L102b: evaluation of liver functions and analytes
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
what substances are evaluated in liver function tests?
substances produced by liver
substances metabolized and excreted by the liver
where does total bilirubin originate from?
breakdown of old RBC by macrophages
why is there very little unconjugated bilirubin in the blood?
degraded and bound to albumin to form delta bilirubin
what are the different ways icterus is classified?
pre-hepatic
hepatic (intra)
post hepatic
what are the causes of pre-hepatic hyperbilirubinemia?
extravascular hemolysis with marked anemia
massive internal hemorrhage
hypophosphatemia
how does hemolysis affect hepatocytes?
causes oxidative damage to hepatocytes which will interfere with bilirubin excretion and result in cholestasis
what typically occurs before jaundice?
bilirubinuria
how does massive internal hemorrhage lead to pre-hepatic hyperbilirubinemia?
marked increase of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
what can cause extravascular hemolysis?
parasites
zinc
copper
IMHA
what are the types of hepatic hyperbilirubinemia?
fasting
functional
obstructive intrahepatic or posthepatic
delta bilirubia
how does fasting lead to hyperbilirubinemia?
decreased uptake of unconjugated bilirubin by hepatocytes leads to regurgitation of bilirubin into the blood
what type of hyperbilirubinemia is sepsis associated cholestasis?
functional
what animal is functional hyperbilirubinemia common in?
sick cats
what is the pathogenesis of functional hyperbilirubinemia?
circulating inflammatory mediators such as TNF-alpha inhibit bile acid transport to canaliculi
what is the pathogenesis of obstructive intrahepatic hyperbilirubinemia?
hepatocyte swelling blocks bile canaliculi leading to decreased excretion
what is the pathogenesis of obstructive posthepatic hyperbilirubinemia?
impaired bile flow in canaliculi, bile ducts, or gall bladder
delta bilirubin
protein (albumin) bound part of conjugated total bilirubin in blood
what is the half-life of albumin and what does this mean for delta bilirubin?
8-20 days meaning that it will remain in blood for longer and cholestasis can persist even if symptoms are gone
what type of bilirubin do labs typically only measure?
total bilirubin
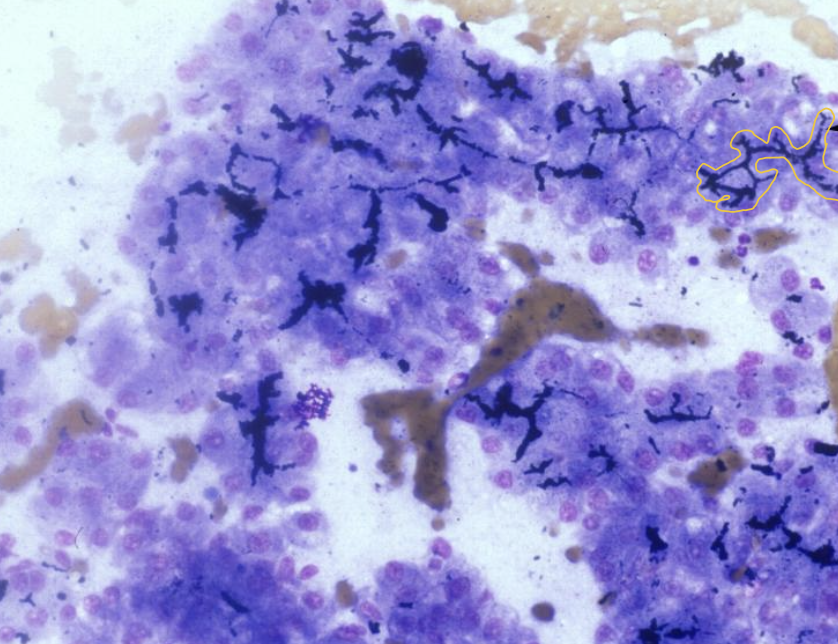
what does the image show?
intercellular bile lakes showing accumulation of bile in canaliculi
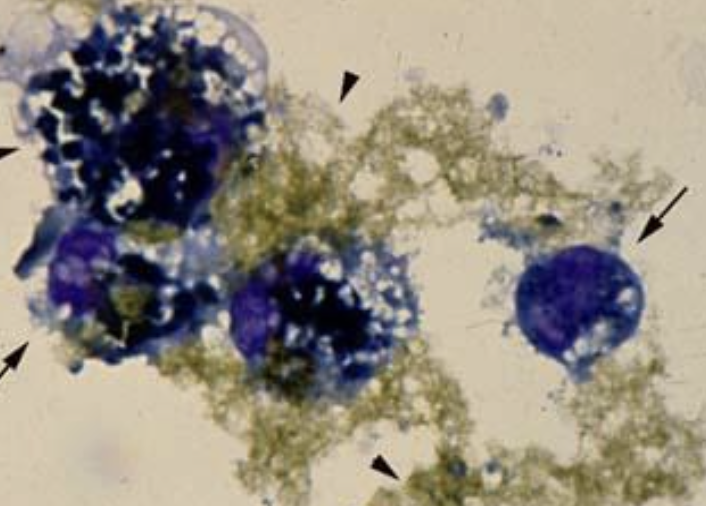
what is the image showing>
leakage of bile due to rupture of gallbladder or bile duct; known as " regurgitation”
which animals have a low renal threshold for bilirubin and will get bilirubinuria?
dogs and rumininants
what value is considered normal in male dogs with concentrated urine in regards to bilirubinemia?
1-2 is normal and should not be considered hyperbilirubinemia
what percentage of cattle have bilirubinemia?
25%
what animals have a high renal threshold and what does this mean?
cats and horses; significant because bilirubinuria usually from cholestatic liver disease
MCQ: in what two species is bilirubinuria the least clinically significant?
dogs and ruminants
bile acids
cholesterol derived anionic acids
what are bile acids required for?
digestion of dietary lipids
when is the highest sensitivity for fasting bile acids?
in dogs with convenital circulatory anomalies and chronic hepatitis
what bile acid value is considered abnormal?
above 25 umol/L
what is important to know for bile acid samples?
does not matter if sample was fasting or post-prandial
what is considered a post-prandial serum sample for bile acid?
you fed animal a small meal of bland food and took sample 2 hours later
hypercholemia
increased bile acids due to decreased clearance from portal blood
what diagnostic tool can be used to measure bile acids?
SNAP-BAT
what can falsely increase bile acids in a sample?
lipemia
when is bile acid testing NOT useful?
if there is high bilirubin
what is the relationship between bile acid and liver malfunction?
degree of increase of bile acids not proportional to degree of liver malfunction
MCQ: what interferent has the most profound effect in artifactually increasing serum bile acids?
lipemia
what are shunts?
vascular anomaly that allows blood from the hepatic portal circulation to bypass the liver & is delivered directly into the systemic circulation
which animals are extrahepatic shunts common in?
small breed dogs
which animals are intrahepatic shunts common in?
large breed dogs
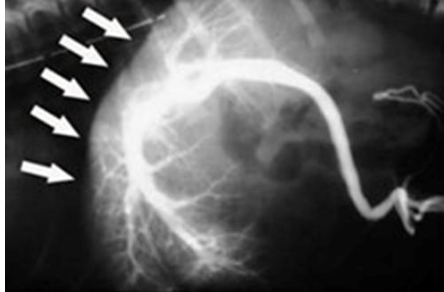
what does the radiograph show?
normal portogram showing hepatic vasculature
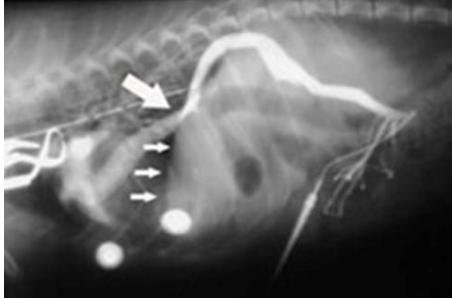
what does the radiograph show?
portosystemic shunt and loss of portal flow to liver
what does the portal vein drain?
intestines
stomach
pancreas
spleen
how are bile acids affected in animals with portosystemic shunts?
bile acids will be increased
what values will decrease if a portosystemic shunt leads to liver failure?
urea
glucose
cholesterol
albumin
coagulation factors
what can be seen on a CBC in animals with portosystemic shunts?
may see microcytic anemia hypoferremia due to abnormal iron sequestration
what are most dogs considered if they have hepatic microvascular dysplasia?
subclinical and rarely needs treatment; may see decrease in proteins
what is hepatic microvascular dysplasia?
congenital defect with abnormal development or absence of the portal microvasculature in the liver
what value will post prandial bile acids be in a dog with HMD?
35-60
what breeds are HMD more common in?
yorkies
sydney silkies
cairn terriers
what is important to know about bile acids in horses?
single bile acid is used
what will most horses with hepatobiliary disease have?
marked increase in bile acids
what will the value of cholesterol be in severe liver disease?
can have low cholesterol due to decreased production
will ammonimum be used over bile acids?
no due to many potential errors
what is the value of cholesterol in cholestasis?
increased due to decreased clearance
what causes a decreased production of cholesterol?
chronic liver disease
portosystemic shunts
what causes a loss of cholesterol?
malabsorption / maldigestion
protein losing enteropathy (PLE)
EPI
what plasma protein is made by the liver?
albumin
when will hypoalbuminemia be noted?
when 60-80% of the functional hepatic mass has been loss
what is an uncommon cause of low albumin?
liver failure unless it is a shunt
what is sometimes seen with plasma proteins in animals with severe liver disease?
polyclonal gammopathy and low albumin
what coagulation factor is NOT produced in the liver?
Factor VII
when would we recommend a coagulation screen to be conducted?
prior to liver FNA or biopsy
when will hepatic failure cause glucose values to decrease?
when there is reduced hepatic function
when will hepatic failure cause glucose levels to increase?
when there is decreased hepatic uptake
is it more common to see a decrease or increase in glucose levels with hepatic failure?
decrease
MCQ: what test result best detects liver malfunction?
increased concentrations of bile acids
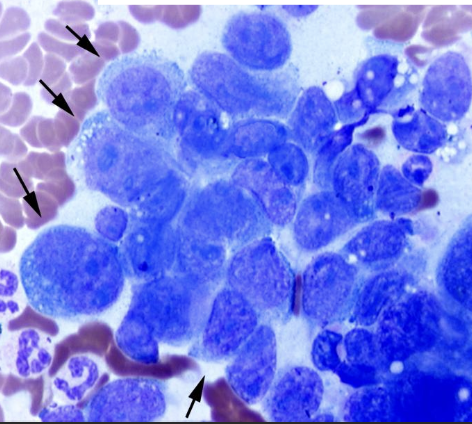
what does the image show?
hepatocellular carcinoma
what is the cause of feline hepatic lipidosis?
massive accumulation of triglycerides in more than 50% of hepatocytes
what cats will we most commonly see hepatic lipidosis?
overweight cats
middle-aged females
what are clinical signs of hepatic lipidosis?
no appetite (1-2 weeks)
lost 25% of body weight
anorexia
lethargy
vomiting
diarrhea or constipation
what will be seen on a physical exam for hepatic lipidosis?
large non-painful liver
jaundice
mild-moderate dehydration
what type of anemia can be seen in cats with hepatic lipidosis?
non-regenerative normocytic normochromic anemia
is there a known association with hepatic lipidosis and FeLV or FIV?
no
MCQ: A 12-year-old Golden Retriever presents with chronic weight loss, polyuria/polydipsia, and mild ascites. Bloodwork as follows:
ALT: ↑↑ (moderate increase)
AST: ↑↑ (moderate increase)
ALP: ↑↑↑ (marked increase)
GGT: ↑ (mild increase)
Bile Acids: ↑↑↑ (marked increase)
Albumin: ↓ (low)
What is the most likely cause of these findings?
chronic hepatitis leading to hepatic insufiiciency
what can be used to confirm hepatic lipidosis?
ultrasound
FNA
biopsy
why is there an increase in ALP with hepatic lipidosis?
swelling of hepatocytes compresses bile canaliculi leading to induction of ALP
why is GGT normal with hepatic lipidosis?
nothing is happening in the biliary tree
what values will be increased in cats with hepatic lipidosis?
ALT
AST
ALP
bilirubin
what cell abnormalities may occur with hepatic lipidosis?
acanthocytes
what is the PCV value in cats with hepatic lipidosis?
WRI