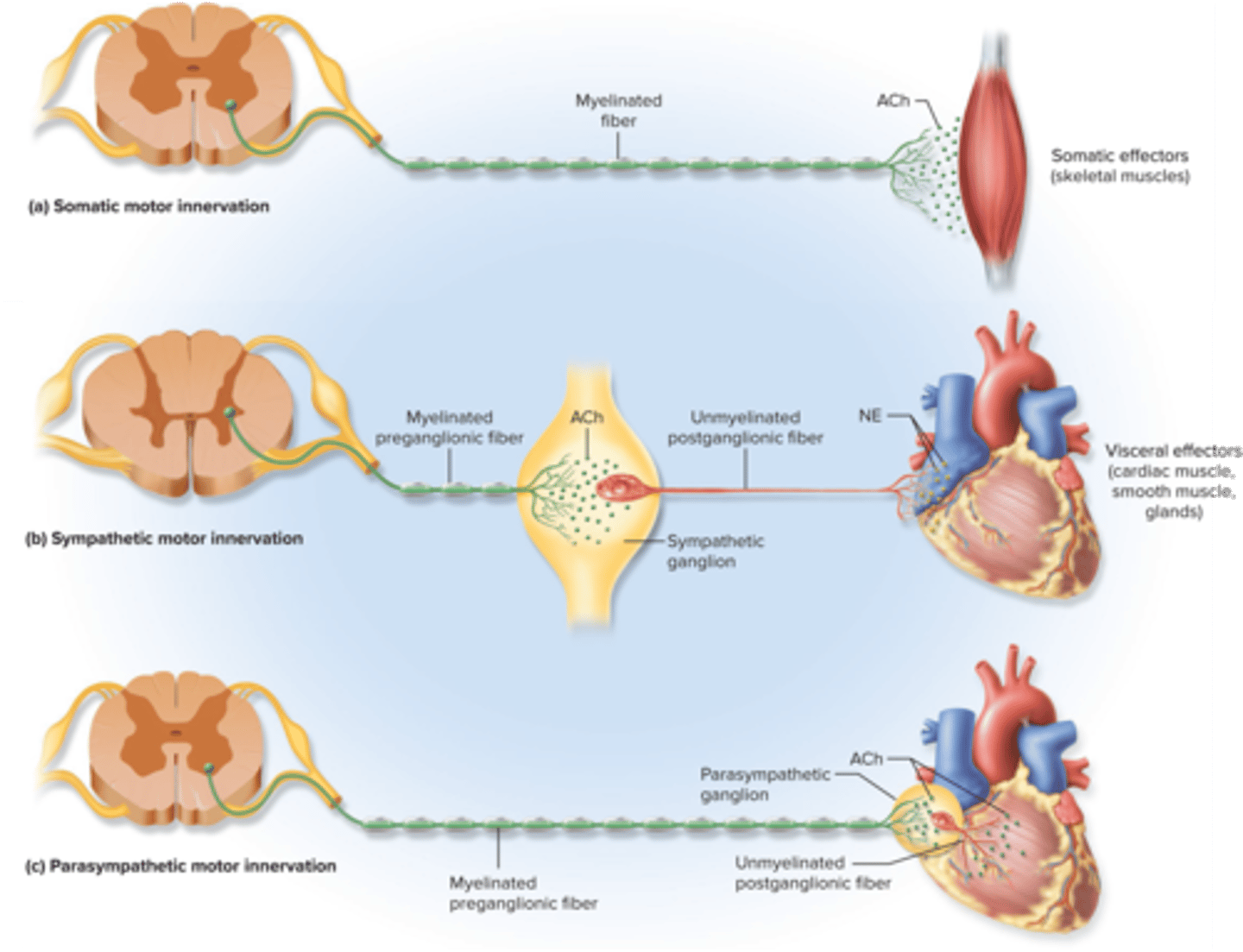
Thoracolumbar division (T1-L2); arises from thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord
What is the sympathetic division also known as?
short, long
The sympathetic motor innervation has ________ preganglionic and _________ postganglionic fibers
Lateral horns and nearby regions of gray matter of spinal cord
Where do the preganglionic cell bodies begin in the sympathetic motor innervation?
By way of spinal nerves T1-L2
How do fibers exit the spinal cord in the sympathetic division?
Nearby sympathetic chain of ganglia (located on both sides of spinal cord)
Where do the spinal nerves of the sympathetic division that exit the spinal cord lead to?
Sympathetic chain of ganglia
series of longitudinal ganglion adjacent to both sides of vertebral column from cervical to coccygeal levels
Every level of the body
Where are sympathetic fibers distributed to?
Communicating rami
Each sympathetic chain ganglion is connected to a spinal nerves by 2 branches, called what?
Preganglionic fibers, white communicating ramus
_______________________________ are small myelinated fibers that travel from the spinal nerves to the ganglion by way of the ________________________________________
White communicating ramus
What is the only way to the sympathetic chain?
Postganglionic fibers, gray communicating ramus
___________________________ leave ganglion by way of ______________________________ (unmyelinated)
The spinal cord
Where does the gray ramus return to?
The rest of the way to the target organ
Where do postganglionic fibers extend to?
By spinal, sympathetic, and splanchnic nerves
After entering the sympathetic chain, how do nerve fibers leave the sympathetic chain?
- Some postganglionic fibers exit a ganglion by way of gray ramus
- Return to spinal nerve and travel rest of the way to the target organ
What is the spinal nerve route?
Most sweat glands, piloerector muscles, and blood vessels of skin and skeletal muscles
Where does the spinal nerve route lead to?
Sympathetic nerve route
some postganglionic fibers leave by way of sympathetic nerves that extend to heart, lungs, esophagus, and thoracic blood vessels
carotid plexus
The sympathetic nerves that leave via the sympathetic nerve route form __________________ around each carotid artery of the neck and issue nerve fibers to effectors in the head
Sweat, salivary, nasal glands; piloerector muscles; blood vessels; dilators of iris
What do the carotid plexuses do?
cardiac nerves
Some fibers of superior and middle cervical ganglia form ____________________ to the heart
Splanchnic nerve route
some fibers that arise from spinal nerves T5 to T12 pass through the sympathetic ganglia without synapsing
Continue on as the splanchnic nerves
What do the fibers in the splanchnic nerve route do?
Second set of ganglia: collateral ganglia and synapse there with postganglionic fibers
What do the splanchnic nerves lead to?
abdominal aortic plexus
Collateral ganglia contribute to a network called ______________________________
Abdominal aorta
What does the abdominal aortic plexus wrap around?
Celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric
What are the 3 major collateral ganglia in the abdominal aortic plexus?
Postganglionic fibers
What accompanies the arteries and their branches to their target organs of the celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric?
Stomach, spleen, liver, pancreas, small intestine, and kidneys
What is the postganglionic target organ of the celiac ganglion (collateral ganglia)?
Small intestine, colon, and kidneys
What is the postganglionic target organ of the celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia (collateral ganglia)?
Rectum, urinary bladder, and reproductive organs
What is the postganglionic target organ of the inferior mesenteric ganglion (collateral ganglia)?
adrenal (suprarenal) glands
Paired _______________________________ on superior poles of kidneys
Adrenal cortex (outer layer) and adrenal medulla (inner core)
What are the 2 glands that make up the adrenal (suprarenal) glands?
Adrenal cortex (outer layer)
part of adrenal glands, secretes steroid hormones
Adrenal medulla (inner core)
part of adrenal glands, sympathetic ganglion consisting of modified postganglionic neurons without dendrites or axons
Preganglionic sympathetic neurons
What is the adrenal medulla stimulated by?
It secretes a mixture of hormones into the bloodstream
What happens when the adrenal medulla is stimulated?
Catecholamines
What is the hormone class the adrenal medulla secretes into the bloodstream?
Epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
What hormones make up the class of catecholamines?
Craniosacral division
What is the parasympathetic division also known as?
Brain and sacral regions of spinal cord
Where does the parasympathetic division arise from?
Certain cranial and sacral nerves
What do the fibers of the parasympathetic division travel in?
- Midbrain, pons, medulla
- Sacral spinal cord segments S2 to S4
What are the origins of the long preganglionic neurons?
terminal ganglia
Preganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic division end in ______________________ in or near target organs
long, short
The parasympathetic division has _________ preganglionic fibers and ______________ postganglionic fibers
- Oculomotor nerve (III)
- Facial nerve (VII)
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
- Vagus nerve (X)
What are the 4 cranial nerves the parasympathetic nerves leave the brainsteam from?
Oculomotor nerve (III)
narrows pupil and focuses lens
Facial nerve (VII)
regulates tear, nasal, and salivary glands
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
parotid salivary gland
Vagus nerve (X)
viscera as far as proximal half of colon, only cranial nerve that goes below diaphragm
Cardiac, pulmonary, and esophageal plexus
What are the plexuses the vagus nerve splits into?
Levels S2 to S4 of spinal cord
What do the remaining parasympathetic fibers arise from (not from the cranial nerves)?
Pelvic splanchnic nerves that lead to inferior hypogastric plexus
What do the parasympathetic fibers that arise from levels S2 to S4 of the spinal cord form?
Synapse at this plexus
What do some fibers of the parasympathetic system do at the hypogastric plexus?
Most pass through, travel through pelvic nerves to terminal ganglia
What do most fibers of the parasympathetic system do (if they don't synapse at the hypogastric plexus)?
Distal half of colon, rectum, urinary bladder, and reproductive organs
What do the parasympathetic fibers that arise from levels S2 to S4 of the spinal cord innervate?
Enteric Nervous System/Enteric Plexus
nervous system of the digestive tract
True
True or False: The enteric system does not arise from the brainstem or spinal cord (no CNS components)
Smooth muscle and glands
What does the Enteric Nervous System innervate?
in the walls of the digestive tract
The enteric nervous system is composed of 100 million neurons found ______________________________________________
Its own ganglia and reflex arcs
What does the enteric nervous system have?
Motility of esophagus, stomach, and intestines and secretion of digestive enzymes and acid
What does the enteric nervous system regulate?
Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
Normal digestive function also requires regulation by what?
- Sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers secrete different neurotransmitters (norepinephrine and acetylcholine)
- Receptors on target cells vary
How can different autonomic neurons have different effects- constricting some vessels but dilating others?
- Target cells respond to same neurotransmitter differently depending on type of receptor they have for it
- There are 2 different classes of receptors for acetylcholine and 2 classes of receptors for norepinephrine
How can receptors on target cells vary?
All preganglionic neurons in both divisions and the postganglionic parasympathetic neurons
What is acetylcholine secreted by?
Cholinergic fibers
axons that secrete ACh
Cholinergic receptor
any receptor that binds ACh
Muscarinic receptors and nicotinic receptors
What are the 2 types of cholinergic receptors?
In all cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and gland cells
Where are muscarinic receptors found?
Either due to subclasses of muscarinic receptors
Are muscarinic receptors excitatory or inhibitory?