Exam 2 Practice Questions (Everything Combined)
1/318
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
319 Terms
What is a group of structurally and functionally related cells and their external environment that together perform common functions called?
tissue
what two basic components do all tissues have?
cells that are similar in structure and function, extracellular matrix
how are tissue types distinguished?
number and kind of cells it contains, function
what are the four primary tissue types?
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
what do epithelial tissues do?
cover and line all body surfaces and cavities
what do specialized epithelial cells form?
glands
what are glands?
groups of cells that manufacture and secrete a product
what type of products to glands secrete and manufacture?
sweat, saliva, hormones
what do connective tissues do?
bind, support, protect, and allow substance transport throughout body
what is the prominent feature in most connective tissues?
extracellular matrix
what are muscle tissues composed of?
cells that can contract and generate force with little ECM between the cells
what are the two main components of the extracellular matrix?
ground substance, protein fibers
what are the three types of protein fibers found within the extracellular matrix?
collagen, elastic, reticular
what are collagen fibers important for?
resisting tension and pressure
what do elastic fibers allow for?
stretching and recoil
what is the function of reticular fibers?
support the cells and ground substance of many tissues
what are the three important types of cell junctions?
tight, gap, desmosomes
what do tight junctions do?
help make spaces between cells impermeable
what do desmosomes do?
increase resistance of the tissue to mechanical stress
what do gap junctions do?
allow small substances to move from one cell to another
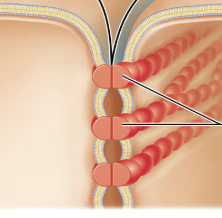
what type of junction is this?
tight junction
what type of junction is this?
desmosome
what type of junction is this?
gap junction
what are the five functions of epithelial tissues?
protection, immune defense, secretion, transport, sensation
how do epithelial tissues function as protection?
they provide a continuous surface that shields underlying tissues
how do epithelial tissues function in immune defense?
they provide a barrier against invading microorganisms
how do epithelial tissues function in secretion?
they form glands that produce substances like oil or hormones
how do epithelial tissues function in transport?
certain substances can cross them to enter other tissues
how does epithelial tissue function in sensation?
they are supplied with nerves that detect changes in environment
what is the “free edge” of an epithelial cell or tissue called?
apical surface
what is the edge attached to deeper cells of epithelial tissue called?
basal surface
what are the two ways to classify epithelia?
number of cell layers, shape of cells
what is the function of simple squamous epithelium?
diffusion, produce serous fluid
where is simple squamous epithelium found?
lungs, serous membranes, kidney tubules, blood vessels
what is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium?
absorption and secretion
where is simple cuboidal epithelium found?
kidney tubules, lower respiratory passages, some glands
what is the function of simple columnar epithelium?
absorption, secretion of mucus and other substances
where is simple columnar epithelium found?
digestive tract, uterine tube, gallbladder, kidney tubules
what is the function of pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
secrete mucus and propel it
where is pseudostratified columnar epithelium found?
nasal cavity, male urethra, upper respiratory passages
what is the function of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
protection, prevention of water loss
where is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium found?
epidermis of skin
what is the function of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
protect from mechanical stress and microorganisms
where is nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium found?
mouth, esophagus, vagina, anal canal
what is the function of stratified cuboidal epithelium?
some absorption and secretion
where is stratified cuboidal epithelium found?
ducts of sweat glands
what is the function of stratified columnar epithelium?
protection, secretion, absorption
where is stratified columnar epithelium found?
ducts of some glands, male urethra
what is the function of transitional epithelium?
protection, allow for stretching
where is transitional epithelium found?
urinary bladder, ureter, urethra
what are the two types of glands?
exocrine, endocrine
how do exocrine glands secrete their products?
through a duct lined with epithelial tissues
where do exocrine glands secrete their products to?
exterior of the body/apical surface of the epithelium
how are endocrine glands different than exocrine glands?
they lack ducts and secrete their products directly into the blood

what epithelium is this?
simple squamous epithelium
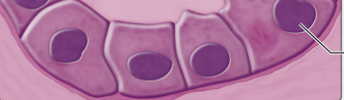
what type of epithelium is this?
simple cuboidal epithelium
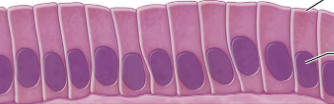
what type of epithelium is this?
simple columnar epithelium
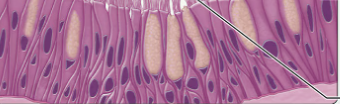
what type of epithelium is this?
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
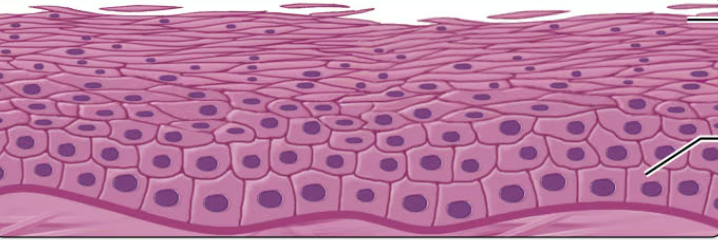
what type of epithelium is this?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
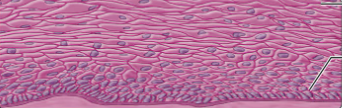
what type of epithelium is this?
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
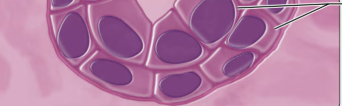
what type of epithelium is this?
stratified cuboidal epithelium
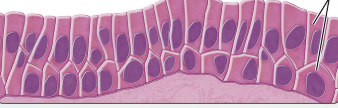
what type of epithelium is this?
stratified columnar epithelium
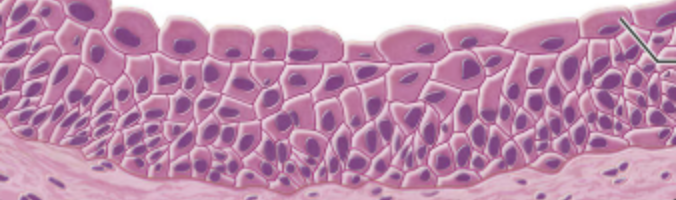
what type of epithelium is this?
transitional epithelium
what is the simplest type of exocrine gland?
unicellular glands
what is the most common unicellular gland in the body?
goblet cell
where are goblet cells found?
digestive and respiratory tracts
what is the function of goblet cells?
secrete mucus that protects underlying epithelium
what are most exocrine glands?
multicellular glands
what are multicellular glands made of?
clusters of secretory cells arranged in different ways
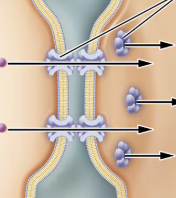
what are the three types of exocrine secretion?
merocrine, holocrine, apocrine
what happens in merocrine secretion?
products are packaged into secretory vesicles for release by exocytosis
what happens in holocrine secretion?
secretory cells accumulate their product and release when the cell ruptures and dies
what happens in apocrine secretion?
portions of the cytoplasm are pinched off with the product being secreted
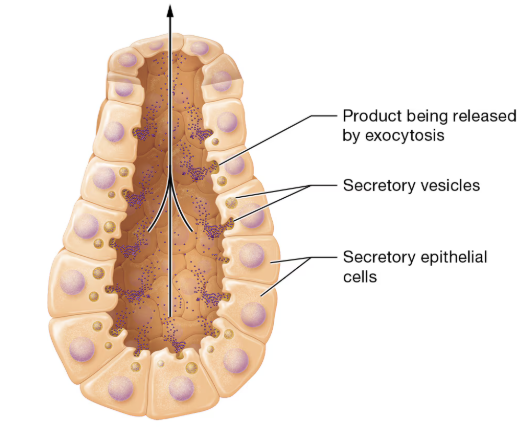
what type of secretion is this?
merocrine secretion
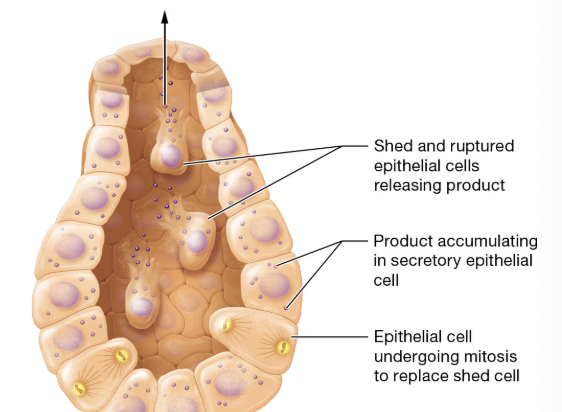
what type of secretion is this?
holocrine secretion
what are the functions of connective tissues?
connecting and binding, support, protection, transport
what are the two basic classes of connective tissue?
connective tissue proper, specialized connective tissue
what are the cells of connective tissue proper?
fibroblasts, adipocytes, mast cells, phagocytes, other immune cells
what is the function of fibroblasts?
produce protein fibers, ground substance, other elements of the ECM
what is the function of phagoyctes?
ingest foreign substances, microorganisms, and dead/damaged cells
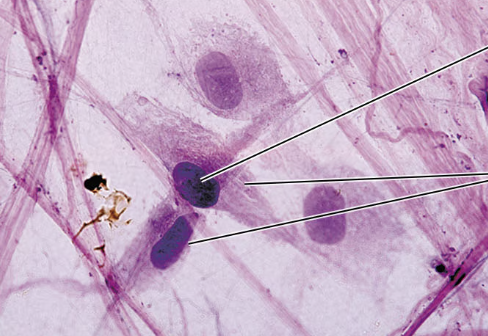
what type of connective tissue cell is seen in this picture?
fibroblasts
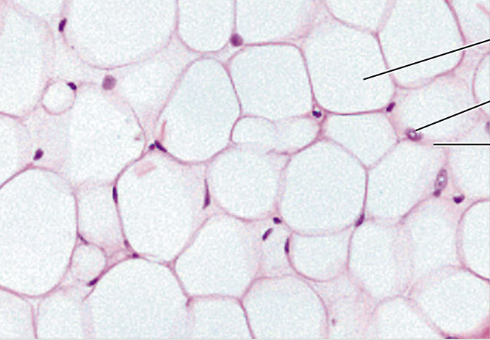
what type of connective tissue cell is seen in this picture?
adipocyte
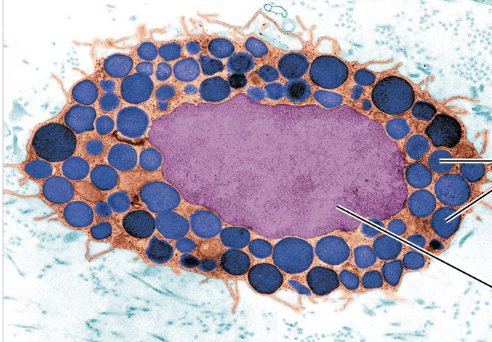
what type of connective tissue cell is seen in this picture?
mast cell
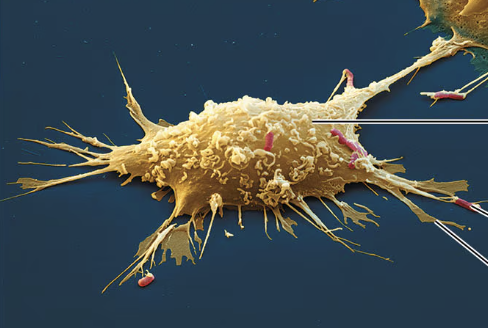
what type of connective tissue cell is seen in this image?
phagocyte (macrophage)
what are the types of connective tissue proper?
loose areolar, dense, reticular, adipose
what is loose areolar connective tissue composed of?
ground substance, all three protein fibers, fibroblasts
where is loose areolar connective tissue found?
papillary dermis
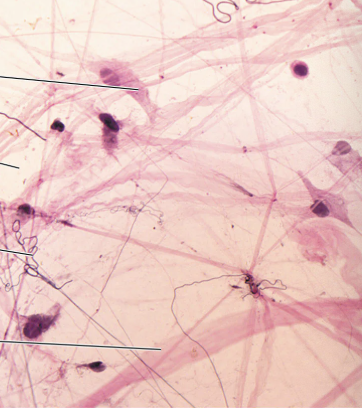
what type of connective tissue is this?
loose areolar connective tissue
what is dense connective tissue primarily composed of?
protein fibers
what are the types of dense connective tissue?
dense irregular, dense regular
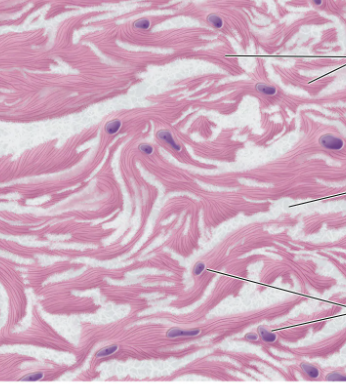
what type of connective tissue is this?
dense irregular connective tissue
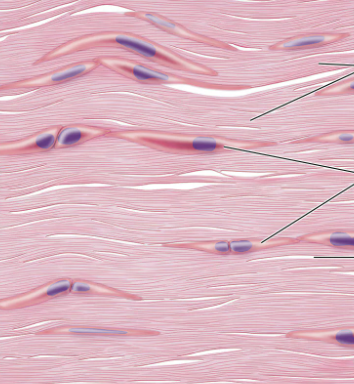
what type of connective tissue is this?
dense regular connective tissue

what type of connective tissue is this?
elastic tissue
what is dense irregular connective tissue composed of?
collagen fibers
where is dense irregular connective tissue found?
dermis, around organs and joints
what is the function of dense irregular connective tissue?
resist tension in all directions
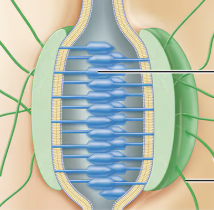
how is the structure of dense regular connective tissue different from dense irregular?
collagen fibers are arranged parallel to one another
what is the function of dense regular connective tissue?
resist tension in one direction
where is dense regular connective tissue found?
tendons, ligaments
what is the structure of elastic connective tissue?
parallel elastic fibers with randomly oriented collagen fibers