Basic Chemistry: Quantum Mechanics, Atomic Spectra, and Electron Behavior
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What is the relationship between wavelength and energy per photon?
Energy per photon decreases with increasing wavelength.
How does frequency relate to energy per photon?
Energy per photon increases with increasing frequency.
Arrange the colors green, red, and blue in order of increasing wavelength.
Red, green, blue.
Arrange the colors green, red, and blue in order of increasing frequency.
Blue, green, red.
Arrange the colors green, red, and blue in order of increasing energy per photon.
Red, green, blue.
What is Einstein's idea regarding light?
Light is quantized.
What happens when a photon at the threshold frequency strikes a metal surface?
It gives the electron just enough energy to escape the atom.
What occurs when an electron absorbs more energy than needed to escape?
The excess energy becomes kinetic energy of the ejected electron.
What observation corresponds to 325 nanometres light in the photoelectric effect?
Observation A: No photoelectrons are observed.
What happens if a surface is struck with ultraviolet light?
Electrons will be ejected, and they will have greater kinetic energy than those ejected by yellow light.
What is an emission spectrum?
A pattern of particular wavelengths of light unique to a type of atom or molecule.
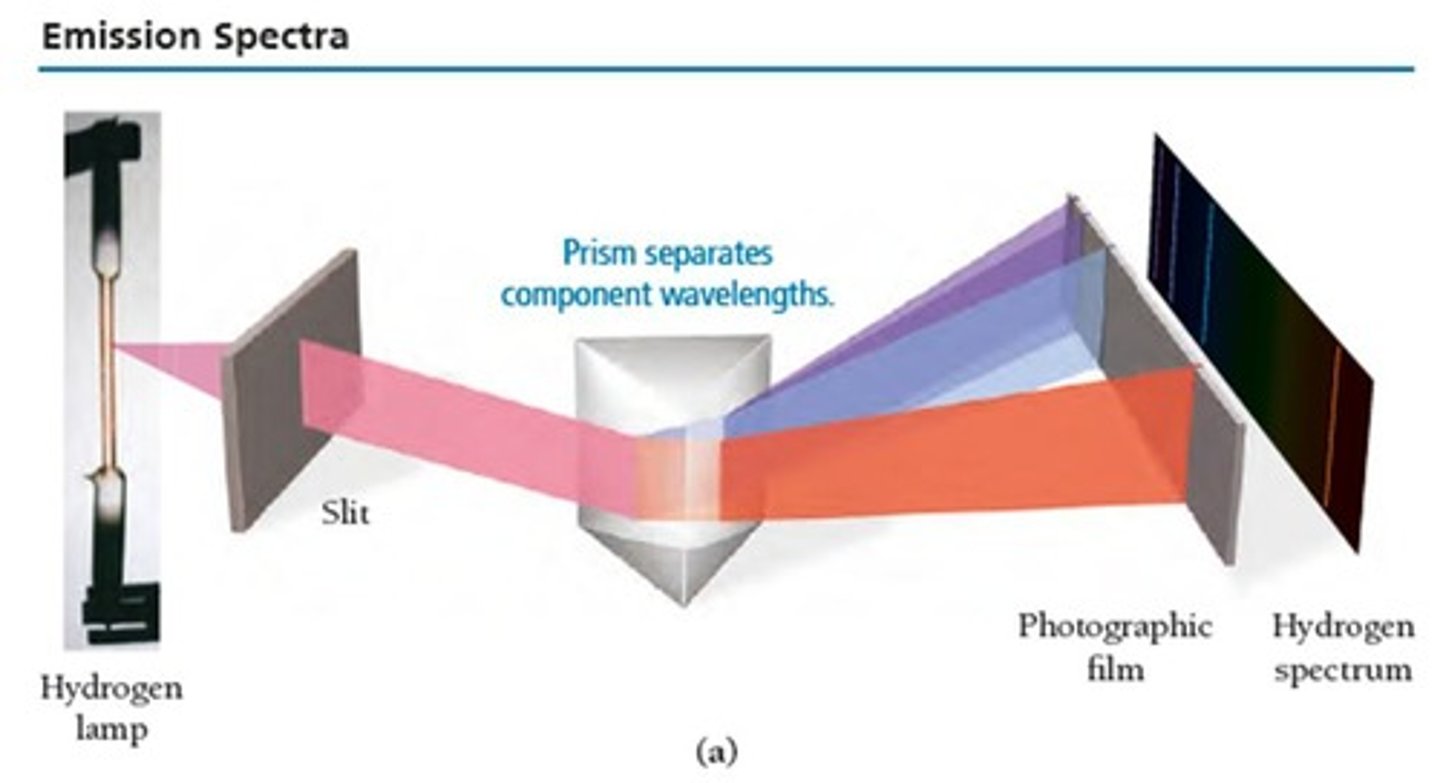
What type of spectra can be used to identify elements present in a material?
Line spectra.
How many distinct lines are in the visible spectrum of hydrogen?
Four distinct lines.
What does the Bohr model explain about atomic structure?
It explains how the structure of the atom changes when it gains or loses energy.
What is meant by quantized energy in the Bohr model?
The atom can have only very specific amounts of energy.
What are stationary states in the Bohr model?
Orbits that electrons travel in at fixed distances from the nucleus.
What happens when electrons jump from a higher energy orbit to a lower energy orbit?
They emit radiation in the form of a photon of light.
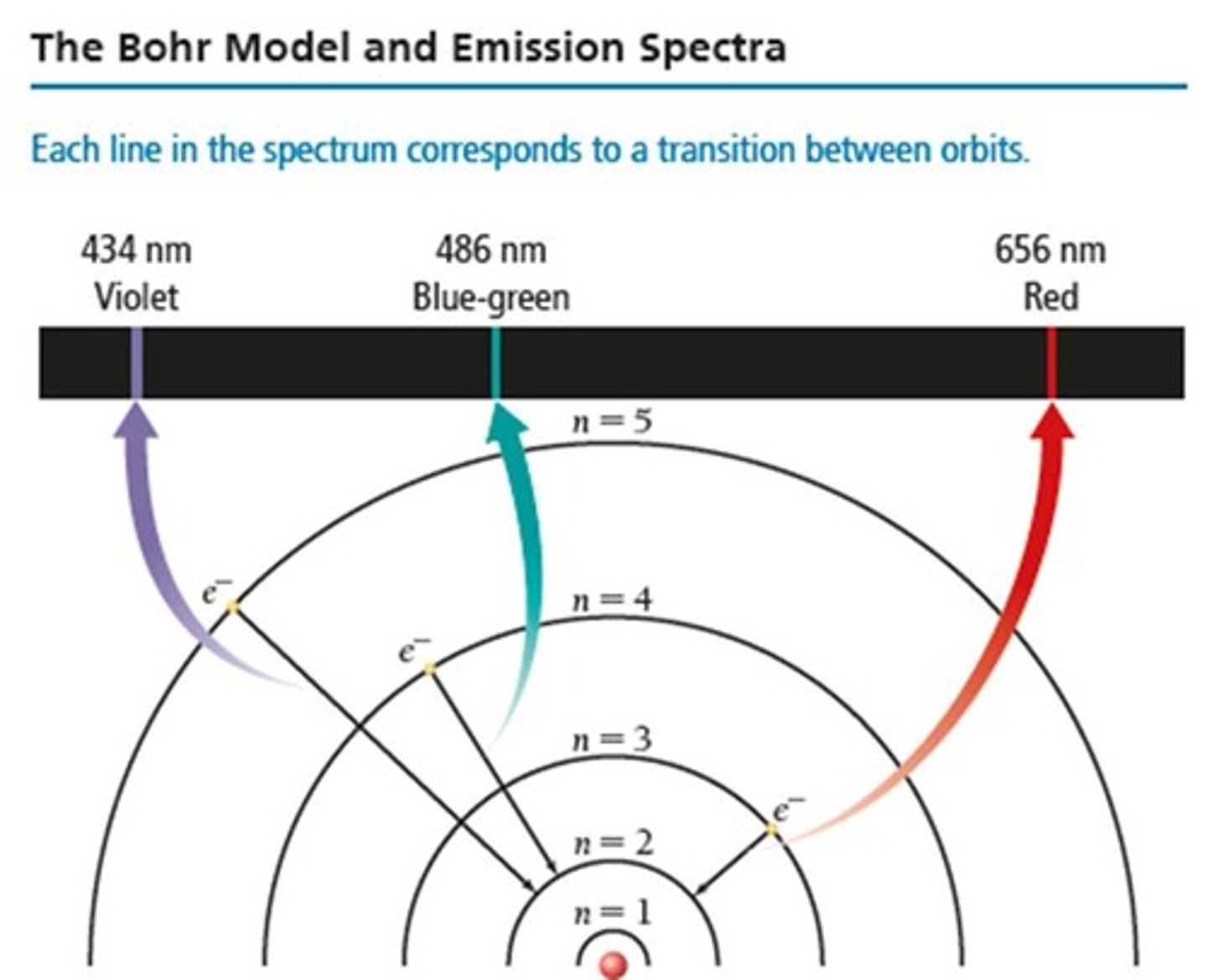
How does the distance between orbits affect the emitted photon?
It determines the energy of the photon of light produced.
What does the Bohr model explain about the atom?
It explains how the structure of the atom changes when it gains or loses energy.
What is meant by the term 'quantized' in the context of the Bohr model?
It means that the atom can have only specific amounts of energy.
How do electrons behave according to the Bohr model?
Electrons travel in orbits at fixed distances from the nucleus.
What determines the energy of the photon emitted by an electron?
The distance between the orbits determines the energy of the photon.
Who proposed that particles could have wave-like behavior?
De Broglie.
What is the relationship between the wavelength of a particle and its momentum according to De Broglie?
The wavelength is inversely proportional to its momentum.
What phenomenon demonstrates the wave nature of electrons?
Electron diffraction produces an interference pattern similar to waves.
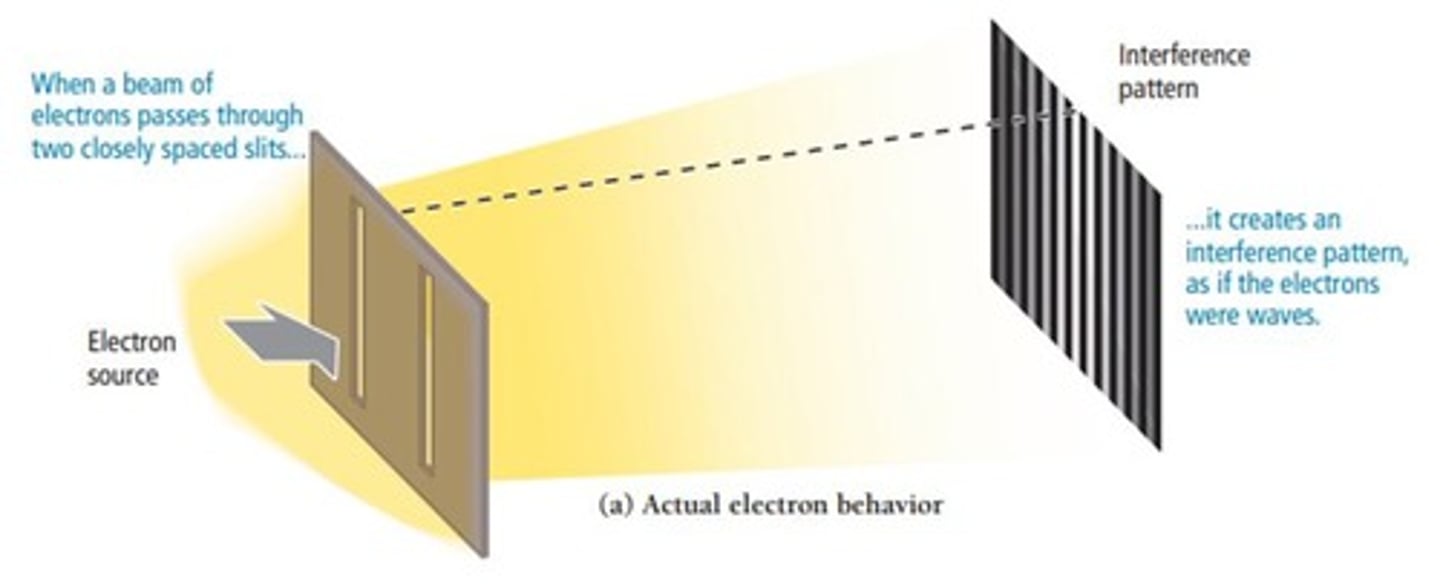
What is the significance of the de Broglie wavelength for small particles like electrons?
The wave character of electrons is significant due to their small size.
What does Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle state?
The product of the uncertainties in position and speed of a particle is inversely proportional to its mass.
What does the uncertainty principle imply about knowing an electron's position and speed?
The more accurately you know one, the less accurately you can know the other.
What is the difference between determinacy and indeterminacy in classical physics versus quantum mechanics?
Classical physics assumes a predictable path for particles, while quantum mechanics states that we cannot predict an electron's path due to uncertainty.
What is a key characteristic of an electron's complementary properties?
An electron exhibits both wave and particle characteristics, but they cannot be observed simultaneously.
What does the term 'stationary states' refer to in the Bohr model?
It refers to the fixed energy levels where electrons reside without radiating energy.
What is the conceptual plan for solving problems using de Broglie's relation?
It relates the wavelength of an electron to its mass and velocity.
Why don't we observe wave properties in larger objects like baseballs?
Their large mass results in a minuscule de Broglie wavelength, making wave properties insignificant.
What is the implication of quantum mechanics being universal?
It applies to all objects, regardless of size, but observable effects are typically only significant for very small particles.
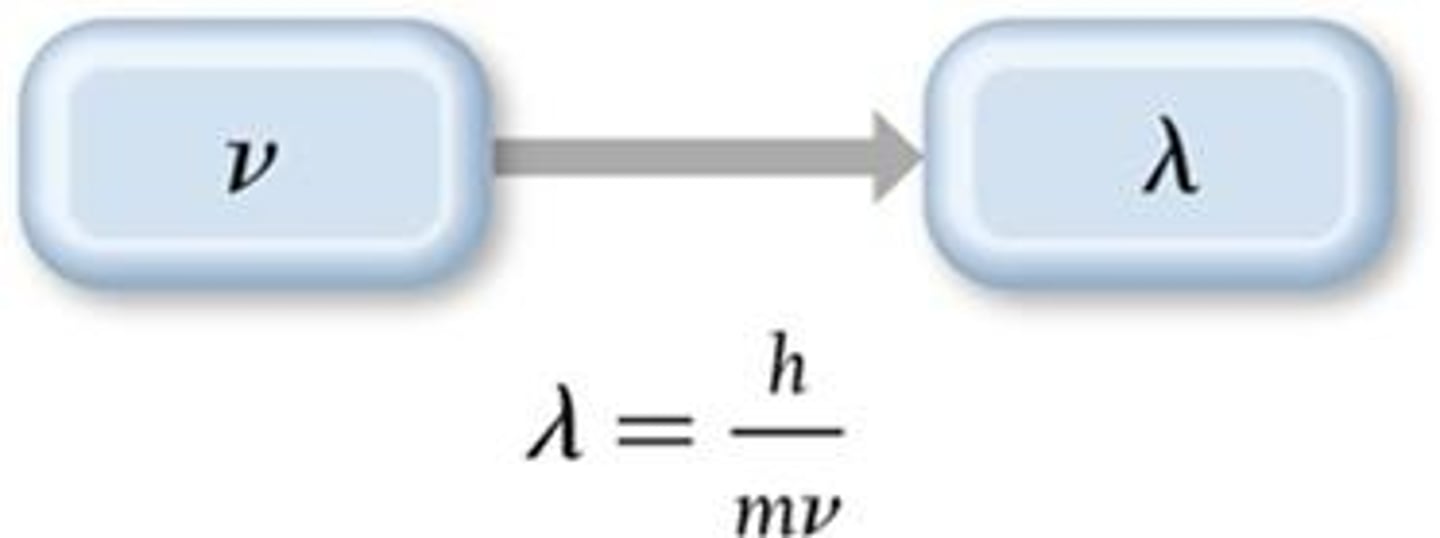
What is the formula for de Broglie's wavelength?
Wavelength = Planck's constant / (mass × velocity).
What is the relationship between energy and the distance of an electron's orbit from the nucleus?
The energy of the electron is proportional to the distance of the orbit from the nucleus.
What happens to the wavelength of an electron as its speed increases?
The wavelength decreases as speed increases.
What type of radiation is emitted when an electron transitions to a lower energy state?
Photon of light.
What does the uncertainty principle imply for measuring an electron's position?
If you measure its position accurately, you will have less certainty about its velocity.
What does indeterminacy in quantum mechanics refer to?
Indeterminacy refers to the indefinite future of an electron's behavior, where only probabilities can be predicted.
What does Schrödinger's equation allow us to calculate?
It allows us to calculate the probability of finding an electron with a particular amount of energy at a specific location in the atom.
What are quantum numbers?
Quantum numbers are integers derived from the wave function that describe the size, shape, and orientation of an orbital.
What is the principal quantum number (n)?
It characterizes the energy level of an electron in a particular orbital and can be any whole number integer.
How does the principal quantum number (n) affect orbital energy?
As n increases, the energy of the orbital becomes greater (less negative) and the size of the orbital increases.
What is the angular momentum quantum number (l)?
It determines the shape of the orbital and can have integer values from 0 to n-1.
What shapes correspond to the angular momentum quantum number (l)?
l = 0 corresponds to s-orbitals (spherical), l = 1 to p-orbitals (dumbbell-shaped), l = 2 to d-orbitals (cloverleaf), and l = 3 to f-orbitals (complex shapes).
What does the magnetic quantum number (m_sub_l) indicate?
It specifies the orientation of the orbital in space and can take integer values from -l to +l.
What is the spin quantum number (m_sub_s)?
It describes the spin behavior of an electron in an orbital and can be either +1/2 (spin up) or -1/2 (spin down).
What values of l are possible for n = 3?
For n = 3, the possible values of l are 0 (s), 1 (p), and 2 (d).
How many orbitals are associated with l = 2?
There are five orbitals associated with l = 2.
What is the relationship between n, l, and orbitals?
Each set of n, l, and m_sub_l describes one orbital, with orbitals of the same n in the same principal energy level.
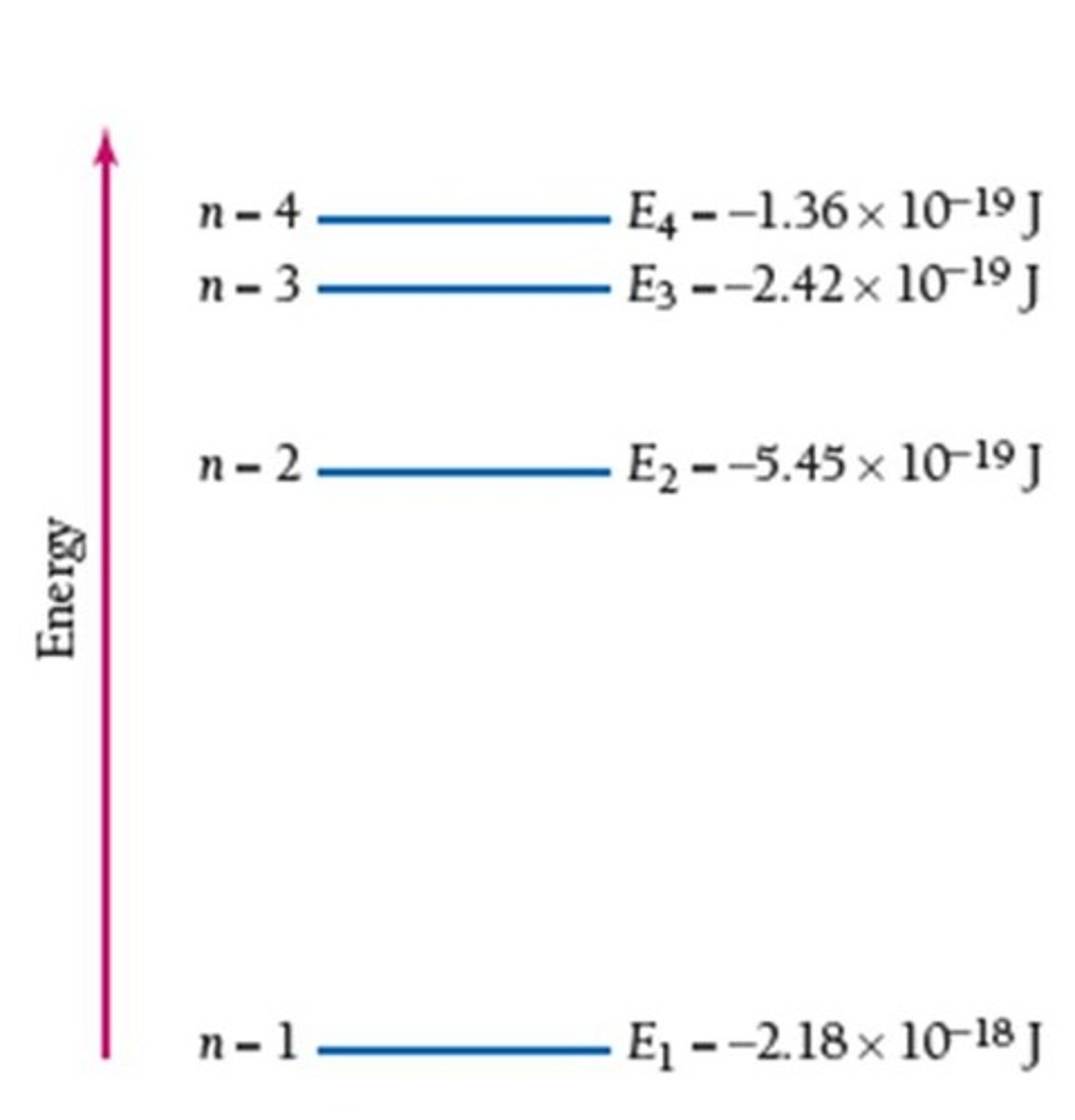
What is the significance of negative energy values for electrons?
Negative energy values indicate that an electron is bound to the nucleus; E = 0 means the electron has escaped the atom.
What is meant by the term 'sublevel' in quantum mechanics?
A sublevel refers to orbitals with the same values of n and l, also known as a subshell.
How do you determine the number of orbitals for a given principal quantum number n?
The total number of orbitals is given by n^2.
What is the principal energy level for hydrogen?
The principal energy levels in hydrogen are characterized by the principal quantum number n.
What does a wave function represent in quantum mechanics?
A wave function represents the probability distribution of an electron's position in an atom.
What is the role of quantum numbers in describing electron orbitals?
Quantum numbers provide a unique set of values that define the energy, shape, and orientation of an electron's orbital.
How does the size of an orbital change with increasing principal quantum number?
As the principal quantum number increases, the size of the orbital becomes larger.
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a single orbital?
A single orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, each with opposite spins.
What is the significance of the term 'probability distribution map' in quantum mechanics?
It visually represents the regions in an atom where an electron is likely to be found.
What happens to the energy difference between orbitals as n increases?
The energy difference between orbitals decreases as n increases.