MCAT- behavioral sciences
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
Parasympathetic
* REST AND DIGEST conserve energy, acetylcholine, digestion and exocrine secretion
* Constrict pupils
* Stimulates saliva
* Constricts bronchi
* Slows heartbeat
* Stimulates peristalsis and secretion
* Stimulates bile release
* Contracts bladder
* Constrict pupils
* Stimulates saliva
* Constricts bronchi
* Slows heartbeat
* Stimulates peristalsis and secretion
* Stimulates bile release
* Contracts bladder
3
New cards
Sympathetic
* FIGHT OR FLIGHT- stress
* Dilates pupils
* Inhibits salvation
* Relaxes bronchi
* Accelerates heartbeat
* Stimulates sweating
* Inhibits peristalsis and secretion
* Stimulates glucose production and release
* Recreation of adrenaline and noradrenaline
* Inhibits bladder contraction
* Stimulates orgasm
* Dilates pupils
* Inhibits salvation
* Relaxes bronchi
* Accelerates heartbeat
* Stimulates sweating
* Inhibits peristalsis and secretion
* Stimulates glucose production and release
* Recreation of adrenaline and noradrenaline
* Inhibits bladder contraction
* Stimulates orgasm
4
New cards
Meninges: 3 layers
* Dura mater- outer layer connective tissue connected to skull
* Arachnoid matter- middle layer fibrous weblike
* Pia matter- inner layer directly connected to brain
\-absorb cerebrospinal fluid that nourishes brain and spinal cord, provides cushion
* Arachnoid matter- middle layer fibrous weblike
* Pia matter- inner layer directly connected to brain
\-absorb cerebrospinal fluid that nourishes brain and spinal cord, provides cushion
5
New cards
Forebrain- prosencephalon
* greatest influence on human behavior
* Divides to form telencephalon: cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system and diencephalon: thalamus hypothalamus posterior pituitary gland and pineal gland
* Divides to form telencephalon: cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system and diencephalon: thalamus hypothalamus posterior pituitary gland and pineal gland
6
New cards
Cerebral cortex
* perception, cognition, behavior processes
7
New cards
Basal ganglia
* movement
8
New cards
limbic system
emotion and memory
9
New cards
thalamus
sensory relay
* Sorts and transmit them to appropriate areas of cerebral cortex
* Sorts and transmit them to appropriate areas of cerebral cortex
10
New cards
hypothalamus
* our main functions: defending, fighting, flighting, sexual function
* Homeostatic functions
* Metabolism, temp, water balance
* Some endocrine function
* Emotional experiences during high arousal aggressive and sexual states
* When any functions are out of balance it detects problem signals body to correct
* Homeostatic functions
* Metabolism, temp, water balance
* Some endocrine function
* Emotional experiences during high arousal aggressive and sexual states
* When any functions are out of balance it detects problem signals body to correct
11
New cards
Midbrain- mesencephalon
receives sensory and motor info from rest of body, involuntary reflex responses
* Inferior (sensory info from auditory) and superior colliculi (sensory info from visual)- sensorimotor reflexes
* Inferior (sensory info from auditory) and superior colliculi (sensory info from visual)- sensorimotor reflexes
12
New cards
Hindbrain-Rhombencephalon
* balance motor coordination breathing digestion arousal sleeping waking: vital functions
* divides to form myelencaphalon: medulla oblongata and mentencephalon: pons and cerebellum
* divides to form myelencaphalon: medulla oblongata and mentencephalon: pons and cerebellum
13
New cards
Cerebellum
refined motor movements, posture balance coordinates body movements
14
New cards
medulla oblongata
herat, vital relfexes
15
New cards
reticular formation
arousal and alertness
16
New cards
pons
communication within brain, breathing : sensory and motor pathways btwn cortex and medulla
17
New cards
Lateral hypothalamus: LH
Lacks Hunger- triggers eating and drinking
18
New cards
Ventromedial hypothalamus: VMH:
Very Much Hungry- provides signal to stop eating - brain lesions lead to obesity
19
New cards
Anterior hypothalamus-
sexual behavior sleep body temp
20
New cards
Posterior pituitary
release for hypothalamic hormones: antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) and oxytocin
21
New cards
pineal gland
biological rhythms- secrets melatonin- directs signals from retinal for coordination with sunlight
22
New cards
Basal ganglia
muscle movement, receive info from cortex and relay info to brain and spinal cord via extrapyramidal motor system
* Parkinson's- destruction of portions of basal ganglia
* Parkinson's- destruction of portions of basal ganglia
23
New cards
extrapyramidal motor system
gathers info about body position and carries info to CNS but does not education directly through motor neurons
24
New cards
Limbic system: main function and primary components
emotion and memory
septal nuclei
amygdala
hippocampus
anterior cingulate cortex
septal nuclei
amygdala
hippocampus
anterior cingulate cortex
25
New cards
anterior cingulate cortex
* connects with frontal and parietal lobes
* Higher order cognitive processes- regulation of impulse control and decision making
* Plays role in emotion and motivation
* Higher order cognitive processes- regulation of impulse control and decision making
* Plays role in emotion and motivation
26
New cards
septal nuclei
* pleasure centers - association between these nuclei and addictive behavior
27
New cards
amygdala
* defensive and aggressive behaviors
* When damages: decrease in aggression and fear reaction
* Lesions result in submissive and hypersexual states
* When damages: decrease in aggression and fear reaction
* Lesions result in submissive and hypersexual states
28
New cards
hippocampus
* memory and learning
* form long term memories and redistribute remote memories to cerebral cortex
* Communicates w other portions of limbic system through long projections: fornix
* Anterograde amnesia- cant form new long term memories but memory for events that occurred before brain injury is intact
* Retrograde amnesia- memory loss of events before brain injury
* form long term memories and redistribute remote memories to cerebral cortex
* Communicates w other portions of limbic system through long projections: fornix
* Anterograde amnesia- cant form new long term memories but memory for events that occurred before brain injury is intact
* Retrograde amnesia- memory loss of events before brain injury
29
New cards
frontal lobe:
* prefrontal cortex: association area
* supervising and directing operations of other brain regions
* Regulate attention and alertness
* Wake up or relax
* Supervises processes with perception memory emotion impulse control
* Projection areas: perceptual and motor tasks
* Primary motor cortex - precentral gyrus : imitate voluntary motor movements by sending neural impulses toward muscles
* Motor homunculus
* Brocas area- speech production - only found in one hemisphere
* supervising and directing operations of other brain regions
* Regulate attention and alertness
* Wake up or relax
* Supervises processes with perception memory emotion impulse control
* Projection areas: perceptual and motor tasks
* Primary motor cortex - precentral gyrus : imitate voluntary motor movements by sending neural impulses toward muscles
* Motor homunculus
* Brocas area- speech production - only found in one hemisphere
30
New cards
parietal lobe
* somatosensory cortex
* Homunculus
* Homunculus
31
New cards
occipital lobe
visual cortex
learning and motor control
learning and motor control
32
New cards
temporal lobe
auditory cortex
* Wernikes area- language perception and comprehension
* Memory processing emotion and language
* Wernikes area- language perception and comprehension
* Memory processing emotion and language
33
New cards
Corpus callosum
connects and shares info between two cerebral hemispheres
34
New cards
Anterior pituitary gland releases what hormones
hormones that regulates actives of endocrine glands
* Endorphins, FHS LH ACTH TSH GH prolactin
* Endorphins, FHS LH ACTH TSH GH prolactin
35
New cards
posterior pituitary gland releases what hormones
ADH and oxytocin
36
New cards
undersupply of serotonin leads to whereas oversupply leads to
undersupply- depression
oversupply-mania
oversupply-mania
37
New cards
norepinephrine: low levels associated with
high levels associated with
high levels associated with
low-depression
high-anxiety and mania
high-anxiety and mania
38
New cards
* GABA
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials- stabilizing neural activity- hyper polarization
39
New cards
* Glycine
inhibitory in CNS increases chloride into neuron- hyper polarizes
40
New cards
* Glutamate
excitatory
41
New cards
dopamine imbalances leads to
affects basal ganglia functions
* schizophrenia-delusions hallucinations and agitation associate w too much dopamine or oversensitivity to dopamine, parkinsons- loss of dopaminergic neurons= tremors jerky movements
* schizophrenia-delusions hallucinations and agitation associate w too much dopamine or oversensitivity to dopamine, parkinsons- loss of dopaminergic neurons= tremors jerky movements
42
New cards
Epinephrine norepinephrine and dopamine:
* catecholamines- experience of emotions
* Epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline)- alertness and wakefulness fight or flight
* Epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline)- alertness and wakefulness fight or flight
43
New cards
Acetylcholine
* efferent limb of somatic nervous and parasympathetic: acts as inhibitory and excitatory
44
New cards
Dominant hemisphere
* usually left- analytic in function- managing details- language logic math
45
New cards
Nondominant hemisphere
* usually right- intuition creativity music spatial processing more sensitive to emotion recognition of others moods due to visual and auditory cues
46
New cards
webers law
* observation that difference thresholds are proportional and computed into a %
47
New cards
signal detection theory
* how internal and external factors influence thresholds
* Trials when signal is presented= noise trials
* Trials where signal is not presented= catch trials
* hit= signal is presented and subject correctly perceives signal
* miss= trial which subject fails to perceive presented signal
* False alarm= subject indicates perceiving a signal even tho it wasn’t presented
* Correct negative= subject correctly identifies no signal was presented
* Trials when signal is presented= noise trials
* Trials where signal is not presented= catch trials
* hit= signal is presented and subject correctly perceives signal
* miss= trial which subject fails to perceive presented signal
* False alarm= subject indicates perceiving a signal even tho it wasn’t presented
* Correct negative= subject correctly identifies no signal was presented
48
New cards
sclera
thick later covering exposed portion of the eye
49
New cards
choroidal vessels
blood vessels between sclera and retina
50
New cards
retina
inner most layer of the eye
contains photoreceptors
contains photoreceptors
51
New cards
cornea
where light first gathers and focuses incoming light
52
New cards
anterior chamber
in front of iris
53
New cards
posterior chamber
in between iris and lens
54
New cards
iris
color part of eye
55
New cards
dilator papillae
opens pupil under sympathetic stimulation - muscle in iris
56
New cards
constrictor papillae
closes pupil under parasympathetic stimulation - muscle in iris
57
New cards
choroid
vascular layer of connective tissue that surrounds and nourishes retina
58
New cards
Ciliary body
produces aqueous humor
59
New cards
Canal of schemm
where the aqueous humor drains
60
New cards
lens
behind the iris- helps to control refraction of light
61
New cards
Amacrine and horizontal cells:
receive input form multiple retinal cells and help to amplify the differences in signals in each bipolar cell
62
New cards
when an object stimulates left eye: crossing over
* object from left stimulates right side of brain Object to the right stimulates temporal fibers and continues to the left side of the brain
63
New cards
when an object stimulates right eye: crossing over
* object to your right stimulates nasal fibers which cross over to the left side through optic chasm
64
New cards
Parvocellular cells
in the LGN: high color spatial resolution, only work with slow moving/stationary objects- low temporal resolution
65
New cards
Magnocellular cells:
LGN: detect motions, high temporal resolution low spatial resolution
* Inputs from periphery of vision
* Inputs from periphery of vision
66
New cards
From optic chasm nerve fibers pass
LGN of thalamus then to parietal and temporal lobes to visual cortex in occipital lobe
67
New cards
the ear
* Pinna
* External auditory canal
* Tympanic membrane (eardrum) - vibrates back in forth - speed depends on the frequency
* Higher frequency= higher rat of vibration
* Louder sounds= higher intensity= increased amplitude
* Middle ear: ossicles
* Malleus
* Incus
* Stapes
* External auditory canal
* Tympanic membrane (eardrum) - vibrates back in forth - speed depends on the frequency
* Higher frequency= higher rat of vibration
* Louder sounds= higher intensity= increased amplitude
* Middle ear: ossicles
* Malleus
* Incus
* Stapes
68
New cards
Middle ear connected to nasal cavity via
* eustachian tube to help equalize pressure between middle ear and environment
69
New cards
Bony labyrinth
hollow region of temporal none containing cochlear vestibule and semicircular canals
70
New cards
endolymph
* potassium rich fluid
71
New cards
Perilymph
transmits vibrations from outside world and cushions inner ear
72
New cards
cochlea
* contains receptors for hearing
* Scale- all three run entire length of cochlea
* Middle: actual hearing organ of Corti: made of hair cells bathed in endolymph
* Tectorial membrane: on top of organ of corti
* basilar membrane: where organ of corgi rests on
* Round window: allows the perilymph to move within cochlea
* Organ of corti does transduction and then sends signals through vestibulocochlear nerve
* Scale- all three run entire length of cochlea
* Middle: actual hearing organ of Corti: made of hair cells bathed in endolymph
* Tectorial membrane: on top of organ of corti
* basilar membrane: where organ of corgi rests on
* Round window: allows the perilymph to move within cochlea
* Organ of corti does transduction and then sends signals through vestibulocochlear nerve
73
New cards
Inferior colliculus
Involved in startle reflex and helps keep eyes fixed on point while head is turned
74
New cards
seterocilia
cause the swaying of hair cells which opens ion channels - amplify sound
75
New cards
Vestibule
* refers to portion of bony labyrinth that contains utricle and saccule
* Sensitive to linear acceleration used to balance apparatus and determine ones orientation in space
* Sensitive to linear acceleration used to balance apparatus and determine ones orientation in space
76
New cards
Otoliths
* utricle and saccule contain hair cells which have otoliths that help to resist motion it bends and stimulates underlying hair sells that send signals to brain
77
New cards
semicircular canals
* sensitive to rotational acceleration
* Each end in ampulla where hair cells are located
* Bending is what sends signals to brain
* Each end in ampulla where hair cells are located
* Bending is what sends signals to brain
78
New cards
Pacinian corpuscles
* deep pressure and vibration
79
New cards
Meissner corpuscles
respond to light tough
80
New cards
Merkel cells
deep pressure and texture
81
New cards
Ruffini endings
stretch
82
New cards
two point threshold
* minimum distance necessary between two points of stimulation of skin so that points will be felt as two different stimuli
83
New cards
gate theory of pain
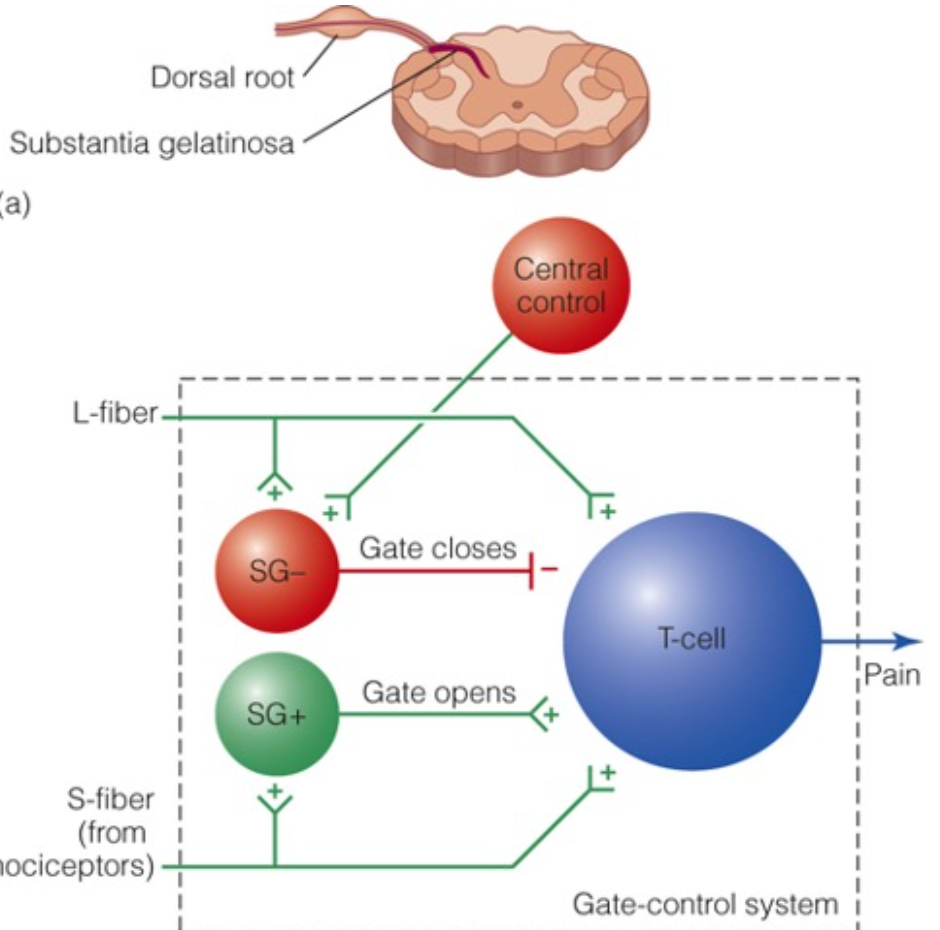
84
New cards
depth perception
* Relative size- objects appear closer than they are
* interpositon- when two objects overlap the one in front is closers
* Linear persepctive- convergence of parallel lines at a distance
* Motion parallax- perception that objects closer is seen to move faster when we change field of vision
* interpositon- when two objects overlap the one in front is closers
* Linear persepctive- convergence of parallel lines at a distance
* Motion parallax- perception that objects closer is seen to move faster when we change field of vision
85
New cards
binocular cues
* involve retinal disparity- slight difference in images projected on two Reinas
86
New cards
associate learning
* the creation of a pairing or sociation between two stimuli or behavior and a response
87
New cards
classical conditioning
* takes advantage of biological responses to create associations between 2 unrelated stimuli
88
New cards
habituation
repeated exposure to the same stimulus causing a decrease in response
89
New cards
dishabituation
* recovery of a response to a stimulus after habituation has occurred=
* It is temporary and always referring to changes in response to the original stimulus
* It is temporary and always referring to changes in response to the original stimulus
90
New cards
pavlov
* turned a neutral stimulus into a conditioned stimulus and through association caused a conditioned response
experiment with dog
experiment with dog
91
New cards
operant conditioning
* examines the ways which consequences of voluntary behaviors change the frequency of those behaviors
92
New cards
positive reinforcement
* increases the frequency of a behavior by adding positive consequences or incentive following the behavior
93
New cards
negative reinforcement
* increases the frequency of behavior but by removing something unpleasant
* example you take an aspirin to reduce a headache so the next time you have a headache you're more likely to take an aspirin
* example you take an aspirin to reduce a headache so the next time you have a headache you're more likely to take an aspirin
94
New cards
escape learning
* describes the situation where the animal experiences the unpleasant stimulus and in response displays the desired behavior in order to trigger the removal of the stimulus
95
New cards
avoidance learning
when animal displays it as desired behavior in anticipation of the unpleasant stimulus in order to avoid the unpleasant stimulus
96
New cards
positive punishment
* adds an unpleasant consequence in response to behavior to reduce that behavior
97
New cards
negative punishment
removing a stimulus in order to cause reduction of behavior
98
New cards
variable ratio schedules
* reinforce the behavior after varying number of performances but such that the number of performances to receive a reward is constant
99
New cards
fixed interval schedules
* reinforce the first instance of a behavior after a specific time period has elapsed
100
New cards
variable interval schedules
* reinforce the behavior for the first time that behavior is performed after a varying interval of time